Lithium Atom on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
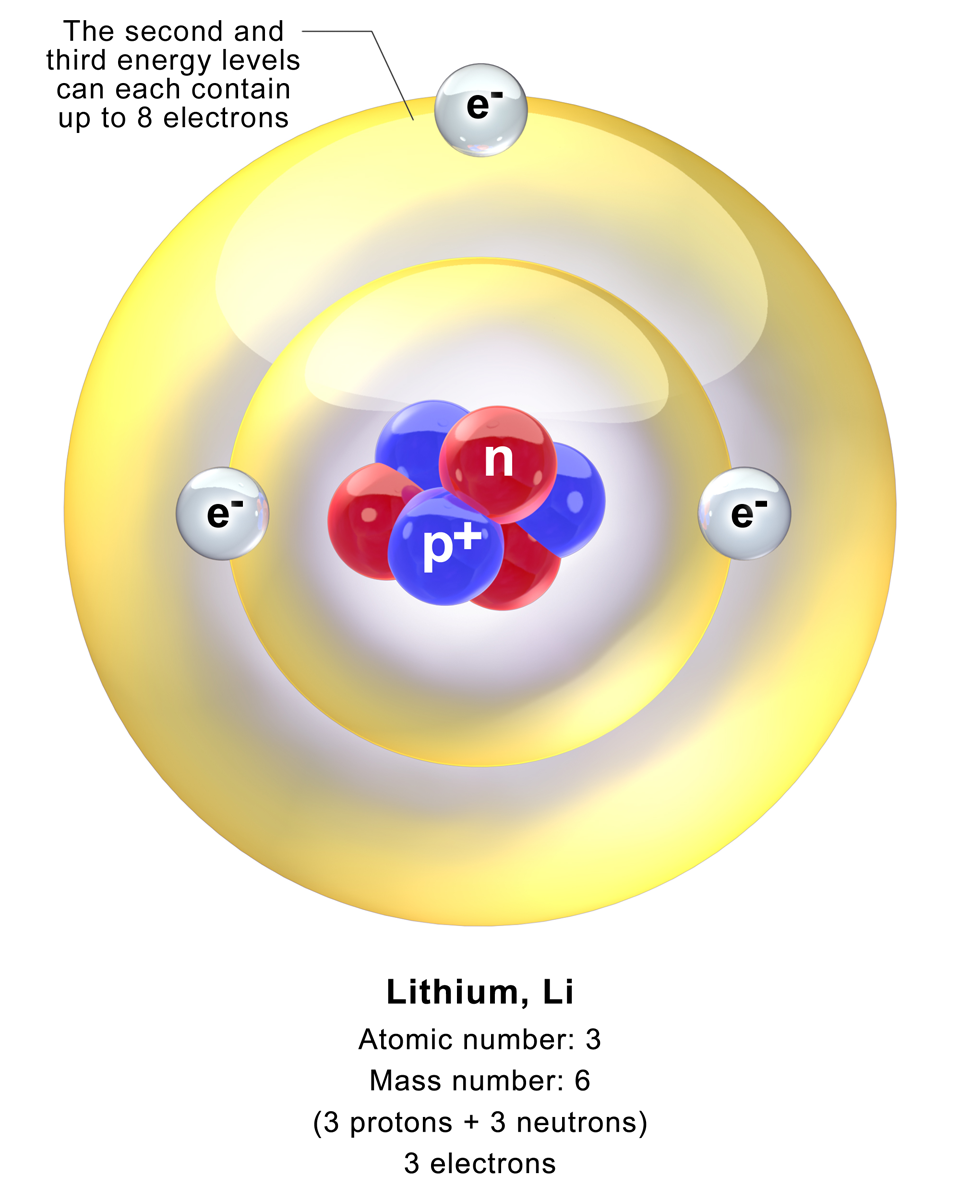 A lithium atom is an
A lithium atom is an
W. Zheng et al. / Appl. Math. Comput. 153 (2004) 685–695
"Numerical solutions of the Schrödinger equation for the ground lithium by the finite element method" Atoms Lithium {{nuclear-stub
 A lithium atom is an
A lithium atom is an atom
Every atom is composed of a nucleus and one or more electrons bound to the nucleus. The nucleus is made of one or more protons and a number of neutrons. Only the most common variety of hydrogen has no neutrons.
Every solid, liquid, gas ...
of the chemical element
A chemical element is a species of atoms that have a given number of protons in their nuclei, including the pure substance consisting only of that species. Unlike chemical compounds, chemical elements cannot be broken down into simpler sub ...
lithium
Lithium (from el, λίθος, lithos, lit=stone) is a chemical element with the symbol Li and atomic number 3. It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard conditions, it is the least dense metal and the least dense solid ...
. Stable lithium is composed of three electrons bound by the electromagnetic force
In physics, electromagnetism is an interaction that occurs between particles with electric charge. It is the second-strongest of the four fundamental interactions, after the strong force, and it is the dominant force in the interactions o ...
to a nucleus containing three protons along with either three or four neutron
The neutron is a subatomic particle, symbol or , which has a neutral (not positive or negative) charge, and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton. Protons and neutrons constitute the nuclei of atoms. Since protons and neutrons behav ...
s, depending on the isotope
Isotopes are two or more types of atoms that have the same atomic number (number of protons in their nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), and that differ in nucleon numbers ( mass number ...
, held together by the strong force
The strong interaction or strong force is a fundamental interaction that confines quarks into proton, neutron, and other hadron particles. The strong interaction also binds neutrons and protons to create atomic nuclei, where it is called the ...
. Similarly to the case of the helium atom
A helium atom is an atom of the chemical element helium. Helium is composed of two electrons bound by the electromagnetic force to a nucleus containing two protons along with either one or two neutrons, depending on the isotope, held together b ...
, a closed-form solution to the Schrödinger equation
The Schrödinger equation is a linear partial differential equation that governs the wave function of a quantum-mechanical system. It is a key result in quantum mechanics, and its discovery was a significant landmark in the development of th ...
for the lithium atom has not been found. However, various approximations, such as the Hartree–Fock method
In computational physics and chemistry, the Hartree–Fock (HF) method is a method of approximation for the determination of the wave function and the energy of a quantum many-body system in a stationary state.
The Hartree–Fock method ofte ...
, can be used to estimate the ground state energy and wavefunction
A wave function in quantum physics is a mathematical description of the quantum state of an isolated quantum system. The wave function is a complex-valued probability amplitude, and the probabilities for the possible results of measurements ma ...
of the atom. The quantum defect is a value that describes the deviation from hydrogenic energy levels.
Further reading
W. Zheng et al. / Appl. Math. Comput. 153 (2004) 685–695
"Numerical solutions of the Schrödinger equation for the ground lithium by the finite element method" Atoms Lithium {{nuclear-stub