|
Tarkhan
Tarkhan (, or ; ; zh, c=達干/達爾罕/答剌罕; ; ; alternative spellings ''Tarkan'', ''Tarkhaan'', ''Tarqan'', ''Tarchan'', ''Turxan'', ''Tarcan'', ''Turgan, Tárkány, Tarján, Tarxan'') is an ancient Central Asian title used by various Turkic peoples, Turkic, Hungarians, Hungarian, Mongols, Mongolic, and Iranian peoples. Its use was common among the successors of the Mongol Empire and First Turkic Khaganate, Turkic Khaganate. Etymology The origin of the word is not known. Various historians identify the word as either Eastern Iranian languages, East Iranian (Sogdian language, Sogdian or Saka language, Khotanese Saka) or Turkic languages, Turkic. Although Richard N. Frye reports that the word "was probably foreign to Sogdian", Gerhard Doerfer points out that even in Turkic languages, its plural is not Turkic (sing. ''tarxan'' → plur. ''tarxat''), suggesting a non-Turkic origin. L. Ligeti comes to the same conclusion, saying that "''tarxan'' and ''tegin'' [prince] form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hephthalites
The Hephthalites (), sometimes called the White Huns (also known as the White Hunas, in Iranian languages, Iranian as the ''Spet Xyon'' and in Sanskrit and Prakrit as the ''Sveta-huna''), were a people who lived in Central Asia during the 5th to 8th centuries CE, part of the larger group of Eastern Iranian Huns. They formed an empire, the Imperial Hephthalites, and were militarily important from 450 CE, when they defeated the Kidarites, to 560 CE, when combined forces from the First Turkic Khaganate and the Sasanian Empire defeated them. After 560 CE, they established "principalities" in the area of Tokharistan, under the suzerainty of the Western Turks (in the areas north of the Amu Daria, Oxus) and of the Sasanian Empire (in the areas south of the Amu Daria, Oxus), before the Tokhara Yabghus took over in 625. The Imperial Hephthalites, based in Bactria, expanded eastwards to the Tarim Basin, westwards to Sogdia and southwards through Afghanistan, but they never went beyond the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Khazars
The Khazars ; 突厥可薩 ''Tūjué Kěsà'', () were a nomadic Turkic people who, in the late 6th century CE, established a major commercial empire covering the southeastern section of modern European Russia, southern Ukraine, Crimea, and Kazakhstan. They created what, for its duration, was the most powerful polity to emerge from the break-up of the Western Turkic Khaganate. Astride a major artery of commerce between Eastern Europe and Southwestern Asia, Khazaria became one of the foremost trading empires of the early medieval world, commanding the western marches of the Silk Road and playing a key commercial role as a crossroad between China, the Middle East, and Kievan Rus'. For some three centuries (–965), the Khazars dominated the vast area extending from the Volga-Don steppes to the eastern Crimea and the northern Caucasus. Khazaria long served as a buffer state between the Byzantine Empire, the nomads of the northern steppes, and the Umayyad and Abbasid Caliph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
First Turkic Khaganate
The First Turkic Khaganate, also referred to as the First Turkic Empire, the Turkic Khaganate or the Göktürk Khaganate, was a Turkic khaganate established by the Ashina clan of the Göktürks in medieval Inner Asia under the leadership of Bumin Qaghan (d. 552) and his brother Istämi. The First Turkic Khaganate succeeded the Rouran Khaganate as the hegemonic power of the Mongolian Plateau and rapidly expanded their territories in Central Asia. The khaganate became the first Central Asian transcontinental empire from Manchuria to the Black Sea. Although the Göktürks spoke a Siberian Turkic language directly antecedent to the Orkhon Turkic of the Second Turkic Khaganate, the First Khaganate's early official texts and coins were written in Sogdian. It was the first Turkic state to use the name ''Türk'' politically. The Old Turkic script was invented at the first half of the sixth century. The Khaganate collapsed in 603, after a series of conflicts and civil wars which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
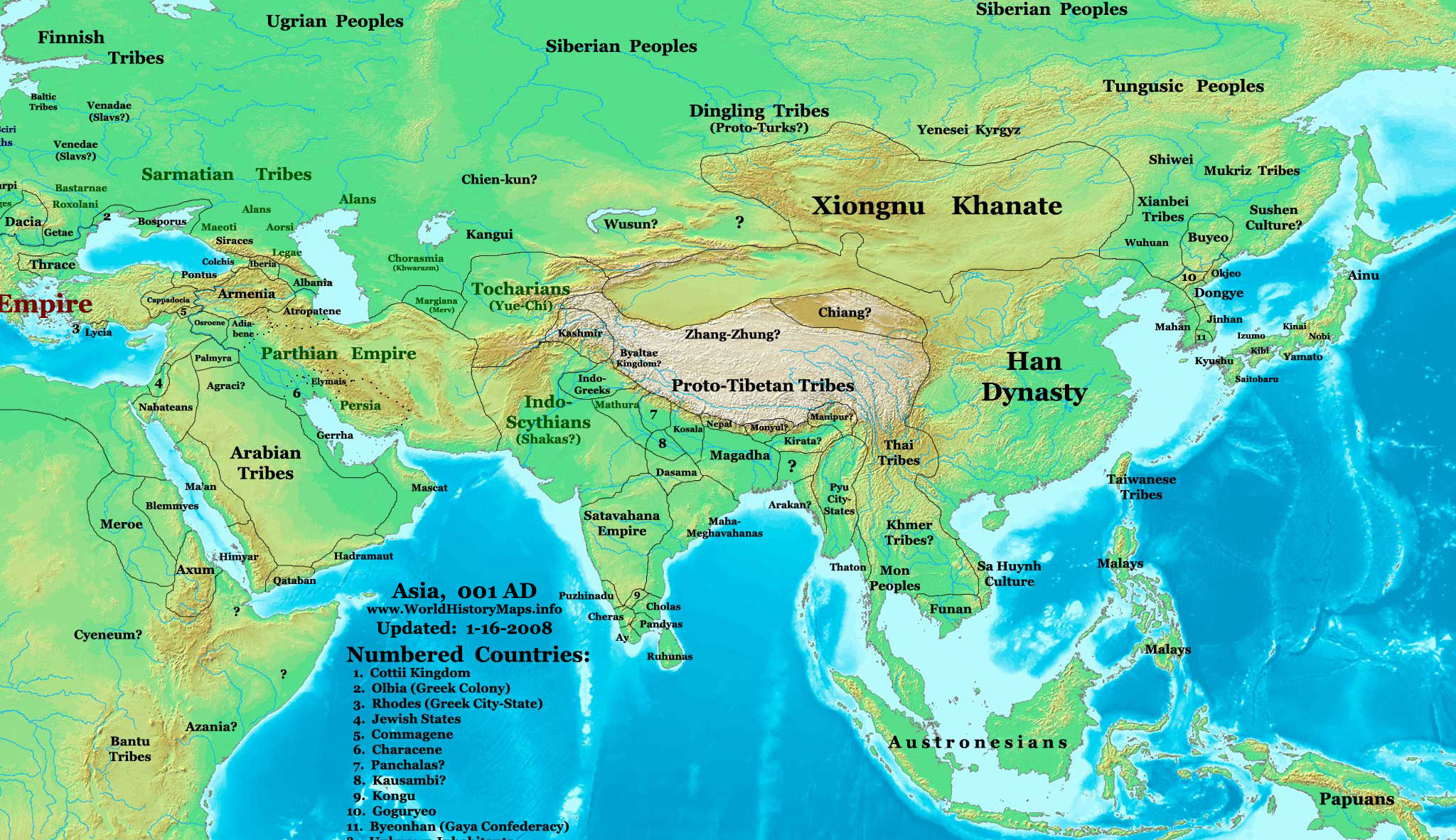
Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of Nomad, nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese historiography, Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 209 BC, founded the Xiongnu Empire. After overthrowing their previous overlords, the Yuezhi, the Xiongnu became the dominant power on the steppes of East Asia, centred on the Mongolian Plateau. The Xiongnu were also active in areas now part of Siberia, Inner Mongolia, Gansu and Xinjiang. Their relations with the Chinese dynasties to the south-east were complex—alternating between various periods of peace, war, and subjugation. Ultimately, the Xiongnu were defeated by the Han dynasty in a Han–Xiongnu Wars, centuries-long conflict, which led to the confederation splitting in two, and forcible resettlement of large numbers of Xiongnu within Han borders. During the Sixteen Kingdoms era, listed as one of the "Fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Korea
Korea is a peninsular region in East Asia consisting of the Korean Peninsula, Jeju Island, and smaller islands. Since the end of World War II in 1945, it has been politically Division of Korea, divided at or near the 38th parallel north, 38th parallel between North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea; DPRK) and South Korea (Republic of Korea; ROK). Both countries proclaimed independence in 1948, and the two countries fought the Korean War from 1950 to 1953. The region is bordered by China to the north and Russia to the northeast, across the Yalu River, Amnok (Yalu) and Tumen River, Duman (Tumen) rivers, and is separated from Japan to the southeast by the Korea Strait. Known human habitation of the Korean peninsula dates to 40,000 BC. The kingdom of Gojoseon, which according to tradition was founded in 2333 BC, fell to the Han dynasty in 108 BC. It was followed by the Three Kingdoms of Korea, Three Kingdoms period, in which Korea was divided into Goguryeo, Baekje, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ossetian Language
Ossetian ( , , ), commonly referred to as Ossetic and rarely as Ossete, is an Eastern Iranian language that is spoken predominantly in Ossetia, a region situated on both sides of the Russian-Georgian border in the Greater Caucasus region. It is the native language of the Ossetian people, and a relative and possibly a descendant of the extinct Scythian, Sarmatian, and Alanic languages. The northern half of the Ossetian region is part of Russia and is known as North Ossetia–Alania, while the southern half is part of the '' de facto'' country of South Ossetia (recognized by the United Nations as Russian-occupied territory that is ''de jure'' part of Georgia). Ossetian-speakers number about 614,350, with 451,000 recorded in Russia per the 2010 Russian census. Despite Ossetian being the official languages of both North and South Ossetia, since 2009 UNESCO has listed Ossetian as "vulnerable". In the 2010 Russian census only 36% of North Ossetians claimed to be fluent i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Timur
Timur, also known as Tamerlane (1320s17/18 February 1405), was a Turco-Mongol conqueror who founded the Timurid Empire in and around modern-day Afghanistan, Iran, and Central Asia, becoming the first ruler of the Timurid dynasty. An undefeated commander, he is widely regarded as one of the greatest military leaders and tacticians in history, as well as one of the most brutal and deadly. Timur is also considered a great patron of art and architecture, for he interacted with intellectuals such as Ibn Khaldun, Hafez, and Hafiz-i Abru and his reign introduced the Timurid Renaissance. Born into the Turkicized Mongol confederation of the Barlas in Transoxiana (in modern-day Uzbekistan) in the 1320s, Timur gained control of the western Chagatai Khanate by 1370. From that base he led military campaigns across Western, South, and Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Southern Russia, defeating in the process the Khans of the Golden Horde, the Mamluks of Egypt and Syria, the emerg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Eurasian Nomads
Eurasian nomads form groups of nomad, nomadic peoples who have lived in various areas of the Eurasian Steppe. History largely knows them via frontier historical sources from Europe and Asia. The steppe nomads had no permanent abode, but travelled from place to place to find fresh pasture for their livestock. The generic designation encompasses the varied ethnic groups who have at times inhabited steppe regions of present-day Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, East Turkestan, Uyghuristan, Mongolia, Russia, and Ukraine. They domestication of the horse, domesticated the horse around 3500 BCE, vastly increasing the possibilities of nomadic lifestyle, and subsequently their economies and cultures emphasised horse breeding, horse riding, and nomadic pastoralism; this usually involved trading with settled peoples around the edges of the steppe. They developed the chariot, the wagon,cavalry, and horse archery, and introduced innovations such as the bridle, Bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Central Asia
Central Asia is a region of Asia consisting of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. The countries as a group are also colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as all have names ending with the Persian language, Persian suffix "-stan" (meaning ) in both respective native languages and most other languages. The region is bounded by the Caspian Sea to the southwest, European Russia to the northwest, China and Mongolia to the east, Afghanistan and Iran to the south, and Siberia to the north. Together, the five Central Asian countries have a total population of around million. In the pre-Islamic and early Islamic eras ( and earlier) Central Asia was inhabited predominantly by Iranian peoples, populated by Eastern Iranian-speaking Bactrians, Sogdians, Khwarezmian language, Chorasmians, and the semi-nomadic Scythians and Dahae. As the result of Turkic migration, Central Asia also became the homeland for the Kazakhs, Kyrgyzs, Volga Tatars, Tatars, Turkmens, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Proto-Mongols
The proto-Mongols emerged from an area that had been inhabited by humans as far back as 45,000 years ago during the Upper Paleolithic. The people there went through the Bronze Age, Bronze and Iron Ages, forming tribal alliances, peopling, and coming into conflict with early polities in the Zhongyuan, Central Plain. The proto-Mongols formed various tribal kingdoms who fought against one other for supremacy, such as the Rouran Khaganate (330–555) until it was defeated by the Göktürks, who founded the First Turkic Khaganate (552–744), which in turn was subdued by the growing strength of the Tang dynasty. The destruction of the Uyghur Khaganate (744–848) by the Yenisei Kyrgyz resulted in the end of Turkic dominance on the Mongolian Plateau. The para-Mongol Khitan people founded also referred to by Chineses sources as Liao dynasty (916–1125) and ruled Mongolia and portions of the eastern coast of Siberia now known as the Russian Far East, northern Korea, and North China. Ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
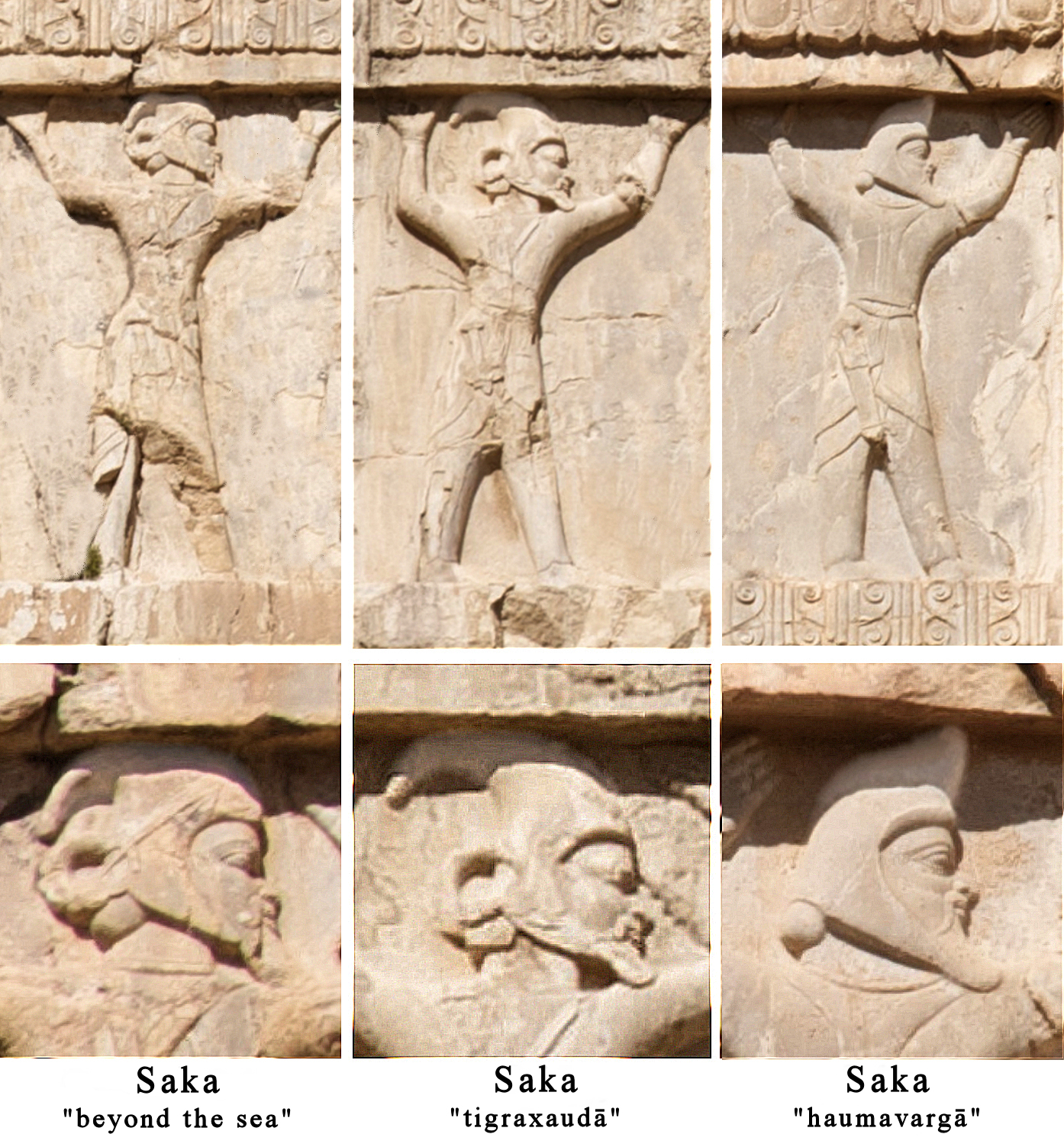
Saka
The Saka, Old Chinese, old , Pinyin, mod. , ), Shaka (Sanskrit (Brāhmī): , , ; Sanskrit (Devanāgarī): , ), or Sacae (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples, Eastern Iranian peoples who lived in the Eurasian Steppe and the Tarim Basin from the 9th century BC to the 5th century AD. "Modern scholars have mostly used the name Saka to refer specifically to Iranians of the Eastern Steppe and Tarim Basin" "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Central Asia and Eastern Turkestan to distinguish them from the related Massagetae of the Aral region and the Scythians of the Pontic steppes. These tribes spoke Iranian languages, and their chief occupation was nomadic pastoralism." The Saka were closely related to the Scythians, and both groups formed part of the wider Scythian cultures. However, they are distinguished from the Scythians by their specific geographical and cultural traits. The Saka la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sogdia
Sogdia () or Sogdiana was an ancient Iranian peoples, Iranian civilization between the Amu Darya and the Syr Darya, and in present-day Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan. Sogdiana was also a province of the Achaemenid Empire, and listed on the Behistun Inscription of Darius the Great. Sogdiana was first conquered by Cyrus the Great, the founder of the Achaemenid Empire, and then was annexed by the Macedonian ruler Alexander the Great in 328 BC. It would continue to change hands under the Seleucid Empire, the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom, the Kushan Empire, the Sasanian Empire, the Hephthalite Empire, the Western Turkic Khaganate, and the Muslim conquest of Transoxiana. The Sogdian city-states, although never politically united, were centered on the city of Samarkand. Sogdian language, Sogdian, an Eastern Iranian language, is no longer spoken. However, a descendant of one of its dialects, Yaghnobi language, Yaghnobi, is still spoken by the Yaghnobis of Taji ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |