John Quincy Adams (; July 11, 1767 – February 23, 1848) was the sixth
president of the United States
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president directs the Federal government of the United States#Executive branch, executive branch of the Federal government of t ...
, serving from 1825 to 1829. He previously served as the eighth
United States secretary of state
The United States secretary of state (SecState) is a member of the executive branch of the federal government of the United States and the head of the U.S. Department of State.
The secretary of state serves as the principal advisor to the ...
from 1817 to 1825. During his long diplomatic and political career, Adams served as an ambassador and also as a member of the
United States Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature, legislative branch of the federal government of the United States. It is a Bicameralism, bicameral legislature, including a Lower house, lower body, the United States House of Representatives, ...
representing
Massachusetts
Massachusetts ( ; ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders the Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of Maine to its east, Connecticut and Rhode ...
in both chambers. He was the eldest son of
John Adams
John Adams (October 30, 1735 – July 4, 1826) was a Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the second president of the United States from 1797 to 1801. Before Presidency of John Adams, his presidency, he was a leader of ...
, who served as the second president of the United States from 1797 to 1801, and
First Lady Abigail Adams. Initially a
Federalist
The term ''federalist'' describes several political beliefs around the world. It may also refer to the concept of parties, whose members or supporters call themselves ''Federalists''.
History Europe federation
In Europe, proponents of deep ...
like his father, he won election to the presidency as a member of the
Democratic-Republican Party
The Democratic-Republican Party (also referred to by historians as the Republican Party or the Jeffersonian Republican Party), was an American political party founded by Thomas Jefferson and James Madison in the early 1790s. It championed li ...
, and later, in the mid-1830s, became affiliated with the
Whig Party.
Born in
Braintree, Massachusetts
Braintree () is a municipality in Norfolk County, Massachusetts, United States. It is officially known as a town, but Braintree is a city with a mayor-council form of government, and it is considered a city under Massachusetts law. The populat ...
, Adams spent much of his youth in Europe, where his father served as a diplomat. After returning to the United States, Adams established a successful legal practice in
Boston
Boston is the capital and most populous city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States. The city serves as the cultural and Financial centre, financial center of New England, a region of the Northeas ...
. In 1794, President
George Washington
George Washington (, 1799) was a Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the first president of the United States, serving from 1789 to 1797. As commander of the Continental Army, Washington led Patriot (American Revoluti ...
appointed Adams as the U.S. ambassador to the
Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
, and Adams would serve in high-ranking diplomatic posts until 1801, when
Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (, 1743July 4, 1826) was an American Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the third president of the United States from 1801 to 1809. He was the primary author of the United States Declaration of Indepe ...
took office as president. Federalist leaders in Massachusetts arranged for Adams's election to the United States Senate in 1802, but Adams broke with the Federalist Party over foreign policy and was denied re-election. In 1809, President
James Madison
James Madison (June 28, 1836) was an American statesman, diplomat, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the fourth president of the United States from 1809 to 1817. Madison was popularly acclaimed as the ...
, a member of the Democratic-Republican Party, appointed Adams as the U.S. ambassador to
Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
.
Multilingual
Multilingualism is the use of more than one language, either by an individual speaker or by a group of speakers. When the languages are just two, it is usually called bilingualism. It is believed that multilingual speakers outnumber monolin ...
, Adams held diplomatic posts for the duration of Madison's presidency, and he served as part of the American delegation that negotiated an end to the
War of 1812
The War of 1812 was fought by the United States and its allies against the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom and its allies in North America. It began when the United States United States declaration of war on the Uni ...
. In 1817, President
James Monroe
James Monroe ( ; April 28, 1758July 4, 1831) was an American Founding Father of the United States, Founding Father who served as the fifth president of the United States from 1817 to 1825. He was the last Founding Father to serve as presiden ...
selected Adams as his secretary of state. In that role, Adams negotiated the
Adams–Onís Treaty
The Adams–Onís Treaty () of 1819, also known as the Transcontinental Treaty, the Spanish Cession, the Florida Purchase Treaty, or the Florida Treaty,Weeks, p. 168. was a treaty between the United States and Spain in 1819 that ceded Florida to ...
, which provided for the American acquisition of Florida. He also helped formulate the
Monroe Doctrine
The Monroe Doctrine is a foreign policy of the United States, United States foreign policy position that opposes European colonialism in the Western Hemisphere. It holds that any intervention in the political affairs of the Americas by foreign ...
, which became a key tenet of
U.S. foreign policy. In 1818, Adams was elected a member of the
American Philosophical Society
The American Philosophical Society (APS) is an American scholarly organization and learned society founded in 1743 in Philadelphia that promotes knowledge in the humanities and natural sciences through research, professional meetings, publicat ...
in Philadelphia.
Adams,
Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson (March 15, 1767 – June 8, 1845) was the seventh president of the United States from 1829 to 1837. Before Presidency of Andrew Jackson, his presidency, he rose to fame as a general in the U.S. Army and served in both houses ...
,
William H. Crawford
William Harris Crawford (February 24, 1772 – September 15, 1834) was an American politician who served as U.S. Secretary of War and U.S. Secretary of the Treasury. He later ran for U.S. president in the 1824 United States presidential electi ...
, and
Henry Clay
Henry Clay (April 12, 1777June 29, 1852) was an American lawyer and statesman who represented Kentucky in both the United States Senate, U.S. Senate and United States House of Representatives, House of Representatives. He was the seventh Spea ...
—all members of the Democratic-Republican Party—competed in the
1824 presidential election. Because no candidate won a majority of
electoral votes, the House of Representatives held a
contingent election
In the United States, a contingent election is used to elect the president or vice president if no candidate receives a majority of the whole number of electors appointed. A presidential contingent election is decided by a special vote of th ...
, which Adams won with the support of
Speaker of the House Henry Clay, whom Adams would controversially appoint as his secretary of state. As president, Adams called for an ambitious agenda that included
federally funded infrastructure projects, the establishment of a national university, and engagement with the countries of Latin America, but Congress refused to pass many of his initiatives. During
Adams's presidency, the Democratic-Republican Party split into two major camps: the
National Republican Party
The National Republican Party, also known as the Anti-Jacksonian Party or simply Republicans, was a political party in the United States which evolved from a conservative-leaning faction of the Democratic-Republican Party that supported John ...
, which supported Adams, and Andrew Jackson's
Democratic Party. The Democrats proved to be more effective political organizers than Adams and his National Republican supporters, and Jackson soundly defeated Adams in the
1828 presidential election, making Adams the second president to fail to win re-election (his father being the first).
Rather than retiring from public service, Adams won election to the House of Representatives, where he would serve from 1831 until his death in 1848. He remains the only former president to be elected to the chamber. After narrowly losing his bids for
Governor of Massachusetts
The governor of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts is the head of government of the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts. The governor is the chief executive, head of the state cabinet and the commander-in-chief of the commonw ...
and Senate re-election, Adams joined the
Anti-Masonic Party
The Anti-Masonic Party was the earliest Third party (United States), third party in the United States. Formally a Single-issue politics, single-issue party, it strongly opposed Freemasonry in the United States. It was active from the late 1820s, ...
in the early 1830s before joining the
Whig Party, which united those opposed to President Jackson. During his time in Congress, Adams became increasingly critical of
slavery
Slavery is the ownership of a person as property, especially in regards to their labour. Slavery typically involves compulsory work, with the slave's location of work and residence dictated by the party that holds them in bondage. Enslavemen ...
and of the Southern leaders whom he believed controlled the Democratic Party. He was particularly opposed to the
annexation of Texas and the
Mexican–American War
The Mexican–American War (Spanish language, Spanish: ''guerra de Estados Unidos-México, guerra mexicano-estadounidense''), also known in the United States as the Mexican War, and in Mexico as the United States intervention in Mexico, ...
, which he saw as a war to extend slavery and
its political grip on Congress. He also led the repeal of the "
gag rule", which had prevented the House of Representatives from debating petitions to
abolish slavery. While historians
typically rank Adams as an average president (he had an ambitious agenda but could not get it passed by Congress), they concur that Adams was one of the greatest diplomats and secretaries of state in American history; historians also credit Adams with a vehement stance against slavery, and his fight for the rights of women and Native Americans during his post-presidency.
Early life, education, and early career
John Quincy Adams was born on July 11, 1767, to
John and
Abigail Adams (née Smith) in a part of
Braintree, Massachusetts
Braintree () is a municipality in Norfolk County, Massachusetts, United States. It is officially known as a town, but Braintree is a city with a mayor-council form of government, and it is considered a city under Massachusetts law. The populat ...
, that is now
Quincy. He was named after his mother's maternal grandfather, Colonel
John Quincy, after whom Quincy, Massachusetts, is also named. Colonel Quincy died two days after his great-grandson's birth. Young Adams was educated by tutors – his cousin James Thaxter and his father's law clerk, Nathan Rice. He soon exhibited literary skills, and in 1779 he started a diary that he kept until just before he died in 1848.
Until the age of ten, Adams grew up on the family farm in Braintree, largely in the care of his mother. Though frequently absent because of his participation in the
American Revolution
The American Revolution (1765–1783) was a colonial rebellion and war of independence in which the Thirteen Colonies broke from British America, British rule to form the United States of America. The revolution culminated in the American ...
, John Adams maintained a correspondence with his son, encouraging him to read works by authors such as
Thucydides
Thucydides ( ; ; BC) was an Classical Athens, Athenian historian and general. His ''History of the Peloponnesian War'' recounts Peloponnesian War, the fifth-century BC war between Sparta and Athens until the year 411 BC. Thucydides has been d ...
and
Hugo Grotius
Hugo Grotius ( ; 10 April 1583 – 28 August 1645), also known as Hugo de Groot () or Huig de Groot (), was a Dutch humanist, diplomat, lawyer, theologian, jurist, statesman, poet and playwright. A teenage prodigy, he was born in Delft an ...
. With his father's encouragement, Adams would also translate
classical authors such as
Virgil
Publius Vergilius Maro (; 15 October 70 BC21 September 19 BC), usually called Virgil or Vergil ( ) in English, was an ancient Rome, ancient Roman poet of the Augustan literature (ancient Rome), Augustan period. He composed three of the most fa ...
,
Horace
Quintus Horatius Flaccus (; 8 December 65 BC – 27 November 8 BC), Suetonius, Life of Horace commonly known in the English-speaking world as Horace (), was the leading Roman lyric poet during the time of Augustus (also known as Octavian). Th ...
,
Plutarch
Plutarch (; , ''Ploútarchos'', ; – 120s) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo (Delphi), Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for his ''Parallel Lives'', ...
, and
Aristotle
Aristotle (; 384–322 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, a ...
.
In 1778, Adams and his father departed for Europe, where John Adams would serve as part of American diplomatic missions in
France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
and the
Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
. During this period, Adams studied
law
Law is a set of rules that are created and are enforceable by social or governmental institutions to regulate behavior, with its precise definition a matter of longstanding debate. It has been variously described as a science and as the ar ...
,
French,
Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
, and
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
, and attended several schools, including
Leiden University
Leiden University (abbreviated as ''LEI''; ) is a Public university, public research university in Leiden, Netherlands. Established in 1575 by William the Silent, William, Prince of Orange as a Protestantism, Protestant institution, it holds the d ...
. In 1781, Adams traveled to
Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg, formerly known as Petrograd and later Leningrad, is the List of cities and towns in Russia by population, second-largest city in Russia after Moscow. It is situated on the Neva, River Neva, at the head of the Gulf of Finland ...
, Russia, where he served as the secretary to the American diplomat,
Francis Dana
Francis Dana (June 13, 1743 – April 25, 1811) was an American Founding Father, lawyer, jurist, and statesman from Massachusetts. He served as a delegate to the Continental Congress in 1777–1778 and 1784. A signer of the Articles of Confederat ...
. He returned to the Netherlands in 1783 and accompanied his father to
Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-west coast of continental Europe, consisting of the countries England, Scotland, and Wales. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the List of European ...
in 1784. Though Adams enjoyed Europe, he and his family decided he needed to return to the United States to complete his education and eventually launch a political career.
Adams returned to the United States in 1785 and earned admission as a member of the
junior class of
Harvard College
Harvard College is the undergraduate education, undergraduate college of Harvard University, a Private university, private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Part of the Harvard Faculty of Arts and Scienc ...
the following year. He joined
Phi Beta Kappa
The Phi Beta Kappa Society () is the oldest academic honor society in the United States. It was founded in 1776 at the College of William & Mary in Virginia. Phi Beta Kappa aims to promote and advocate excellence in the liberal arts and sciences, ...
and excelled academically, graduating second in his class in 1787. After graduating from Harvard, he
studied law with
Theophilus Parsons in
Newburyport, Massachusetts
Newburyport is a coastal city in Essex County, Massachusetts, United States, northeast of Boston. The population was 18,289 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. A historic seaport with a vibrant tourism industry, Newburyport includes p ...
, from 1787 to 1789. Adams initially opposed the ratification of the
United States Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the Supremacy Clause, supreme law of the United States, United States of America. It superseded the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first constitution, on March 4, 1789. Originally includi ...
, but he ultimately came to accept the document, and in
1789
Events
January–March
* January – Emmanuel Joseph Sieyès publishes the pamphlet '' What Is the Third Estate?'' ('), influential on the French Revolution.
* January 7 – The 1788-89 United States presidential election ...
his father was elected as the first
vice president of the United States
The vice president of the United States (VPOTUS) is the second-highest ranking office in the Executive branch of the United States government, executive branch of the U.S. federal government, after the president of the United States, and ranks f ...
. In 1790, Adams opened his own legal practice in
Boston
Boston is the capital and most populous city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States. The city serves as the cultural and Financial centre, financial center of New England, a region of the Northeas ...
. Despite some early struggles, he was successful as an attorney and established financial independence from his parents.
Early political career (1793–1817)
Early diplomatic career and marriage
Adams initially avoided becoming involved in politics, instead focusing on building his legal career. In 1791, he wrote a series of pseudonymously published essays arguing that Britain provided a better governmental model than France. Two years later, he published another series of essays attacking
Edmond-Charles Genêt
Edmond-Charles Genêt (January 8, 1763July 14, 1834), also known as Citizen Genêt, was the French envoy to the United States appointed by the Girondins during the French Revolution. His actions on arriving in the United States led to a major po ...
, a French diplomat who sought to undermine President
George Washington
George Washington (, 1799) was a Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the first president of the United States, serving from 1789 to 1797. As commander of the Continental Army, Washington led Patriot (American Revoluti ...
's policy of neutrality in the
French Revolutionary Wars
The French Revolutionary Wars () were a series of sweeping military conflicts resulting from the French Revolution that lasted from 1792 until 1802. They pitted French First Republic, France against Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain, Habsb ...
. In 1794, Washington appointed Adams as the
U.S. ambassador to the Netherlands. Adams considered declining the role, but ultimately took the position on the advice of his father. While abroad, Adams continued to urge neutrality, arguing that the United States would benefit economically by staying out of the ongoing French Revolutionary Wars. His chief duty as the ambassador to the Netherlands was to secure and maintain loans essential to U.S. finances. On his way to the Netherlands, he met with
John Jay
John Jay (, 1745 – May 17, 1829) was an American statesman, diplomat, signatory of the Treaty of Paris (1783), Treaty of Paris, and a Founding Father of the United States. He served from 1789 to 1795 as the first chief justice of the United ...
, who was then negotiating the
Jay Treaty
The Treaty of Amity, Commerce, and Navigation, Between His Britannic Majesty and the United States of America, commonly known as the Jay Treaty, and also as Jay's Treaty, was a 1794 treaty between the United States and Great Britain that averted ...
with Great Britain. Adams supported the Jay Treaty, but it proved unpopular with many in the United States, contributing to a growing partisan split between the
Federalist Party
The Federalist Party was a conservativeMultiple sources:
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* and nationalist American political party and the first political party in the United States. It dominated the national government under Alexander Hamilton from 17 ...
of
Alexander Hamilton
Alexander Hamilton (January 11, 1755 or 1757July 12, 1804) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the first U.S. secretary of the treasury from 1789 to 1795 dur ...
and the
Democratic-Republican Party
The Democratic-Republican Party (also referred to by historians as the Republican Party or the Jeffersonian Republican Party), was an American political party founded by Thomas Jefferson and James Madison in the early 1790s. It championed li ...
of
Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (, 1743July 4, 1826) was an American Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the third president of the United States from 1801 to 1809. He was the primary author of the United States Declaration of Indepe ...
. In 1794 he supported
John Skey Eustace who wanted to return to the United States via the Netherlands.
Adams spent the winter of 1795–1796 in
London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ...
, where he met
Louisa Catherine Johnson
Louisa Catherine Adams (; February 12, 1775 – May 15, 1852) was the first lady of the United States from 1825 to 1829 during the presidency of John Quincy Adams. She was born in Kingdom of Great Britain, England and raised in early modern Fra ...
, the second daughter of American merchant Joshua Johnson. In April 1796, Louisa accepted Adams's proposal of marriage. Adams's parents disapproved of his decision to marry a woman who had grown up in England, but he informed his parents that he would not reconsider his decision. Adams initially wanted to delay his wedding to Louisa until he returned to the United States, but they married in
All Hallows-by-the-Tower on July 26, 1797. Shortly after the wedding, Joshua Johnson fled England to escape his creditors, and Adams did not receive the dowry that Johnson had promised him, much to the embarrassment of Louisa. Adams noted in his own diary that he had no regrets about his decision to marry Louisa.
In 1796, Washington appointed Adams as the
U.S. ambassador to Portugal. Later that year, John Adams defeated Jefferson in the
1796 presidential election. When the elder Adams became president, he appointed his son as the
U.S. ambassador to Prussia. Though concerned that his appointment would be criticized as
nepotistic, Adams accepted the position and traveled to the Prussian capital of Berlin with his wife and his younger brother,
Thomas Boylston Adams. The State Department tasked Adams with developing commercial relations with Prussia and Sweden, but President Adams also asked his son to write to him frequently about affairs in Europe. His advice that he regularly gave to his father based on his experiences on the ground in Europe proved particularly valuable during the
Quasi-War
The Quasi-War was an undeclared war from 1798 to 1800 between the United States and the French First Republic. It was fought almost entirely at sea, primarily in the Caribbean and off the East Coast of the United States, with minor actions in ...
with France, although President Adams also relied heavily on his official staff for such advice and not primarily on his son. In 1799, Adams negotiated a
new trade agreement between the United States and Prussia, though he could never complete an agreement with Sweden. He frequently wrote to family members in the United States, and in 1801 his letters about the Prussian region of
Silesia
Silesia (see names #Etymology, below) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at 8, ...
were published in a book titled ''Letters on Silesia''. During his time in Prussia, Adams befriended the German diplomat and writer
Friedrich von Gentz, whose work, ''The Origins and Principles of the American Revolution, Compared with the Origins and Principles of the French Revolution,'' Adams would translate into English in 1800. In the
1800 presidential election, Jefferson defeated John Adams, and both Adams and his son left office in early 1801.
U.S. senator from Massachusetts
On his return to the United States, Adams re-established a legal practice in
Boston
Boston is the capital and most populous city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States. The city serves as the cultural and Financial centre, financial center of New England, a region of the Northeas ...
, and in April 1802 he was elected to the
Massachusetts Senate
The Massachusetts Senate is the upper house of the Massachusetts General Court, the bicameral state legislature of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts. The Senate comprises 40 elected members from 40 single-member senatorial districts in the st ...
. In November of that year, he ran unsuccessfully for the
United States House of Representatives
The United States House of Representatives is a chamber of the Bicameralism, bicameral United States Congress; it is the lower house, with the U.S. Senate being the upper house. Together, the House and Senate have the authority under Artic ...
. In February 1803, the Massachusetts legislature elected Adams to the
United States Senate
The United States Senate is a chamber of the Bicameralism, bicameral United States Congress; it is the upper house, with the United States House of Representatives, U.S. House of Representatives being the lower house. Together, the Senate and ...
. Though somewhat reluctant to affiliate with any political party, Adams joined the Federalist minority in Congress. Like his Federalist colleagues, he opposed
the impeachment of Associate Justice
Samuel Chase
Samuel Chase (April 17, 1741 – June 19, 1811) was a Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father of the United States, signer of the Continental Association and United States Declaration of Independence as a representative of Maryla ...
, an outspoken supporter of the Federalist Party.
Adams had strongly opposed Jefferson's 1800 presidential candidacy, but he gradually became alienated from the Federalist Party. His disaffection was driven by the party's declining popularity, disagreements over foreign policy, and Adams's hostility to
Timothy Pickering, a Federalist Party leader whom Adams viewed as overly favorable to Britain. Unlike other New England Federalists, Adams supported the Jefferson administration's
Louisiana Purchase
The Louisiana Purchase () was the acquisition of the Louisiana (New France), territory of Louisiana by the United States from the French First Republic in 1803. This consisted of most of the land in the Mississippi River#Watershed, Mississipp ...
and expansionist policies. Adams was the lone Federalist in Congress to vote for the
Non-importation Act of 1806 that punished Britain for its attacks on American shipping during the ongoing
Napoleonic Wars
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Napoleonic Wars
, partof = the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars
, image = Napoleonic Wars (revision).jpg
, caption = Left to right, top to bottom:Battl ...
. Adams became increasingly frustrated with the unwillingness of other Federalists to condemn British actions, including
impressment
Impressment, colloquially "the press" or the "press gang", is a type of conscription of people into a military force, especially a naval force, via intimidation and physical coercion, conducted by an organized group (hence "gang"). European nav ...
, and he moved closer to the Jefferson administration. After Adams supported the
Embargo Act of 1807
The Embargo Act of 1807 was a general trade embargo on all foreign nations that was enacted by the United States Congress. Much broader than the ineffectual 1806 Non-importation Act, it represented an escalation of attempts to persuade Br ...
, the Federalist-controlled Massachusetts legislature elected Adams's successor several months before the end of his term, and Adams resigned from the Senate shortly thereafter.
While a member of the Senate, Adams served as a professor of logic at
Brown University
Brown University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in Providence, Rhode Island, United States. It is the List of colonial colleges, seventh-oldest institution of higher education in the US, founded in 1764 as the ' ...
and as the
Boylston Professor of Rhetoric and Oratory at
Harvard University
Harvard University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Founded in 1636 and named for its first benefactor, the History of the Puritans in North America, Puritan clergyma ...
. Adams's devotion to classical rhetoric shaped his response to public issues, and he would remain inspired by those rhetorical ideals long after the neo-classicalism and deferential politics of the founding generation were eclipsed by the commercial ethos and mass democracy of the
Jacksonian Era. Many of Adams's idiosyncratic positions were rooted in his abiding devotion to the
Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero ( ; ; 3 January 106 BC – 7 December 43 BC) was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, orator, writer and Academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises tha ...
nian ideal of the citizen-orator "speaking well" to promote the welfare of the polis. He was also influenced by the classical republican ideal of civic eloquence espoused by British philosopher
David Hume
David Hume (; born David Home; – 25 August 1776) was a Scottish philosopher, historian, economist, and essayist who was best known for his highly influential system of empiricism, philosophical scepticism and metaphysical naturalism. Beg ...
. Adams adapted these classical republican ideals of public oratory to the American debate, viewing its multilevel political structure as ripe for "the renaissance of Demosthenic eloquence". His ''Lectures on Rhetoric and Oratory'' (1810) looks at the fate of ancient oratory, the necessity of liberty for it to flourish, and its importance as a unifying element for a new nation of diverse cultures and beliefs. Just as civic eloquence failed to gain popularity in Britain, in the United States interest faded in the second decade of the 19th century, as the "public spheres of heated oratory" disappeared in favor of the private sphere.
Minister to Russia

After resigning from the Senate, Adams was ostracized by Massachusetts Federalist leaders, but he declined Democratic-Republican entreaties to seek office. In 1809, he argued before the
Supreme Court of the United States
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all Federal tribunals in the United States, U.S. federal court cases, and over Stat ...
in ''
Fletcher v. Peck'', and the Supreme Court ultimately agreed with Adams's argument that the Constitution's
Contract Clause prevented the state of Georgia from invalidating a land sale to out-of-state companies. Later that year, President
James Madison
James Madison (June 28, 1836) was an American statesman, diplomat, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the fourth president of the United States from 1809 to 1817. Madison was popularly acclaimed as the ...
appointed Adams as the first
United States Minister to Russia in 1809. Though Adams had only recently broken with the Federalist Party, his support of Jefferson's foreign policy had earned him goodwill with the Madison Administration. Adams was well-qualified for the role after his experiences in Europe generally and Russia specifically.
After a difficult passage through the
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by the countries of Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North European Plain, North and Central European Plain regions. It is the ...
, Adams arrived in the Russian capital of St. Petersburg in October 1809. He quickly established a productive working relationship with Russian official
Nikolay Rumyantsev and eventually befriended Tsar
Alexander I of Russia
Alexander I (, ; – ), nicknamed "the Blessed", was Emperor of Russia from 1801, the first king of Congress Poland from 1815, and the grand duke of Finland from 1809 to his death in 1825. He ruled Russian Empire, Russia during the chaotic perio ...
. Adams continued to favor American neutrality between France and Britain during the
Napoleonic War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Napoleonic Wars
, partof = the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars
, image = Napoleonic Wars (revision).jpg
, caption = Left to right, top to bottom:Battl ...
. Louisa was initially distraught at the prospect of living in Russia, but she became a popular figure at the Russian court. From his diplomatic post, Adams observed the French Emperor
Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte (born Napoleone di Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French general and statesman who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led Military career ...
's
invasion of Russia, which ended in defeat for the French. In February 1811, President Madison nominated Adams as an
Associate Justice of the United States Supreme Court
An associate justice of the Supreme Court of the United States is a justice of the Supreme Court of the United States, other than the chief justice of the United States. The number of associate justices is eight, as set by the Judiciary Act of 1 ...
. The nomination was unanimously confirmed by the Senate, but Adams declined the seat, preferring a career in politics and diplomacy, so
Joseph Story
Joseph Story (September18, 1779September10, 1845) was an American lawyer, jurist, and politician who served as an associate justice of the Supreme Court of the United States from 1812 to 1845. He is most remembered for his opinions in ''Martin ...
took the seat instead.
Treaty of Ghent and ambassador to Britain

Adams had long feared that the United States would enter a war it could not win against Britain, and by early 1812, he saw such a war as inevitable due to the constant British attacks on American shipping and the British practice of
impressment
Impressment, colloquially "the press" or the "press gang", is a type of conscription of people into a military force, especially a naval force, via intimidation and physical coercion, conducted by an organized group (hence "gang"). European nav ...
. In mid-1812, the United States declared war against Britain, beginning the
War of 1812
The War of 1812 was fought by the United States and its allies against the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom and its allies in North America. It began when the United States United States declaration of war on the Uni ...
. Tsar Alexander attempted to mediate the conflict between Britain and the United States, and President Madison appointed Adams, Secretary of the Treasury
Albert Gallatin, and Federalist Senator
James A. Bayard to a delegation charged with negotiating an end to the war. Gallatin and Bayard arrived in St. Petersburg in July 1813, but the British declined Tsar Alexander's offer of mediation. Hoping to start negotiations at another venue, Adams left Russia in April 1814. Negotiations finally began in mid-1814 in
Ghent
Ghent ( ; ; historically known as ''Gaunt'' in English) is a City status in Belgium, city and a Municipalities of Belgium, municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of the Provinces of Belgium, province ...
, where Adams, Gallatin, and Bayard were joined by two additional American delegates,
Jonathan Russell
Jonathan Russell (February 27, 1771 – February 17, 1832) was a United States representative from Massachusetts and diplomat. He served the Massachusetts's 11th congressional district, 11th congressional district from 1821 to 1823 and was the ...
and former
Speaker of the House Henry Clay
Henry Clay (April 12, 1777June 29, 1852) was an American lawyer and statesman who represented Kentucky in both the United States Senate, U.S. Senate and United States House of Representatives, House of Representatives. He was the seventh Spea ...
. Adams, the nominal head of the delegation, got along well with Gallatin, Bayard, and Russell, but he occasionally clashed with Clay.
The British delegation initially treated the United States as a defeated power, demanding the creation of an
Indian barrier state from American territory near the
Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes spanning the Canada–United States border. The five lakes are Lake Superior, Superior, Lake Michigan, Michigan, Lake Huron, H ...
. The American delegation unanimously rejected this offer, and their negotiating position was bolstered by the American victory in the
Battle of Plattsburgh. By November 1814, the government of
Lord Liverpool
Robert Banks Jenkinson, 2nd Earl of Liverpool (7 June 1770 – 4 December 1828) was a British Tory statesman who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1812 to 1827. Before becoming Prime Minister he had been Foreign Secretary, ...
decided to seek an end to hostilities with the U.S. on the basis of ''status quo ante bellum''. Even though a return to the status quo would mean the continuation of the British practice of impressment, Adams and his fellow commissioners had hoped for similar terms. The treaty was signed on December 24, 1814. The United States did not gain any concessions from the treaty but could boast that it had survived a war against the strongest power in the world. Following the signing of the treaty, Adams traveled to Paris, where he witnessed first-hand the
Hundred Days
The Hundred Days ( ), also known as the War of the Seventh Coalition (), marked the period between Napoleon's return from eleven months of exile on the island of Elba to Paris on20 March 1815 and the second restoration of King Louis XVIII o ...
of Napoleon's restoration.
In May 1815, Adams learned that President Madison had appointed him as the
U.S. ambassador to Britain. With the aid of Clay and Gallatin, Adams negotiated a limited trade agreement with Britain. Following the conclusion of the trade agreement, much of Adams's time as ambassador was spent helping stranded American sailors and prisoners of war.
In pursuit of national unity, newly elected president
James Monroe
James Monroe ( ; April 28, 1758July 4, 1831) was an American Founding Father of the United States, Founding Father who served as the fifth president of the United States from 1817 to 1825. He was the last Founding Father to serve as presiden ...
decided a Northerner would be optimal for the position of
Secretary of State, and he chose the respected and experienced Adams for the role. Having spent several years in Europe, Adams returned to the United States in August 1817.
Secretary of State (1817–1825)
Adams served as Secretary of State during Monroe's eight-year presidency, from 1817 to 1825. Many of his successes as secretary, such as the convention of 1818 with the United Kingdom, the Transcontinental Treaty with Spain, and the Monroe Doctrine, were not preplanned strategies but responses to unexpected events. Adams wanted to delay American recognition of the newly independent republics of Latin America to avoid the risk of war with Spain and its European allies. However, Andrew Jackson's military campaign in Florida and Henry Clay's threats in Congress forced Spain to cut a deal, which Adams negotiated successfully. Biographer James Lewis says, "He managed to play the cards that he had been dealt – cards that he very clearly had not wanted – in ways that forced the Spanish cabinet to recognize the weakness of its own hand". Apart from the Monroe doctrine, his last four years as Secretary of State were less successful because he was preoccupied with his presidential campaign and refused to make compromises with other countries that might have weakened his candidacy; the result was a small-scale trade war but a successful election to the White House.

Taking office in the aftermath of the War of 1812, Adams thought that the country had been fortunate in avoiding territorial losses, and he prioritized avoiding another war with a European power, particularly Britain.
He also sought to avoid exacerbating sectional tensions, which had been a major issue for the country during the War of 1812. One of the major challenges confronting Adams was how to respond to the power vacuum in Latin America that arose from Spain's weakness following the
Peninsular War
The Peninsular War (1808–1814) was fought in the Iberian Peninsula by Kingdom of Portugal, Portugal, Spain and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom against the invading and occupying forces of the First French ...
. In addition to his foreign policy role, Adams held several domestic duties, including overseeing the
1820 United States census and writing an extensive report on
weights and measures
A unit of measurement, or unit of measure, is a definite magnitude (mathematics), magnitude of a quantity, defined and adopted by convention or by law, that is used as a standard for measurement of the same kind of quantity. Any other qua ...
. The weights and measures report, a particular passion of Adams', provided an extensive historical perspective on the topic and advocated for adoption of the
metric system
The metric system is a system of measurement that standardization, standardizes a set of base units and a nomenclature for describing relatively large and small quantities via decimal-based multiplicative unit prefixes. Though the rules gover ...
.
Monroe and Adams agreed on most major foreign policy issues: both favored neutrality in
Latin American independence wars, peace with the United Kingdom, rejection of a trade agreement with the French, and peaceful expansion into the
Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire, sometimes referred to as the Hispanic Monarchy (political entity), Hispanic Monarchy or the Catholic Monarchy, was a colonial empire that existed between 1492 and 1976. In conjunction with the Portuguese Empire, it ushered ...
's North American territories. The president and his secretary of state developed a strong working relationship, and while Adams often influenced Monroe's policies, he respected that Monroe made the final decisions on major issues. Monroe met regularly with his five-person
cabinet, which initially consisted of Adams, Secretary of the Treasury
William H. Crawford
William Harris Crawford (February 24, 1772 – September 15, 1834) was an American politician who served as U.S. Secretary of War and U.S. Secretary of the Treasury. He later ran for U.S. president in the 1824 United States presidential electi ...
, Secretary of War
John C. Calhoun, Secretary of the Navy
Benjamin Crowninshield, and Attorney General
William Wirt. Adams developed a strong respect for Calhoun but believed that Crawford was unduly focused on succeeding Monroe in 1824.
During his time as ambassador to Britain, Adams had begun negotiations over several contentious issues that had not been solved by the War of 1812 or the Treaty of Ghent. In 1817, the two countries agreed to the
Rush–Bagot Treaty, which limited naval armaments on the
Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes spanning the Canada–United States border. The five lakes are Lake Superior, Superior, Lake Michigan, Michigan, Lake Huron, H ...
. Negotiations between the two powers continued, resulting in the
Treaty of 1818, which defined the
Canada–United States border
The international border between Canada and the United States is the longest in the world by total length. The boundary (including boundaries in the Great Lakes, Atlantic, and Pacific coasts) is long. The land border has two sections: Canada' ...
west of the Great Lakes. The boundary was set at the
49th parallel to the
Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in great-circle distance, straight-line distance from the northernmost part of Western Can ...
, while the territory to the west of the mountains, known as
Oregon Country
Oregon Country was a large region of the Pacific Northwest of North America that was subject to a long Oregon boundary dispute, dispute between the United Kingdom and the United States in the early 19th century. The area, which had been demarcat ...
, would be jointly occupied. The agreement marked a watershed moment in
United Kingdom–United States relations, as the United States focused on its southern and western borders and British concerns about American expansionism subsided.
Adams–Onís Treaty
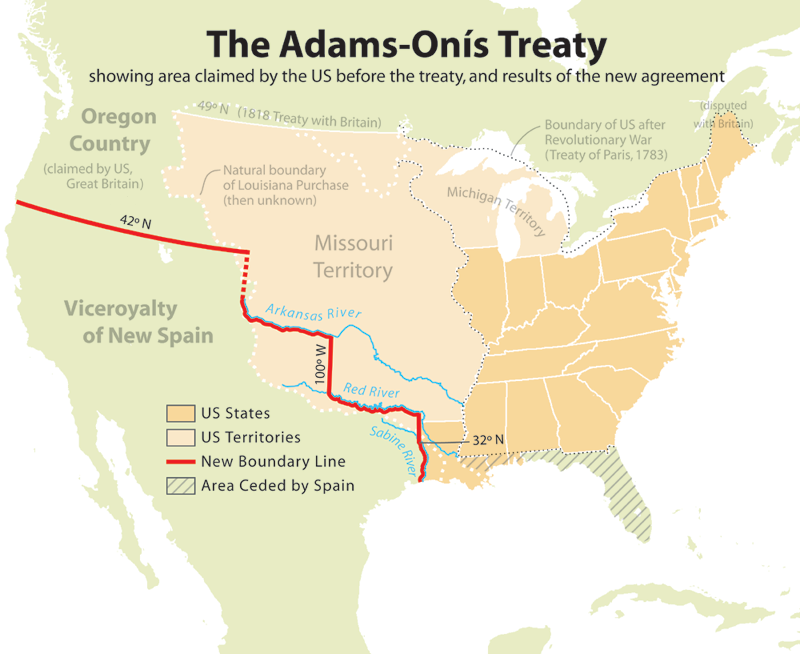
When Adams took office, Spanish possessions bordered the United States to the south and west. To the south, Spain retained control of
Florida
Florida ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders the Gulf of Mexico to the west, Alabama to the northwest, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the north, the Atlantic ...
, which the U.S. had long sought to purchase. Spain struggled to control the Indian tribes active in Florida, and some of those tribes raided United States territory. To the west,
New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( ; Nahuatl: ''Yankwik Kaxtillan Birreiyotl''), originally the Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain. It was one of several ...
bordered the territory acquired by the United States in the Louisiana Purchase, but no clear boundary had been established between United States and Spanish territory.
After taking office, Adams began negotiations with
Luis de Onís, the Spanish minister to the United States, for the purchase of Florida and the settlement of a border between the United States and New Spain. The negotiations were interrupted by an escalation of the
Seminole War, and in December 1818, Monroe ordered General
Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson (March 15, 1767 – June 8, 1845) was the seventh president of the United States from 1829 to 1837. Before Presidency of Andrew Jackson, his presidency, he rose to fame as a general in the U.S. Army and served in both houses ...
to enter Florida and retaliate against
Seminole
The Seminole are a Native American people who developed in Florida in the 18th century. Today, they live in Oklahoma and Florida, and comprise three federally recognized tribes: the Seminole Nation of Oklahoma, the Seminole Tribe of Florida, ...
s that had raided Georgia. Exceeding his orders, Jackson captured the Spanish outposts of
St. Marks and
Pensacola
Pensacola ( ) is a city in the Florida panhandle in the United States. It is the county seat and only city in Escambia County. The population was 54,312 at the 2020 census. It is the principal city of the Pensacola metropolitan area, which ha ...
and executed two Englishmen. While Jackson's actions outraged the rest of the cabinet, Adams defended them as necessary to the country's self-defense, and he eventually convinced Monroe and most of the cabinet to support Jackson.
Adams informed Spain that its failure to police its own territory had compelled Jackson to act, and he advised Spain to either secure the region or sell it to the United States. The British, meanwhile, declined to risk their recent rapprochement with the United States, and did not make a major diplomatic issue out of Jackson's execution of two British nationals.
Negotiations between Spain and the United States continued, and Spain agreed to cede Florida. The determination of the western boundary of the United States proved more difficult. American expansionists favored setting the border at the
Rio Grande
The Rio Grande ( or ) in the United States or the Río Bravo (del Norte) in Mexico (), also known as Tó Ba'áadi in Navajo language, Navajo, is one of the principal rivers (along with the Colorado River) in the Southwestern United States a ...
, but Spain, intent on protecting its colony of
Mexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundar ...
from American encroachment, insisted on setting the boundary at the
Sabine River. At Monroe's direction, Adams agreed to the
Sabine River boundary, but he insisted that Spain cede its claims on Oregon Country. Adams was deeply interested in establishing American control over the Oregon Country, partly because he believed that control of that region would spur trade with Asia. The acquisition of Spanish claims to the Pacific Northwest also allowed the Monroe administration to pair the acquisition of Florida, which was chiefly sought by Southerners, with territorial gains favored primarily by those in the North. After extended negotiations, Spain and the United States agreed to the
Adams–Onís Treaty
The Adams–Onís Treaty () of 1819, also known as the Transcontinental Treaty, the Spanish Cession, the Florida Purchase Treaty, or the Florida Treaty,Weeks, p. 168. was a treaty between the United States and Spain in 1819 that ceded Florida to ...
, which was ratified in February 1821.
Adams was deeply proud of the treaty, though he privately was concerned by the potential expansion of slavery into the newly acquired territories. In 1824, the Monroe administration would strengthen US claims to Oregon by ratifying the
Russo-American Treaty of 1824, which established
Russian Alaska's southern border at 54°40′ north.
Monroe Doctrine
As the Spanish Empire continued to fracture during Monroe's second term, Adams, Monroe and Clay became increasingly concerned that the "
Holy Alliance" of
Prussia
Prussia (; ; Old Prussian: ''Prūsija'') was a Germans, German state centred on the North European Plain that originated from the 1525 secularization of the Prussia (region), Prussian part of the State of the Teutonic Order. For centuries, ...
, Austria, and Russia would seek to bring Spain's erstwhile colonies under their control, to the point of even contemplating a Holy Alliance of their own to defend democracy. In his 1821 Fourth of July address, Adams addressed this issue, noting a shared "chain of sympathy" between the U.S. and Latin America, but arguing for neutrality rather than a Holy Alliance. In 1822, following the conclusion of the Adams–Onís Treaty, the Monroe administration recognized the independence of several Latin American countries, including
Argentina
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourt ...
and Mexico. In 1823, British Foreign Secretary
George Canning suggested that the United States and Britain should work together to preserve the independence of these fledgling republics. The cabinet debated whether to accept the offer, but Adams opposed it. Instead, Adams urged Monroe to publicly declare the United States' opposition to any European attempt to colonize or re-take control of territory in the Americas, while also committing the United States to neutrality in European affairs. In his December 1823
annual message to Congress, Monroe laid out the Monroe Doctrine, which was largely built upon Adams's ideas.
In issuing the Monroe Doctrine, the United States displayed a new level of assertiveness in international relations, as the doctrine represented the country's first claim to a
sphere of influence
In the field of international relations, a sphere of influence (SOI) is a spatial region or concept division over which a state or organization has a level of cultural, economic, military, or political exclusivity.
While there may be a formal a ...
. It also marked the country's shift in psychological orientation away from Europe and towards the Americas. Debates over foreign policy would no longer center on relations with Britain and France, but instead focus on western expansion and relations with Native Americans. The doctrine became one of the foundational principles of
U.S. foreign policy.
1824 presidential election

Immediately upon becoming Secretary of State, Adams emerged as one of Monroe's most likely successors, as the last three presidents had all served in the role before taking office. As the
1824 election approached, Henry Clay, John C. Calhoun (who later dropped out of the race), and William H. Crawford appeared to be Adams's primary competition to succeed Monroe. Crawford favored state sovereignty and a
strict constructionist view of the
Constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organization or other type of entity, and commonly determines how that entity is to be governed.
When these pri ...
, while Clay, Calhoun, and Adams embraced federally funded
internal improvements
Internal improvements is the term used historically in the United States for public works from the end of the American Revolution through much of the 19th century, mainly for the creation of a transportation infrastructure: roads, turnpikes, can ...
, high
tariffs, and the
Second Bank of the United States
The Second Bank of the United States was the second federally authorized Second Report on Public Credit, Hamiltonian national bank in the United States. Located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, the bank was chartered from February 1816 to January ...
, which was also known as the national bank.
Because the Federalist Party had all but collapsed after the War of 1812, all the major presidential candidates were members of the Democratic-Republican Party.
Adams felt that his own election as president would vindicate his father, while also allowing him to pursue an ambitious domestic policy. Though he lacked the charisma of his competitors, Adams was widely respected and benefited from the lack of other prominent Northern political leaders.
Adams's top choice for the role of vice president was General Andrew Jackson; Adams noted that "the Vice-Presidency was a station in which
acksoncould hang no one, and in which he would need to quarrel with no one". However, as the 1824 election approached, Jackson jumped into the race for president, and Calhoun ended up receiving the Vice-presidential support of Adams supporters.
While the other candidates based their candidacies on their long tenure as congressmen, ambassadors, or members of the cabinet, Jackson's appeal rested on his military service, especially in the
Battle of New Orleans
The Battle of New Orleans was fought on January 8, 1815, between the British Army under Major General Sir Edward Pakenham and the United States Army under Brevet Major General Andrew Jackson, roughly 5 miles (8 km) southeast of the Frenc ...
. The
congressional nominating caucus had decided upon previous Democratic-Republican presidential nominees, but it had become largely discredited by 1824. Candidates were instead nominated by state legislatures or nominating conventions, and Adams received the endorsement of the New England legislatures. The regional strength of each candidate played an important role in the election; Adams was popular in
New England
New England is a region consisting of six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the ...
, Clay and Jackson were strong in the West, and Jackson and Crawford competed for the South.
In the 1824 presidential election, Jackson won a plurality in the
Electoral College
An electoral college is a body whose task is to elect a candidate to a particular office. It is mostly used in the political context for a constitutional body that appoints the head of state or government, and sometimes the upper parliament ...
, taking 99 of the 261 electoral votes, while Adams won 84, Crawford won 41, and Clay took 37. Calhoun, meanwhile, won a majority of the electoral votes for vice president.
Adams nearly swept the electoral votes of New England and won a majority of the electoral votes in
New York, but he won just six electoral votes from the slave states. Most of Jackson's support came from slave-holding states, but he also won
New Jersey
New Jersey is a U.S. state, state located in both the Mid-Atlantic States, Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern United States, Northeastern regions of the United States. Located at the geographic hub of the urban area, heavily urbanized Northeas ...
,
Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania, officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a U.S. state, state spanning the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern United States, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes region, Great Lakes regions o ...
, and some electoral votes from the Northwest. As no candidate won a majority of the electoral votes, the House was required to hold a contingent election under the terms of the
Twelfth Amendment. The House would decide among the top three electoral vote winners, with each state's delegation having one vote; thus, unlike his three rivals, Clay was not eligible to be elected by the House.
Adams knew that his own victory in the contingent election would require the support of Clay, who wielded immense influence in the House of Representatives. Though they were quite different in temperament and had clashed in the past, Adams and Clay shared similar views on national issues. By contrast, Clay viewed Jackson as a dangerous
demagogue
A demagogue (; ; ), or rabble-rouser, is a political leader in a democracy who gains popularity by arousing the common people against elites, especially through oratory that whips up the passions of crowds, Appeal to emotion, appealing to emo ...
, and he was unwilling to support Crawford due to the latter's health issues. Adams and Clay met before the contingent election, and Clay agreed to support Adams in the election.
Adams also met with Federalists such as
Daniel Webster
Daniel Webster (January 18, 1782 – October 24, 1852) was an American lawyer and statesman who represented New Hampshire and Massachusetts in the U.S. Congress and served as the 14th and 19th United States Secretary of State, U.S. secretary o ...
, promising that he would not deny governmental positions to members of their party. On February 9, 1825, Adams won the contingent election on the first ballot, taking 13 of the 24 state delegations. Adams won the House delegations of all the states in which he or Clay had won a majority of the electoral votes, as well as the delegations of
Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern United States. It borders on Lake Michigan to its northeast, the Mississippi River to its west, and the Wabash River, Wabash and Ohio River, Ohio rivers to its ...
,
Louisiana
Louisiana ( ; ; ) is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It borders Texas to the west, Arkansas to the north, and Mississippi to the east. Of the 50 U.S. states, it ranks 31st in area and 25 ...
, and
Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It borders the states of Virginia to its south, West Virginia to its west, Pennsylvania to its north, and Delaware to its east ...
.
Adams's victory made him the first child of a president to serve as president himself. After the election, many of Jackson's supporters claimed that Adams and Clay had reached a "
Corrupt bargain
In American political jargon, corrupt bargain is a backdoor deal for or involving the U.S. presidency. Three events in particular in American political history have been called the corrupt bargain: the 1824 United States presidential election, ...
" whereby Adams promised Clay the position of Secretary of State in return for Clay's support.
Presidency (1825–1829)
Inauguration
Adams was
inaugurated on March 4, 1825, becoming the first son of a former United States president to himself become president, a feat only repeated 176 years later by
George W. Bush
George Walker Bush (born July 6, 1946) is an American politician and businessman who was the 43rd president of the United States from 2001 to 2009. A member of the Bush family and the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party, he i ...
, son of
George H. W. Bush
George Herbert Walker BushBefore the outcome of the 2000 United States presidential election, he was usually referred to simply as "George Bush" but became more commonly known as "George H. W. Bush", "Bush Senior," "Bush 41," and even "Bush th ...
. As Adams took the
oath of office
An oath of office is an oath or affirmation a person takes before assuming the duties of an office, usually a position in government or within a religious body, although such oaths are sometimes required of officers of other organizations. Suc ...
, he departed from tradition by placing his hand on a book of
constitutional law
Constitutional law is a body of law which defines the role, powers, and structure of different entities within a state, namely, the executive, the parliament or legislature, and the judiciary; as well as the basic rights of citizens and, in ...
instead of on a
Bible
The Bible is a collection of religious texts that are central to Christianity and Judaism, and esteemed in other Abrahamic religions such as Islam. The Bible is an anthology (a compilation of texts of a variety of forms) originally writt ...
. In his inaugural address, he adopted a post-partisan tone, promising to avoid party-building and politically motivated appointments. He also proposed an elaborate program of "internal improvements": roads, ports, and canals. Though some were worried about the constitutionality of such federal projects, Adams argued that the
General Welfare Clause provided for broad constitutional authority. He promised that he would ask Congress to authorize many such projects.
Administration
Adams presided over a harmonious and productive cabinet that he met with on a weekly basis. Like Monroe, Adams sought a geographically balanced cabinet that would represent the various party factions, and he asked the members of the Monroe cabinet to remain in place for his own administration.
Samuel L. Southard of
New Jersey
New Jersey is a U.S. state, state located in both the Mid-Atlantic States, Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern United States, Northeastern regions of the United States. Located at the geographic hub of the urban area, heavily urbanized Northeas ...
stayed on as
Secretary of the Navy
The Secretary of the Navy (SECNAV) is a statutory officer () and the head (chief executive officer) of the Department of the Navy, a military department within the United States Department of Defense. On March 25, 2025, John Phelan was confirm ...
,
William Wirt kept his post of
Attorney General
In most common law jurisdictions, the attorney general (: attorneys general) or attorney-general (AG or Atty.-Gen) is the main legal advisor to the government. In some jurisdictions, attorneys general also have executive responsibility for law enf ...
, and
John McLean of
Ohio
Ohio ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders Lake Erie to the north, Pennsylvania to the east, West Virginia to the southeast, Kentucky to the southwest, Indiana to the ...
continued to serve as the
Postmaster General, an important position that was not part of the cabinet at that time.
Adams's first choices for
Secretary of War
The secretary of war was a member of the U.S. president's Cabinet, beginning with George Washington's administration. A similar position, called either "Secretary at War" or "Secretary of War", had been appointed to serve the Congress of the ...
and
Secretary of the Treasury
The United States secretary of the treasury is the head of the United States Department of the Treasury, and is the chief financial officer of the federal government of the United States. The secretary of the treasury serves as the principal a ...
were Andrew Jackson and William Crawford, but each declined to serve in the administration. Adams instead selected
James Barbour of
Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States between the East Coast of the United States ...
, a prominent supporter of Crawford, to lead the
War Department. Leadership of the
Treasury Department went to
Richard Rush of
Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania, officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a U.S. state, state spanning the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern United States, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes region, Great Lakes regions o ...
, who would become a prominent advocate of internal improvements and protective tariffs within the administration. Adams chose
Henry Clay
Henry Clay (April 12, 1777June 29, 1852) was an American lawyer and statesman who represented Kentucky in both the United States Senate, U.S. Senate and United States House of Representatives, House of Representatives. He was the seventh Spea ...
as
Secretary of State, angering those who believed Clay had offered Adams his support in the 1824 election in exchange for the most prestigious position in the cabinet. Clay would later regret accepting the job since it reinforced the "Corrupt Bargain" accusation. However, Clay's strength in the West and interest in foreign policy made him a natural choice for the position.
Domestic affairs
Ambitious agenda

In his 1825 annual message to Congress, Adams presented a comprehensive and ambitious agenda. He called for major investments in internal improvements as well as the creation of a national university, a naval academy, and a national astronomical observatory. Noting the healthy status of the treasury and the possibility for more revenue via land sales, Adams argued for the completion of several projects that were in various stages of construction or planning, including a road from
Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from Virginia, and shares land borders with ...
to
New Orleans
New Orleans (commonly known as NOLA or The Big Easy among other nicknames) is a Consolidated city-county, consolidated city-parish located along the Mississippi River in the U.S. state of Louisiana. With a population of 383,997 at the 2020 ...
. He also proposed the establishment of a Department of the Interior as a new cabinet-level department that would preside over these internal improvements. Adams hoped to fund these measures primarily through Western land sales, rather than increased taxes or public debt.
The domestic agenda of Adams and Clay, which would come to be known as the
American System, was designed to unite disparate regional interests in the promotion of a thriving national economy.
Adams's programs faced opposition from various quarters. Many disagreed with his broad interpretation of the constitution and preferred that power be concentrated in state governments rather than the federal government. Others disliked interference from any level of government and were opposed to central planning.
Some in the South feared that Adams was secretly an
abolitionist
Abolitionism, or the abolitionist movement, is the political movement to end slavery and liberate enslaved individuals around the world.
The first country to fully outlaw slavery was Kingdom of France, France in 1315, but it was later used ...
and that he sought to subordinate the states to the federal government. Most of the president's proposals were defeated in Congress. Adams's ideas for a national university, a national observatory, and the establishment of a uniform system of weights and measures never received congressional votes.
His proposal for the creation of a naval academy won the approval of the Senate but was defeated in the House; opponents objected to the naval academy's cost and worried that the establishment of such an institution would "produce degeneracy and corruption of the public morality". Adams's proposal to establish a
national bankruptcy law was also defeated.
Unlike other aspects of his domestic agenda, Adams won congressional approval for several ambitious infrastructure projects. Between 1824 and 1828, the
United States Army Corps of Engineers
The United States Army Corps of Engineers (USACE) is the military engineering branch of the United States Army. A direct reporting unit (DRU), it has three primary mission areas: Engineer Regiment, military construction, and civil wo ...
conducted surveys for a bevy of potential roads, canals, railroads, and improvements in river navigation. Adams presided over major repairs and further construction on the National Road, and shortly after he left office the National Road extended from
Cumberland, Maryland
Cumberland is a city in Allegany County, Maryland, United States, and its county seat. At the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the city had a population of 19,075. Located on the Potomac River, Cumberland is a regional business and comm ...
, to
Zanesville, Ohio
Zanesville is a city in Muskingum County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. Located at the confluence of the Licking River (Ohio), Licking and Muskingum River, Muskingum rivers, the city is approximately east of Columbus, Ohio, Columb ...
. The Adams administration also saw the beginning of the
Chesapeake and Ohio Canal
The Chesapeake and Ohio Canal, abbreviated as the C&O Canal and occasionally called the Grand Old Ditch, operated from 1831 until 1924 along the Potomac River between Washington, D.C., and Cumberland, Maryland. It replaced the Patowmack Canal ...
; the construction of the
Chesapeake & Delaware Canal and the
Louisville and Portland Canal around the
Falls of the Ohio; the connection of the
Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes spanning the Canada–United States border. The five lakes are Lake Superior, Superior, Lake Michigan, Michigan, Lake Huron, H ...
to the
Ohio River system in
Ohio
Ohio ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders Lake Erie to the north, Pennsylvania to the east, West Virginia to the southeast, Kentucky to the southwest, Indiana to the ...
and
Indiana
Indiana ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders Lake Michigan to the northwest, Michigan to the north and northeast, Ohio to the east, the Ohio River and Kentucky to the s ...
; and the enlargement and rebuilding of the
Dismal Swamp Canal in
North Carolina
North Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, South Carolina to the south, Georgia (U.S. stat ...
. Additionally, the first passenger railroad in the United States, the
Baltimore and Ohio Railroad
The Baltimore and Ohio Railroad was the oldest railroads in North America, oldest railroad in the United States and the first steam engine, steam-operated common carrier. Construction of the line began in 1828, and it operated as B&O from 1830 ...
, was constructed during Adams's presidency. Though many of these projects were undertaken by private actors, the government often provided money or land to aid the completion of such projects.
Formation of political parties

In the immediate aftermath of the 1825 contingent election, Jackson was gracious to Adams. Nevertheless, Adams's appointment of Clay rankled Jackson, who received a flood of letters encouraging him to run. In 1825, Jackson accepted the presidential nomination of the
Tennessee
Tennessee (, ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders Kentucky to the north, Virginia to the northeast, North Carolina t ...
legislature for the 1828 election. Though he had been close to Adams during Monroe's presidency, Vice President Calhoun was also politically alienated from the president by the appointment of Clay, since that appointment established Clay as the natural heir to Adams. Adams's ambitious December 1825 annual message to Congress further galvanized the opposition, with important figures such as
Francis Preston Blair of
Kentucky
Kentucky (, ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north, West Virginia to the ...
and
Thomas Hart Benton of Missouri breaking with the Adams administration. By the end of the first session of the 19th United States Congress, an anti-Adams congressional coalition consisting of Jacksonians (led by Benton and Hugh Lawson White), Crawfordites (led by Martin Van Buren and Nathaniel Macon), and Calhounites (led by Robert Y. Hayne and George McDuffie) had emerged. Aside from Clay, Adams lacked strong supporters outside of the North, and Edward Everett, John W. Taylor (politician), John Taylor, and
Daniel Webster
Daniel Webster (January 18, 1782 – October 24, 1852) was an American lawyer and statesman who represented New Hampshire and Massachusetts in the U.S. Congress and served as the 14th and 19th United States Secretary of State, U.S. secretary o ...
served as his strongest advocates in Congress.
Supporters of Adams began calling themselves National Republicans, while supporters of Jackson began calling themselves Democratic Party (United States), Democrats. In the press, they were often described as "Adams Men" and "Jackson Men".
In the United States elections, 1826, 1826 elections, Adams's opponents picked up seats throughout the country, as allies of Adams failed to coordinate among themselves.
[.] Andrew Stevenson, a Jackson supporter, replaced John Taylor, an Adams supporter, as Speaker of the House. As Adams himself noted, the United States had never seen a Congress that was firmly under the control of political opponents of the president. After the elections, Van Buren and Calhoun agreed to throw their support behind Jackson in 1828, with Van Buren bringing along many of Crawford's supporters. Though Jackson did not articulate a detailed political platform in the same way that Adams did, his coalition united in opposition to Adams's reliance on government planning. Adams, meanwhile, clung to the hope of a non-partisan nation, and he refused to make full use of the power of patronage to build up his own party structure.
Tariff of 1828

During the first half of his administration, Adams avoided taking a strong stand on tariffs, partly because he wanted to avoid alienating his allies in the South and New England. After Jacksonians took power in 1827, they devised a tariff bill designed to appeal to Western states while instituting high rates on imported materials important to the economy of New England. It is unclear whether Van Buren, who shepherded the bill through Congress, meant for the bill to pass, or if he had deliberately designed it to force Adams and his allies to oppose it.
Regardless, Adams signed the Tariff of 1828, which became known as the "Tariff of Abominations" by opponents. Adams was denounced in the South, and he received little credit for the tariff in the North.
Indian policy
Adams sought the gradual assimilation of Native Americans in the United States, Native Americans via consensual agreements, a priority shared by few whites in the 1820s. Yet Adams was also deeply committed to the westward expansion of the United States. Settlers on the frontier, constantly seeking to move westward, cried for a more expansionist policy that disregarded the concerns of Native Americans. Early in his term, Adams suspended the Treaty of Indian Springs (1825), Treaty of Indian Springs after learning that the Governor of Georgia, George Troup, had forced the treaty on the Muscogee. Adams signed a new treaty with the Muscogee in January 1826 that allowed the Muscogee to stay but ceded most of their land to Georgia. Troup refused to accept its terms and authorized all Georgian citizens to evict the Muscogee. A showdown between Georgia and the federal government was only averted after the Muscogee agreed to a third treaty. Though many saw Troup as unreasonable in his dealings with the federal government and the Native Americans, the administration's handling of the incident alienated those in the Deep South who favored immediate Indian removal.
Foreign affairs
Adams famously said, "America goes not abroad, in search of monsters to destroy".
Trade and claims

One of the major foreign policy goals of the Adams administration was the expansion of American trade. His administration reached Reciprocity (international relations), reciprocity treaties with a number of nations, including Denmark,
Prussia
Prussia (; ; Old Prussian: ''Prūsija'') was a Germans, German state centred on the North European Plain that originated from the 1525 secularization of the Prussia (region), Prussian part of the State of the Teutonic Order. For centuries, ...
, and the Federal Republic of Central America. The administration also reached commercial agreements with the Kingdom of Hawaii and the Kingdom of Tahiti. Agreements with Denmark and Sweden opened their colonies to American trade, but Adams was especially focused on opening trade with the British West Indies. The United States had reached a commercial agreement with Britain in 1815, but that agreement excluded British possessions in the Western Hemisphere. In response to United States pressure, the British had begun to allow a limited amount of American imports to the West Indies in 1823, but United States leaders continued to seek an end to Britain's protective Imperial Preference system. In 1825, Britain banned United States trade with the British West Indies, dealing a blow to Adams's prestige.
The Adams administration negotiated extensively with the British to lift this ban, but the two sides could not reach an agreement. Despite the loss of trade with the British West Indies, the other commercial agreements secured by Adams helped expand the overall volume of United States exports.
Latin America
Aside from an unsuccessful attempt to purchase Mexican Texas, Texas from Mexico, President Adams did not seek to expand into Latin America or North America. Adams and Clay instead sought engagement with Latin America to prevent it from falling under the British Empire's economic influence.
As part of this goal, the administration favored sending a United States delegation to the Congress of Panama, an 1826 conference of New World republics organized by Simón Bolívar.
Clay and Adams hoped that the conference would inaugurate a "Good Neighbor policy, Good Neighborhood Policy" among the independent states of the Americas.
However, the funding for a delegation and the confirmation of delegation nominees became entangled in a political battle over Adams's domestic policies, with opponents such as Van Buren impeding the confirmation of a delegation.
While Van Buren saw the Panama Congress as an unwelcome deviation from the more United States non-interventionism, isolationist foreign policy established by President Washington,
many Southerners opposed involvement with any conference attended by delegates from Haiti, a republic that had been established through a Haitian Revolution, slave revolt. Though the United States delegation finally won confirmation from the Senate, it never reached the Congress of Panama due to the Senate's delay.
1828 presidential election

The Jacksonians formed an effective party apparatus that adopted many modern campaign techniques. Rather than focusing on issues, they emphasized Jackson's popularity and the supposed corruption of Adams and the federal government. Jackson himself described the campaign as a "struggle between the virtue of the people and executive patronage". Adams, meanwhile, refused to adapt to the new reality of political campaigns, and he avoided public functions and refused to invest in pro-administration tools such as newspapers. In early 1827, Jackson was publicly accused of having encouraged his wife, Rachel Jackson, Rachel, to desert her first husband. In response, followers of Jackson attacked Adams's personal life, and the campaign turned increasingly nasty. The Jacksonian press portrayed Adams as an out-of-touch elitist, while pro-Adams newspapers attacked Jackson's past involvement in various duels and scuffles, portraying him as too emotional and impetuous for the presidency. Though Adams and Clay had hoped that the campaign would focus on the American System, it was instead dominated by the personalities of Jackson and Adams.
Vice President Calhoun joined Jackson's ticket, while Adams turned to Secretary of the Treasury Richard Rush as his running mate. The 1828 election thus marked the first time in United States history that a presidential ticket composed of two Northerners faced off against a presidential ticket composed of two Southerners. In the election, Jackson won 178 of the 261 electoral votes and just under 56% of the popular vote.
Jackson won 50.3% of the popular vote in the free states, but 72.6% of the vote in the slave states. No future presidential candidate would match Jackson's proportion of the popular vote until Theodore Roosevelt's 1904 campaign, while Adams's loss made him the second one-term president, after his own father.
By 1828, only two states did not hold a popular vote for president, and the number of votes in the 1828 election was triple that in the 1824 election. This increase in votes was due not only to the recent wave of democratization, but also because of increased interest in elections and the growing ability of the parties to mobilize voters. Adams did not attend Jackson's inauguration, making him one of only four presidents who finished their terms but skipped the event.
Later congressional career (1830–1848)
Jackson administration, 1830–1836

Adams considered permanently retiring from public life after his 1828 defeat, and he was deeply hurt by the suicide of his son, George Washington Adams, in 1829. He was appalled by many of the Jackson administration's actions, including its embrace of the spoils system and the prosecution of his close friend, Treasury Auditor Tobias Watkins, for embezzlement. Though they had once maintained a cordial relationship, Adams and Jackson each came to loathe the other in the decades after the 1828 election. Adams grew bored with his retirement and still felt that his career was unfinished, so he ran for and won a seat in the
United States House of Representatives
The United States House of Representatives is a chamber of the Bicameralism, bicameral United States Congress; it is the lower house, with the U.S. Senate being the upper house. Together, the House and Senate have the authority under Artic ...
in the United States House of Representatives elections, 1830, 1830 elections. His election went against the generally held opinion, shared by his own wife and youngest son, that former presidents should not run for public office. Nonetheless, he would win election to nine terms, serving from 1831 until his death in 1848.
Adams and Andrew Johnson are the only President of the United States#Activities, former presidents to serve in Congress.
After winning election, Adams became affiliated with the
Anti-Masonic Party
The Anti-Masonic Party was the earliest Third party (United States), third party in the United States. Formally a Single-issue politics, single-issue party, it strongly opposed Freemasonry in the United States. It was active from the late 1820s, ...
, partly because the National Republican Party's leadership in Massachusetts included many of the former Federalists that Adams had clashed with earlier in his career. The Anti-Masonic Party originated as a movement against Freemasonry, but it developed into the country's first Third party (United States), third party and embraced a general program of anti-elitism.
Adams expected a light workload when he returned to Washington at 64 years old, but Speaker Andrew Stevenson selected Adams chair of the United States House Committee on Energy and Commerce, Committee on Commerce and Manufactures. Though he identified as a member of the Anti-Masonic Party, Congress was broadly polarized into allies of Jackson and opponents of Jackson, and Adams generally aligned with the latter camp. Stevenson, an ally of Jackson, expected that the committee chairmanship would keep Adams busy defending the tariff even while the Jacksonian majority on the committee would prevent Adams from accruing any real power. As chair of the committee charged with writing tariff laws, Adams became an important player in the nullification crisis, which stemmed largely from Southern objections to the high rates imposed by the Tariff of Abominations, Tariff of 1828. South Carolina leaders argued that states could Nullification (U.S. Constitution), nullify federal laws, and they announced that they would bar the federal government from enforcing the tariff in their state. Adams helped pass the Tariff of 1832, which lowered rates, but not enough to mollify the South Carolina nullifiers. The crisis ended when Clay and Calhoun agreed to another tariff bill, the Tariff of 1833, that furthered lower tariff rates. Adams was appalled by the Nullification Crisis's outcome, as he felt that the Southern states had unfairly benefited from challenging federal law. After the crisis, Adams was convinced that Southerners exercised undue influence over the federal government through their control of Jackson's Democratic Party.
In the 1833 Massachusetts gubernatorial election, the Anti-Masonic Party nominated Adams in a four-way race between Adams, the National Republican candidate, the Democratic candidate, and a candidate of the Working Men's Party. The National Republican candidate, John Davis (Massachusetts governor), John Davis, won 40% of the vote, while Adams finished in second place with 29%. Because no candidate won a majority of the vote, the state legislature decided the election. Rather than seek election by the legislature, Adams withdrew his name from contention, and the legislature selected Davis. Adams was nearly elected to the Senate in 1835 by a coalition of Anti-Masons and National Republicans, but his support for Jackson in a minor foreign policy matter annoyed National Republican leaders enough that they dropped their support for his candidacy. After 1835, Adams never again sought higher office, focusing instead on his service in the House of Representatives.
Van Buren, Harrison and Tyler administrations, 1837–1843
In the mid-1830s, the Anti-Masonic Party, the National Republicans, and other groups opposed to Jackson coalesced into the
Whig Party. In the 1836 United States presidential election, 1836 presidential election Democrats put forward Martin Van Buren, while the Whigs fielded multiple presidential candidates. Because he disdained all the major party contenders for president, Adams did not take part in the campaign; Van Buren won the election. Nonetheless, Adams became aligned with the Whig Party in Congress. Adams generally opposed the initiatives of President Van Buren, long a political adversary, though they maintained a cordial public relationship.
The Republic of Texas won its independence from Mexico in the Texas Revolution of 1835–1836. Texas had largely been settled by Americans from the Southern United States, and many of those settlers owned slaves despite an 1829 Mexican law that abolished slavery. Many in the United States and Texas thus favored the admission of Texas into the union as a Slave states and free states, slave state. Adams considered the issue of Texas to be "a question of far deeper root and more overshadowing branches than any or all others that agitate the country", and he emerged as one of the leading congressional opponents of annexation. When he served as secretary of state, Adams had sought to acquire Texas, but he argued that, because Mexico had abolished slavery, the acquisition of Texas would transform the region from a free territory into a slave state. He also feared that the annexation of Texas would encourage Southern expansionists to pursue other potential slave states, including Cuba. Adams's firm stance may have played a role in discouraging Van Buren from pushing for the annexation of Texas during his presidency.
Whig nominee William Henry Harrison defeated Van Buren in the 1840 United States presidential election, 1840 presidential election, and the Whigs gained control of both houses of Congress for the first time. Despite his low regard for Harrison as a person, Adams was enthusiastic about the new Whig administration and the end of the long-standing Democratic dominance of the federal government. However, Harrison died in April 1841 and was succeeded by Vice President John Tyler, a Southerner who, unlike Adams, Henry Clay, and many other prominent Whigs, did not embrace the American System. Adams saw Tyler as an agent of "the slave-driving, Virginia, Jeffersonian school, principled against all improvement". After Tyler vetoed a bill to restore the national bank, Whig congressmen expelled Tyler from the party. Adams was appointed chairman of a special committee that explored impeaching Tyler, and Adams presented a scathing report of Tyler that argued that his actions warranted impeachment. The impeachment process did not move forward, though, because the Whigs did not believe that the Senate would vote to remove Tyler from office.
Opposition to the Mexican-American War, 1844–1848

Tyler made the annexation of Texas the main foreign policy priority of the later stages of his administration. He attempted to win ratification of an annexation treaty in 1844, but, to Adams's surprise and relief, the Senate rejected the treaty. The annexation of Texas became the central issue of the 1844 United States presidential election, 1844 presidential election, and Southerners blocked the nomination of Van Buren at the 1844 Democratic National Convention due to the latter's opposition to annexation; the party instead nominated James K. Polk, an acolyte of Andrew Jackson. Though he once again did not take part in the campaigning, Adams was deeply disappointed that Polk defeated his old ally, Henry Clay, in the 1844 election. He attributed the outcome of the election partly to the Liberty Party (United States, 1840), Liberty Party, a small,
abolitionist
Abolitionism, or the abolitionist movement, is the political movement to end slavery and liberate enslaved individuals around the world.
The first country to fully outlaw slavery was Kingdom of France, France in 1315, but it was later used ...
third party that may have siphoned votes from Clay in the crucial state of New York. After the election, Tyler, whose term would end in March 1845, once again submitted an annexation treaty to Congress. Adams strongly attacked the treaty, arguing that the annexation of Texas would involve the United States in "a war for slavery". Despite Adams's opposition, both houses of Congress approved the treaty, with most Democrats voting for annexation and most Whigs voting against it. Texas thus joined the United States as a slave state in 1845.
Adams had served with James K. Polk in the House of Representatives, and Adams loathed the new president, seeing him as another expansionist, pro-slavery Southern Democrat. Adams favored the annexation of the entirety of
Oregon Country
Oregon Country was a large region of the Pacific Northwest of North America that was subject to a long Oregon boundary dispute, dispute between the United Kingdom and the United States in the early 19th century. The area, which had been demarcat ...
, a Oregon boundary dispute, disputed region occupied by both the United States and Britain, and was disappointed when President Polk signed the Oregon Treaty, which divided the land between the two claimants at the 49th parallel. Polk's expansionist aims centered instead on the Mexican province of Alta California, and he attempted to buy the province from Mexico. The Mexican government refused to sell California or recognize the independence and subsequent American annexation of Texas. Polk deployed a military detachment led by General Zachary Taylor to back up his assertion that the
Rio Grande
The Rio Grande ( or ) in the United States or the Río Bravo (del Norte) in Mexico (), also known as Tó Ba'áadi in Navajo language, Navajo, is one of the principal rivers (along with the Colorado River) in the Southwestern United States a ...
constituted the Southern border of both Texas and the United States. After Taylor's forces clashed with Mexican soldiers north of the Rio Grande, Polk asked for a declaration of war in early 1846, asserting that Mexico had invaded American territory. Though some Whigs questioned whether Mexico had started an aggressive war, both houses of Congress declared war, with the House voting 174-to-14 to approve the declaration. One of the 14 dissenting votes was Adams, who believed that Polk was seeking to wage an offensive to expand slavery. After the start of the war, he supported the Wilmot Proviso, an unsuccessful legislative proposal that would have banned slavery in any territory ceded by Mexico. After 1846, ill health increasingly affected Adams, but he continued to oppose the Mexican–American War until his death in 1848.
Anti-slavery movement
In the 1830s, slavery emerged as an increasingly polarizing issue in the United States. A longtime opponent of slavery, Adams used his new role in Congress to fight it, and he became the most prominent national leader opposing slavery. After one of his reelection victories, he said that he must "bring about a day prophesied when slavery and war shall be banished from the face of the Earth". He wrote in his private journal in 1820:
In 1836, partially in response to Adams's consistent presentation of citizen petitions requesting the abolition of slavery in the Washington, D.C., District of Columbia, the United States House of Representatives, U.S. House of Representatives imposed a
gag rule that immediately Table (parliamentary procedure), tabled any petitions about slavery. Democrats and Southern Whigs favored the rule, but Northern Whigs, like Adams, opposed it. In late 1836, Adams began a campaign to ridicule slave owners and the gag rule. He frequently attempted to present anti-slavery petitions, often in ways that provoked strong reactions from Southern representatives. Though the gag rule remained in place,
the discussion ignited by his actions and the attempts of others to quiet him raised questions of the right to petition, the right to legislative debate, and the morality of slavery. Adams fought actively against the gag rule for another seven years, eventually moving the resolution that led to its repeal in 1844.
In 1841, at the request of Lewis Tappan and Ellis Gray Loring, Adams joined the case of ''United States v. The Amistad''. Adams went before the Supreme Court of the United States, Supreme Court on behalf of African slaves who had revolted and seized the Spanish ship ''Amistad''. Adams appeared on February 24, 1841, and spoke for four hours. His argument succeeded: the Court ruled that the Africans were free and they returned to their homes.
Smithsonian Institution

Adams also became a leading force for the promotion of science. In 1829, British scientist James Smithson died, and he left his fortune for the "increase and diffusion of knowledge". In Smithson's will, he stated that should his nephew, Henry James Hungerford, die without heirs, the Smithson estate would go to the government of the United States to create an "Establishment for the increase and diffusion of Knowledge among men". After the nephew died without heirs in 1835, President Andrew Jackson informed United States Congress, Congress of the bequest, which amounted to about US$500,000 (equivalent to US$ in ). Adams realized that this might allow the United States to realize his dream of building a national institution of science and learning. Adams thus became Congress's primary supporter of the future Smithsonian Institution.
The money was invested in shaky state Bond (finance), bonds, which quickly defaulted. After heated debate in Congress, Adams successfully argued to restore the lost funds with interest. Though Congress wanted to use the money for other purposes, Adams successfully persuaded Congress to preserve the money for an institution of science and learning. Congress also debated whether the federal government had the authority to accept the gift, though with Adams leading the initiative, Congress accepted the legacy bequeathed to the nation and pledged the faith of the United States to the charitable trust on July 1, 1836. Partly due to Adams's efforts, Congress voted to establish the Smithsonian Institution in 1846. A nonpolitical board of regents was established to lead the institution, which included a museum, art gallery, library, and laboratory.
Death

In 1846, the 78-year-old former president suffered a stroke that left him partially paralyzed. After a few months of rest, he made a full recovery and resumed his duties in Congress. When Adams entered the House chamber on February 13, 1847, everyone "stood up and applauded".

On February 21, 1848, the House of Representatives was discussing the matter of honoring United States Army officers who served in the Mexican–American War. Adams had been a vehement critic of the war, and as Congressmen rose up to say, "Aye!" in favor of the measure, he instead yelled, "No!"
He rose to answer a question put forth by Speaker of the House Robert Charles Winthrop.
Immediately thereafter, Adams collapsed, having suffered a massive cerebral hemorrhage.
Two days later, on February 23, he died at 7:20 p.m. with his wife at his side in the Speaker's Room inside the United States Capitol, Capitol Building in Washington, D.C.; his only living child, Charles Francis, did not arrive in time to see his father alive. His last words were "This is the last of Earth. I am content".
Among those present for his death was future president Abraham Lincoln, then a freshman representative from Illinois.
His original interment was temporary, in the public vault at the Congressional Cemetery in Washington, D.C. Later, he was interred in the family burial ground in Quincy, Massachusetts, across from the (Unitarianism, Unitarian) United First Parish Church, called Hancock Cemetery. After Louisa's death in 1852, his son had his parents re-interred in the expanded family crypt in the United First Parish Church across the street, next to John and Abigail. Both tombs are viewable by the public. Adams's original tomb at Hancock Cemetery is still there and marked simply "J.Q. Adams".
Personal life
Adams and Louisa had three sons and a daughter. Their daughter, Louisa, was born in 1811, but died in 1812, from unknown reasons. They named their first son George Washington Adams (1801–1829) after the first president. This decision upset Adams's mother, and, by her account, his father as well. Both George and their second son, John Adams II, John (1803–1834), led troubled lives and died in early adulthood. George, who had long suffered from alcoholism, died in 1829 after going overboard on a steamboat; it is not clear whether he fell or purposely jumped from the boat. John, who ran an unprofitable flour and grist mill owned by his father, died of an unknown illness in 1834. Adams's youngest son, Charles Francis Adams Sr., was an important leader of the "Conscience Whigs", a Northern, anti-slavery faction of the Whig Party.
Charles served as the Free Soil Party's vice presidential candidate in the 1848 United States presidential election, 1848 presidential election and later became a prominent member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party, serving as United States Minister to England during the American Civil War.
Personality
Adams's personality and political beliefs were much like his father's.
He always preferred solitary reading to social engagements, and he was repeatedly persuaded to stay in public service by others. Historian Paul Nagel states that, like Abraham Lincoln after him, Adams often suffered from depression, for which he sought treatment in early years. Adams thought his depression was due to the high expectations demanded of him by his father and mother. Throughout his life, he felt inadequate and socially awkward because of his depression, and was constantly bothered by his physical appearance.
He was closer to his father, with whom he spent much of his early life while abroad, than he was to his mother. In his youth, while the American Revolution raged on, Adams heard from his mother about his father's work and the substantial risks he took to support it. As a result, he developed a deep respect for his father.
In contrast, Adams had a rocky relationship with his mother, due to her high expectations of him, and her fear that her children would follow in the footsteps of her brother, who died of alcoholism.
His biographer, Nagel, concludes that his mother's disapproval of Louisa Johnson motivated him to marry Johnson in 1797, despite Adams's reservations that Johnson, like his mother, had a forceful personality.
Though Adams wore a wig#19th and 20th centuries, powdered wig tied in a queue in his youth, he abandoned this fashion while serving as the List of ambassadors of the United States to Russia, U.S. Minister to Russia (1809–1814) and List of United States presidential firsts#John Quincy Adams (1825–1829), became the first president 1795–1820 in Western fashion#Men's hairstyles and headgear, to adopt a short haircut instead of long hair tied in a Queue (hairstyle)#Other queues, queue and to regularly wear long trousers instead of Culottes, knee breeches according to the 1820s in Western fashion#Men's wear, fashion of the 19th century. It has been suggested that John Quincy Adams had the highest Intelligence quotient, I.Q. of any U.S. president. Dean Simonton, a professor of psychology at University of California, Davis, UC Davis, estimated his I.Q. score at 165. He reportedly spoke eight foreign languages (Dutch, French, German, Greek, Italian, Latin, Russian, and Spanish), more than any other U.S. president. He remains the only U.S. president who could converse in Russian.
Legacy
Historical reputation
Adams is widely regarded as one of the most effective diplomats and secretaries of state in American history,
but Historical rankings of presidents of the United States, scholars generally rank him as an average president. Adams is remembered as a man eminently qualified for the presidency, yet hopelessly weakened in his presidential leadership potential because of the 1824 election. Most importantly, Adams is remembered as a poor politician in an era when politics had begun to matter more. He spoke of trying to serve as a man above the "baneful weed of party strife" at the precise moment in history when the Second Party System was emerging with nearly revolutionary force.
Biographer and historian William J. Cooper Jr. comments that Adams "does not loom large in the American imagination", but that he has received more public attention since the late 20th century due to his anti-slavery stances. Cooper writes that Adams was the first "major public figure" to publicly question whether the United States could remain united so long as the institution of slavery persisted.
Historian Daniel Walker Howe writes that Adams's "intellectual ability and courage were above reproach, and his wisdom in perceiving the national interest has stood the test of time". He has also been praised as a strong prose stylist, with James Parker describing him as one of the "three authentically muddy-eyed and pained-by-subjectivity ''writers''" that the White House has harbored, along with Abraham Lincoln and Barack Obama.
Memorials
The John Quincy Adams Birthplace is now part of Adams National Historical Park and open to the public. Adams House (Harvard University), Adams House, one of twelve undergraduate residential Houses at Harvard University, is named for John Adams, John Quincy Adams, and other members of the Adams family associated with Harvard. John Quincy Adams tower, located in the Southwest residential area of the University of Massachusetts Amherst, is named for the president. In 1870, Charles Francis built the first Presidential library system, presidential library in the United States, to honor his father. The Adams National Historical Park#Stone Library, Stone Library includes over 14,000 books written in twelve languages. The library is located at Peacefield (the "Old House") at Adams National Historical Park in Quincy, Massachusetts.
An Adams Memorial has been proposed in Washington, D.C., honoring Adams and his wife, son, father, mother, and other members of their family. The Oyster-Adams Bilingual School, John Quincy Adams School in Washington, D.C., was named after him. It merged with the James F. Oyster School and now is called the Oyster-Adams Bilingual School.
Adams's middle name of Quincy has been used by several locations in the United States, including the town of Quincy, Illinois. Adams County, Illinois and Adams County, Indiana are also named after Adams. Adams County, Iowa, and Adams County, Wisconsin, were each named for either John Adams or John Quincy Adams.
Some sources contend that in 1843 Adams sat for the earliest confirmed photograph of a United States president, although others maintain that William Henry Harrison had posed even earlier for his portrait, in 1841.
The original daguerreotype is in the collection of the National Portrait Gallery (United States), National Portrait Gallery of the Smithsonian Institution.
Film and television
Adams occasionally is featured in the mass media. In the PBS miniseries ''The Adams Chronicles'' (1976), he was portrayed by David Birney, William Daniels, Marcel Trenchard, Steven Grover and Mark Winkworth. He was also portrayed by Anthony Hopkins in the 1997 film ''Amistad (film), Amistad'', and again by Ebon Moss-Bachrach and Steven Hinkle in the 2008 HBO television miniseries ''John Adams (TV miniseries), John Adams''.
See also
* Adams's method, Adams's method for apportionment
* List of abolitionists
* List of presidents of the United States
* List of presidents of the United States by previous experience
* List of United States Congress members who died in office (1790–1899)
* List of United States political appointments across party lines
* Mendi Bible
* Quincy Institute for Responsible Statecraft
Notes
References
Works cited
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Georgini, Sara. ''Household Gods: The Religious Lives of the Adams Family'' (Oxford University Press, 2019).
*
*
*
* Lewis Jr, James E. ''John Quincy Adams: Policymaker for the Union'' (Rowman & Littlefield Publishers, 2001).
*
*
*
*
*
*
excerpt and text search*
*
*
*
*
*
Further reading
Secondary sources
*
*
* Morgan, William G. "Henry Clay's Biographers and the 'Corrupt Bargain' Charge." ''Register of the Kentucky Historical Society'' 66#3 (1968), pp. 242–58
online* Morgan, William G. "John Quincy Adams Versus Andrew Jackson: Their Biographers And The 'Corrupt Bargain' Charge." ''Tennessee Historical Quarterly'' 26#1 (1967), pp. 43–58
online*
*
* Edward Pessen, Pessen, Edward. "John Quincy Adams" in Henry Graff, ed. ''The Presidents: A Reference History'' (3rd ed. 2002
online*
*
excerpt and text search*
Primary sources
* Waldstreicher, David, ed. ''The Diaries of John Quincy Adams, 1779–1821'' (Library of America, 20170. xiv, 727 pp.)
*
*
*
Founders Online, searchable edition
External links
Scholarly coverage of Adams at Miller Center, U of Virginia
The Diaries of John Quincy Adams: A Digital Collection at the Massachusetts Historical Society
"Life Portrait of John Quincy Adams" from C-SPAN's ''American Presidents: Life Portraits'', April 18, 1999
*
*
*
*
{{DEFAULTSORT:Adams, John Quincy
John Quincy Adams,
1767 births
1848 deaths
18th-century Massachusetts politicians
18th-century American diplomats
18th-century Unitarians
19th-century American diplomats
19th-century Unitarians
19th-century presidents of the United States
Adams family
Ambassadors of the United States to Prussia
Ambassadors of the United States to the Russian Empire
Ambassadors of the United States to the Netherlands
Ambassadors of the United States to the United Kingdom
American expatriates in the Dutch Republic
American lawyers admitted to the practice of law by reading law
American nationalists
American people of English descent
American political party founders
American Unitarians
Anti-Masonic Party members of the United States House of Representatives from Massachusetts
Candidates in the 1820 United States presidential election
Candidates in the 1824 United States presidential election
Candidates in the 1828 United States presidential election
Children of John Adams
Deans of the United States House of Representatives
Democratic-Republican Party presidents of the United States
Federalist Party United States senators
Fellows of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences
George Washington University trustees
Hall of Fame for Great Americans inductees
Harvard College alumni
Harvard University faculty
Leiden University alumni
Massachusetts Democratic-Republicans
Massachusetts Federalists
Massachusetts lawyers
Massachusetts state senators
Members of the American Philosophical Society
Monroe administration cabinet members
National Republican Party members of the United States House of Representatives from Massachusetts
Politicians from Braintree, Massachusetts
Politicians from Quincy, Massachusetts
Presidency of John Quincy Adams
Presidents of the United States
Quincy family
United States secretaries of state
United States senators from Massachusetts
Unsuccessful nominees to the United States Supreme Court
U.S. Congressional gag rules and their sponsors
Whig Party members of the United States House of Representatives from Massachusetts
American free speech activists
Activists for Native American rights
American women's rights activists
19th-century members of the Massachusetts General Court
19th-century United States senators
19th-century members of the United States House of Representatives
Candidates in the 1802 United States elections
Diplomats from Massachusetts
 After resigning from the Senate, Adams was ostracized by Massachusetts Federalist leaders, but he declined Democratic-Republican entreaties to seek office. In 1809, he argued before the
After resigning from the Senate, Adams was ostracized by Massachusetts Federalist leaders, but he declined Democratic-Republican entreaties to seek office. In 1809, he argued before the  Adams had long feared that the United States would enter a war it could not win against Britain, and by early 1812, he saw such a war as inevitable due to the constant British attacks on American shipping and the British practice of
Adams had long feared that the United States would enter a war it could not win against Britain, and by early 1812, he saw such a war as inevitable due to the constant British attacks on American shipping and the British practice of  Taking office in the aftermath of the War of 1812, Adams thought that the country had been fortunate in avoiding territorial losses, and he prioritized avoiding another war with a European power, particularly Britain. He also sought to avoid exacerbating sectional tensions, which had been a major issue for the country during the War of 1812. One of the major challenges confronting Adams was how to respond to the power vacuum in Latin America that arose from Spain's weakness following the
Taking office in the aftermath of the War of 1812, Adams thought that the country had been fortunate in avoiding territorial losses, and he prioritized avoiding another war with a European power, particularly Britain. He also sought to avoid exacerbating sectional tensions, which had been a major issue for the country during the War of 1812. One of the major challenges confronting Adams was how to respond to the power vacuum in Latin America that arose from Spain's weakness following the  When Adams took office, Spanish possessions bordered the United States to the south and west. To the south, Spain retained control of
When Adams took office, Spanish possessions bordered the United States to the south and west. To the south, Spain retained control of  In his 1825 annual message to Congress, Adams presented a comprehensive and ambitious agenda. He called for major investments in internal improvements as well as the creation of a national university, a naval academy, and a national astronomical observatory. Noting the healthy status of the treasury and the possibility for more revenue via land sales, Adams argued for the completion of several projects that were in various stages of construction or planning, including a road from
In his 1825 annual message to Congress, Adams presented a comprehensive and ambitious agenda. He called for major investments in internal improvements as well as the creation of a national university, a naval academy, and a national astronomical observatory. Noting the healthy status of the treasury and the possibility for more revenue via land sales, Adams argued for the completion of several projects that were in various stages of construction or planning, including a road from  In the immediate aftermath of the 1825 contingent election, Jackson was gracious to Adams. Nevertheless, Adams's appointment of Clay rankled Jackson, who received a flood of letters encouraging him to run. In 1825, Jackson accepted the presidential nomination of the
In the immediate aftermath of the 1825 contingent election, Jackson was gracious to Adams. Nevertheless, Adams's appointment of Clay rankled Jackson, who received a flood of letters encouraging him to run. In 1825, Jackson accepted the presidential nomination of the  During the first half of his administration, Adams avoided taking a strong stand on tariffs, partly because he wanted to avoid alienating his allies in the South and New England. After Jacksonians took power in 1827, they devised a tariff bill designed to appeal to Western states while instituting high rates on imported materials important to the economy of New England. It is unclear whether Van Buren, who shepherded the bill through Congress, meant for the bill to pass, or if he had deliberately designed it to force Adams and his allies to oppose it. Regardless, Adams signed the Tariff of 1828, which became known as the "Tariff of Abominations" by opponents. Adams was denounced in the South, and he received little credit for the tariff in the North.
During the first half of his administration, Adams avoided taking a strong stand on tariffs, partly because he wanted to avoid alienating his allies in the South and New England. After Jacksonians took power in 1827, they devised a tariff bill designed to appeal to Western states while instituting high rates on imported materials important to the economy of New England. It is unclear whether Van Buren, who shepherded the bill through Congress, meant for the bill to pass, or if he had deliberately designed it to force Adams and his allies to oppose it. Regardless, Adams signed the Tariff of 1828, which became known as the "Tariff of Abominations" by opponents. Adams was denounced in the South, and he received little credit for the tariff in the North.
 Adams considered permanently retiring from public life after his 1828 defeat, and he was deeply hurt by the suicide of his son, George Washington Adams, in 1829. He was appalled by many of the Jackson administration's actions, including its embrace of the spoils system and the prosecution of his close friend, Treasury Auditor Tobias Watkins, for embezzlement. Though they had once maintained a cordial relationship, Adams and Jackson each came to loathe the other in the decades after the 1828 election. Adams grew bored with his retirement and still felt that his career was unfinished, so he ran for and won a seat in the
Adams considered permanently retiring from public life after his 1828 defeat, and he was deeply hurt by the suicide of his son, George Washington Adams, in 1829. He was appalled by many of the Jackson administration's actions, including its embrace of the spoils system and the prosecution of his close friend, Treasury Auditor Tobias Watkins, for embezzlement. Though they had once maintained a cordial relationship, Adams and Jackson each came to loathe the other in the decades after the 1828 election. Adams grew bored with his retirement and still felt that his career was unfinished, so he ran for and won a seat in the  Tyler made the annexation of Texas the main foreign policy priority of the later stages of his administration. He attempted to win ratification of an annexation treaty in 1844, but, to Adams's surprise and relief, the Senate rejected the treaty. The annexation of Texas became the central issue of the 1844 United States presidential election, 1844 presidential election, and Southerners blocked the nomination of Van Buren at the 1844 Democratic National Convention due to the latter's opposition to annexation; the party instead nominated James K. Polk, an acolyte of Andrew Jackson. Though he once again did not take part in the campaigning, Adams was deeply disappointed that Polk defeated his old ally, Henry Clay, in the 1844 election. He attributed the outcome of the election partly to the Liberty Party (United States, 1840), Liberty Party, a small,
Tyler made the annexation of Texas the main foreign policy priority of the later stages of his administration. He attempted to win ratification of an annexation treaty in 1844, but, to Adams's surprise and relief, the Senate rejected the treaty. The annexation of Texas became the central issue of the 1844 United States presidential election, 1844 presidential election, and Southerners blocked the nomination of Van Buren at the 1844 Democratic National Convention due to the latter's opposition to annexation; the party instead nominated James K. Polk, an acolyte of Andrew Jackson. Though he once again did not take part in the campaigning, Adams was deeply disappointed that Polk defeated his old ally, Henry Clay, in the 1844 election. He attributed the outcome of the election partly to the Liberty Party (United States, 1840), Liberty Party, a small,  Adams also became a leading force for the promotion of science. In 1829, British scientist James Smithson died, and he left his fortune for the "increase and diffusion of knowledge". In Smithson's will, he stated that should his nephew, Henry James Hungerford, die without heirs, the Smithson estate would go to the government of the United States to create an "Establishment for the increase and diffusion of Knowledge among men". After the nephew died without heirs in 1835, President Andrew Jackson informed United States Congress, Congress of the bequest, which amounted to about US$500,000 (equivalent to US$ in ). Adams realized that this might allow the United States to realize his dream of building a national institution of science and learning. Adams thus became Congress's primary supporter of the future Smithsonian Institution.
The money was invested in shaky state Bond (finance), bonds, which quickly defaulted. After heated debate in Congress, Adams successfully argued to restore the lost funds with interest. Though Congress wanted to use the money for other purposes, Adams successfully persuaded Congress to preserve the money for an institution of science and learning. Congress also debated whether the federal government had the authority to accept the gift, though with Adams leading the initiative, Congress accepted the legacy bequeathed to the nation and pledged the faith of the United States to the charitable trust on July 1, 1836. Partly due to Adams's efforts, Congress voted to establish the Smithsonian Institution in 1846. A nonpolitical board of regents was established to lead the institution, which included a museum, art gallery, library, and laboratory.
Adams also became a leading force for the promotion of science. In 1829, British scientist James Smithson died, and he left his fortune for the "increase and diffusion of knowledge". In Smithson's will, he stated that should his nephew, Henry James Hungerford, die without heirs, the Smithson estate would go to the government of the United States to create an "Establishment for the increase and diffusion of Knowledge among men". After the nephew died without heirs in 1835, President Andrew Jackson informed United States Congress, Congress of the bequest, which amounted to about US$500,000 (equivalent to US$ in ). Adams realized that this might allow the United States to realize his dream of building a national institution of science and learning. Adams thus became Congress's primary supporter of the future Smithsonian Institution.
The money was invested in shaky state Bond (finance), bonds, which quickly defaulted. After heated debate in Congress, Adams successfully argued to restore the lost funds with interest. Though Congress wanted to use the money for other purposes, Adams successfully persuaded Congress to preserve the money for an institution of science and learning. Congress also debated whether the federal government had the authority to accept the gift, though with Adams leading the initiative, Congress accepted the legacy bequeathed to the nation and pledged the faith of the United States to the charitable trust on July 1, 1836. Partly due to Adams's efforts, Congress voted to establish the Smithsonian Institution in 1846. A nonpolitical board of regents was established to lead the institution, which included a museum, art gallery, library, and laboratory.
 On February 21, 1848, the House of Representatives was discussing the matter of honoring United States Army officers who served in the Mexican–American War. Adams had been a vehement critic of the war, and as Congressmen rose up to say, "Aye!" in favor of the measure, he instead yelled, "No!" He rose to answer a question put forth by Speaker of the House Robert Charles Winthrop. Immediately thereafter, Adams collapsed, having suffered a massive cerebral hemorrhage. Two days later, on February 23, he died at 7:20 p.m. with his wife at his side in the Speaker's Room inside the United States Capitol, Capitol Building in Washington, D.C.; his only living child, Charles Francis, did not arrive in time to see his father alive. His last words were "This is the last of Earth. I am content". Among those present for his death was future president Abraham Lincoln, then a freshman representative from Illinois.
His original interment was temporary, in the public vault at the Congressional Cemetery in Washington, D.C. Later, he was interred in the family burial ground in Quincy, Massachusetts, across from the (Unitarianism, Unitarian) United First Parish Church, called Hancock Cemetery. After Louisa's death in 1852, his son had his parents re-interred in the expanded family crypt in the United First Parish Church across the street, next to John and Abigail. Both tombs are viewable by the public. Adams's original tomb at Hancock Cemetery is still there and marked simply "J.Q. Adams".
On February 21, 1848, the House of Representatives was discussing the matter of honoring United States Army officers who served in the Mexican–American War. Adams had been a vehement critic of the war, and as Congressmen rose up to say, "Aye!" in favor of the measure, he instead yelled, "No!" He rose to answer a question put forth by Speaker of the House Robert Charles Winthrop. Immediately thereafter, Adams collapsed, having suffered a massive cerebral hemorrhage. Two days later, on February 23, he died at 7:20 p.m. with his wife at his side in the Speaker's Room inside the United States Capitol, Capitol Building in Washington, D.C.; his only living child, Charles Francis, did not arrive in time to see his father alive. His last words were "This is the last of Earth. I am content". Among those present for his death was future president Abraham Lincoln, then a freshman representative from Illinois.
His original interment was temporary, in the public vault at the Congressional Cemetery in Washington, D.C. Later, he was interred in the family burial ground in Quincy, Massachusetts, across from the (Unitarianism, Unitarian) United First Parish Church, called Hancock Cemetery. After Louisa's death in 1852, his son had his parents re-interred in the expanded family crypt in the United First Parish Church across the street, next to John and Abigail. Both tombs are viewable by the public. Adams's original tomb at Hancock Cemetery is still there and marked simply "J.Q. Adams".