|
Third Shot
The Third Shot was the first of a series of American nuclear weapons intended for use against Japan in World War II, subsequent to Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, the nuclear attacks on Hiroshima and Nagasaki. It was intended to be used on 19 August 1945, ten days after the bombing of Nagasaki. It was never used, as the surrender of Japan on 15 August brought the war to a close first. The Third Shot was a plutonium-239-based implosion bomb of the "Fat Man" design, similar to the bomb that was dropped on Nagasaki. Chronology Lieutenant General Leslie Groves expected to have another "Fat Man" atomic bomb ready for use on 19 August, with three more in September and a further three in October; On 10 August, he sent a memorandum to Brigadier general (United States), Brigadier General James C. Marshall: "the next bomb ... should be ready for delivery on the first suitable weather after 17 or 18 August." The memo today contains hand-written comment written by Marsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fat Man (replica Of Nuclear Bomb)
"Fat Man" (also known as Mark III) was the Code name, codename for the type of nuclear weapon the United States Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki#Bombing of Nagasaki, detonated over the Japanese city of Nagasaki on 9 August 1945. It was the second of the only two nuclear weapons ever used in warfare, the first being Little Boy, and its detonation marked the third nuclear explosion in history. The first one was built by scientists and engineers at Los Alamos Laboratory using plutonium manufactured at the Hanford Site and was dropped from the Boeing B-29 Superfortress ''Bockscar'' piloted by Major Charles Sweeney. The name Fat Man refers to the early design of the bomb because it had a wide, round shape. Fat Man was an implosion-type nuclear weapon with a solid plutonium Nuclear reactor core, core. The first of that type to be detonated was the Gadget in the Trinity (nuclear test), Trinity nuclear test less than a month earlier on 16 July at the Holloman Air Force Base, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harry S
Harry may refer to: TV shows * ''Harry'' (American TV series), a 1987 American comedy series starring Alan Arkin * ''Harry'' (British TV series), a 1993 BBC drama that ran for two seasons * ''Harry'' (talk show), a 2016 American daytime talk show hosted by Harry Connick Jr. People and fictional characters *Harry (given name), a list of people and fictional characters with the given name *Harry (surname), a list of people with the surname *Dirty Harry (musician) (born 1982), British rock singer who has also used the stage name Harry *Harry Potter (character), the main protagonist in a Harry Potter fictional series by J. K. Rowling Other uses *Harry (derogatory term), derogatory term used in Norway * ''Harry'' (album), a 1969 album by Harry Nilsson *The tunnel used in the Stalag Luft III escape , partof = ''Luftwaffe'' , location = Sagan, Lower Silesia, Nazi Germany (now Żagań, Poland) , image = , caption = Model of the set used to film the movie ''The Great Escape.'' I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The New Yorker
''The New Yorker'' is an American weekly magazine featuring journalism, commentary, criticism, essays, fiction, satire, cartoons, and poetry. Founded as a weekly in 1925, the magazine is published 47 times annually, with five of these issues covering two-week spans. Although its reviews and events listings often focus on the cultural life of New York City, ''The New Yorker'' has a wide audience outside New York and is read internationally. It is well known for its illustrated and often topical covers, its commentaries on popular culture and eccentric American culture, its attention to modern fiction by the inclusion of short stories and literary reviews, its rigorous fact checking and copy editing, its journalism on politics and social issues, and its single-panel cartoons sprinkled throughout each issue. Overview and history ''The New Yorker'' was founded by Harold Ross and his wife Jane Grant, a ''New York Times'' reporter, and debuted on February 21, 1925. Ros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Criticality Accident
A criticality accident is an accidental uncontrolled nuclear fission chain reaction. It is sometimes referred to as a critical excursion, critical power excursion, or divergent chain reaction. Any such event involves the unintended accumulation or arrangement of a critical mass of fissile material, for example enriched uranium or plutonium. Criticality accidents can release potentially fatal radiation doses, if they occur in an unprotected environment. Under normal circumstances, a critical or supercritical fission reaction (one that is self-sustaining in power or increasing in power) should only occur inside a safely shielded location, such as a reactor core or a suitable test environment. A criticality accident occurs if the same reaction is achieved unintentionally, for example in an unsafe environment or during reactor maintenance. Though dangerous and frequently lethal to humans within the immediate area, the critical mass formed would not be capable of producing a massi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demon Core
The demon core was a spherical subcritical mass of plutonium in diameter, manufactured during World War II by the United States nuclear weapon development effort, the Manhattan Project, as a fissile core for an early atomic bomb. The core was prepared for shipment as part of the third nuclear weapon to be used in Japan, but when Japan surrendered, the core was retained at Los Alamos for testing and potential later use. It was involved in two criticality accidents at the Los Alamos Laboratory on August 21, 1945, and May 21, 1946, each resulting in a fatality. Both experiments were designed to demonstrate how close the core was to criticality with a tamper, but in each case, the core was accidentally placed into a supercritical configuration. Physicists Harry Daghlian and Louis Slotin suffered acute radiation syndrome (ARS) and died soon after, while others present in the lab were also exposed. Manufacturing and early history The demon core (like the second core used i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plutonium Core
The pit, named after the hard core found in fruits such as peaches and apricots, is the core of an implosion nuclear weapon – the fissile material and any neutron reflector or tamper bonded to it. Some weapons tested during the 1950s used pits made with U-235 alone, or in composite with plutonium, but all-plutonium pits are the smallest in diameter and have been the standard since the early 1960s. Pit designs Christy pits The pits of the first nuclear weapons were solid, with an ''urchin'' neutron initiator in their center. The Gadget and Fat Man used pits made of 6.2 kg of solid hot pressed plutonium-gallium alloy (at 400 °C and 200 MPa in steel dies – and ) half-spheres of diameter, with a internal cavity for the initiator. The Gadget's pit was electroplated with 0.13 mm of silver; the layer, however, developed blistering and the blisters had to be ground and plated with gold leaf before the test. The Fat Man pit, and those of subsequent models, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Project Y
The Los Alamos Laboratory, also known as Project Y, was a secret laboratory established by the Manhattan Project and operated by the University of California during World War II. Its mission was to design and build the first atomic bombs. Robert Oppenheimer was its first director, serving from 1943 to December 1945, when he was succeeded by Norris Bradbury. In order to enable scientists to freely discuss their work while preserving security, the laboratory was located in a remote part of New Mexico. The wartime laboratory occupied buildings that had once been part of the Los Alamos Ranch School. The development effort initially concentrated on a gun-type fission weapon using plutonium called Thin Man. In April 1944, the Los Alamos Laboratory determined that the rate of spontaneous fission in plutonium bred in a nuclear reactor was too great due to the presence of plutonium-240 and would cause a predetonation, a nuclear chain reaction before the core was fully assembled. Op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curtis LeMay
Curtis Emerson LeMay (November 15, 1906 – October 1, 1990) was an American Air Force general who implemented a controversial strategic bombing campaign in the Pacific theater of World War II. He later served as Chief of Staff of the U.S. Air Force, from 1961 to 1965. LeMay joined the U.S. Army Air Corps, the precursor to the U.S. Air Force, in 1929 while studying civil engineering at Ohio State University. He had risen to the rank of major by the time of Japan's Attack on Pearl Harbor in December 1941 and the United States's subsequent entry into World War II. He commanded the 305th Operations Group from October 1942 until September 1943, and the 3rd Air Division in the European theatre of World War II until August 1944, when he was transferred to the China Burma India Theater. He was then placed in command of strategic bombing operations against Japan, planning and executing a massive fire bombing campaign against Japanese cities and Operation Starvation, a crippling minel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Tibbets
Paul Warfield Tibbets Jr. (23 February 1915 – 1 November 2007) was a brigadier general in the United States Air Force. He is best known as the aircraft captain who flew the B-29 Superfortress known as the ''Enola Gay'' (named after his mother) when it dropped a Little Boy, the first of two atomic bombs used in warfare, on the Japanese city of Hiroshima. Tibbets enlisted in the United States Army in 1937 and qualified as a pilot in 1938. After the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor, he flew anti-submarine patrols over the Atlantic. In February 1942, he became the commanding officer of the 340th Bombardment Squadron of the 97th Bombardment Group, which was equipped with the Boeing B-17. In July 1942, the 97th became the first heavy bombardment group to be deployed as part of the Eighth Air Force, and Tibbets became deputy group commander. He flew the lead plane in the first American daylight heavy bomber mission against Occupied Europe on 17 August 1942, and the first America ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tinian Naval Base
Tinian Naval Base and Naval Air Facility Tinian (NAF Tinian) was a major United States Navy sea and airbase base on Tinian Island, part of the Northern Mariana Islands on the east side of the Philippine Sea in the Pacific Ocean. The Base was built during World War II to support the many bombers and aircraft fighting and patrolling in the South West Pacific theatre of war as part of the Pacific War. A number of naval facilities were built on the entire island of 101.22 km (39 sq miles). The main port was built at the city and port of San Jose, also called Tinian Harbor. All construction was done by the Navy's Seabees Sixth Construction Brigade with minor help from the 64th Army Engineers, including the main two airports: West Field and North Field. United States Army Air Forces operated long-range bombers out of the air base built and maintained by the Seabees. History Tinian was taken after the Battle of Tinian, against Empire of Japan, which began on July 24 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kirtland Air Force Base
Kirtland Air Force Base is a United States Air Force base located in the southeast quadrant of the Albuquerque, New Mexico, Albuquerque, New Mexico urban area, adjacent to the Albuquerque International Sunport. The base was named for the early Army aviator Col. Roy C. Kirtland. The military and the international airport share the same runways, making ABQ a joint civil-military airport. Kirtland AFB is the largest installation in Air Force Global Strike Command and sixth largest in the United States Air Force. The base occupies 51,558 acres and employs over 23,000 people, including more than 4,200 active duty and 1,000 Guard, plus 3,200 part-time Reserve personnel. In 2000, Kirtland AFB's economic impact on the City of Albuquerque was over $2.7 billion. Kirtland is the home of the Air Force Materiel Command's Nuclear Weapons Center (NWC). The NWC's responsibilities include acquisition, modernization and sustainment of nuclear system programs for both the United States Depart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
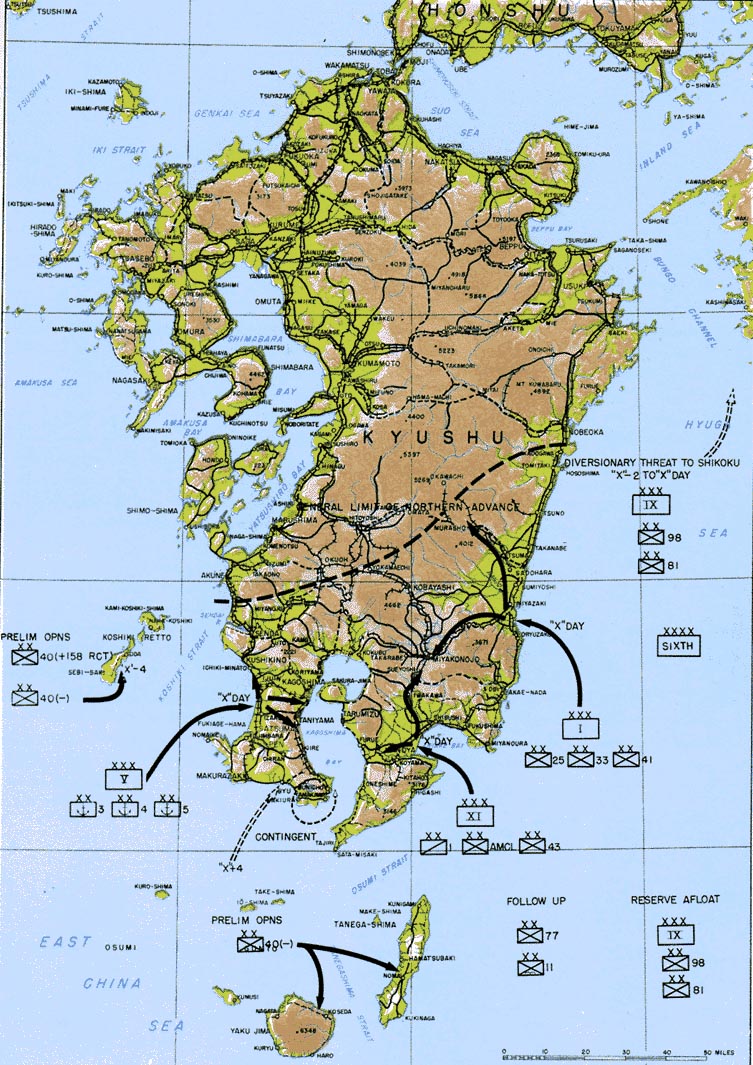
Operation Downfall
Operation Downfall was the proposed Allied plan for the invasion of the Japanese home islands near the end of World War II. The planned operation was canceled when Japan surrendered following the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, the Soviet declaration of war, and the invasion of Manchuria. The operation had two parts: Operation Olympic and Operation Coronet. Set to begin in November 1945, Operation Olympic was intended to capture the southern third of the southernmost main Japanese island, Kyūshū, with the recently captured island of Okinawa to be used as a staging area. In early 1946 would come Operation Coronet, the planned invasion of the Kantō Plain, near Tokyo, on the main Japanese island of Honshu. Airbases on Kyūshū captured in Operation Olympic would allow land-based air support for Operation Coronet. If Downfall had taken place, it would have been the largest amphibious operation in history, surpassing D-Day. Japan's geography made this invasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |