|
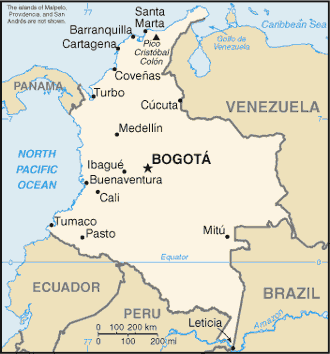
Turbo, Colombia
Turbo is a port city in Antioquia Department, Colombia. Part of the Urabá Antioquia sub-region, it is located on the coast of Gulf of Urabá, 340 km north of Medellín (the department capital and second largest city). This port city is the capital of the Urabá region of Antioquia. The place where Turbo is today was known as Pisisí, but by 1741 people were already talking about Turbo. By a decree on May 11, 1839, the central government spent one thousand pesos for military service barracks in Turbo. In 1840, the republican president assigned one thousand fanegas of uncultivated lands for the new population. It was established as a municipality in 1847. Turbo lies near the southeastern tip of the Darién Gap and is the northern terminus of the main route of the Pan-American Highway in South America. There is currently no paved road connecting through the region to Yaviza, Panama, where the highway continues through Central and North America. Geography Climate Turbo has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cities And Towns In Colombia ...
This article lists cities and towns in Colombia by population, according to the 2005 census. A city is displayed in bold if it is a capital city of a department. List See also * List of cities * List of cities in Colombia by population, a list that only includes cities with no less than 100,000 residents in order of population size (instead of alphabetical order). *Departments of Colombia *Municipalities of Colombia References External links * {{DEFAULTSORT:List Of Cities In Colombia Colombia Colombia Colombia Cities A city is a human settlement of a substantial size. The term "city" has different meanings around the world and in some places the settlement can be very small. Even where the term is limited to larger settlements, there is no universally agree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yaviza
Yaviza is a town and corregimiento in Pinogana District, Darién Province, Panama with a population of 4,441 as of 2010. Location The town marks the southeastern end of the northern half of the Pan-American Highway, at the north end of the Darién Gap.Leonard, Thomas MHistorical Dictionary of Panama p. xxxv (2015) It lies on the Chucunaque River, a major tributary of the Tuira River, along which travel by boat into the Darién Gap occurs. The nearest town on the river route is El Real de Santa María, which is the capital of Pinogana District. Demographics The population of Yaviza as of 1990 was 8,452, falling to 3,317 as recorded in the year 2000, and rising to 4,441 as of 2010. History The town was founded by Spanish missionaries as San Jerónimo de Yaviza in September 1638.Rutkow, EricThe Longest Line on the Map p. 322 (2019) A Spanish fort (Fuerte de San Geronimo de Yaviza) was built in 1760, and heavily damaged by an attack of the Indigenous Guna in 1780. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institute Of Hydrology, Meteorology And Environmental Studies (Colombia)
The Institute of Hydrology, Meteorology and Environmental Studies (), also known by its acronym in Spanish, IDEAM, is a government agency of the Ministry of Environment and Sustainable Development (Colombia), Ministry of Environment and Sustainable Development of Colombia. It is in charge of producing and managing the scientific and technical information on the environment of Colombia, and its territorial composition. The IDEAM also serves as the Colombian meteorology, institute of meteorology and studies the climate of Colombia. The agency is currently led by the Director General, forestry engineer Yolanda González Hernandez. González Hernández is a specialist in Geographic information system, Geographic Information Systems with a Masters in Meteorology Sciences from the National University of Colombia, and is the first woman to lead the agency. Creation It was created on December 22, 1993, when Congress of Colombia, Congress passed ''Law 99 of 1993'', replacing the Colombia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intertropical Convergence Zone
The Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ , or ICZ), known by sailors as the doldrums or the calms because of its monotonous windless weather, is the area where the northeast and the southeast trade winds converge. It encircles Earth near the thermal equator though its specific position varies seasonally. When it lies near the geographic equator, it is called the near-equatorial trough. Where the ITCZ is drawn into and merges with a monsoon, monsoonal circulation, it is sometimes referred to as a ''monsoon trough'' (a usage that is more common in Australia and parts of Asia). Meteorology The ITCZ was originally identified from the 1920s to the 1940s as the ''Intertropical Front'' (''ITF''), but after the recognition in the 1940s and the 1950s of the significance of convergence zone, wind field convergence in tropics, tropical weather production, the term ''Intertropical Convergence Zone'' (''ITCZ'') was then applied. The ITCZ appears as a band of clouds, usually thunderstorms, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
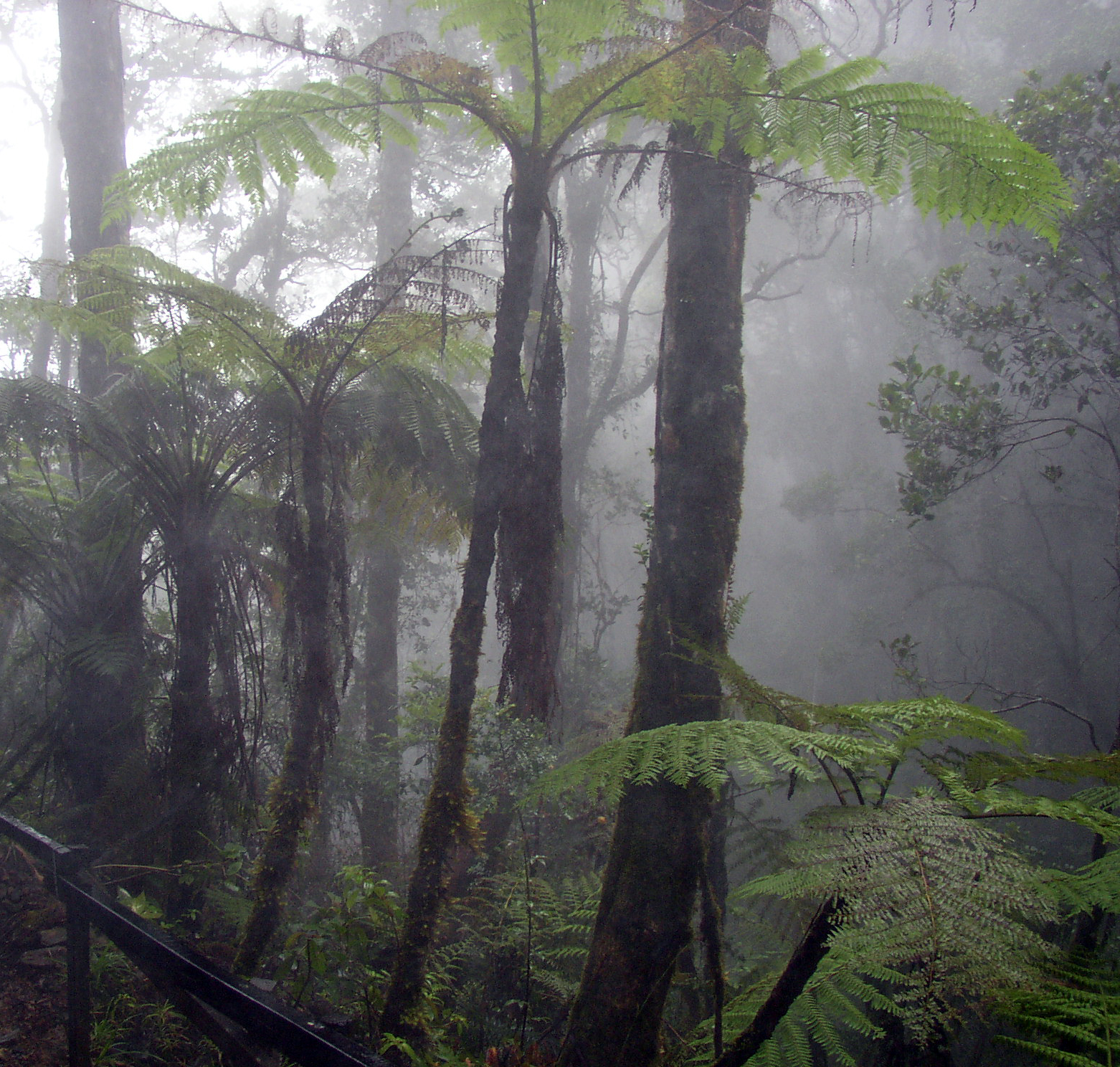
Tropical Rainforest Climate
A tropical rainforest climate or equatorial climate is a tropical climate sub-type usually found within 10 to 15 degrees latitude of the equator. There are some other areas at higher latitudes, such as the coast of southeast Florida, United States, and Okinawa, Japan that fall into the tropical rainforest climate category. They experience high mean annual temperatures, small temperature ranges, and rain that falls throughout the year. Regions with this climate are typically designated ''Af'' by the Köppen climate classification. A tropical rainforest climate is typically hot, very humid, and wet with no dry season. Description Tropical rainforests have a type of tropical climate (with an average temperature of at least in their coldest month) in which there is no dry season—all months have an average precipitation value of at least . There are no distinct wet or dry seasons as rainfall is high throughout the months. One day in a tropical rainforest climate can be very simil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Monsoon Climate
An area of tropical monsoon climate (occasionally known as a sub-equatorial, tropical wet climate or a tropical monsoon and trade-wind littoral climate) is a tropical climate subtype that corresponds to the Köppen climate classification category ''Am''. Tropical monsoon climates have monthly mean temperatures above in every month of the year and a dry season. The tropical monsoon climate is the intermediate climate between the wet Af (or tropical rainforest climate) and the drier Aw (or tropical savanna climate). A tropical monsoon climate's driest month has on average less than 60 mm, but more than 100-\left(\frac\right). This is in direct contrast to a tropical savanna climate, whose driest month has less than 60 mm of precipitation and also less than 100-\left(\frac\right) of average monthly precipitation. In essence, a tropical monsoon climate tends to either have more rainfall than a tropical savanna climate or have less pronounced dry seasons. A tropical monsoon cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köppen Climate Classification
The Köppen climate classification divides Earth climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on patterns of seasonal precipitation and temperature. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (temperate), ''D'' (continental), and ''E'' (polar). Each group and subgroup is represented by a letter. All climates are assigned a main group (the first letter). All climates except for those in the ''E'' group are assigned a seasonal precipitation subgroup (the second letter). For example, ''Af'' indicates a tropical rainforest climate. The system assigns a temperature subgroup for all groups other than those in the ''A'' group, indicated by the third letter for climates in ''B'', ''C'', ''D'', and the second letter for climates in ''E''. Other examples include: ''Cfb'' indicating an oceanic climate with warm summers as indicated by the ending ''b.'', while ''Dwb'' indicates a semi-Monsoon continental climate, monsoonal continental climate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Caribbean Sea, and to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean. The region includes Middle America (Americas), Middle America (comprising the Caribbean, Central America, and Mexico) and Northern America. North America covers an area of about , representing approximately 16.5% of Earth's land area and 4.8% of its total surface area. It is the third-largest continent by size after Asia and Africa, and the list of continents and continental subregions by population, fourth-largest continent by population after Asia, Africa, and Europe. , North America's population was estimated as over 592 million people in list of sovereign states and dependent territories in North America, 23 independent states, or about 7.5% of the world's popula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central America
Central America is a subregion of North America. Its political boundaries are defined as bordering Mexico to the north, Colombia to the southeast, the Caribbean to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the southwest. Central America is usually defined as consisting of seven countries: Belize, Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua, and Panama. Within Central America is the Mesoamerican biodiversity hotspot, which extends from southern Mexico to southeastern Panama. Due to the presence of several active geologic faults and the Central America Volcanic Arc, there is a high amount of seismic activity in the region, such as volcanic eruptions and earthquakes, which has resulted in death, injury, and property damage. Most of Central America falls under the Isthmo-Colombian cultural area. Before the Spanish expedition of Christopher Columbus' voyages to the Americas, hundreds of indigenous peoples made their homes in the area. From the year 1502 onwards, Spain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panama
Panama, officially the Republic of Panama, is a country in Latin America at the southern end of Central America, bordering South America. It is bordered by Costa Rica to the west, Colombia to the southeast, the Caribbean Sea to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the south. Its capital and largest city is Panama City, whose metropolitan area is home to nearly half of the country's over million inhabitants. Before the arrival of Spanish Empire, Spanish colonists in the 16th century, Panama was inhabited by a number of different Indigenous peoples of Panama, indigenous tribes. It Independence Act of Panama, broke away from Spain in 1821 and joined the Republic of Gran Colombia, a union of Viceroyalty of New Granada, Nueva Granada, Ecuador, and Venezuela. After Gran Colombia dissolved in 1831, Panama and Nueva Granada eventually became the Republic of Colombia. With the backing of the United States, Panama seceded from Colombia in 1903, allowing the construction of the Panama Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a considerably smaller portion in the Northern Hemisphere. It can also be described as the southern Subregion#Americas, subregion of the Americas. South America is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean, on the north and east by the Atlantic Ocean, and to the south by the Drake Passage; North America and the Caribbean Sea lie to the northwest. The continent includes twelve sovereign states: Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, Uruguay, and Venezuela; two dependent territory, dependent territories: the Falkland Islands and South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands; and one administrative division, internal territory: French Guiana. The Dutch Caribbean ABC islands (Leeward Antilles), ABC islands (Aruba, Bonaire, and Curaçao) and Trinidad and Tobago are geologically located on the South-American continental shel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Departments Of Colombia
Colombia is a unitary state, unitary republic made up of thirty-two administrative divisions referred to as departments (Spanish language, Spanish: ''departamentos'', sing. ) and one Capital District (''Capital districts and territories, Distrito Capital''). Departments are administrative division, country subdivisions and are granted a certain degree of autonomy. Each department has a governor (''gobernador'') and an Assembly (''Asamblea Departamental''), elected by popular vote for a four-year period. The governor cannot be re-elected in consecutive periods. Departments are formed by a grouping of municipalities of Colombia, municipalities (''municipios'', sing. ''municipio''). Municipal government is headed by mayor (''alcalde'') and administered by a municipal council (''concejo municipal''), both of which are elected by popular vote for four-year periods. Internal subdivisions within departments The current borders and number of the departments of Colombia was finally se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |