|
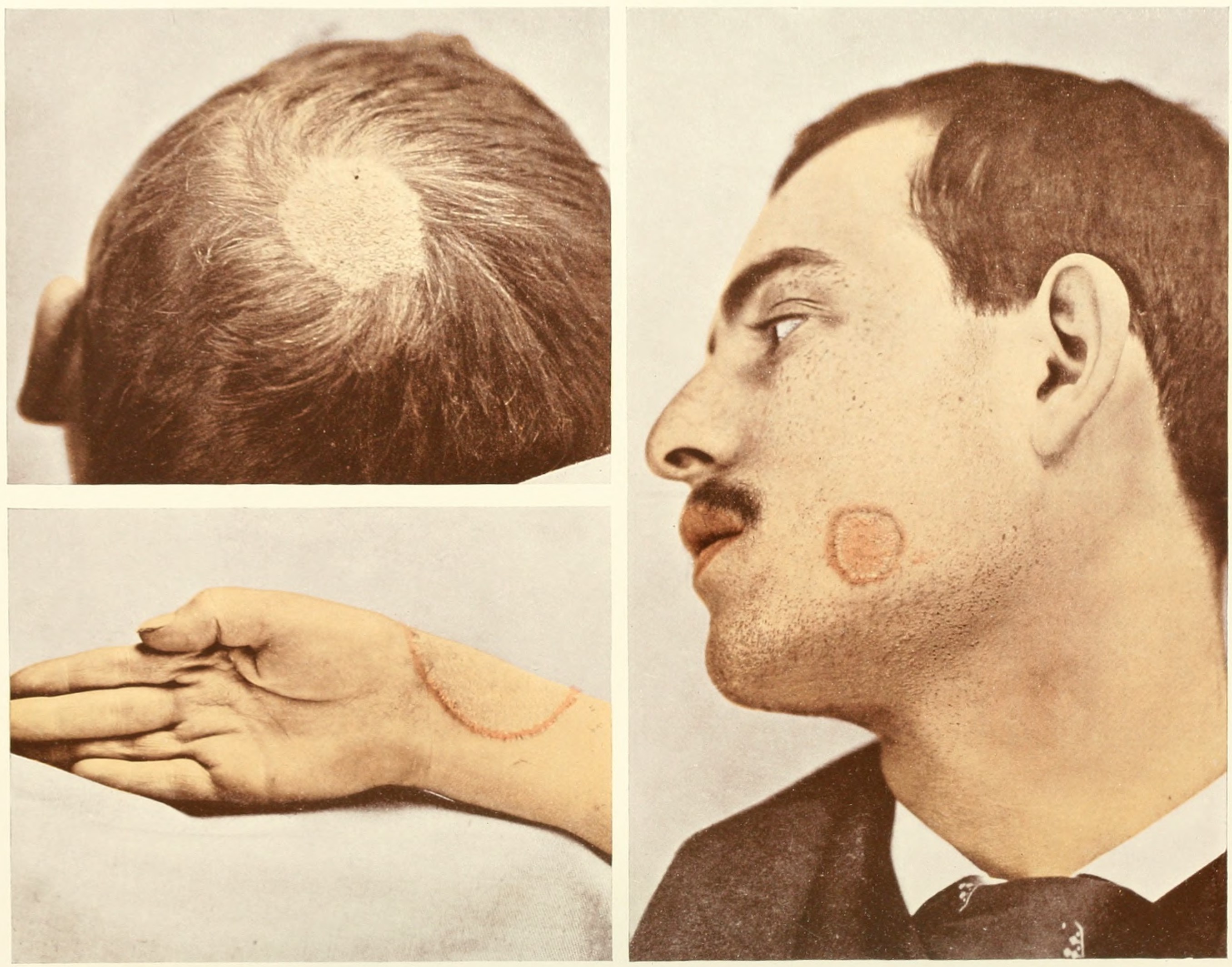
Tinea Pedis Interdigitalis
Dermatophytosis, also known as tinea and ringworm, is a fungal infection of the skin (a dermatomycosis), that may affect skin, hair, and nails. Typically it results in a red, itchy, scaly, circular rash. Hair loss may occur in the area affected. Symptoms begin four to fourteen days after exposure. The types of dermatophytosis are typically named for area of the body that they affect. Multiple areas can be affected at a given time. About 40 types of fungus can cause dermatophytosis. They are typically of the '' Trichophyton'', '' Microsporum'', or '' Epidermophyton'' type. Risk factors include using public showers, contact sports such as wrestling, excessive sweating, contact with animals, obesity, and poor immune function. Ringworm can spread from other animals or between people. Diagnosis is often based on the appearance and symptoms. It may be confirmed by either culturing or looking at a skin scraping under a microscope. Prevention is by keeping the skin dry, not wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermatology
Dermatology is the branch of medicine dealing with the Human skin, skin.''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary.'' Random House, Inc. 2001. Page 537. . It is a speciality with both medical and surgical aspects. A List of dermatologists, dermatologist is a specialist medical doctor who manages diseases related to skin. Etymology Attested in English in 1819, the word "dermatology" derives from the Ancient Greek, Greek δέρματος (''dermatos''), genitive of δέρμα (''derma''), "skin" (itself from δέρω ''dero'', "to flay") and -λογία ''wikt:-logia, -logia''. Neo-Latin ''dermatologia'' was coined in 1630, an anatomical term with various French and German uses attested from the 1730s. History In 1708, the first great school of dermatology became a reality at the famous Hôpital Saint-Louis in Paris, and the first textbooks (Willan's, 1798–1808) and atlases (Jean-Louis-Marc Alibert, Alibert's, 1806–1816) appeared in print around the same time.Freedber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsporum
''Microsporum'' is a genus of fungi that causes tinea capitis, tinea corporis, ringworm, and other dermatophytoses (fungal infections of the skin). ''Microsporum'' forms both macroconidia (large asexual reproductive structures) and microconidia (smaller asexual reproductive structures) on short conidiophores. Macroconidia are hyaline, multiseptate, variable in form, fusiform, spindle-shaped to obovate, 7–20 by 30–160 um in size, with thin or thick echinulate to verrucose cell walls. Their shape, size and cell wall features are important characteristics for species identification. Microconidia are hyaline, single-celled, pyriform to clavate, smooth-walled, 2.5–3.5 by 4–7 um in size and are not diagnostic for any one species. The separation of this genus from ''Trichophyton'' is essentially based on the roughness of the macroconidial cell wall, although in practice this may sometimes be difficult to observe. Seventeen species of ''Microsporum'' have been de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toenail
A nail is a protective plate characteristically found at the tip of the digits (fingers and toes) of all primates, corresponding to the claws in other tetrapod animals. Fingernails and toenails are made of a tough rigid protein called alpha-keratin, a polymer also found in the claws, hooves, and horns of vertebrates. Structure The nail consists of the nail plate, the nail matrix and the nail bed below it, and the grooves surrounding it. Parts of the nail The nail matrix is the active tissue (or germinal matrix) that generates cells. The cells harden as they move outward from the nail root to the nail plate. The nail matrix is also known as the ''matrix unguis'', keratogenous membrane, or onychostroma. It is the part of the nail bed that is beneath the nail and contains nerves, lymph, and blood vessels. The matrix produces cells that become the nail plate. The width and thickness of the nail plate is determined by the size, length, and thickness of the matrix, while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tinea Unguium
Dermatophytosis, also known as tinea and ringworm, is a fungal infection of the skin (a dermatomycosis), that may affect skin, hair, and nails. Typically it results in a red, itchy, scaly, circular rash. Hair loss may occur in the area affected. Symptoms begin four to fourteen days after exposure. The types of dermatophytosis are typically named for area of the body that they affect. Multiple areas can be affected at a given time. About 40 types of fungus can cause dermatophytosis. They are typically of the '' Trichophyton'', '' Microsporum'', or '' Epidermophyton'' type. Risk factors include using public showers, contact sports such as wrestling, excessive sweating, contact with animals, obesity, and poor immune function. Ringworm can spread from other animals or between people. Diagnosis is often based on the appearance and symptoms. It may be confirmed by either culturing or looking at a skin scraping under a microscope. Prevention is by keeping the skin dry, not w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athlete's Foot
Athlete's foot, known medically as ''tinea pedis'', is a common skin infection of the feet caused by a fungus. Signs and symptoms often include itching, scaling, cracking and redness. In rare cases the skin may blister. Athlete's foot fungus may infect any part of the foot, but most often grows between the toes. The next most common area is the bottom of the foot. The same fungus may also affect the nails or the hands. It is a member of the group of diseases known as '' tinea''. Athlete's foot is caused by a number of different funguses, including species of '' Trichophyton'', '' Epidermophyton'', and '' Microsporum''. The condition is typically acquired by coming into contact with infected skin, or fungus in the environment. Common places where the funguses can survive are around swimming pools and in locker rooms. They may also be spread from other animals. Usually diagnosis is made based on signs and symptoms; however, it can be confirmed either by culture or seeing hy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tinea Pedis
Dermatophytosis, also known as tinea and ringworm, is a fungal infection of the skin (a dermatomycosis), that may affect skin, hair, and nails. Typically it results in a red, itchy, scaly, circular rash. Hair loss may occur in the area affected. Symptoms begin four to fourteen days after exposure. The types of dermatophytosis are typically named for area of the body that they affect. Multiple areas can be affected at a given time. About 40 types of fungus can cause dermatophytosis. They are typically of the '' Trichophyton'', '' Microsporum'', or '' Epidermophyton'' type. Risk factors include using public showers, contact sports such as wrestling, excessive sweating, contact with animals, obesity, and poor immune function. Ringworm can spread from other animals or between people. Diagnosis is often based on the appearance and symptoms. It may be confirmed by either culturing or looking at a skin scraping under a microscope. Prevention is by keeping the skin dry, not w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermatophytes
Dermatophyte (from Greek '' derma'' "skin" ( GEN ''dermatos'') and ''phyton'' "plant") is a common label for a group of fungus of '' Arthrodermataceae'' that commonly causes skin disease in animals and humans. Traditionally, these anamorphic (asexual or imperfect fungi) mold genera are: '' Microsporum'', '' Epidermophyton'' and ''Trichophyton''. There are about 40 species in these three genera. Species capable of reproducing sexually belong in the teleomorphic genus Arthroderma, of the Ascomycota (see Teleomorph, anamorph and holomorph for more information on this type of fungal life cycle). As of 2019 a total of nine genera are identified and new phylogenetic taxonomy has been proposed. Dermatophytes cause infections of the skin, hair, and nails, obtaining nutrients from keratinized material. The organisms colonize the keratin tissues causing inflammation as the host responds to metabolic byproducts. Colonies of dermatophytes are usually restricted to the nonliving cornifie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fox Plate LXXXIX
Foxes are small-to-medium-sized omnivorous mammals belonging to several genera of the family Canidae. They have a flattened skull; upright, triangular ears; a pointed, slightly upturned snout; and a long, bushy tail ("brush"). Twelve species belong to the monophyly, monophyletic "true fox" group of genus ''Vulpes''. Another 25 current or extinction, extinct species are sometimes called foxes – they are part of the paraphyly, paraphyletic group of the South American foxes or an outlying group, which consists of the bat-eared fox, gray fox, and island fox. Foxes live on every continent except Antarctica. The most common and widespread species of fox is the red fox (''Vulpes vulpes'') with about 47 recognized subspecies. The global distribution of foxes, together with their widespread reputation for cunning, has contributed to their prominence in popular culture and folklore in many societies around the world. The Fox hunting, hunting of foxes with packs of hounds, long an est ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient History
Ancient history is a time period from the History of writing, beginning of writing and recorded human history through late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the development of Sumerian language, Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history covers all continents inhabited by humans in the period 3000 BCAD 500, ending with the Early Muslim conquests, expansion of Islam in late antiquity. The three-age system periodises ancient history into the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, and the Iron Age, with recorded history generally considered to begin with the Bronze Age. The start and end of the three ages vary between world regions. In many regions the Bronze Age is generally considered to begin a few centuries prior to 3000 BC, while the end of the Iron Age varies from the early first millennium BC in some regions to the late first millennium AD in others. During the time period of ancient history, the world population was Exponential growth, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluconazole
Fluconazole is an antifungal medication used for a number of fungal infections. These include candidiasis, blastomycosis, coccidioidomycosis, cryptococcosis, histoplasmosis, dermatophytosis, and tinea versicolor. It is also used to prevent candidiasis in those who are at high risk such as following organ transplantation, low birth weight babies, and those with low blood neutrophil counts. It is given either by mouth or by injection into a vein. Common side effects include vomiting, diarrhea, rash, and increased liver enzymes. Serious side effects may include liver problems, QT prolongation, and seizures. During pregnancy it may increase the risk of miscarriage while large doses may cause birth defects. Fluconazole is in the azole antifungal family of medication. It is believed to work by affecting the fungal cellular membrane. Fluconazole was patented in 1981 and came into commercial use in 1988. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antifungal Cream
An antifungal medication, also known as an antimycotic medication, is a pharmaceutical fungicide or fungistatic used to treat and prevent mycosis such as athlete's foot, ringworm, candidiasis (thrush), serious systemic infections such as cryptococcal meningitis, and others. Such drugs are usually obtained by a doctor's prescription, but a few are available over the counter (OTC). The evolution of antifungal resistance is a growing threat to health globally. Routes of administration Ocular Indicated when the fungal infection is located in the eye. There is currently only one ocular antifungal available: natamycin. However, various other antifungal agents could be compounded in this formulation. Intrathecal Used occasionally when there's an infection of the central nervous system and other systemic options cannot reach the concentration required in that region for therapeutic benefit. Example(s): amphotericin B. Vaginal This may be used to treat some fungal infect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |