|
Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid cancer is cancer that develops from the tissues of the thyroid gland. It is a disease in which cells grow abnormally and have the potential to spread to other parts of the body. Symptoms can include swelling or a lump in the neck, difficulty swallowing or voice changes including hoarseness, or a feeling of something being in the throat due to mass effect from the tumor. However, most cases are asymptomatic. Cancer can also occur in the thyroid after spread from other locations, in which case it is not classified as thyroid cancer. Risk factors include radiation exposure at a young age, having an enlarged thyroid, family history and obesity Obesity is a medical condition, considered by multiple organizations to be a disease, in which excess Adipose tissue, body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it can potentially have negative effects on health. People are classifi .... The four main types are papillary thyroid cancer, follicular thyroid canc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrograph
A micrograph is an image, captured photographically or digitally, taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnify, magnified image of an object. This is opposed to a macrograph or photomacrograph, an image which is also taken on a microscope but is only slightly magnified, usually less than 10 times. Micrography is the practice or art of using microscopes to make photographs. A photographic micrograph is a photomicrograph, and one taken with an electron microscope is an electron micrograph. A micrograph contains extensive details of microstructure. A wealth of information can be obtained from a simple micrograph like behavior of the material under different conditions, the phases found in the system, failure analysis, grain size estimation, elemental analysis and so on. Micrographs are widely used in all fields of microscopy. Types Photomicrograph A light micrograph or photomicrograph is a micrograph prepared using an optical microscope, a process referred to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Five Year Survival Rates
The five-year survival rate is a type of survival rate for estimating the prognosis of a particular disease, normally calculated from the point of diagnosis. Lead time bias from earlier diagnosis can affect interpretation of the five-year survival rate. There are absolute and relative survival rates, but the latter are more useful and commonly used. __TOC__ Relative and absolute rates Five-year relative survival rates are more commonly cited in cancer statistics. Five-year absolute survival rates may sometimes also be cited. * Five-year ''absolute'' survival rates describe the percentage of patients alive five years after the disease is diagnosed. * Five-year ''relative'' survival rates describe the percentage of patients with a disease alive five years after the disease is diagnosed, divided by the percentage of the general population of corresponding sex and age alive after five years. Typically, cancer five-year relative survival rates are well below 100%, reflecting excess m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surgery
Surgery is a medical specialty that uses manual and instrumental techniques to diagnose or treat pathological conditions (e.g., trauma, disease, injury, malignancy), to alter bodily functions (e.g., malabsorption created by bariatric surgery such as gastric bypass), to reconstruct or alter aesthetics and appearance (cosmetic surgery), or to remove unwanted tissue (biology), tissues (body fat, glands, scars or skin tags) or foreign bodies. The act of performing surgery may be called a surgical procedure or surgical operation, or simply "surgery" or "operation". In this context, the verb "operate" means to perform surgery. The adjective surgical means pertaining to surgery; e.g. surgical instruments, operating theater, surgical facility or surgical nurse. Most surgical procedures are performed by a pair of operators: a surgeon who is the main operator performing the surgery, and a surgical assistant who provides in-procedure manual assistance during surgery. Modern surgical opera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound with frequency, frequencies greater than 20 Hertz, kilohertz. This frequency is the approximate upper audible hearing range, limit of human hearing in healthy young adults. The physical principles of acoustic waves apply to any frequency range, including ultrasound. Ultrasonic devices operate with frequencies from 20 kHz up to several gigahertz. Ultrasound is used in many different fields. Ultrasonic devices are used to detect objects and measure distances. Ultrasound imaging or sonography is often used in medicine. In the nondestructive testing of products and structures, ultrasound is used to detect invisible flaws. Industrially, ultrasound is used for cleaning, mixing, and accelerating chemical processes. Animals such as bats and porpoises use ultrasound for locating prey and obstacles. History Acoustics, the science of sound, starts as far back as Pythagoras in the 6th century BC, who wrote on the mathematical properties of String instrument ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
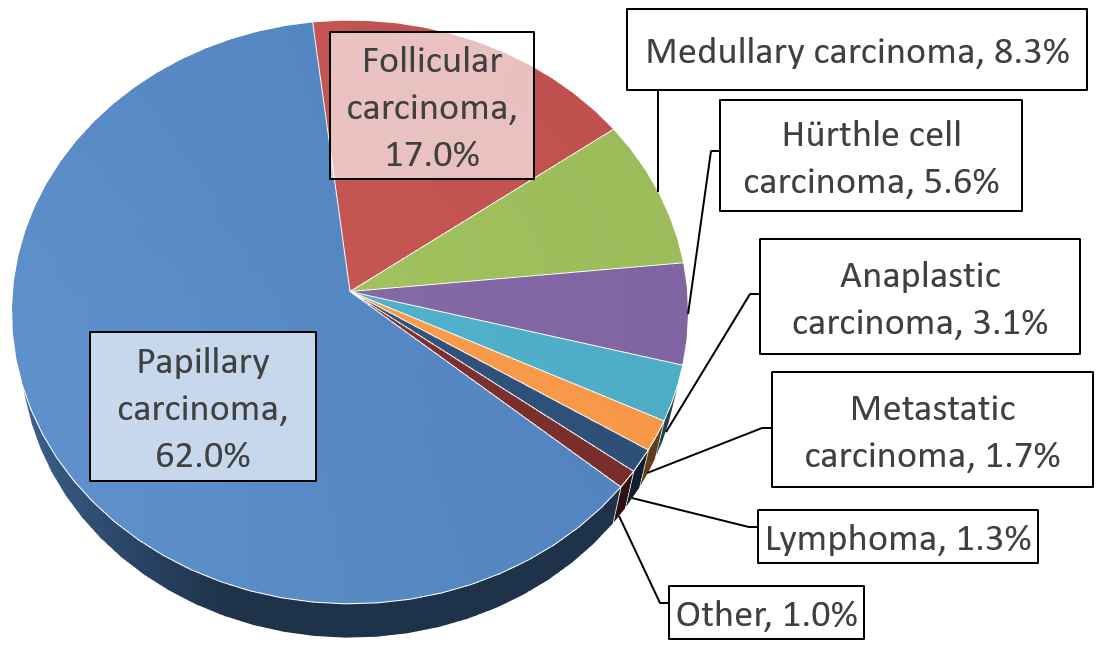
Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer
Anaplastic thyroid cancer (ATC), also known as anaplastic thyroid carcinoma, is an aggressive form of thyroid cancer characterized by uncontrolled growth of cells in the thyroid gland. This form of cancer generally carries a very poor prognosis due to its aggressive behavior and resistance to cancer treatments. The cells of anaplastic thyroid cancer are highly abnormal and usually Anaplasia, no longer resemble the original thyroid cells and have poor cellular differentiation, differentiation. ATC is an uncommon form of thyroid cancer only accounting for 1-2% of cases, but due to its high mortality, is responsible for 20-50% of deaths from thyroid cancer. The Survival rate#Median survival, median survival time after diagnosis is three to six months. Some studies report that 10% to 15% survive more than 1 year; 3-year and 5-year survival is very rare. It occurs more commonly in women than in men and is seen most commonly in people ages 40 to 70. Signs and symptoms Anaplastic thy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medullary Thyroid Cancer
Medullary thyroid cancer is a form of thyroid carcinoma which originates from the parafollicular cells (C cells), which produce the hormone calcitonin.Hu MI, Vassilopoulou-Sellin R, Lustig R, Lamont JP"Thyroid and Parathyroid Cancers"in Pazdur R, Wagman LD, Camphausen KA, Hoskins WJ (EdsCancer Management: A Multidisciplinary Approach 11 ed. 2008. Medullary tumors are the third most common of all thyroid cancers and together make up about 3% of all thyroid cancer cases. MTC was first characterized in 1959. Approximately 25% of medullary thyroid cancer cases are genetic in nature, caused by a mutation in the RET proto-oncogene. When MTC occurs by itself it is termed sporadic medullary thyroid cancer. Medullary thyroid cancer is seen in people with multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2, subtypes 2A and 2B. When medullary thyroid cancer due to a hereditary genetic disorder occurs without other endocrine tumours it is termed familial medullary thyroid cancer. Signs and symptoms The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Follicular Thyroid Cancer
Follicular thyroid cancer accounts for 15% of thyroid cancer and occurs more commonly in women over 50 years of age. Thyroglobulin (Tg) can be used as a tumor marker for well-differentiated follicular thyroid cancer. Thyroid follicular cells are the thyroid cells responsible for the production and secretion of thyroid hormones. Cause Associated mutations Approximately one-half of follicular thyroid carcinomas have mutations in the Ras subfamily of oncogenes, most notably HRAS, NRAS, and KRAS. Mutations in MINPP1 have likewise been observed, as well as germline PTEN gene mutations responsible for Cowden syndrome of which follicular thyroid cancer is a feature. Also, a chromosomal translocation specific for follicular thyroid carcinomas is one between paired box gene 8 (PAX-8), a gene important in thyroid development, and the gene encoding peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ 1 (PPARγ1), a nuclear hormone receptor contributing to terminal differentiation of cells. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Papillary thyroid cancer (papillary thyroid carcinoma, PTC) is the most common type of thyroid cancer, representing 75 percent to 85 percent of all thyroid cancer cases.Chapter 20 in: 8th edition. It occurs more frequently in women and presents in the 20–55 year age group. It is also the predominant cancer type in children with thyroid cancer, and in patients with thyroid cancer who have had previous radiation to the head and neck. It is often well- differentiated, slow-growing, and localized, although it can metastasize. Diagnosis Papillary thyroid carcinoma is usually discovered on routine examination as an asymptomatic thyroid nodule that appears as a neck mass. In some instances, the mass may have produced local symptoms. This mass is normally referred to a fine needle aspiration biopsy (FNA) for investigation. FNA accuracy is very high and it is a process widely used in these cases. Other investigation methods include ultrasound imaging and nuclear scan. The ultrasound is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiation
In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or a material medium. This includes: * ''electromagnetic radiation'' consisting of photons, such as radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, x-rays, and Gamma ray, gamma radiation (γ) * ''particle radiation'' consisting of particles of non-zero rest energy, such as alpha radiation (α), beta radiation (β), proton radiation and neutron radiation * ''acoustics, acoustic radiation'', such as ultrasound, sound, and seismic waves, all dependent on a physical transmission medium * ''gravitational radiation'', in the form of gravitational waves, ripples in spacetime Radiation is often categorized as either ''ionizing radiation, ionizing'' or ''non-ionizing radiation, non-ionizing'' depending on the energy of the radiated particles. Ionizing radiation carries more than 10 electron volt, electron volts (eV), which is enough to ionize atoms and molecul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Globus Sensation
Globus pharyngeus (also termed globus sensation) is the persistent but painless sensation of having a pill, food bolus, or some other sort of obstruction in the throat when there is none. Swallowing is typically performed normally, so it is not a true case of dysphagia, but it can become quite irritating. It is common, with 22–45% of people experiencing it at least once in their lifetime. Causes The "lump in the throat" sensation that characterizes globus pharyngis is often caused by inflammation of one or more parts of the throat, such as the larynx or hypopharynx, due to cricopharyngeal spasm, gastroesophageal reflux (GERD), or laryngopharyngeal reflux. In some cases the cause is unknown and symptoms may be attributed to a psychogenic cause ''i.e.'' a somatoform or anxiety disorder. It has been recognised as a symptom of depression, which responds to anti-depressive treatment. The results of recent studies have strongly suggested that GERD is a major cause of globus, thou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metastasize
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spreading from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, then, are metastases (mets). It is generally distinguished from cancer invasion, which is the direct extension and penetration by cancer cells into neighboring tissues. Cancer occurs after cells are genetically altered to proliferate rapidly and indefinitely. This uncontrolled proliferation by mitosis produces a primary tumor, primary tumour heterogeneity, heterogeneic tumour. The cells which constitute the tumor eventually undergo metaplasia, followed by dysplasia then anaplasia, resulting in a Malignancy, malignant phenotype. This malignancy allows for invasion into the circulation, followed by invasion to a second site for tumorigenesis. Some cancer cells, known as circulating tumor cells (CTCs), are able to penetrate the walls of lymp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all life, forms of life. Every cell consists of cytoplasm enclosed within a Cell membrane, membrane; many cells contain organelles, each with a specific function. The term comes from the Latin word meaning 'small room'. Most cells are only visible under a light microscope, microscope. Cells Abiogenesis, emerged on Earth about 4 billion years ago. All cells are capable of Self-replication, replication, protein synthesis, and cell motility, motility. Cells are broadly categorized into two types: eukaryotic cells, which possess a Cell nucleus, nucleus, and prokaryotic, prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus but have a nucleoid region. Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms such as bacteria, whereas eukaryotes can be either single-celled, such as amoebae, or multicellular organism, multicellular, such as some algae, plants, animals, and fungi. Eukaryotic cells contain organelles including Mitochondrion, mitochondria, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |