|
Two-electron Atom
In atomic physics, a two-electron atom or helium-like ion is a quantum mechanical system consisting of one nucleus with a charge of ''Z e'' and just two electrons. This is the first case of many-electron systems where the Pauli exclusion principle plays a central role. It is an example of a three-body problem. The first few two-electron atoms are: Schrödinger equation The Schrödinger equation for any two-electron system, such as the neutral Helium atom (He, ''Z'' = 2), the negative Hydrogen ion (H−, ''Z'' = 1), or the positive Lithium ion (Li+, ''Z'' = 3) is:Physics of Atoms and Molecules, B.H. Bransden, C.J.Joachain, Longman, 1983, For a more rigorous mathematical derivation of the Schrödinger equation, see also. E\psi = -\hbar^2\left frac\left(\nabla_1^2 +\nabla_2^2 \right) + \frac \nabla_1 \cdot \nabla_2\right\psi + \frac\left \frac -Z\left( \frac + \frac \right) \right\psi where r1 is the position of one electron (''r''1 = , r1, is its magnitude), r2 is the posit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomic Physics
Atomic physics is the field of physics that studies atoms as an isolated system of electrons and an atomic nucleus. Atomic physics typically refers to the study of atomic structure and the interaction between atoms. It is primarily concerned with the way in which electrons are arranged around the nucleus and the processes by which these arrangements change. This comprises ions, neutral atoms and, unless otherwise stated, it can be assumed that the term ''atom'' includes ions. The term ''atomic physics'' can be associated with nuclear power and nuclear weapons, due to the synonymous use of ''atomic'' and ''nuclear'' in standard English. Physicists distinguish between atomic physics—which deals with the atom as a system consisting of a nucleus and electrons—and nuclear physics, which studies nuclear reactions and special properties of atomic nuclei. As with many scientific fields, strict delineation can be highly contrived and atomic physics is often considered in the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helium Atom
A helium atom is an atom of the chemical element helium. Helium is composed of two electrons bound by the electromagnetic force to a nucleus containing two protons along with two neutrons, depending on the isotope, held together by the strong force. Unlike for hydrogen, a closed-form solution to the Schrödinger equation for the helium atom has not been found. However, various approximations, such as the Hartree–Fock method, can be used to estimate the ground state energy and wavefunction of the atom. Historically, the first attempt to obtain the helium spectrum from quantum mechanics was done by Albrecht Unsöld in 1927. Egil Hylleraas obtained an accurate approximation in 1929. Its success was considered to be one of the earliest signs of validity of Schrödinger's wave mechanics. Introduction The quantum mechanical description of the helium atom is of special interest, because it is the simplest multi-electron system and can be used to understand the concept of q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
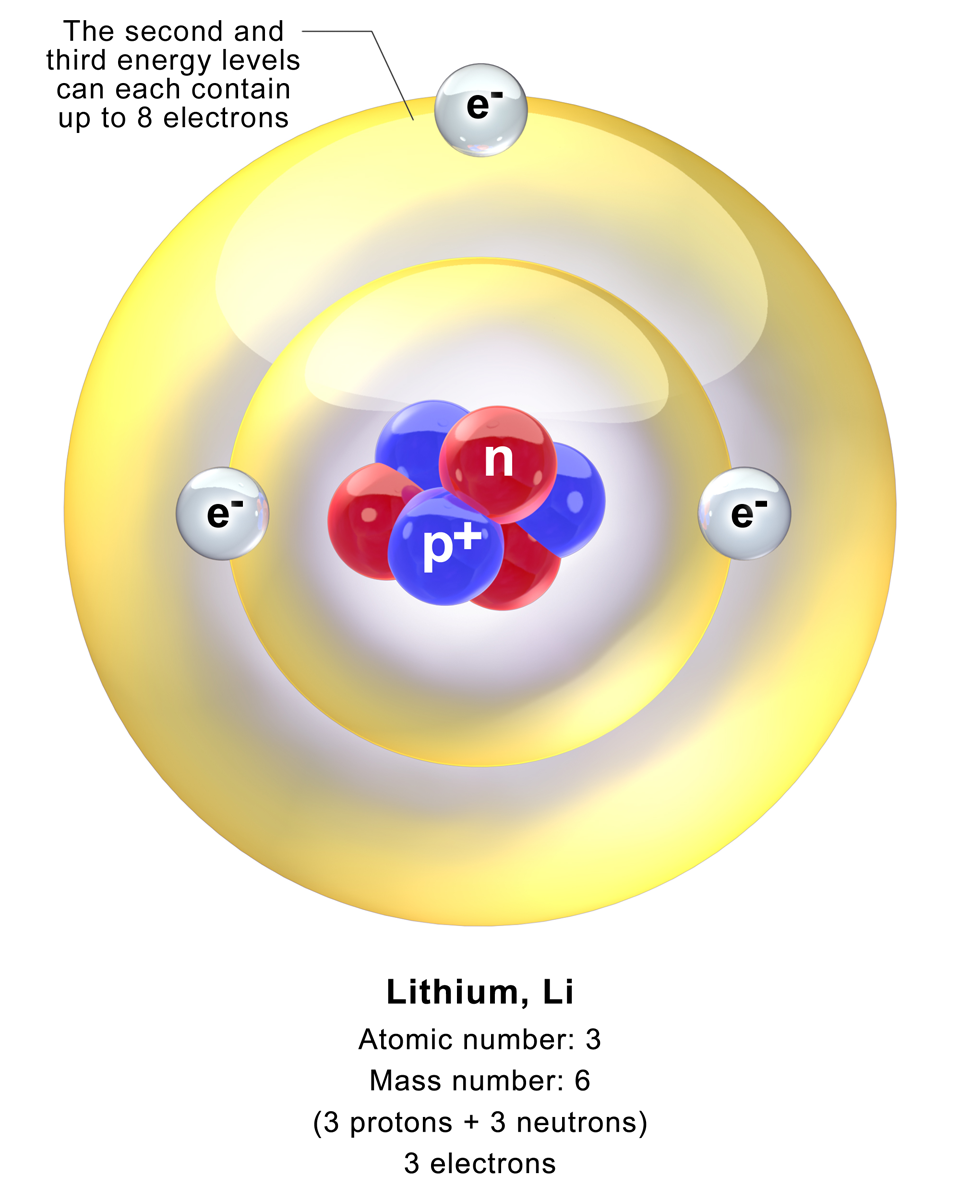
Lithium Atom
A lithium atom is an atom of the chemical element lithium. Stable lithium is composed of three electrons bound by the electromagnetic force to a nucleus containing three protons along with either three or four neutrons, depending on the isotope, held together by the strong force. Similarly to the case of the helium atom, a closed-form solution to the Schrödinger equation for the lithium atom has not been found. However, various approximations, such as the Hartree–Fock method, can be used to estimate the ground state energy and wavefunction In quantum physics, a wave function (or wavefunction) is a mathematical description of the quantum state of an isolated quantum system. The most common symbols for a wave function are the Greek letters and (lower-case and capital psi (letter) ... of the atom. The quantum defect is a value that describes the deviation from hydrogenic energy levels. Further reading W. Zheng et al. / Appl. Math. Comput. 153 (2004) 685–695"Numerical s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Molecular Ion
The dihydrogen cation or molecular hydrogen ion is a cation (positive ion) with formula H2^+. It consists of two hydrogen nuclei (protons), each sharing a single electron. It is the simplest molecular ion. The ion can be formed from the ionization of a neutral hydrogen molecule (H2) by electron impact. It is commonly formed in molecular clouds in space by the action of cosmic rays. The dihydrogen cation is of great historical, theoretical, and experimental interest. Historically it is of interest because, having only one electron, the equations of quantum mechanics that describe its structure can be solved approximately in a relatively straightforward way, as long as the motion of the nuclei and relativistic and quantum electrodynamic effects are neglected. The first such solution was derived by Ø. Burrau in 1927, just one year after the wave theory of quantum mechanics was published. The theoretical interest arises because an accurate mathematical description, taking into a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen-like Atom
A hydrogen-like atom (or hydrogenic atom) is any atom or ion with a single valence electron. These atoms are isoelectronic with hydrogen. Examples of hydrogen-like atoms include, but are not limited to, hydrogen itself, all alkali metals such as Rb and Cs, singly ionized alkaline earth metals such as Ca+ and Sr+ and other ions such as He+, Li2+, and Be3+ and isotopes of any of the above. A hydrogen-like atom includes a positively charged core consisting of the atomic nucleus and any core electrons as well as a single valence electron. Because helium is common in the universe, the spectroscopy of singly ionized helium is important in EUV astronomy, for example, of DO white dwarf stars. The non-relativistic Schrödinger equation and relativistic Dirac equation for the hydrogen atom can be solved analytically, owing to the simplicity of the two-particle physical system. The one-electron wave function solutions are referred to as ''hydrogen-like atomic orbitals''. Hydrogen-li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercury (element)
Mercury is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Hg and atomic number 80. It is commonly known as quicksilver. A Heavy metal element, heavy, silvery d-block element, mercury is the only metallic element that is known to be liquid at standard temperature and pressure; the only other element that is liquid under these conditions is the halogen bromine, though metals such as caesium, gallium, and rubidium melt just above room temperature. Mercury occurs in deposits throughout the world mostly as cinnabar (mercuric sulfide). The red pigment vermilion is obtained by Mill (grinding), grinding natural cinnabar or synthetic mercuric sulfide. Exposure to mercury and mercury-containing organic compounds is toxic to the nervous system, immune system and kidneys of humans and other animals; mercury poisoning can result from exposure to water-soluble forms of mercury (such as mercuric chloride or methylmercury) either directly or through mechanisms of biomagnification. Mercu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkaline Earth Metal
The alkaline earth metals are six chemical elements in group (periodic table), group 2 of the periodic table. They are beryllium (Be), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), strontium (Sr), barium (Ba), and radium (Ra).. The elements have very similar properties: they are all shiny, silvery-white, somewhat reactivity (chemistry), reactive metals at standard temperature and pressure. Together with helium, these elements have in common an outer atomic orbital, s orbital which is full —that is, this orbital contains its full complement of two electrons, which the alkaline earth metals readily lose to form cations with electric charge, charge +2, and an oxidation state of +2. Helium is grouped with the noble gases and not with the alkaline earth metals, but it is theorized to have some similarities to beryllium when forced into bonding and has sometimes been suggested to belong to group 2. All the discovered alkaline earth metals occur in nature, although radium occurs only through the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dover Publications
Dover Publications, also known as Dover Books, is an American book publisher founded in 1941 by Hayward and Blanche Cirker. It primarily reissues books that are out of print from their original publishers. These are often, but not always, books in the public domain. The original published editions may be scarce or historically significant. Dover republishes these books, making them available at a significantly reduced cost. Classic reprints Dover reprints classic works of literature, classical sheet music, and public-domain images from the 18th and 19th centuries. Dover also publishes an extensive collection of mathematical, scientific, and engineering texts. It often targets its reprints at a niche market, such as woodworking. Starting in 2015, the company branched out into graphic novel reprints, overseen by Dover acquisitions editor and former comics writer and editor Drew Ford. Most Dover reprints are photo facsimiles of the originals, retaining the original pagination ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Number
In quantum physics and chemistry, quantum numbers are quantities that characterize the possible states of the system. To fully specify the state of the electron in a hydrogen atom, four quantum numbers are needed. The traditional set of quantum numbers includes the principal, azimuthal, magnetic, and spin quantum numbers. To describe other systems, different quantum numbers are required. For subatomic particles, one needs to introduce new quantum numbers, such as the flavour of quarks, which have no classical correspondence. Quantum numbers are closely related to eigenvalues of observables. When the corresponding observable commutes with the Hamiltonian of the system, the quantum number is said to be " good", and acts as a constant of motion in the quantum dynamics. History Electronic quantum numbers In the era of the old quantum theory, starting from Max Planck's proposal of quanta in his model of blackbody radiation (1900) and Albert Einstein's adaptation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomic Number
The atomic number or nuclear charge number (symbol ''Z'') of a chemical element is the charge number of its atomic nucleus. For ordinary nuclei composed of protons and neutrons, this is equal to the proton number (''n''p) or the number of protons found in the nucleus of every atom of that element. The atomic number can be used to uniquely identify ordinary chemical elements. In an ordinary uncharged atom, the atomic number is also equal to the number of electrons. For an ordinary atom which contains protons, neutrons and electrons, the sum of the atomic number ''Z'' and the neutron number ''N'' gives the atom's atomic mass number ''A''. Since protons and neutrons have approximately the same mass (and the mass of the electrons is negligible for many purposes) and the mass defect of the nucleon binding is always small compared to the nucleon mass, the atomic mass of any atom, when expressed in daltons (making a quantity called the " relative isotopic mass"), is within 1% ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithium
Lithium (from , , ) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Li and atomic number 3. It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard temperature and pressure, standard conditions, it is the least dense metal and the least dense solid element. Like all alkali metals, lithium is highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive and flammable, and must be stored in vacuum, inert atmosphere, or inert liquid such as purified kerosene or mineral oil. It exhibits a metallic luster (mineralogy), luster. It corrosion, corrodes quickly in air to a dull silvery gray, then black tarnish. It does not occur freely in nature, but occurs mainly as pegmatite, pegmatitic minerals, which were once the main source of lithium. Due to its solubility as an ion, it is present in ocean water and is commonly obtained from brines. Lithium metal is isolated electrolysis, electrolytically from a mixture of lithium chloride and potassium chloride. The Atomic nucleus, nucleus of the lithiu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter. Under standard conditions, hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules with the chemical formula, formula , called dihydrogen, or sometimes hydrogen gas, molecular hydrogen, or simply hydrogen. Dihydrogen is colorless, odorless, non-toxic, and highly combustible. Stars, including the Sun, mainly consist of hydrogen in a plasma state, while on Earth, hydrogen is found as the gas (dihydrogen) and in molecular forms, such as in water and organic compounds. The most common isotope of hydrogen (H) consists of one proton, one electron, and no neutrons. Hydrogen gas was first produced artificially in the 17th century by the reaction of acids with metals. Henry Cavendish, in 1766–1781, identified hydrogen gas as a distinct substance and discovere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |