|
Utigurs
Utigurs were Turkic nomadic equestrians who flourished in the Pontic–Caspian steppe in the 6th century AD. They possibly were closely related to the Kutrigurs and Bulgars. Etymology The name ''Ut(r)igur'', recorded as , and , is generally considered as a metathesized form suggested by Gyula Németh of Turkic ''*Otur- Oğur'', thus the ''*Uturğur'' mean "Thirty Oğurs (tribes)". Lajos Ligeti proposed ''utur-'' (to resist), while Louis Bazin ''uturkar'' (the victors-conquerors), ''Quturgur'' and ''qudurmaq'' (the enrages). There has been little scholarly support for theories linking the names Kutrigur and Utigur to peoples such as the Guti/Quti and/or Udi/Uti, of Ancient Southwest Asia and the Caucasus respectively, which have been posited by scholars such as Osman Karatay, and Yury Zuev. No evidence has been presented that the Guti moved from their homeland in the Zagros Mountains (modern Iran/Iraq) to the Steppes, and they are widely believed to have spoken an Indo-Europe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kutrigurs
Kutrigurs were Turkic nomadic equestrians who flourished on the Pontic–Caspian steppe in the 6th century AD. To their east were the similar Utigurs and both possibly were closely related to the Bulgars. They warred with the Byzantine Empire and the Utigurs. Towards the end of the 6th century they were absorbed by the Pannonian Avars under pressure from the Turks. Etymology The name ''Kutrigur'', also recorded as ''Kwrtrgr'', ''Κουτρίγουροι'', ''Κουτούργουροι'', ''Κοτρίγουροι'', ''Κοτρίγοροι'', ''Κουτρίγοροι'', ''Κοτράγηροι'', ''Κουτράγουροι'', ''Κοτριαγήροι'', has been suggested as a metathecized form of Turkic ''*Toqur- Oğur'', with ''*quturoğur'' meaning "nine Oğur (tribes)". David Marshall Lang derived it from Turkic ''kötrügür'' (conspicuous, eminent, renowned). Few scholars support theories deriving the Kutrigurs from the Guti/Quti and the Utigurs from the Udi/Uti, of ancient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgars
The Bulgars (also Bulghars, Bulgari, Bolgars, Bolghars, Bolgari, Proto-Bulgarians) were Turkic semi-nomadic warrior tribes that flourished in the Pontic–Caspian steppe and the Volga region during the 7th century. They became known as nomadic equestrians in the Volga-Ural region, but some researchers say that their ethnic roots can be traced to Central Asia. During their westward migration across the Eurasian steppe, the Bulgar tribes absorbed other tribal groups and cultural influences in a process of ethnogenesis, including Iranian, Finnic and Hunnic tribes. Modern genetic research on Central Asian Turkic people and ethnic groups related to the Bulgars points to an affiliation with Western Eurasian populations. The Bulgars spoke a Turkic language, i.e. Bulgar language of Oghuric branch. They preserved the military titles, organization and customs of Eurasian steppes, as well as pagan shamanism and belief in the sky deity Tangra. The Bulgars became semi-sedentary du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkic People
The Turkic peoples are a collection of diverse ethnic groups of West Asia, West, Central Asia, Central, East Asia, East, and North Asia as well as parts of Europe, who speak Turkic languages.. "Turkic peoples, any of various peoples whose members speak languages belonging to the Turkic subfamily...". "The Turkic peoples represent a diverse collection of ethnic groups defined by the Turkic languages." According to historians and linguists, the Proto-Turkic language originated in Central-East Asia region, potentially in Mongolia or Tuva. Initially, Proto-Turkic speakers were potentially both hunter-gatherers and farmers, but later became nomadic Pastoralism, pastoralists. Early and Post-classical history, medieval Turkic groups exhibited a wide range of both East Asian and West-Eurasian physical appearances and genetic origins, in part through long-term contact with neighboring peoples such as Iranian peoples, Iranian, Mongolic peoples, Mongolic, Tocharians, Yeniseian people, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkic Tribal Confederations
The Turkic term ''oğuz'' or ''oğur'' (in z- and r-Turkic, respectively) is a historical term for "military division, clan, or tribe" among the Turkic peoples. With the Mongol invasions of 1206–21, the Turkic khaganates were replaced by Mongol or hybrid Turco-Mongol confederations, where the corresponding military division came to be known as '' orda''. Background The 8th-century Kül Tigin stela has the earliest instance of the term in Old Turkic epigraphy: ''Toquz Oghuz'', the "nine tribes". Later the word appears often for two largely separate groups of the Turkic migration in the early medieval period, namely: * Onogur "ten tribes" * Utigurs *Kutrigurs * Uyghur The stem ''uq-, oq-'' "kin, tribe" is from a Proto-Turkic ''*uk''. The Old Turkic word has often been connected with ''oq'' "arrow"; Pohl (2002) in explanation of this connection adduces the Chinese ''T'ang-shu'' chronicle, which reports "the khan divided his realm into ten tribes. To the leader of each tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scythian
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern * : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Central Asia and Eastern Turkestan to distinguish them from the related Massagetae of the Aral region and the Scythians of the Pontic steppes. These tribes spoke Iranian languages, and their chief occupation was nomadic pastoralism." * : "Near the end of the 19th century V.F. Miller (1886, 1887) theorized that the Scythians and their kindred, the Sauromatians, were Iranian-speaking peoples. This has been a popular point of view and continues to be accepted in linguistics and historical science .. * : "From the end of the 7th century B.C. to the 4th century B.C. the Central- Eurasian steppes were inhabited by two large groups of kin Iranian-speaking tribes – the Scythians and Sarmatians .. * : "All contemporary historians, archeologists and li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural History (Pliny)
The ''Natural History'' ( la, Naturalis historia) is a work by Pliny the Elder. The largest single work to have survived from the Roman Empire to the modern day, the ''Natural History'' compiles information gleaned from other ancient authors. Despite the work's title, its subject area is not limited to what is today understood by natural history; Pliny himself defines his scope as "the natural world, or life". It is encyclopedic in scope, but its structure is not like that of a modern encyclopedia. It is the only work by Pliny to have survived, and the last that he published. He published the first 10 books in AD 77, but had not made a final revision of the remainder at the time of his death during the AD 79 eruption of Vesuvius. The rest was published posthumously by Pliny's nephew, Pliny the Younger. The work is divided into 37 books, organised into 10 volumes. These cover topics including astronomy, mathematics, geography, ethnography, anthropology, human physio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aorsi
The Aorsi, known in Greek sources as the Aorsoi (Ἄορσοι), were an ancient Iranian people of the Sarmatian group, who played a major role in the events of the Pontic Steppe from the 1st century BC to the 1st century AD. They are often regarded as connected to the contemporaneous Eurasian steppe state of ''Yancai'' (or ''Yentsai'') mentioned in ancient Chinese records. The Alans, first mentioned by Middle Eastern and European scholars in the 1st century AD, are regarded as successors of the Aorsi. Name The ethnonym ''Aorsi'' is generally linked to the Avestan ''auruša-'' and the Ossetic ''ūrs'' or ''ors'', meaning 'white'. The names '' Arsīyah'' and ''Arsā'', mentioned by Al-Masudi and Al-Garnati in the 10–12th century AD, may also be related. History The Aorsi and an associated tribe, the Siraces, are believed to have migrated during the late 5th century BC from Central Asia to areas north and west of the Caspian Sea. The territory of the Aorsi is believed to hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perseus Project
The Perseus Project is a digital library project of Tufts University, which assembles digital collections of humanities resources. Version 4.0 is also known as the "Perseus Hopper", and it is hosted by the Department of Classical Studies. The project is mirrored by the Max Planck Society in Berlin, Germany, as well as by the University of Chicago. History The project was founded in 1987 to collect and present materials for the study of ancient Greece. It has published two CD-ROMs and established the Perseus Digital Library on the World Wide Web in 1995. The project has expanded its original scope; current collections cover Greco-Roman classics and the English Renaissance. Other materials, such as the papers of Edwin Bolles and the history of Tufts University, have been moved into the Tufts Digital Library. The editor-in-chief of the project is Gregory R. Crane, the Tufts Winnick Family Chair in Technology and Entrepreneurship. He has held that position since the founding of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarmatians
The Sarmatians (; grc, Σαρμαται, Sarmatai; Latin: ) were a large confederation of ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic peoples of classical antiquity who dominated the Pontic steppe from about the 3rd century BC to the 4th century AD. Originating in the central parts of the Eurasian Steppe, the Sarmatians were part of the wider Scythian cultures. They started migrating westward around the fourth and third centuries BC, coming to dominate the closely related Scythians by 200 BC. At their greatest reported extent, around 100 BC, these tribes ranged from the Vistula River to the mouth of the Danube and eastward to the Volga, bordering the shores of the Black and Caspian seas as well as the Caucasus to the south. In the first century AD, the Sarmatians began encroaching upon the Roman Empire in alliance with Germanic tribes. In the third century AD, their dominance of the Pontic Steppe was broken by the Germanic Goths. With the Hunnic invasions of the fourth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
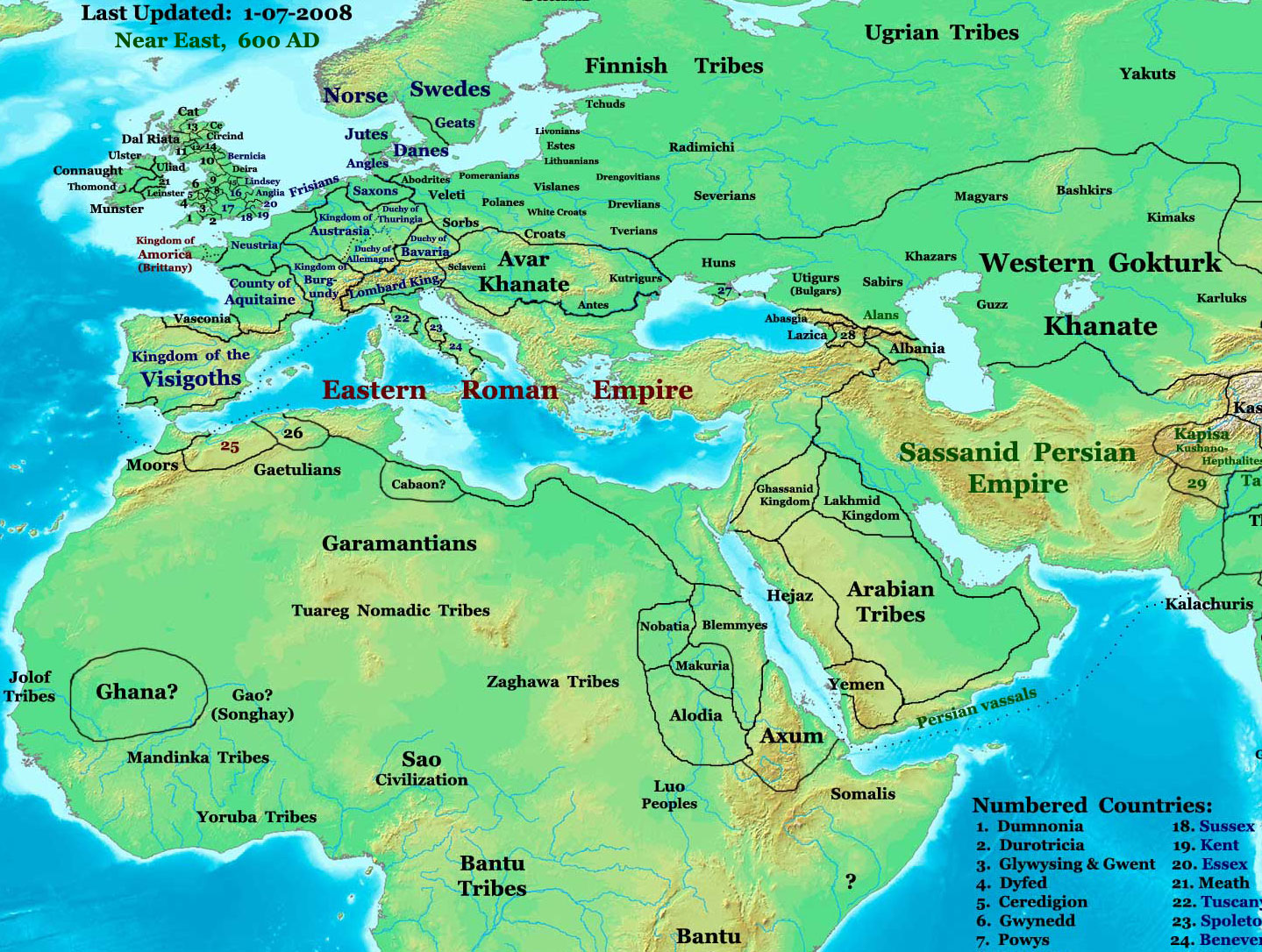
NE 600ad
NE, Ne or ne may refer to: Arts and entertainment * Neutral Evil, an alignment in the American role-playing game ''Dungeons & Dragons'' * New Edition, an American vocal group * Nicomachean Ethics, a collection of ten books by Greek philosopher Aristotle Businesses and organizations * National Express, an English public transport operator * Natural England, an English government agency * New England Patriots, a professional American football team in Foxborough, Massachusetts * New Hope (Macau), a Macau political party * SkyEurope Airlines, a Slovakian airline * New Era Cap Company, an American headwear company Language * Ne (cuneiform), a cuneiform sign * Ne (kana), a Japanese written character * Nepali language * Modern English, sometimes abbreviated NE (to avoid confusion with Middle English) Places * NE postcode area, UK, a postcode for the City of Newcastle upon Tyne, Tyne and Wear * Ne, Liguria, Italy, a ''comune'' in the Province of Genoa * Né (river), a river in so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Farmers
A farmer is a person engaged in agriculture, raising living organisms for food or raw materials. The term usually applies to people who do some combination of raising field crops, orchards, vineyards, poultry, or other livestock. A farmer might own the farm land or might work as a laborer on land owned by others. In most developed economies, a "farmer" is usually a farm owner (landowner), while employees of the farm are known as ''farm workers'' (or farmhands). However, in other older definitions a farmer was a person who promotes or improves the growth of plants, land or crops or raises animals (as livestock or fish) by labor and attention. Over half a billion farmers are smallholders, most of whom are in developing countries, and who economically support almost two billion people. Globally, women constitute more than 40% of agricultural employees. History Farming dates back as far as the Neolithic, being one of the defining characteristics of that era. By the Bronze Age, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caucasian Albania
Caucasian Albania is a modern exonym for a former state located in ancient times in the Caucasus: mostly in what is now Azerbaijan (where both of its capitals were located). The modern endonyms for the area are ''Aghwank'' and ''Aluank'', among the Udi people, who regard themselves as descended from the inhabitants of Caucasian Albania. However, its original endonym is unknown.Robert H. Hewsen. "Ethno-History and the Armenian Influence upon the Caucasian Albanians", in: Samuelian, Thomas J. (Ed.), ''Classical Armenian Culture. Influences and Creativity''. Chicago: 1982, pp. 27-40. Bosworth, Clifford E.br>Arran ''Encyclopædia Iranica''. The name Albania is derived from the Ancient Greek name and Latin . James Stuart Olson. An Ethnohistorical Dictionary of the Russian and Soviet Empires. The prefix "Caucasian" is used purely to avoid confusion with modern Albania of the Balkans, which has no known geographical or historical connections to Caucasian Albania. Little is known of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)