|
Uisnech
The Hill of Uisneach or Ushnagh ( or ) is a hill and ancient ceremonial site in the barony of Rathconrath in County Westmeath, Ireland. It is a protected national monument. It consists of numerous monuments and earthworks—prehistoric and medieval—including a probable megalithic tomb, burial mounds, enclosures, standing stones, holy wells and a medieval road. Uisneach is near the geographical centre of Ireland, and in Irish mythology it is deemed to be the symbolic and sacred centre of the island.Alwyn Rees and Brinley Rees. ''Celtic Heritage.'' Thames and Hudson: New York, 1961. . pp. 159-161. It was said to be the burial place of the mythical Tuatha Dé Danann, and a place of assembly associated with the druids and the festival of Bealtaine. The summit is above sea levelOrdnance Survey map . Select ''Wind Report'' option fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Westmeath
County Westmeath (; or simply ) is a Counties of Ireland, county in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster and is part of the Eastern and Midland Region. It formed part of the historic Kingdom of Meath, which was named Mide because the kingdom was located in the geographical centre of Ireland (the word Mide meaning 'middle'). Westmeath County Council is the administrative body for the county, and the county town is Mullingar. At the 2022 census, the population of the county was 95,840. History Following the Norman invasion of Ireland, the territory of the Gaelic Kingdom of Meath formed the basis for the Anglo-Norman Lordship of Meath granted by King Henry II of England to Hugh de Lacy, Lord of Meath, Hugh de Lacy in 1172. Following the failure of de Lacy's male heirs in 1241, the Lordship was split between two great-granddaughters. One moiety, a central eastern portion, was awarded to Maud de Lacy, Baroness Geneville, Maud (de G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuatha Dé Danann
The Tuatha Dé Danann (, meaning "the folk of the goddess Danu"), also known by the earlier name Tuath Dé ("tribe of the gods"), are a supernatural race in Irish mythology. Many of them are thought to represent deities of pre-Christian Gaelic Ireland. The Tuath Dé Danann are often depicted as kings, queens, druids, bards, warriors, heroes, healers and craftsmen who have supernatural powers. They dwell in the Otherworld but interact with humans and the human world. They are associated with the ''sídhe'': prominent ancient burial mounds such as Brú na Bóinne, which are entrances to Otherworld realms. Their traditional rivals are the Fomorians (Fomoire), who might represent the destructive powers of nature, and whom the Tuatha Dé Danann defeat in the Battle of Mag Tuired. Prominent members include the Dagda ("the great god"); The Morrígan ("the great queen" or "phantom queen"); Lugh; Nuada; Aengus; Brigid; Manannán; Dian Cecht the healer; and Goibniu the smith ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
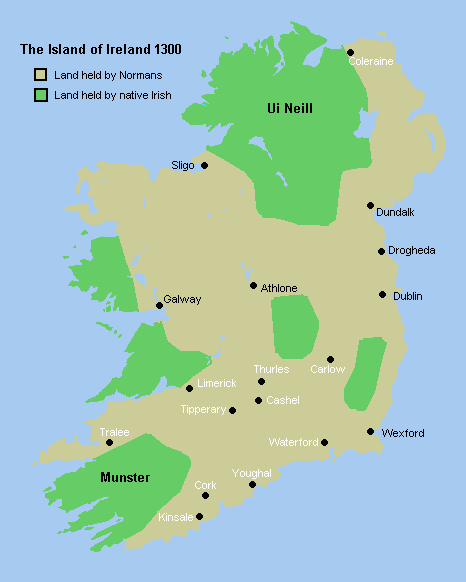
Counties Of Ireland
The counties of Ireland (Irish language, Irish: ) are historic administrative divisions of the island. They began as Normans in Ireland, Norman structures, and as the powers exercised by the Cambro-Norman barons and the Old English (Ireland), Old English nobility waned over time, new offices of political control came to be established at a county level. The number of counties varied depending on the time period, however thirty-two is the traditionally accepted and used number. Upon the partition of Ireland in 1921, six of the traditional counties became part of Northern Ireland. In Northern Ireland, Counties of Northern Ireland, counties ceased to be used for local government in 1973; Local government in Northern Ireland, districts are instead used. In the Republic of Ireland, some counties have been split resulting in the creation of new counties: there are currently 26 counties, 3 cities and 2 cities and counties that demarcate areas of local government in the Republic of Ire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts of the world. This "Neolithic package" included the History of agriculture, introduction of farming, domestication of animals, and change from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to one of sedentism, settlement. The term 'Neolithic' was coined by John Lubbock, 1st Baron Avebury, Sir John Lubbock in 1865 as a refinement of the three-age system. The Neolithic began about 12,000 years ago, when farming appeared in the Epipalaeolithic Near East and Mesopotamia, and later in other parts of the world. It lasted in the Near East until the transitional period of the Chalcolithic (Copper Age) from about 6,500 years ago (4500 BCE), marked by the development ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brill Publishers
Brill Academic Publishers () is a Dutch international academic publisher of books, academic journals, and Bibliographic database, databases founded in 1683, making it one of the oldest publishing houses in the Netherlands. Founded in the South Holland city of Leiden, it maintains its headquarters there, while also operating offices in Boston, Paderborn, Vienna, Singapore, and Beijing. Since 1896, Brill has been a public limited company (). Brill is especially known for its work in subject areas such as Oriental studies, classics, religious studies, Jewish studies, Islamic studies, Asian studies, international law, and human rights. The publisher offers traditional print books, academic journals, primary source materials online, and publications on microform. In recent decades, Brill has expanded to Electronic publishing, digital publishing with ebooks and online resources including databases and specialty collections varying by discipline. History Founding by Luchtmans, 16 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Celtic
Proto-Celtic, or Common Celtic, is the hypothetical ancestral proto-language of all known Celtic languages, and a descendant of Proto-Indo-European. It is not attested in writing but has been partly Linguistic reconstruction, reconstructed through the comparative method. Proto-Celtic is generally thought to have been spoken between 1300 and 800 BC, after which it began to split into different languages. Proto-Celtic is often associated with the Urnfield culture and particularly with the Hallstatt culture. Celtic languages share common features with Italic languages that are not found in other branches of Indo-European, suggesting the possibility of an earlier Italo-Celtic linguistic unity. Proto-Celtic is currently being reconstructed through the comparative method by relying on later Celtic languages. Though Continental Celtic presents much substantiation for Proto-Celtic phonology, and some for its morphology (linguistics), morphology, recorded material is too scanty to allow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eric P
The given name Eric, Erich, Erikk, Erik, Erick, Eirik, or Eiríkur is derived from the Old Norse name ''Eiríkr'' (or ''Eríkr'' in Old East Norse due to monophthongization). The first element, ''ei-'' may be derived from the older Proto-Norse ''* aina(z)'', meaning "one, alone, unique", ''as in the form'' ''Æ∆inrikr'' explicitly, but it could also be from ''* aiwa(z)'' "everlasting, eternity", as in the Gothic form '' Euric''. The second element ''- ríkr'' stems either from Proto-Germanic ''* ríks'' "king, ruler" (cf. Gothic ''reiks'') or the therefrom derived ''* ríkijaz'' "kingly, powerful, rich, prince"; from the common Proto-Indo-European root * h₃rḗǵs. The name is thus usually taken to mean "sole ruler, autocrat" or "eternal ruler, ever powerful". ''Eric'' used in the sense of a proper noun meaning "one ruler" may be the origin of '' Eriksgata'', and if so it would have meant "one ruler's journey". The tour was the medieval Swedish king's journey, when newly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Irish
Middle Irish, also called Middle Gaelic (, , ), is the Goidelic language which was spoken in Ireland, most of Scotland and the Isle of Man from AD; it is therefore a contemporary of Late Old English and Early Middle English. The modern Goidelic languages—Modern Irish, Scottish Gaelic and Manx Gaelic—are all descendants of Middle Irish. Grammar Middle Irish is a fusional, VSO, nominative-accusative language, and makes frequent use of lenition. Nouns decline for two genders: masculine and feminine, though traces of neuter declension persist; three numbers: singular, dual, plural; and five cases: nominative, accusative, genitive, prepositional, vocative. Adjectives agree with nouns in gender, number, and case. Verbs conjugate for three tenses: past, present, future; four moods: indicative, subjunctive, conditional, imperative; independent and dependent forms. Verbs conjugate for three persons and an impersonal, agentless form ( agent). There are a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Irish
Old Irish, also called Old Gaelic (, Ogham, Ogham script: ᚌᚑᚔᚇᚓᚂᚉ; ; ; or ), is the oldest form of the Goidelic languages, Goidelic/Gaelic language for which there are extensive written texts. It was used from 600 to 900. The main contemporary texts are dated 700–850; by 900 the language had already transitioned into early Middle Irish. Some Old Irish texts date from the 10th century, although these are presumably copies of texts written at an earlier time. Old Irish is forebear to Modern Irish, Manx language, Manx and Scottish Gaelic. Old Irish is known for having a particularly complex system of morphology (linguistics), morphology and especially of allomorphy (more or less unpredictable variations in stems and suffixes in differing circumstances), as well as a complex phonology, sound system involving grammatically significant Irish initial mutations, consonant mutations to the initial consonant of a word. Apparently,It is difficult to know for sure, giv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Townland
A townland (; Ulster-Scots: ''toonlann'') is a traditional small land division used in Ireland and in the Western Isles of Scotland, typically covering . The townland system is of medieval Gaelic origin, predating the Norman invasion, and most have Irish-derived names. However, some townland names and boundaries come from Norman manors, plantation divisions, or later creations of the Ordnance Survey.Connolly, S. J., ''The Oxford Companion to Irish History, page 577. Oxford University Press, 2002. ''Maxwell, Ian, ''How to Trace Your Irish Ancestors'', page 16. howtobooks, 2009. Townlands cover the whole island of Ireland, and the total number of inhabited townlands in Ireland was 60,679 in 1911. The total number recognised by the Placenames Database of Ireland as of 2014 was 61,098, including uninhabited townlands. Etymology The term "townland" in English is derived from the Old English word ''tūn'', denoting an enclosure. The term describes the smallest unit of land di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loughnavalley
Louaghnavalley or Loughnavally () is a village in County Westmeath, Ireland. It is located at the crossroads of the R389 and the R390, to the west of Mullingar. The Hill of Uisneach stands to the west of the town, near the village of Killare. The village contains a Roman Catholic church, the Church of the Assumption, a national school and a bar. Sport Loughnavalley GAA is a Gaelic football Gaelic football (; short name '')'', commonly known as simply Gaelic, GAA, or football, is an Irish team sport. A form of football, it is played between two teams of 15 players on a rectangular grass pitch. The objective of the sport is to score ... club that competes at Junior grade. The club was established in 1976 and its grounds are from the Hill of Uisneach. The club's underage teams are amalgamated with Castletown Geoghegan to form Lilliput Gaels. See also * List of towns and villages in Ireland References Towns and villages in County Westmeath {{Westmea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ballymore, County Westmeath
Ballymore () is a village in County Westmeath, Ireland. It is on the R390 road between Athlone and Mullingar, and the historic Hill of Uisneach is nearby. The village was known in medieval times as the medieval borough of Ballymore Lough Sewdy, or Loughsewdy, after the nearby lake, the site of an ancient bruighean, or hostel. History Evidence of the area's history can be deduced by translation of some of its placenames. For example, one townland is Lugnacaha (often pronounced locally as "Lugahaca"), which translates as "the hollow of the battle". There is a field in Shinglis referred to as "Lug na Fola", which translates as "the hollow of the blood". Plary Abbey was founded before the year 700, and a monastery, in honour of the Virgin Mary, for Gilbertin canons, which order consisted of canons of the Premonstre order, and Benedictine nuns, was erected here by the de Lacey family. The church of this monastery was for a short time the cathedral church of the diocese of Meath. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |