|
The Chemical Basis Of Morphogenesis
"The Chemical Basis of Morphogenesis" is an article that the English mathematician Alan Turing wrote in 1952. It describes how patterns in nature, such as stripes and spirals, can arise naturally from a homogeneous, uniform state. The theory, which can be called a reaction–diffusion theory of morphogenesis, has become a basic model in theoretical biology. Such patterns have come to be known as Turing patterns. For example, it has been postulated that the protein VEGFC can form Turing patterns to govern the formation of lymphatic vessels in the zebrafish embryo. Reaction–diffusion systems Reaction–diffusion systems have attracted much interest as a prototype model for pattern formation. Patterns such as fronts, spirals, targets, hexagons, stripes and dissipative solitons are found in various types of reaction-diffusion systems in spite of large discrepancies e.g. in the local reaction terms. Such patterns have been dubbed " Turing patterns". Reaction–diffusion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Giant Pufferfish Skin Pattern Detail
In folklore, giants (from Ancient Greek: ''gigas'', cognate giga-) are beings of humanoid appearance, but are at times prodigious in size and strength or bear an otherwise notable appearance. The word ''giant'' is first attested in 1297 from Robert of Gloucester's chronicle. It is derived from the ''Gigantes'' () of Greek mythology. Fairy tales such as ''Jack the Giant Killer'' have formed the modern perception of giants as dimwitted and violent ogres, sometimes said to eat humans, while other giants tend to eat livestock. In more recent portrayals, like those of Jonathan Swift and Roald Dahl, some giants are both intelligent and friendly. Literary and cultural analysis Giants appear many times in folklore and myths. Representing the human body enlarged to the point of being monstrous, giants evoke terror and remind humans of their body's frailty and mortality. They are often portrayed as monsters and antagonists, but there are exceptions. Some giants intermingle with human ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
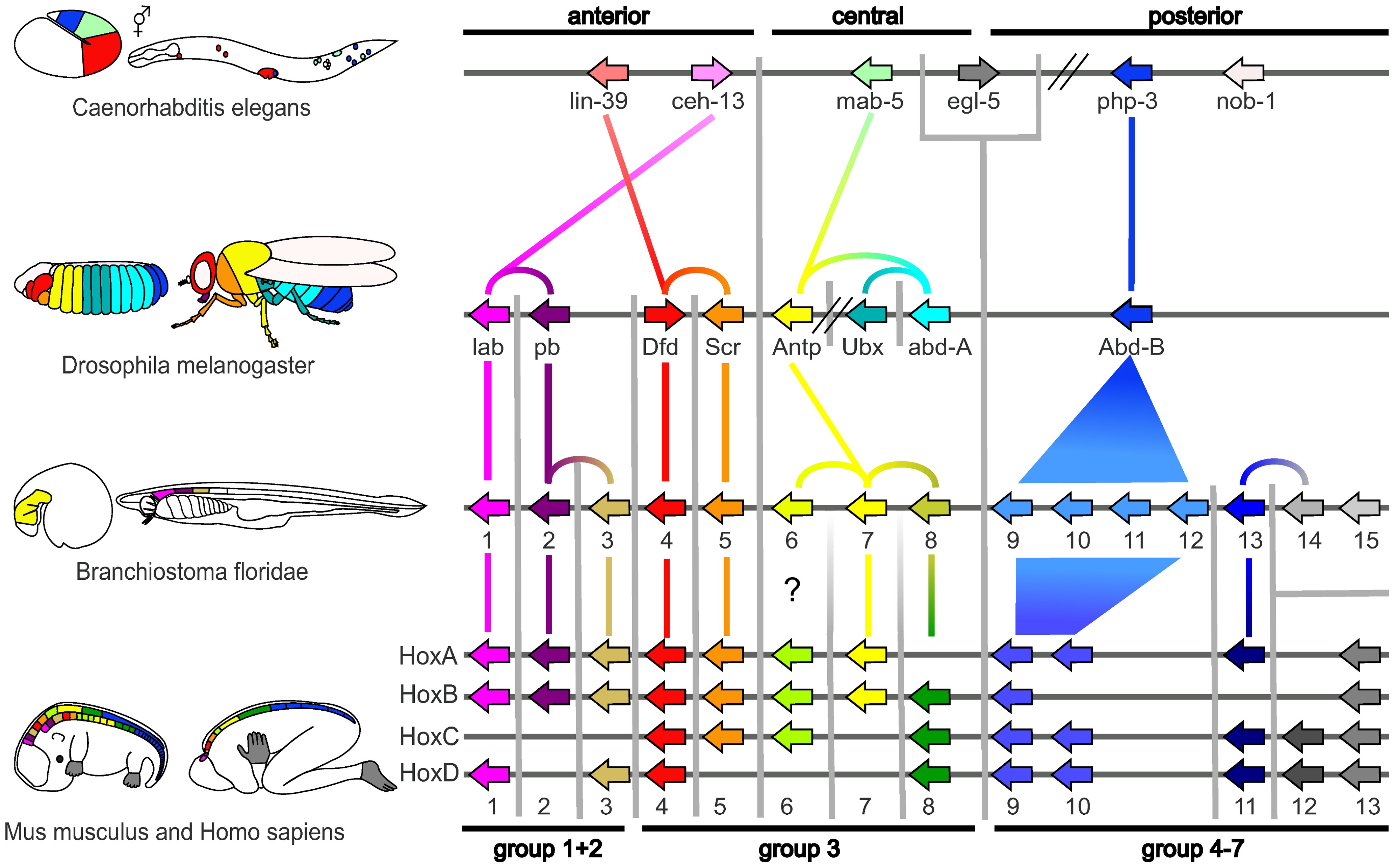
Evolutionary Developmental Biology
Evolutionary developmental biology, informally known as evo-devo, is a field of biological research that compares the developmental biology, developmental processes of different organisms to infer how developmental processes evolution, evolved. The field grew from 19th-century beginnings, where embryology faced a mystery: zoology, zoologists did not know how embryogenesis, embryonic development was controlled at the molecular level. Charles Darwin noted that having similar embryos implied common ancestry, but little progress was made until the 1970s. Then, recombinant DNA technology at last brought embryology together with molecular genetics. A key early discovery was that of homeotic genes that regulate development in a wide range of eukaryotes. The field is composed of multiple core evolutionary concepts. One is deep homology, the finding that dissimilar organs such as the eyes of insects, vertebrates and cephalopod molluscs, long thought to have evolved separately, are contr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Works By English People
Works may refer to: People * Caddy Works (1896–1982), American college sports coach * John D. Works (1847–1928), California senator and judge * Samuel Works (c. 1781–1868), New York politician Albums * ''Works'' (Pink Floyd album), a Pink Floyd album from 1983 * ''Works'', a Gary Burton album from 1972 * ''Works'', a Status Quo album from 1983 * ''Works'', a John Abercrombie album from 1991 * ''Works'', a Pat Metheny album from 1994 * ''Works'', an Alan Parson Project album from 2002 * ''Works Volume 1'', a 1977 Emerson, Lake & Palmer album * ''Works Volume 2'', a 1977 Emerson, Lake & Palmer album * '' The Works'', a 1984 Queen album Other uses *Good works, a topic in Christian theology * Microsoft Works, a collection of office productivity programs created by Microsoft * IBM Works, an office suite for the IBM OS/2 operating system * Mount Works, Victoria Land, Antarctica See also * The Works (other) * Work (other) Work may refer to: * Work (h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Chaos Theory
Chaos theory is an interdisciplinary area of Scientific method, scientific study and branch of mathematics. It focuses on underlying patterns and Deterministic system, deterministic Scientific law, laws of dynamical systems that are highly sensitive to initial conditions. These were once thought to have completely random states of disorder and irregularities. Chaos theory states that within the apparent randomness of chaotic complex systems, there are underlying patterns, interconnection, constant feedback loops, repetition, self-similarity, fractals and self-organization. The butterfly effect, an underlying principle of chaos, describes how a small change in one state of a deterministic nonlinear system can result in large differences in a later state (meaning there is sensitive dependence on initial conditions). A metaphor for this behavior is that a butterfly flapping its wings in Brazil can cause or prevent a tornado in Texas. Text was copied from this source, which is avai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Biological Processes
Biological processes are those processes that are necessary for an organism to live and that shape its capacities for interacting with its environment. Biological processes are made of many chemical reactions or other events that are involved in the persistence and transformation of life forms. Regulation of biological processes occurs when any process is modulated in its frequency, rate or extent. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule. * Homeostasis: regulation of the internal environment to maintain a constant state; for example, sweating to reduce temperature * Organization: being structurally composed of one or more cells – the basic units of life * Metabolism: transformation of energy by converting chemicals and energy into cellular components (anabolism) and decomposing organic matter ( catabolism). Living things require energy to mai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Parabolic Partial Differential Equations
Parabolic usually refers to something in a shape of a parabola, but may also refer to a parable. Parabolic may refer to: *In mathematics: **In elementary mathematics, especially elementary geometry: **Parabolic coordinates **Parabolic cylindrical coordinates ** parabolic Möbius transformation ** Parabolic geometry (other) ** Parabolic spiral ** Parabolic line **In advanced mathematics: *** Parabolic cylinder function ***Parabolic induction ***Parabolic Lie algebra ***Parabolic partial differential equation *In physics: **Parabolic trajectory *In technology: **Parabolic antenna **Parabolic microphone **Parabolic reflector **Parabolic trough - a type of solar thermal energy collector **Parabolic flight - a way of achieving weightlessness ** Parabolic action, or parabolic bending curve - a term often used to refer to a progressive bending curve in fishing rods. *In commodities and stock markets: ** Parabolic SAR - a chart pattern in which prices rise or fall with an increasin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mathematical Modeling
A mathematical model is an abstract and concrete, abstract description of a concrete system using mathematics, mathematical concepts and language of mathematics, language. The process of developing a mathematical model is termed ''mathematical modeling''. Mathematical models are used in applied mathematics and in the natural sciences (such as physics, biology, earth science, chemistry) and engineering disciplines (such as computer science, electrical engineering), as well as in non-physical systems such as the social sciences (such as economics, psychology, sociology, political science). It can also be taught as a subject in its own right. The use of mathematical models to solve problems in business or military operations is a large part of the field of operations research. Mathematical models are also used in music, linguistics, and philosophy (for example, intensively in analytic philosophy). A model may help to explain a system and to study the effects of different components, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
1952 Documents
Year 195 ( CXCV) was a common year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known in Rome as the Year of the Consulship of Scrapula and Clemens (or, less frequently, year 948 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 195 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Emperor Septimius Severus has the Roman Senate deify the previous emperor Commodus, in an attempt to gain favor with the family of Marcus Aurelius. * King Vologases V and other eastern princes support the claims of Pescennius Niger. The Roman province of Mesopotamia rises in revolt with Parthian support. Severus marches to Mesopotamia to battle the Parthians. * The Roman province of Syria is divided and the role of Antioch is diminished. The Romans annex the Syrian cities of Edessa and Nisibis. Severus re-establishes his headquarters and the colonies the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Symmetry Breaking
In physics, symmetry breaking is a phenomenon where a disordered but Symmetry in quantum mechanics, symmetric state collapses into an ordered, but less symmetric state. This collapse is often one of many possible Bifurcation theory, bifurcations that a particle can take as it approaches a lower energy state. Due to the many possibilities, an observer may assume the result of the collapse to be arbitrary. This phenomenon is fundamental to quantum field theory (QFT), and further, contemporary understandings of physics. Specifically, it plays a central role in the Glashow–Weinberg–Salam model which forms part of the Standard model modelling the electroweak sector.In an infinite system (Minkowski space, Minkowski spacetime) symmetry breaking occurs, however in a finite system (that is, any real super-condensed system), the system is less predictable, but in many cases Quantum tunnelling, quantum tunneling occurs. Symmetry breaking and tunneling relate through the collapse of a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Evolutionary Developmental Biology
Evolutionary developmental biology, informally known as evo-devo, is a field of biological research that compares the developmental biology, developmental processes of different organisms to infer how developmental processes evolution, evolved. The field grew from 19th-century beginnings, where embryology faced a mystery: zoology, zoologists did not know how embryogenesis, embryonic development was controlled at the molecular level. Charles Darwin noted that having similar embryos implied common ancestry, but little progress was made until the 1970s. Then, recombinant DNA technology at last brought embryology together with molecular genetics. A key early discovery was that of homeotic genes that regulate development in a wide range of eukaryotes. The field is composed of multiple core evolutionary concepts. One is deep homology, the finding that dissimilar organs such as the eyes of insects, vertebrates and cephalopod molluscs, long thought to have evolved separately, are contr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kluwer Academic Publishers
Springer Science+Business Media, commonly known as Springer, is a German multinational publishing company of books, e-books and peer-reviewed journals in science, humanities, technical and medical (STM) publishing. Originally founded in 1842 in Berlin, it expanded internationally in the 1960s, and through mergers in the 1990s and a sale to venture capitalists it fused with Wolters Kluwer and eventually became part of Springer Nature in 2015. Springer has major offices in Berlin, Heidelberg, Dordrecht, and New York City. History Julius Springer founded Springer-Verlag in Berlin in 1842 and his son Ferdinand Springer grew it from a small firm of 4 employees into Germany's then second-largest academic publisher with 65 staff in 1872.Chronology ". Springer Science+Business Media. In 1964, Springer expanded its business internationally, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |