|
Tissue-resident Memory T Cells
Tissue-resident memory T cells or TRM cells represent a subset of a long-lived memory T cells that occupies epithelial, mucosal and other tissues (skin, mucosa, lung, brain, pancreas, gastrointestinal tract) without recirculating. TRM cells are transcriptionally, phenotypically and functionally distinct from central memory (TCM) and effector memory (TEM) T cells which recirculate between blood, the T cell zones of secondary lymphoid organ, lymph and nonlymphoid tissues. Moreover, TRM cells consist of diverse populations both between tissues and within a single tissue. TRM cells provide protection against infection in extralymphoid tissues. Phenotype Three cell surface markers that has been associated with TRM are CD69, CD49a, and CD103. CD69 suppresses response to the S1P chemoattractant from blood and lymph and prevents TRM cells from exiting peripheral tissue. CD49a mediates tissue residency directly and marks cells with the most effector-like capabilities including IFN-gamma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T Cell
T cells (also known as T lymphocytes) are an important part of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell surface receptor, cell surface. T cells are born from hematopoietic stem cells, found in the bone marrow. Developing T cells then migrate to the thymus gland to develop (or mature). T cells derive their name from the thymus. After migration to the thymus, the precursor cells mature into several distinct types of T cells. T cell differentiation also continues after they have left the thymus. Groups of specific, differentiated T cell subtypes have a variety of important functions in controlling and shaping the immune response. One of these functions is immune-mediated cell death, and it is carried out by two major subtypes: Cytotoxic T cell, CD8+ "killer" (cytotoxic) and T helper cell, CD4+ "helper" T cells. (These are named for the presen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interleukin 33
Interleukin 33 (IL-33) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''IL33'' gene. Interleukin 33 is a member of the IL-1 family that potently drives production of T helper-2 (Th2)-associated cytokines (e.g., IL-4). IL33 is a ligand for ST2 (IL1RL1), an IL-1 family receptor that is highly expressed on Th2 cells, mast cells and group 2 innate lymphocytes. IL-33 is expressed by a wide variety of cell types, including fibroblasts, mast cells, dendritic cells, macrophages, osteoblasts, endothelial cells, and epithelial cells. Structure IL-33 is a member of the IL-1 superfamily of cytokines, a determination based in part on the molecules β-trefoil structure, a conserved structure type described in other IL-1 cytokines, including IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-1Ra and IL-18. In this structure, the 12 β-strands of the β-trefoil are arranged in three pseudorepeats of four β-strand units, of which the first and last β-strands are antiparallel staves in a six-stranded β-barrel, while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects synovial joint, joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and hands are involved, with the same joints typically involved on both sides of the body. The disease may also affect other parts of the body, including skin, eyes, lungs, heart, nerves, and blood. This may result in a anemia, low red blood cell count, pleurisy, inflammation around the lungs, and pericarditis, inflammation around the heart. Fever and low energy may also be present. Often, symptoms come on gradually over weeks to months. While the cause of rheumatoid arthritis is not clear, it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. The underlying mechanism involves the body's immune system attacking the joints. This results in inflammation and thickening of the synovium, joint capsule. It also affects the und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lupus Nephritis
Lupus nephritis is an inflammation of the kidneys caused by systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus which is a more severe form of SLE that develops in children up to 18 years old; both are autoimmune diseases. It is a type of glomerulonephritis in which the glomerulus (kidney), glomeruli become inflamed. Since it is a result of SLE, this type of glomerulonephritis is said to be ''secondary'', and has a different pattern and outcome from conditions with a ''primary'' cause originating in the kidney. The diagnosis of lupus nephritis depends on blood tests, urinalysis, X-rays, ultrasound scans of the kidneys, and a kidney biopsy. On urinalysis, a nephritic picture is found and urinary cast#Red blood cell casts, red blood cell casts, red blood cells and proteinuria is found. Signs and symptoms In lupus nephritis, common symptoms of lupus such as fever, arthralgia, joint pain, myalgia, muscle pain, and a malar rash, butterfly-shaped rash on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease resulting in damage to myelinthe insulating covers of nerve cellsin the brain and spinal cord. As a demyelinating disease, MS disrupts the nervous system's ability to Action potential, transmit signals, resulting in a range of signs and symptoms, including physical, cognitive disability, mental, and sometimes psychiatric problems. Symptoms include double vision, vision loss, eye pain, muscle weakness, and loss of Sensation (psychology), sensation or coordination. MS takes several forms, with new symptoms either occurring in isolated attacks (relapsing forms) or building up over time (progressive forms). In relapsing forms of MS, symptoms may disappear completely between attacks, although some permanent neurological problems often remain, especially as the disease advances. In progressive forms of MS, bodily function slowly deteriorates once symptoms manifest and will steadily worsen if left untreated. While its cause is unclear, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
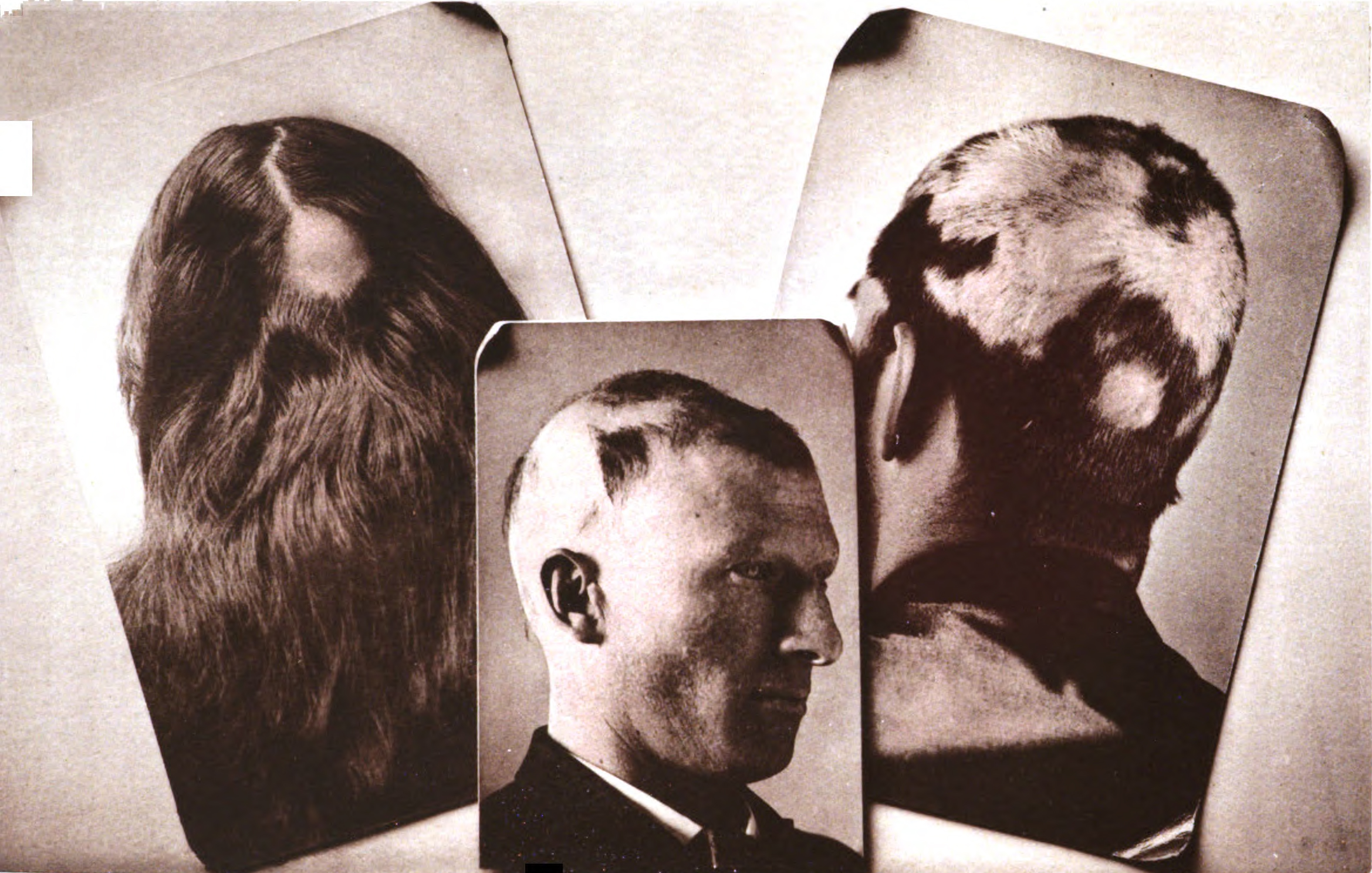
Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata (AA), also known as spot baldness, is a condition in which hair loss, hair is lost from some or all areas of the body. It often results in a few Baldness, bald spots on the scalp, each about the size of a coin. Psychological stress and illness are possible factors in bringing on alopecia areata in individuals at risk, but in most cases there is no obvious trigger. People are generally otherwise healthy. In a few cases, all the hair on the scalp is lost (''alopecia totalis''), or all body hair is lost (''alopecia universalis''). Hair loss can be permanent or temporary. Alopecia areata is believed to be an autoimmune disease resulting from a breach in the immune privilege of the hair follicles. Risk factors include a family history of the condition. Among identical twins, if one is affected, the other has about a 50% chance of also being affected. The underlying mechanism involves failure by the body to recognize its own cells, with subsequent immune-mediated des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a long-lasting, noncontagious autoimmune disease characterized by patches of abnormal skin. These areas are red, pink, or purple, dry, itchy, and scaly. Psoriasis varies in severity from small localized patches to complete body coverage. Injury to the skin can trigger psoriatic skin changes at that spot, which is known as the Koebner phenomenon. The five main types of psoriasis are plaque, guttate, inverse, pustular, and erythrodermic. Plaque psoriasis, also known as psoriasis vulgaris, makes up about 90% of cases. It typically presents as red patches with white scales on top. Areas of the body most commonly affected are the back of the forearms, shins, navel area, and scalp. Guttate psoriasis has drop-shaped lesions. Pustular psoriasis presents as small, noninfectious, pus-filled blisters. Inverse psoriasis forms red patches in skin folds. Erythrodermic psoriasis occurs when the rash becomes very widespread and can develop from any of the other types. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitiligo
Vitiligo (, ) is a chronic autoimmune disorder that causes patches of skin to lose pigment or color. The cause of vitiligo is unknown, but it may be related to immune system changes, genetic factors, stress, or sun exposure, and susceptibility to it may be affected by regional environmental risk factors, especially early in life. Treatment options include topical medications, light therapy, surgery and cosmetics. The condition causes patches of a light peachy color of any size, which can appear on any place on the body; in particular, nonsegmental vitiligo, the common form, tends to progress, affecting more of the skin over time. Vitiligo spots on the skin can also vary in pigmentation over long periods, although they will stay in relatively the same areas. Signs and symptoms The only sign of vitiligo is the presence of pale patchy areas of depigmented skin which tend to occur on the extremities. Some people may experience itching before a new patch appears. The patches ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granzyme B
Granzyme B (GrB) is one of the serine protease granzymes most commonly found in the granules of natural killer cells (NK cells) and cytotoxic T cells. It is secreted by these cells along with the pore forming protein perforin to mediate apoptosis in target cells. Granzyme B has also been found to be produced by a wide range of non-cytotoxic cells ranging from basophils and mast cells to smooth muscle cells. The secondary functions of granzyme B are also numerous. Granzyme B has shown to be involved in inducing inflammation by stimulating cytokine release and is also involved in extracellular matrix remodelling. Elevated levels of granzyme B are also implicated in a number of autoimmune diseases, several skin diseases, and type 1 diabetes. Structure In humans, granzyme B is encoded by ''GZMB'' on chromosome 14q.11.2, which is 3.2kb long and consists of 5 exons. It is one of the most abundant granzymes of which there are 5 in humans and 10 in mice. Granzyme B is thought to hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathogen
In biology, a pathogen (, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of"), in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a Germ theory of disease, germ. The term ''pathogen'' came into use in the 1880s. Typically, the term ''pathogen'' is used to describe an ''infectious'' microorganism or agent, such as a virus, bacterium, protozoan, prion, viroid, or fungus. Small animals, such as helminths and insects, can also cause or Transmission (medicine), transmit disease. However, these animals are usually referred to as parasites rather than pathogens. The scientific study of microscopic organisms, including microscopic pathogenic organisms, is called microbiology, while parasitology refers to the scientific study of parasites and the organisms that host them. There are several pathways through which pathogens can invade a host. The principal pathways have different episodic time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eomes
Eomesodermin also known as T-box brain protein 2 (Tbr2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''EOMES'' gene. The Eomesodermin/Tbr2 gene, ''EOMES'', encodes a member of a Conserved sequence, conserved protein family that shares a common DNA-binding domain, the T-box. T-box genes encode transcription factors, which control gene expression, involved in the regulation of developmental processes. Eomesodermin/Tbr2 itself controls regulation of Neural stem cell, radial glia, as well as other related cells. Eomesodermin/Tbr2 has also been found to have a role in Immune system, immune response, and there exists some loose evidence for its connections in other systems. Nervous system development Neurogenesis Eomesodermin/Tbr2 is expressed highly in the intermediate progenitor stage of the developing neuron. Neurons, the primary functional cells of the brain, are developed from Radial glial cell, radial glia cells. This process of cells developing into other types of cells ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interleukin 18
Interleukin-18 (IL-18), also known as interferon-gamma inducing factor is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''IL18'' gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a proinflammatory cytokine. Many cell types, both hematopoietic cells and non-hematopoietic cells, have the potential to produce IL-18. It was first described in 1989 as a factor that induced interferon-gamma, interferon-γ (IFN-γ) production in mouse spleen cells. Originally, IL-18 production was recognized in Kupffer cells, and liver-resident macrophages. However, IL-18 is constitutively expressed in non-hematopoietic cells, such as Intestinal epithelium, intestinal epithelial cells, keratinocytes, and endothelial cells. IL-18 can modulate both Innate immune system, innate and Adaptive immune system, adaptive immunity and its dysregulation can cause Autoimmunity, autoimmune or Inflammation, inflammatory diseases. Processing Cytokines usually contain the signal peptide which is necessary for their extracellul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |