|
TFIIB
Transcription factor II B (TFIIB) is a general transcription factor that is involved in the formation of the RNA polymerase II preinitiation complex (PIC) and aids in stimulating transcription initiation. TFIIB is localised to the nucleus and provides a platform for PIC formation by binding and stabilising the DNA-TBP (TATA-binding protein) complex and by recruiting RNA polymerase II and other transcription factors. It is encoded by the gene, and is homologous to archaeal transcription factor B and analogous to bacterial sigma factors. Structure TFIIB is a single 33kDa polypeptide consisting of 316 amino acids. TFIIB is made up of four functional regions: the C-terminal core domain; the B linker; the B reader and the amino terminal zinc ribbon. TFIIB makes protein-protein interactions with the TATA-binding protein (TBP) subunit of transcription factor IID, and the RPB1 subunit of RNA polymerase II. TFIIB makes sequence-specific protein-DNA interactions with the B rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
B Recognition Element
The B recognition element (BRE) is a DNA sequence found in the promoter region of most genes in eukaryotes and Archaea. The BRE is a cis-regulatory element that is found immediately near TATA box, and consists of 7 nucleotides. There are two sets of BREs: one (BREu) found immediately upstream of the TATA box, with the consensus SSRCGCC; the other (BREd) found around 7 nucleotides downstream, with the consensus RTDKKKK. The BREu was discovered in 1998 by Richard H. EbRichard Ebright and co-workers. The BREd was named in 2005 by Deng and Roberts; such a downstream recognition was reported earlier in 2000 in Tsai and Sigler's crystal structure. Binding The transcription factor II B (TFIIB) recognizes either BRE and binds to it. Both BREs work in conjunction with the TATA box (and TATA box binding protein), and have various effects on levels of transcription. TFIIB uses the cyclin-like repeats to recognize DNA. The C-terminal alpha helix, alpha helices of TFIIB intercalate with the D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Archaeal Transcription Factor B
Archaeal transcription factor B (ATFB or TFB) is a protein family of extrinsic transcription factors that guide the initiation of RNA transcription in organisms that fall under the domain of Archaea. It is homologous to eukaryotic TFIIB and, more distantly, to bacterial sigma factor. Like these proteins, it is involved in forming transcription preinitiation complexes. Its structure includes several conserved motifs which interact with DNA and other transcription factors, notably the single type of RNA polymerase that performs transcription in Archaea. History In bacteria and eukaryotes, proteins TFIIB and sigma factor are involved in the initiation of transcription, where they facilitate preinitiation complex formation and specific RNA Polymerase-DNA binding. The archaeal counterpart to these two proteins is TFB, which was first identified in the species '' Pyrococcus woesei'' in 1992. Since then, research has found that archaeal species must contain at least one copy of TFB t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
TATA-binding Protein
The TATA-binding protein (TBP) is a general transcription factor that binds to a DNA sequence called the TATA box. This DNA sequence is found about 30 base pairs upstream of the transcription start site in some eukaryotic gene promoters. TBP gene family TBP is a member of a small gene family of TBP-related factors. The first TBP-related factor (TRF/TRF1) was identified in the fruit fly Drosophila, but appears to be fly or insect-specific. Subsequently TBPL1/TRF2 was found in the genomes of many metazoans, whereas vertebrate genomes encode a third vertebrate family member, TBPL2/TRF3. In specific cell types or on specific promoters TBP can be replaced by one of these TBP-related factors, some of which interact with the TATA box similarly to TBP. Role as transcription factor TBP is a subunit of the eukaryotic general transcription factor TFIID. TFIID is the first protein to bind to DNA during the formation of the transcription preinitiation complex of RNA polymerase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
General Transcription Factor
General transcription factors (GTFs), also known as basal transcriptional factors, are a class of protein transcription factors that bind to specific sites ( promoter) on DNA to activate transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA. GTFs, RNA polymerase, and the mediator (a multi-protein complex) constitute the basic transcriptional apparatus that first bind to the promoter, then start transcription. GTFs are also intimately involved in the process of gene regulation, and most are required for life. A transcription factor is a protein that binds to specific DNA sequences ( enhancer or promoter), either alone or with other proteins in a complex, to control the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA by promoting (serving as an activator) or blocking (serving as a repressor) the recruitment of RNA polymerase. As a class of protein, general transcription factors bind to promoters along the DNA sequence or form a large transcription p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Transcription Preinitiation Complex
The preinitiation complex (abbreviated PIC) is a complex of approximately 100 proteins that is necessary for the transcription (genetics), transcription of protein-coding genes in eukaryotes and archaea. The preinitiation complex positions RNA polymerase II (Pol II) at gene transcription start sites, DNA melting, denatures the DNA, and positions the DNA in the RNA polymerase II active site for transcription. The minimal PIC includes RNA polymerase II and six general transcription factors: Transcription factor II A, TFIIA, Transcription factor II B, TFIIB, Transcription factor II D, TFIID, Transcription factor II E, TFIIE, Transcription factor II F, TFIIF, and Transcription factor II H, TFIIH. Additional regulatory complexes (such as the mediator (coactivator), mediator coactivator and chromatin structure remodeling (RSC) complex, chromatin remodeling complexes) may also be components of the PIC. Preinitiation complexes are also formed during RNA Polymerase I and RNA Polymerase II ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sigma Factor
A sigma factor (σ factor or specificity factor) is a protein needed for initiation of Transcription (biology), transcription in bacteria. It is a bacterial transcription initiation factor that enables specific binding of RNA polymerase (RNAP) to gene promoter (biology), promoters. It is homologous to archaeal transcription factor B and to Eukaryote, eukaryotic factor TFIIB. The specific sigma factor used to initiate transcription of a given gene will vary, depending on the gene and on the environmental signals needed to initiate transcription of that gene. Selection of promoters by RNA polymerase is dependent on the sigma factor that associates with it. They are also found in plant chloroplasts as a part of the bacteria-like plastid-encoded polymerase (PEP). The sigma factor, together with RNA polymerase, is known as the RNA polymerase Enzyme#Cofactors, holoenzyme. Every molecule of RNA polymerase holoenzyme contains exactly one sigma factor subunit, which in the model bacterium '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
TATA Box
In molecular biology, the TATA box (also called the Goldberg–Hogness box) is a sequence of DNA found in the core promoter region of genes in archaea and eukaryotes. The bacterial homolog of the TATA box is called the Pribnow box which has a shorter consensus sequence. The TATA box is considered a non-coding DNA sequence (also known as a cis-regulatory element). It was termed the "TATA box" as it contains a consensus sequence characterized by repeating T and A base pairs. How the term "box" originated is unclear. In the 1980s, while investigating nucleotide sequences in mouse genome loci, the Hogness box sequence was found and "boxed in" at the -31 position. When consensus nucleotides and alternative ones were compared, homologous regions were "boxed" by the researchers. The boxing in of sequences sheds light on the origin of the term "box". The TATA box was first identified in 1978 as a component of eukaryotic promoters. Transcription is initiated at the TATA box in TA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Transcription (genetics)
Transcription is the process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA for the purpose of gene expression. Some segments of DNA are transcribed into RNA molecules that can encode proteins, called messenger RNA (mRNA). Other segments of DNA are transcribed into RNA molecules called non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs). Both DNA and RNA are nucleic acids, which use base pairs of nucleotides as a complementary language. During transcription, a DNA sequence is read by an RNA polymerase, which produces a complementary, antiparallel RNA strand called a primary transcript. In virology, the term transcription is used when referring to mRNA synthesis from a viral RNA molecule. The genome of many RNA viruses is composed of negative-sense RNA which acts as a template for positive sense viral messenger RNA - a necessary step in the synthesis of viral proteins needed for viral replication. This process is catalyzed by a viral RNA dependent RNA polymerase. Background A DNA transcription unit encoding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
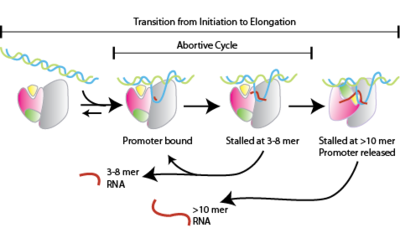
Abortive Initiation
Abortive initiation, also known as abortive transcription, is an early process of genetic transcription in which RNA polymerase binds to a DNA promoter and enters into cycles of synthesis of short mRNA transcripts which are released before the transcription complex leaves the promoter. This process occurs in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes. Abortive initiation is typically studied in the T3 and T7 RNA polymerases in bacteriophages and in '' E. coli''. Overall process Abortive initiation occurs prior to promoter clearance. # RNA polymerase binds to promoter DNA to form an RNA polymerase-promoter ''closed'' complex # RNA polymerase then unwinds one turn of DNA surrounding the transcription start site to yield an RNA polymerase-promoter ''open'' complex # RNA polymerase enters into abortive cycles of synthesis and releases short RNA products (contains less than 10 nucleotides) # RNA polymerase escapes the promoter and enters into the elongation step of transcription Mechanism Abort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three Evolution of mammalian auditory ossicles, middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles and birds, from which their ancestors Genetic divergence, diverged in the Carboniferous Period over 300 million years ago. Around 6,640 Neontology#Extant taxon, extant species of mammals have been described and divided into 27 Order (biology), orders. The study of mammals is called mammalogy. The largest orders of mammals, by number of species, are the rodents, bats, and eulipotyphlans (including hedgehogs, Mole (animal), moles and shrews). The next three are the primates (including humans, monkeys and lemurs), the Artiodactyl, even-toed ungulates (including pigs, camels, and whales), and the Carnivora (including Felidae, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kinase
In biochemistry, a kinase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of phosphate groups from high-energy, phosphate-donating molecules to specific substrates. This process is known as phosphorylation, where the high-energy ATP molecule donates a phosphate group to the substrate molecule. As a result, kinase produces a phosphorylated substrate and ADP. Conversely, it is referred to as dephosphorylation when the phosphorylated substrate donates a phosphate group and ADP gains a phosphate group (producing a dephosphorylated substrate and the high energy molecule of ATP). These two processes, phosphorylation and dephosphorylation, occur four times during glycolysis. Kinases are part of the larger family of phosphotransferases. Kinases should not be confused with phosphorylases, which catalyze the addition of inorganic phosphate groups to an acceptor, nor with phosphatases, which remove phosphate groups (dephosphorylation). The phosphorylation state of a molecule, whether it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
TFIIH
Transcription factor II H (TFIIH) is an important protein complex, having roles in transcription of various protein-coding genes and DNA nucleotide excision repair (NER) pathways. TFIIH first came to light in 1989 when general transcription factor-δ or basic transcription factor 2 was characterized as an indispensable transcription factor in vitro. This factor was also isolated from yeast and finally named TFIIH in 1992. TFIIH consists of ten subunits, 7 of which ( ERCC2/XPD, ERCC3/XPB, GTF2H1/p62, GTF2H4/p52, GTF2H2/p44, GTF2H3/p34 and GTF2H5/TTDA) form the core complex. The cyclin-activating kinase-subcomplex ( CDK7, MAT1, and cyclin H) is linked to the core via the XPD protein. Two of the subunits, ERCC2/XPD and ERCC3/ XPB, have helicase and ATPase activities and help create the transcription bubble. In a test tube, these subunits are only required for transcription if the DNA template is not already denatured or if it is supercoiled. Two other TFIIH subunits, CD ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |