|
U.S. Naval Observatory
The United States Naval Observatory (USNO) is a scientific and military facility that produces geopositioning, navigation and timekeeping data for the United States Navy and the United States Department of Defense. Established in 1830 as the Depot of Charts and Instruments, it is one of the oldest scientific agencies in the United States, and remains the country's leading facility for astronomical and timing data. The observatory is located in Northwest Washington, D.C. at the northwestern end of Embassy Row. It is among the few pre-20th century astronomical observatories located in an urban area. In 1893, in an effort to escape light pollution, it was relocated from Foggy Bottom near the city's center, to its Northwest Washington, D.C. location. The USNO has conducted significant scientific studies throughout its history, including measuring the speed of light, observing solar eclipses, and discovering the moons of Mars. Its achievements include providing data for the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northwest (Washington, D
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, Radius, radially arrayed compass directions (or Azimuth#In navigation, azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A ''compass rose'' is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each separated by 90 degree (angle), degrees, and secondarily divided by four ordinal (intercardinal) directions—northeast, southeast, southwest, and northwest—each located halfway between two cardinal directions. Some disciplines such as meteorology and navigation further divide the compass with additional azimuths. Within European tradition, a fully defined compass has 32 "points" (and any finer subdivisions are described in fractions of points). Compass points or compass directions are valuable in that they allow a user to refer to a specific azimuth in a Colloquialism, colloquial fashion, without having to compute or remember degrees. Designations The names of the compass point directions follow these r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coordinated Universal Time
Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) is the primary time standard globally used to regulate clocks and time. It establishes a reference for the current time, forming the basis for civil time and time zones. UTC facilitates international communication, navigation, scientific research, and commerce. UTC has been widely embraced by most countries and is the effective successor to Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) in everyday usage and common applications. In specialised domains such as scientific research, navigation, and timekeeping, other standards such as Universal Time, UT1 and International Atomic Time (TAI) are also used alongside UTC. UTC is based on TAI (International Atomic Time, abbreviated from its French name, ''temps atomique international''), which is a weighted average of hundreds of atomic clocks worldwide. UTC is within about one second of mean solar time at 0° longitude, the currently used prime meridian, and is not adjusted for daylight saving time. The coordination of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Branch
John Branch Jr. (November 4, 1782January 4, 1863) was an American politician who served as U.S. Senator, Secretary of the Navy, the 19th Governor of the state of North Carolina, and was the sixth and last governor of the Florida Territory. Biography Branch was born in Halifax County, North Carolina, on November 4, 1782, the son of wealthy landowners. Educated at the University of North Carolina, where he was a member of the Philanthropic Society, he occupied himself as a planter and civic leader. Branch served in the North Carolina Senate from 1811 to 1817 and was the state's Governor from 1817 to 1820. After further service in the state Senate, he represented North Carolina in the United States Senate from 1823 until 1829 and was a strong supporter of Andrew Jackson. When Jackson became President, he selected Branch as his Secretary of the Navy. In that post, Branch promoted several reforms in the Navy's policies and administration, many of which were not implemented until ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Secretary Of The Navy
The Secretary of the Navy (SECNAV) is a statutory officer () and the head (chief executive officer) of the United States Department of the Navy, Department of the Navy, a military department within the United States Department of Defense. On March 25, 2025, John Phelan (businessman), John Phelan was confirmed as Secretary of the Navy. By law, the Secretary of the Navy must civilian control of the military, be a civilian at least five years removed from active military service. The secretary is appointed by the President of the United States, president and requires confirmation by the United States Senate, Senate. History The position of Secretary of the Navy was created in 1798. It was a member of the president's United States Cabinet, Cabinet until 1949, when the Secretary of the Navy (and the secretaries of the United States Secretary of the Army, Army and United States Secretary of the Air Force, Air Force) were by amendments to the National Security Act of 1947 made subord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Quincy Adams
John Quincy Adams (; July 11, 1767 – February 23, 1848) was the sixth president of the United States, serving from 1825 to 1829. He previously served as the eighth United States secretary of state from 1817 to 1825. During his long diplomatic and political career, Adams served as an ambassador and also as a member of the United States Congress representing Massachusetts in both chambers. He was the eldest son of John Adams, who served as the second president of the United States from 1797 to 1801, and First Lady of the United States, First Lady Abigail Adams. Initially a Federalist Party, Federalist like his father, he won election to the presidency as a member of the Democratic-Republican Party, and later, in the mid-1830s, became affiliated with the Whig Party (United States), Whig Party. Born in Braintree, Massachusetts, Adams spent much of his youth in Europe, where his father served as a diplomat. After returning to the United States, Adams established a successful leg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vice President Of The United States
The vice president of the United States (VPOTUS) is the second-highest ranking office in the Executive branch of the United States government, executive branch of the U.S. federal government, after the president of the United States, and ranks first in the United States presidential line of succession, presidential line of succession. The vice president is also an officer in the Legislative branch of the United States federal government, legislative branch, as the president of the Senate. In this capacity, the vice president is empowered to Presiding Officer of the United States Senate, preside over the United States Senate, but may not vote except to List of tie-breaking votes cast by the vice president of the United States, cast a tie-breaking vote. The vice president is indirect election, indirectly elected at the same time as the president to a four-year term of office by the people of the United States through the Electoral College (United States), Electoral College, but the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
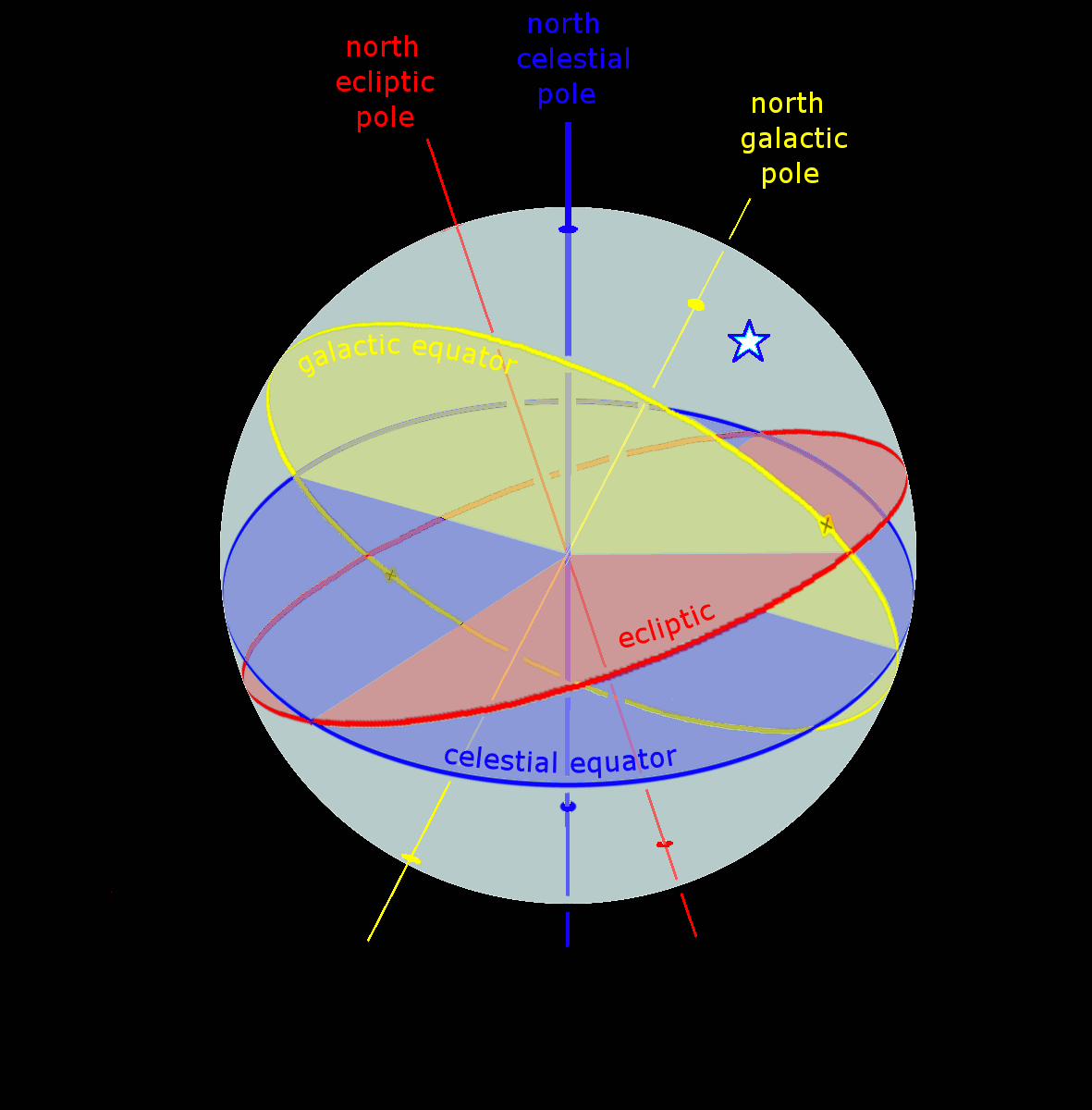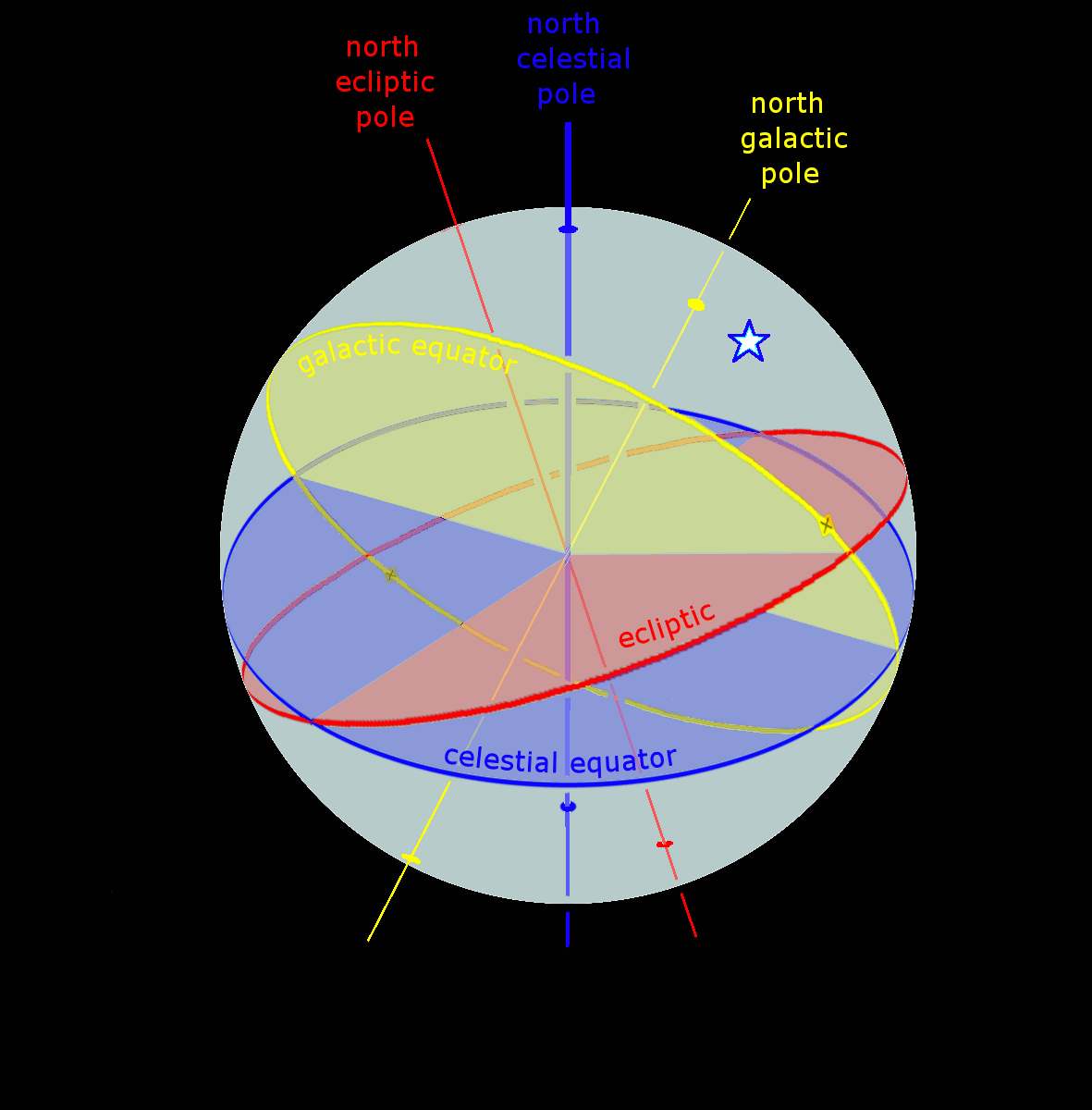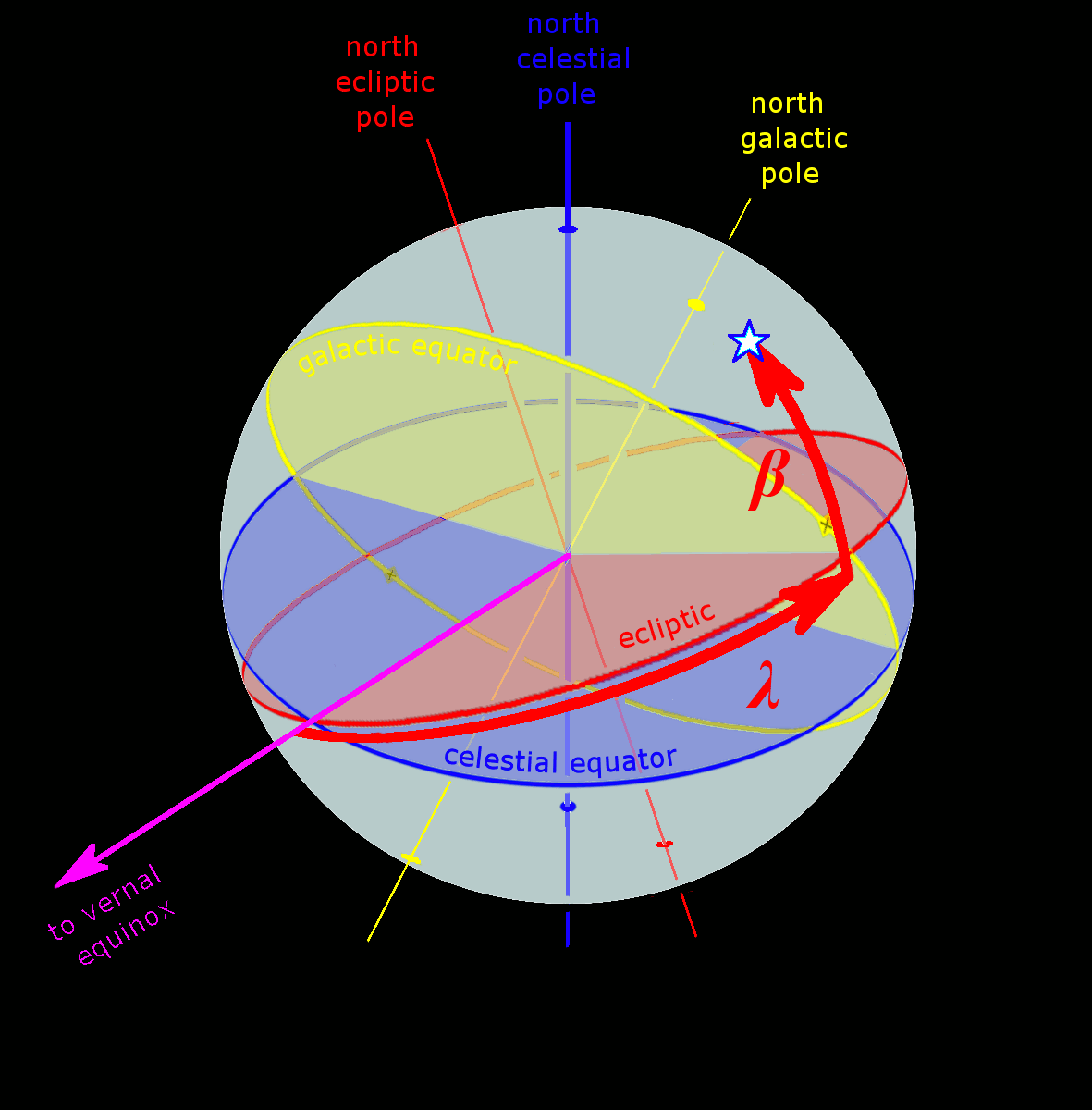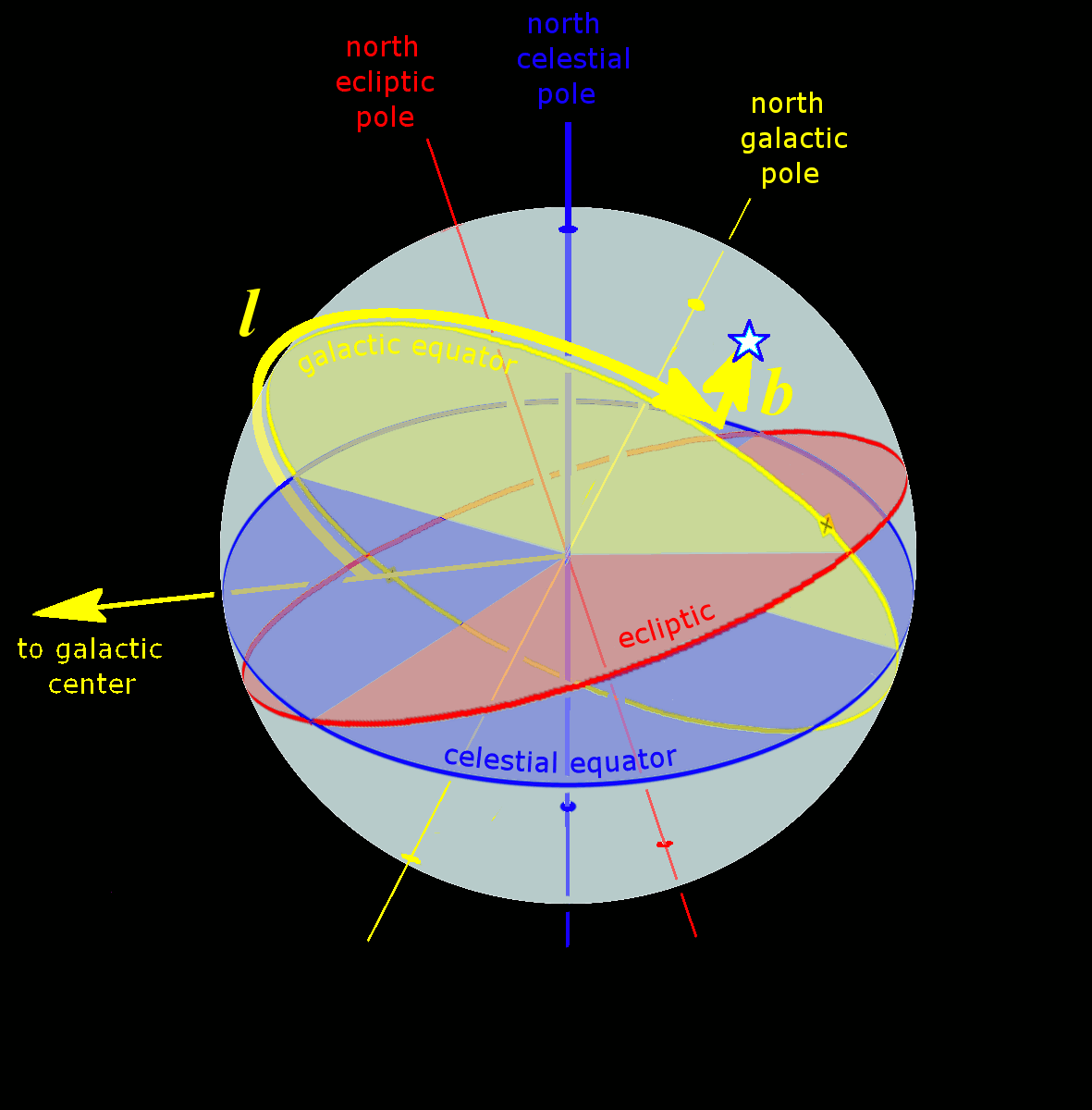
International Celestial Reference Frame
The International Celestial Reference System (ICRS) is the current standard celestial reference system adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). Its origin is at the barycenter of the Solar System, with axes that are intended to "show no global rotation with respect to a set of distant extragalactic objects". This fixed reference system differs from previous reference systems, which had been based on Catalogues of Fundamental Stars that had published the positions of stars based on direct "observations of [their] Equatorial coordinate system, equatorial coordinates, right ascension and declination" and had adopted as "privileged axes ... the mean equator and the dynamical equinox" at a particular Epoch (astronomy)#Date-references for coordinate systems, date and time. The International Celestial Reference Frame (ICRF) is a realization of the International Celestial Reference System using reference celestial sources observed at radio wavelengths. In the context of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celestial Reference System
In astronomy, coordinate systems are used for specifying position (geometry), positions of astronomical object, celestial objects (natural satellite, satellites, planets, stars, galaxy, galaxies, etc.) relative to a given reference frame, based on physical reference points available to a situated observer (e.g. the true horizon and true north, north to an observer on Earth's surface). Coordinate systems in astronomy can specify an object's relative position in three-dimensional space or plot (graphics), plot merely by its direction (geometry), direction on a celestial sphere, if the object's distance is unknown or trivial. spherical coordinate system, Spherical coordinates, projected on the celestial sphere, are analogous to the geographic coordinate system used on the surface of Earth. These differ in their choice of fundamental plane (spherical coordinates), fundamental plane, which divides the celestial sphere into two equal sphere, hemispheres along a great circle. Cartesian c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth Orientation Parameters
In geodesy and astrometry, earth orientation parameters (EOP) describe irregularities in the rotation of planet Earth. EOP provide the rotational transform from the International Terrestrial Reference System (ITRS) to the International Celestial Reference System (ICRS), or vice versa, as a function of time. Earth's rotational velocity is not constant over time. Any motion of mass in or on Earth causes a slowdown or speedup of the rotation speed, or a change of rotation axis. Small motions produce changes too small to be measured, but movements of very large mass, like sea currents, tides, or those resulting from earthquakes, can produce discernible changes in the rotation and can change very precise astronomical observations. Global simulations of atmosphere, ocean, and land dynamics are used to create effective angular momentum (EAM) functions that can be used to predict changes in EOP. Components Universal time Universal time ( UT1) tracks the Earth's rotation in time, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Earth Rotation And Reference Systems Service
The International Earth Rotation and Reference Systems Service (IERS), formerly the International Earth Rotation Service, is the body responsible for maintaining global time and reference frame standards, notably through its Earth Orientation Parameter (EOP) and International Celestial Reference System (ICRS) groups. History The IERS was established in its present form in 1987 by the International Astronomical Union and the International Union of Geodesy and Geophysics, replacing the earlier International Polar Motion Service (IPMS) and the Earth rotation section of the Bureau International de l'Heure (BIH). The service began operation on January 1, 1988. Since its inception, the IERS has established new bureaus including the GPS Coordinating Centre in 1990, the DORIS Coordinating Centre in 1994 and the Global Geophysical Fluids Centre in 1998. The organization was formerly known as International Earth Rotation Service until 2003 when it formally changed its name to its pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geodesy
Geodesy or geodetics is the science of measuring and representing the Figure of the Earth, geometry, Gravity of Earth, gravity, and Earth's rotation, spatial orientation of the Earth in Relative change, temporally varying Three-dimensional space, 3D. It is called planetary geodesy when studying other astronomical body, astronomical bodies, such as planets or Natural satellite, circumplanetary systems. Geodynamics, Geodynamical phenomena, including crust (geology), crustal motion, tides, and polar motion, can be studied by designing global and national Geodetic control network, control networks, applying space geodesy and terrestrial geodetic techniques, and relying on Geodetic datum, datums and coordinate systems. Geodetic job titles include geodesist and geodetic surveyor. History Geodesy began in pre-scientific Classical antiquity, antiquity, so the very word geodesy comes from the Ancient Greek word or ''geodaisia'' (literally, "division of Earth"). Early ideas about t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |