|
Terahertz Nondestructive Evaluation
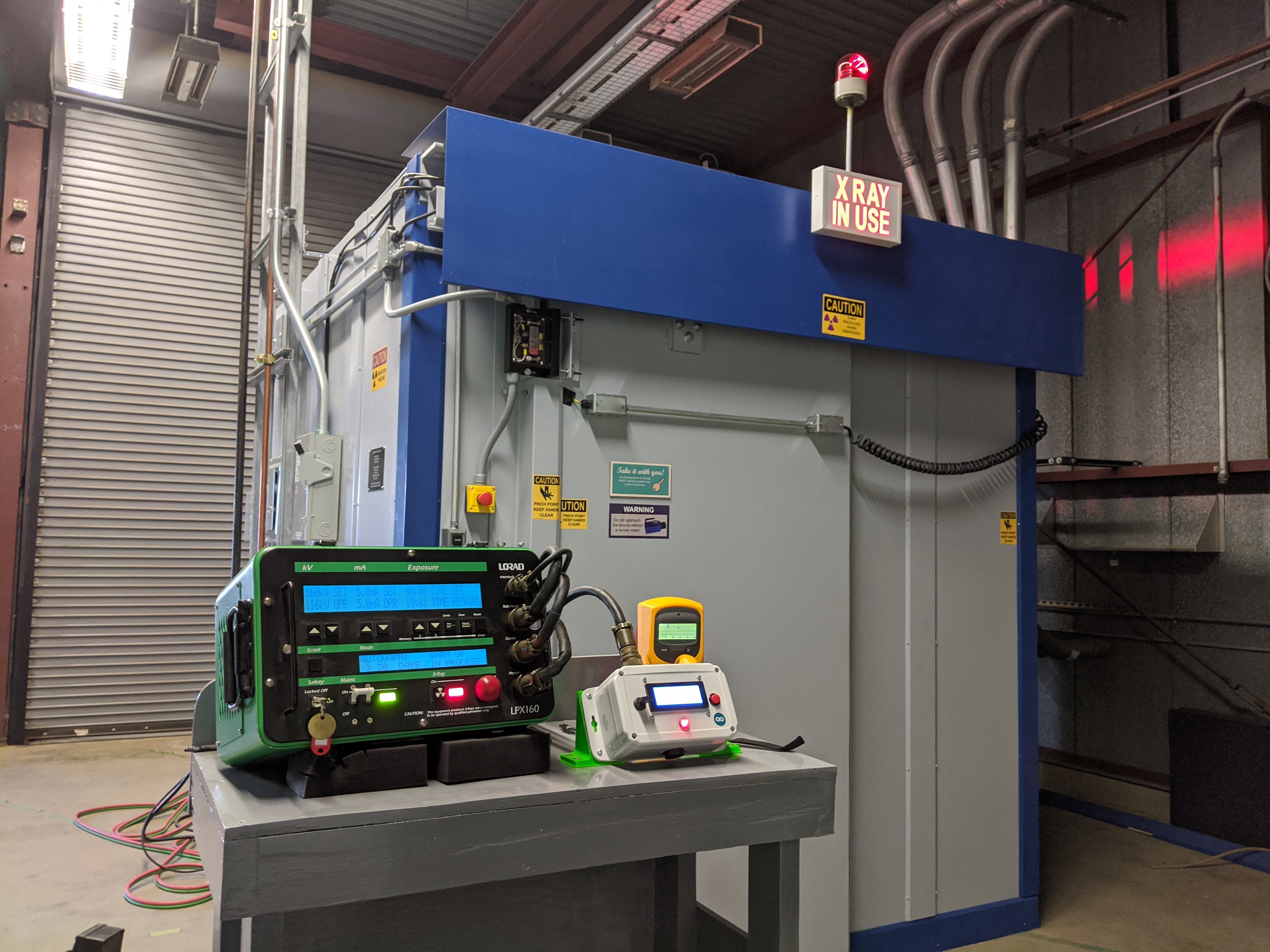
Terahertz nondestructive evaluation pertains to devices, and techniques of analysis occurring in the terahertz domain of electromagnetic radiation. These devices and techniques evaluate the properties of a material, component or system without causing damage. Terahertz imaging Terahertz imaging is an emerging and significant nondestructive evaluation (NDE) technique used for dielectric (nonconducting, i.e., an insulator) materials analysis and quality control in the pharmaceutical, biomedical, security, materials characterization, and aerospace industries. It has proved to be effective in the inspection of layers in paints and coatings, detecting structural defects in ceramic and composite materials and imaging the physical structure of paintings and manuscripts. The use of THz waves for non-destructive evaluation enables inspection of multi-layered structures and can identify abnormalities from foreign material inclusions, disbond and delamination, mechanical impac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nondestructive Testing
Nondestructive testing (NDT) is any of a wide group of analysis techniques used in science and technology industry to evaluate the properties of a material, component or system without causing damage. The terms nondestructive examination (NDE), nondestructive inspection (NDI), and nondestructive evaluation (NDE) are also commonly used to describe this technology. Because NDT does not permanently alter the article being inspected, it is a highly valuable technique that can save both money and time in product evaluation, troubleshooting, and research. The six most frequently used NDT methods are eddy-current testing, eddy-current, magnetic-particle inspection, magnetic-particle, liquid penetrant testing, liquid penetrant, radiographic testing, radiographic, ultrasonic testing, ultrasonic, and Visual inspection, visual testing. NDT is commonly used in forensic engineering, mechanical engineering, petroleum engineering, electrical engineering, civil engineering, systems engineering, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromagnetic Wave
In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) is a self-propagating wave of the electromagnetic field that carries momentum and radiant energy through space. It encompasses a broad spectrum, classified by frequency or its inverse, wavelength, ranging from radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays. All forms of EMR travel at the speed of light in a vacuum and exhibit wave–particle duality, behaving both as waves and as discrete particles called photons. Electromagnetic radiation is produced by accelerating charged particles such as from the Sun and other celestial bodies or artificially generated for various applications. Its interaction with matter depends on wavelength, influencing its uses in communication, medicine, industry, and scientific research. Radio waves enable broadcasting and wireless communication, infrared is used in thermal imaging, visible light is essential for vision, and higher-energy radiation, such as X ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
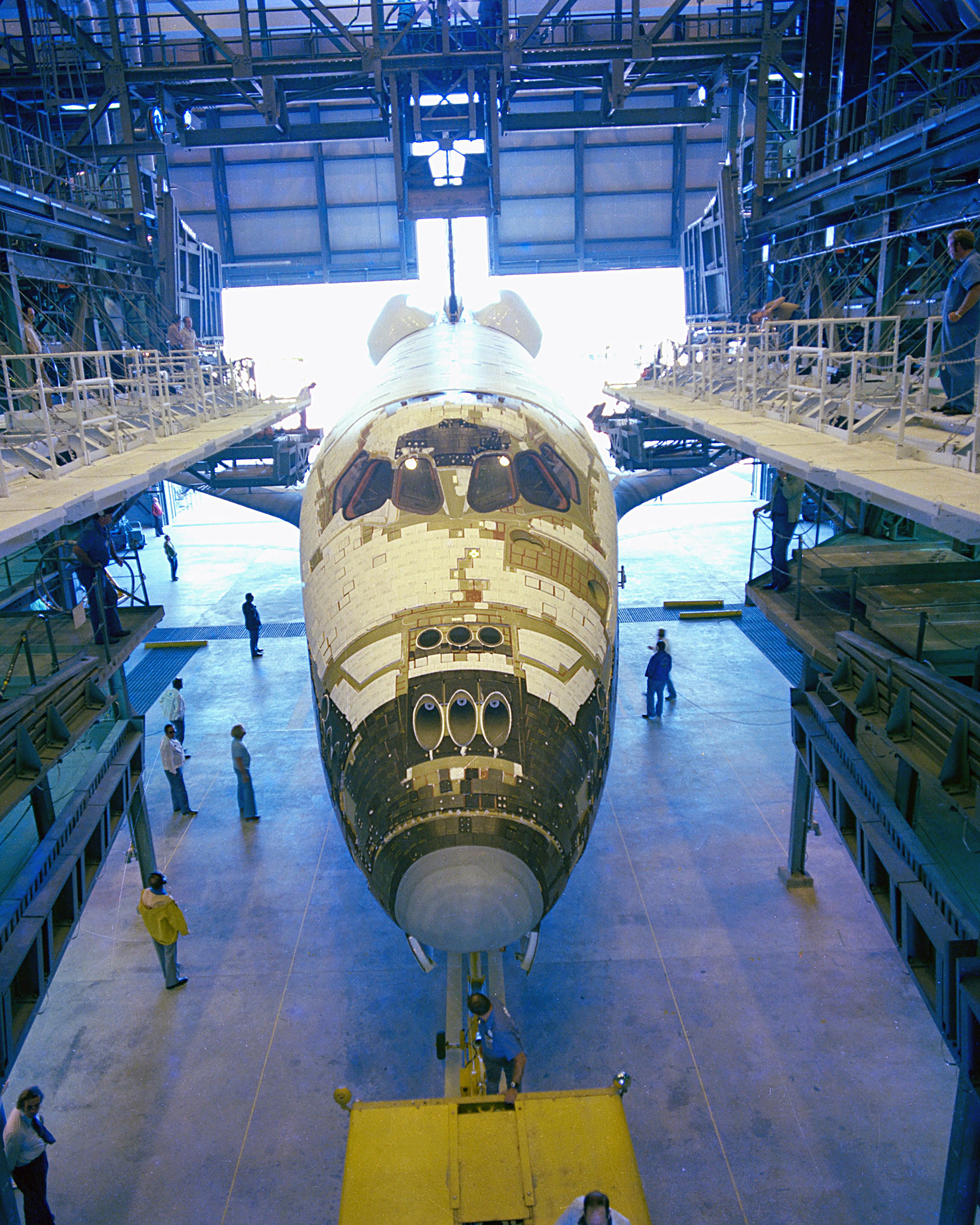
Space Shuttle Discovery
Space Shuttle ''Discovery'' (Orbiter Vehicle Designation: OV-103) is a retired American Space Shuttle orbiter. The spaceplane was one of the Space Shuttle orbiter, orbiters from NASA's Space Shuttle program and the third of five fully operational orbiters to be built. Its first mission, STS-41-D, flew from August 30 to September 5, 1984. Over 27 years of service it launched and landed 39 times, aggregating more spaceflights than any other spacecraft . The Space Shuttle launch vehicle had three main components: the Space Shuttle orbiter, a single-use central fuel tank, and two reusable solid rocket boosters. Nearly 25,000 Space Shuttle thermal protection system, heat-resistant tiles cover the orbiter to protect it from high temperatures on re-entry. ''Discovery'' became the third operational orbiter to enter service, preceded by ''Space Shuttle Columbia, Columbia'' and ''Space Shuttle Challenger, Challenger''. After the Challenger and Columbia accidents, Discovery became the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-114
STS-114 was the first "Return to Flight" Space Shuttle mission following the Space Shuttle ''Columbia'' disaster. ''Discovery'' launched at 10:39 EDT (14:39 UTC) on her 31st flight on July 26, 2005. The launch, 907 days (approx. 29 months) after the loss of ''Columbia'', was approved despite unresolved fuel sensor anomalies in the external tank that had prevented the shuttle from launching on July 13, its originally scheduled date. The mission ended on August 9, 2005, when ''Discovery'' landed at Edwards Air Force Base in California. Poor weather over the Kennedy Space Center in Florida hampered the shuttle from using its primary landing site. Analysis of the launch footage showed debris separating from the external tank during ascent; this was of particular concern because it was the issue that had set off the ''Columbia'' disaster. As a result, NASA decided on July 27 to postpone future shuttle flights pending additional modifications to the flight hardware. Shuttle fligh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Columbia Accident Investigation Board
The ''Columbia'' Accident Investigation Board (CAIB) was an internal commission convened by NASA to investigate the Space Shuttle Columbia disaster, destruction of the Space Shuttle Columbia, Space Shuttle ''Columbia'' during STS-107 upon atmospheric re-entry on February 1, 2003. The panel determined that the accident was caused by foam insulation breaking off from the external fuel tank, forming debris which damaged the orbiter's wing, and that the problem of "debris shedding" was well known but considered "acceptable" by management. The panel also recommended changes that should be made to increase the safety of future shuttle flights. The CAIB released its final report on August 26, 2003. Major findings The board found both the immediate physical cause of the accident and also what it called organizational causes. Immediate cause of the accident 82 seconds after launch a large piece of foam insulating material, the "left bipod foam ramp", broke free from the external tank ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shuttle Columbia
Space Shuttle ''Columbia'' (OV-102) was a Space Shuttle orbiter manufactured by Rockwell International and operated by NASA. Named after the first American ship to circumnavigate the globe, and the female personification of the United States, ''Columbia'' was the first of five Space Shuttle orbiters to fly in space, debuting the Space Shuttle launch vehicle on its maiden flight on April 12, 1981 and becoming the first spacecraft to be re-used after its first flight when it launched on STS-2 on November 12, 1981. As only the second full-scale orbiter to be manufactured after the Approach and Landing Test vehicle ''Enterprise'', ''Columbia'' retained unique external and internal features compared to later orbiters, such as test instrumentation and distinctive black chines. In addition to a heavier aft fuselage and the retention of an internal airlock throughout its lifetime, these made ''Columbia'' the heaviest of the five spacefaring orbiters: around heavier than '' Challe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
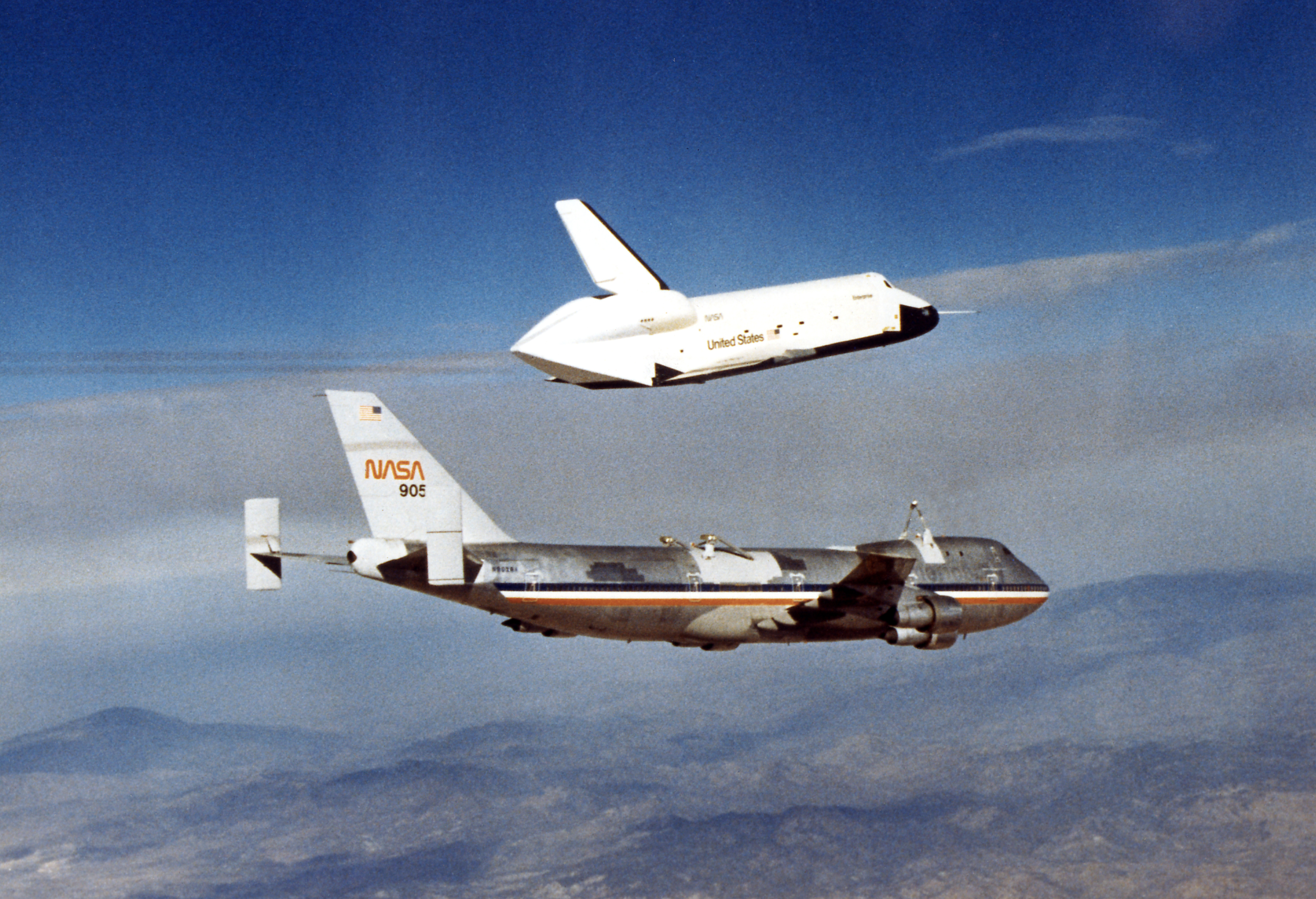
Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable launch system, reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. Its official program name was the Space Transportation System (STS), taken from the 1969 plan led by U.S. vice president Spiro Agnew for a system of reusable spacecraft where it was the only item funded for development. The first (STS-1) of four orbital test flights occurred in 1981, leading to operational flights (STS-5) beginning in 1982. Five complete Space Shuttle orbiter vehicles were built and flown on a total of 135 missions from 1981 to 2011. They launched from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida. Operational missions launched numerous satellites, interplanetary probes, and the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), conducted science experiments in orbit, participated in the Shuttle–Mir program, Shuttle-''Mir'' program with Russia, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States's civil list of government space agencies, space program, aeronautics research and outer space, space research. National Aeronautics and Space Act, Established in 1958, it succeeded the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) to give the American space development effort a distinct civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. It has since led most of America's space exploration programs, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968–1972 Apollo program missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. Currently, NASA supports the International Space Station (ISS) along with the Commercial Crew Program and oversees the development of the Orion (spacecraft), Orion spacecraft and the Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
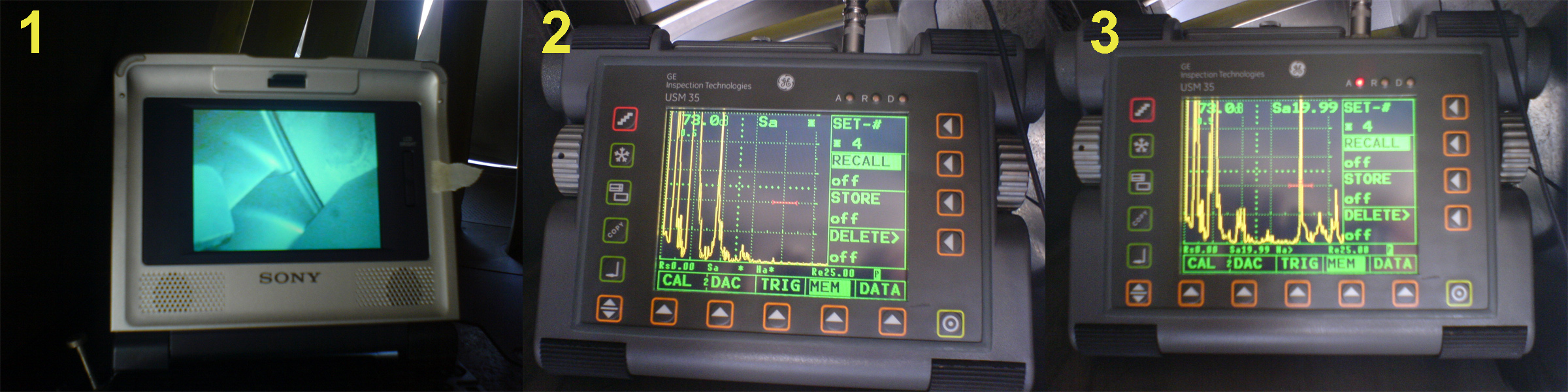
Ultrasonic Testing
Ultrasonic testing (UT) is a family of non-destructive testing techniques based on the propagation of ultrasonic waves in the object or material tested. In most common UT applications, very short ultrasonic pulse waves with centre frequencies ranging from 0.1-15MHz and occasionally up to 50MHz, are transmitted into materials to detect internal flaws or to characterize materials. A common example is ultrasonic thickness measurement, which tests the thickness of the test object, for example, to monitor pipework corrosion and erosion. Ultrasonic testing is extensively used to detect flaws in welds. Ultrasonic testing is often performed on steel and other metals and alloys, though it can also be used on concrete, wood and composites, albeit with less resolution. It is used in many industries including steel and aluminum construction, metallurgy, manufacturing, aerospace, automotive and other transportation sectors. History The first efforts to use ultrasonic testing to dete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat
In thermodynamics, heat is energy in transfer between a thermodynamic system and its surroundings by such mechanisms as thermal conduction, electromagnetic radiation, and friction, which are microscopic in nature, involving sub-atomic, atomic, or molecular particles, or small surface irregularities, as distinct from the macroscopic modes of energy transfer, which are thermodynamic work and transfer of matter. For a closed system (transfer of matter excluded), the heat involved in a process is the difference in internal energy between the final and initial states of a system, after subtracting the work done in the process. For a closed system, this is the formulation of the first law of thermodynamics. Calorimetry is measurement of quantity of energy transferred as heat by its effect on the states of interacting bodies, for example, by the amount of ice melted or by change in temperature of a body. In the International System of Units (SI), the unit of measurement for he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
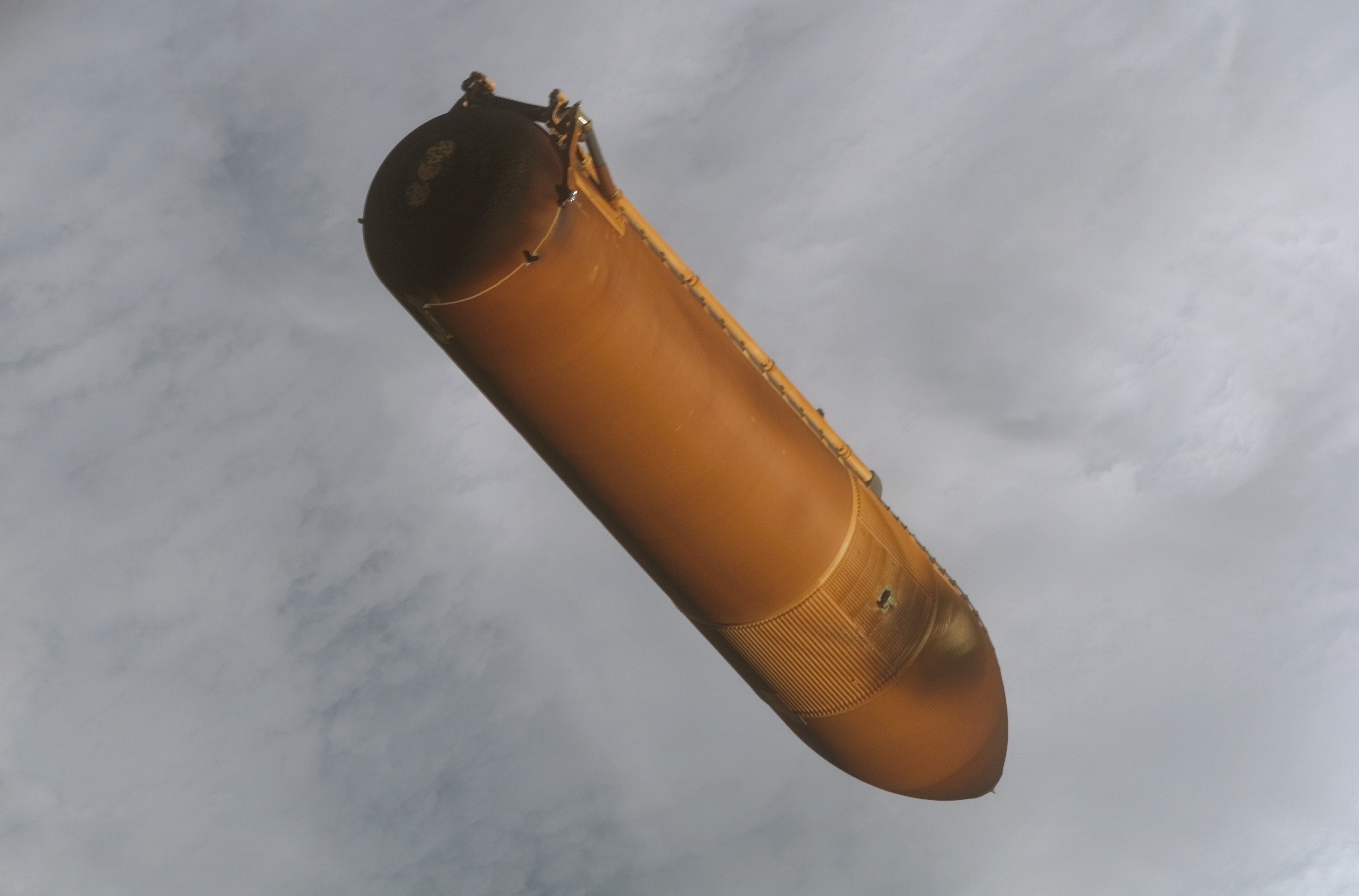
Space Shuttle External Tank
The Space Shuttle external tank (ET) was the component of the Space Shuttle launch vehicle that contained the liquid hydrogen fuel and liquid oxygen oxidizer. During lift-off and ascent it supplied the fuel and oxidizer under pressure to the three RS-25 main engines in the orbiter. The ET was jettisoned just over 10 seconds after main engine cut-off (MECO) and it re-entered the Earth's atmosphere. Unlike the Solid Rocket Boosters, external tanks were not re-used. They broke up before impact in the Indian Ocean (or Pacific Ocean in the case of direct-insertion launch trajectories), away from shipping lanes and were not recovered. Overview The ET was the largest element of the Space Shuttle, and when loaded, it was also the heaviest. It consisted of three major components: * the forward liquid oxygen (LOX) tank * an unpressurized intertank that contains most of the electrical components * the aft liquid hydrogen (LH2) tank; this was the largest part, but it was relatively l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insulator (electrical)
An electrical insulator is a material in which electric current does not flow freely. The atoms of the insulator have tightly bound electrons which cannot readily move. Other materials—semiconductors and electrical conductor, conductors—conduct electric current more easily. The property that distinguishes an insulator is its resistivity; insulators have higher resistivity than semiconductors or conductors. The most common examples are Nonmetal (chemistry), non-metals. A perfect insulator does not exist because even the materials used as insulators contain small numbers of mobile charges (charge carriers) which can carry current. In addition, all insulators become electrically conductive when a sufficiently large voltage is applied that the electric field tears electrons away from the atoms. This is known as electrical breakdown, and the voltage at which it occurs is called the breakdown voltage of an insulator. Some materials such as glass, Electrical insulation paper, paper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |