|
Tiberius Julius Rhescuporis VI
Rhescuporis VI ( el, Τιβέριος Ἰούλιος Ῥησκούπορις, translit=Tiberios Ioulios Rheskoúporis), also transliterated as Rheskuporis or Rheskouporis and sometimes known as Rhescuporis the Last, is the last well-known king of the Bosporan Kingdom (), a Roman client state, and the last known representative of its ancient Tiberian-Julian ruling dynasty. Little is known of the background and reign of Rhescuporis VI; he began his tenure as king through either co-rule or competition with his predecessor Rhadamsades until 322. Rhescuporis VI reign came to an end around 341, when he might have been overthrown by the Sarmatians or Alans, groups which at the time were becoming increasingly influential and powerful in Crimea. Reign The last known member of the Tiberian-Julian dynasty, Rhescuporis VI's reign can be dated precisely through numismatic (coins) and archaeological data, which places him as ruling from 314 to 341. His reign overlaps with the other Bosporan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Kings Of The Cimmerian Bosporus
The Bosporan kings were the rulers of the Bosporan Kingdom, an ancient Hellenistic Greco-Scythian state centered on the Kerch Strait (the Cimmerian Bosporus) and ruled from the city of Panticapaeum. Panticapaeum was founded in the 7th or 6th century BC; the earliest known king of the Bosporus is Archaeanax, who seized control of the city 480 BC as a usurper. The Archaeanactid dynasty ruled the city until it was displaced by the more long-lived Spartocid dynasty in 438 BC. After ruling for over three centuries, the Spartocids were then displaced by the Mithridatic dynasty of Pontus and then its offshoot the Tiberian-Julian dynasy. The Tiberian-Julian kings ruled as client kings of the Roman Empire until late antiquity. After several successive periods of rule by groups such as the Sarmatians, Alans, Goths and Huns, the remnants of the Bosporan Kingdom were finally absorbed into the Roman Empire by Justinian I in the 6th century AD. List of kings Joint rulers are indicated with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
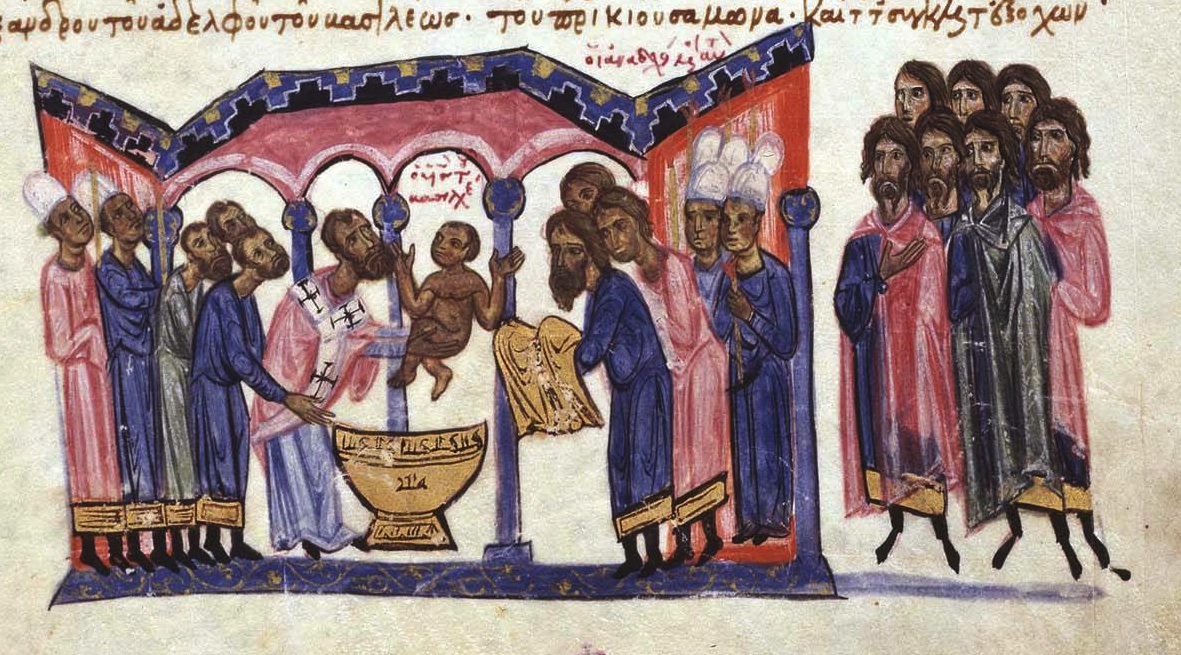
Constantine VII
Constantine VII Porphyrogenitus (; 17 May 905 – 9 November 959) was the fourth Emperor of the Macedonian dynasty of the Byzantine Empire, reigning from 6 June 913 to 9 November 959. He was the son of Emperor Leo VI and his fourth wife, Zoe Karbonopsina, and the nephew of his predecessor Alexander. Most of his reign was dominated by co-regents: from 913 until 919 he was under the regency of his mother, while from 920 until 945 he shared the throne with Romanos Lekapenos, whose daughter Helena he married, and his sons. Constantine VII is best known for the ''Geoponika'' (τά γεοπονικά), an important agronomic treatise compiled during his reign, and three, perhaps four, books; ''De Administrando Imperio'' (bearing in Greek the heading Πρὸς τὸν ἴδιον υἱὸν Ῥωμανόν), '' De Ceremoniis'' (Περὶ τῆς Βασιλείου Τάξεως), '' De Thematibus'' (Περὶ θεμάτων Άνατολῆς καὶ Δύσεως), and ''Vita Basilii'' ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3rd-century Births
The 3rd century was the period from 201 ( CCI) to 300 (CCC) Anno Domini (AD) or Common Era (CE) in the Julian calendar.. In this century, the Roman Empire saw a crisis, starting with the assassination of the Roman Emperor Severus Alexander in 235, plunging the empire into a period of economic troubles, barbarian incursions, political upheavals, civil wars, and the split of the Roman Empire through the Gallic Empire in the west and the Palmyrene Empire in the east, which all together threatened to destroy the Roman Empire in its entirety, but the reconquests of the seceded territories by Emperor Aurelian and the stabilization period under Emperor Diocletian due to the administrative strengthening of the empire caused an end to the crisis by 284. This crisis would also mark the beginning of Late Antiquity. In Persia, the Parthian Empire was succeeded by the Sassanid Empire in 224 after Ardashir I defeated and killed Artabanus V during the Battle of Hormozdgan. The Sassanids ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Client Rulers
Roman or Romans most often refers to: *Rome, the capital city of Italy *Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD *Roman people, the people of ancient Rome *''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter in the New Testament of the Christian Bible Roman or Romans may also refer to: Arts and entertainment Music * Romans (band), a Japanese pop group * ''Roman'' (album), by Sound Horizon, 2006 * ''Roman'' (EP), by Teen Top, 2011 *" Roman (My Dear Boy)", a 2004 single by Morning Musume Film and television *Film Roman, an American animation studio * ''Roman'' (film), a 2006 American suspense-horror film * ''Romans'' (2013 film), an Indian Malayalam comedy film * ''Romans'' (2017 film), a British drama film * ''The Romans'' (''Doctor Who''), a serial in British TV series People *Roman (given name), a given name, including a list of people and fictional characters *Roman (surname), including a list of people named Roman or Romans *Ῥωμα� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
342 Deaths
34 may refer to: * 34 (number), the natural number following 33 and preceding 35 * one of the years 34 BC, AD 34, 1934, 2034 * ''34'' (album), a 2015 album by Dre Murray * "#34" (song), a 1994 song by Dave Matthews Band * "34", a 2006 song by Saves the Day from '' Sound the Alarm'' * +34, the international calling code for Spain * "Thirty Four", a song by Karma to Burn from the album ''Almost Heathen'', 2001 See also * 3/4 (other) * Rule 34 (other) Rule 34 is an internet meme that states "If it exists, there is porn of it. No exceptions." Rule 34 may also refer to: * ''Rule 34'' (novel), a novel by Charles Stross * Rule 34 of the Federal Rules of Civil Procedure, which governs requests for ... * List of highways numbered 34 {{Numberdis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rulers Of The Bosporan Kingdom
A ruler, sometimes called a rule, line gauge, or scale, is a device used in geometry and technical drawing, as well as the engineering and construction industries, to measure distances or draw straight lines. Variants Rulers have long been made from different materials and in multiple sizes. Some are wooden. Plastics have also been used since they were invented; they can be molded with length markings instead of being scribed. Metal is used for more durable rulers for use in the workshop; sometimes a metal edge is embedded into a wooden desk ruler to preserve the edge when used for straight-line cutting. in length is useful for a ruler to be kept on a desk to help in drawing. Shorter rulers are convenient for keeping in a pocket. Longer rulers, e.g., , are necessary in some cases. Rigid wooden or plastic yardsticks, 1 yard long, and meter sticks, 1 meter long, are also used. Classically, long measuring rods were used for larger projects, now superseded by ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gordas
Gordas () was a prince of the Crimean Huns. He was a ruler of the Huns near the Maeotis, near the Cimmerian Bosporus. In 527 he went to Constantinople la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه , alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ..., where he received baptism. He then returned to his people and started to destroy their idols. This caused a revolt, led by his brother, in which he was killed. His murderers then fled, fearing Byzantine reprisals. References {{Huns Hunnic kings 6th-century monarchs in Europe History of Crimea Christianization of Europe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Justinian I
Justinian I (; la, Iustinianus, ; grc-gre, Ἰουστινιανός ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was the Byzantine emperor from 527 to 565. His reign is marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renovatio imperii'', or "restoration of the Empire". This ambition was expressed by the partial recovery of the territories of the defunct Western Roman Empire. His general, Belisarius, swiftly conquered the Vandal Kingdom in North Africa. Subsequently, Belisarius, Narses, and other generals conquered the Ostrogothic kingdom, restoring Dalmatia, Sicily, Italy, and Rome to the empire after more than half a century of rule by the Ostrogoths. The praetorian prefect Liberius reclaimed the south of the Iberian peninsula, establishing the province of Spania. These campaigns re-established Roman control over the western Mediterranean, increasing the Empire's annual revenue by over a million ''solidi''. During his reign, Justinian also subdued the ''Tz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Justin I
Justin I ( la, Iustinus; grc-gre, Ἰουστῖνος, ''Ioustînos''; 450 – 1 August 527) was the Eastern Roman emperor from 518 to 527. Born to a peasant family, he rose through the ranks of the army to become commander of the imperial guard, and when Emperor Anastasius died he out-maneouvered his rivals and was elected as his successor, in spite of being almost 70 years old. His reign is significant for the founding of the Byzantine Empire under the Justinian dynasty, Justinian dynasty that included his eminent nephew Justinian I and three succeeding emperors. His Queen consort, consort was Empress Euphemia (empress), Euphemia. He was noted for his strongly orthodox Christian views. This facilitated the ending of the Acacian schism between the churches of Rome and Constantinople, resulting in good relations between Justin and the papacy. Throughout his reign he stressed the religious nature of his office and passed edicts against various Christian groups seen at the tim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
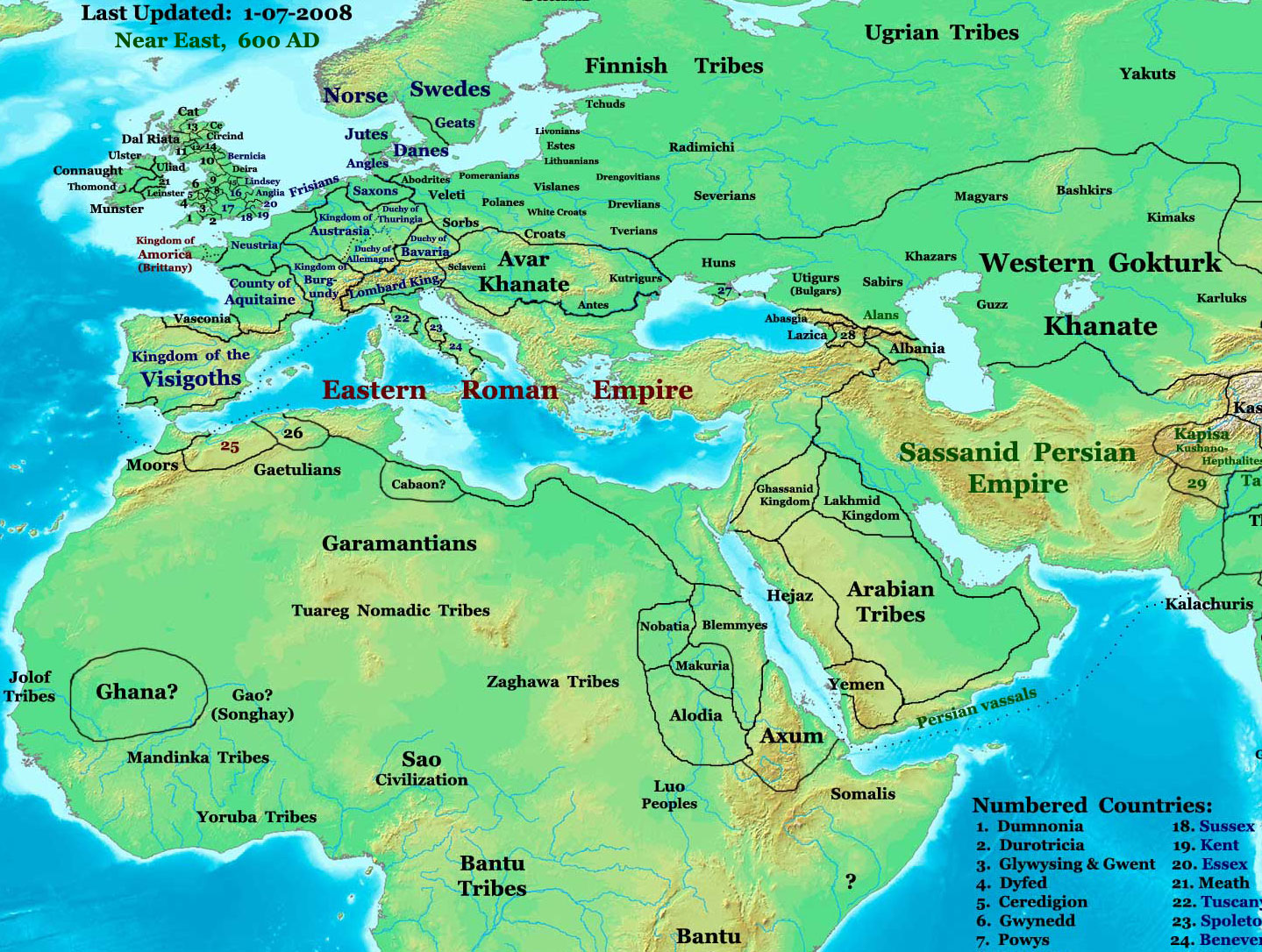
Utigurs
Utigurs were Turkic nomadic equestrians who flourished in the Pontic–Caspian steppe in the 6th century AD. They possibly were closely related to the Kutrigurs and Bulgars. Etymology The name ''Ut(r)igur'', recorded as , and , is generally considered as a metathesized form suggested by Gyula Németh of Turkic ''*Otur- Oğur'', thus the ''*Uturğur'' mean "Thirty Oğurs (tribes)". Lajos Ligeti proposed ''utur-'' (to resist), while Louis Bazin ''uturkar'' (the victors-conquerors), ''Quturgur'' and ''qudurmaq'' (the enrages). There has been little scholarly support for theories linking the names Kutrigur and Utigur to peoples such as the Guti/Quti and/or Udi/Uti, of Ancient Southwest Asia and the Caucasus respectively, which have been posited by scholars such as Osman Karatay, and Yury Zuev. No evidence has been presented that the Guti moved from their homeland in the Zagros Mountains (modern Iran/Iraq) to the Steppes, and they are widely believed to have spoken an Indo-Europea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |