|
Samuel Mudd
Samuel Alexander Mudd Sr. (December 20, 1833 – January 10, 1883) was an American physician who was imprisoned for conspiring with John Wilkes Booth concerning the assassination of Abraham Lincoln. Mudd worked as a doctor and tobacco farmer in Southern Maryland. The Civil War seriously damaged his business, especially when Maryland abolished slavery in 1864. That year, he first met Booth, who was planning to kidnap Lincoln, and Mudd was seen in company with three of the conspirators. However, his part in the plot, if any, remains unclear. Booth fatally shot Lincoln on April 14, 1865, but was injured during his escape from the scene. He subsequently rode with conspirator David Herold to Mudd's home in the early hours of April 15 for surgery on his fractured leg before he crossed into Virginia. Sometime that day, Mudd must have learned of the assassination but did not report Booth's visit to the authorities for another 24 hours. This fact appeared to link him to the crime, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles County, Maryland
Charles County is a county in Southern Maryland. As of the 2020 census, the population was 166,617. The county seat is La Plata. The county was named for Charles Calvert (1637–1715), third Baron Baltimore. Charles County is part of the Washington metropolitan area and the Southern Maryland region. With a median household income of $103,678, it is the 39th wealthiest county in the United States and the highest-income county with a Black-majority population. History Charles County was created in 1658 by an Order in Council. There was also an earlier Charles County from 1650 to 1654, sometimes referred to in historic documents as Old Charles County, which consisted largely of lands within today’s borders but "included parts of St. Mary’s, Calvert, present-day Charles and Prince George’s County". In April 1865, John Wilkes Booth made his escape through Charles County after shooting President Abraham Lincoln. He was on his way to Virginia. He stopped briefly in Waldorf ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orestes Brownson
Orestes Augustus Brownson (September 16, 1803 – April 17, 1876) was an American intellectual and activist, preacher, labor organizer, and noted Catholic convert and writer. Brownson was a publicist, a career which spanned his affiliation with the New England Transcendentalists through his subsequent conversion to Roman Catholicism. Early years and education Brownson was born on September 16, 1803, to Sylvester Augustus Brownson and Relief Metcalf, who were farmers in Stockbridge, Vermont. Sylvester Brownson died when Orestes was young and Relief decided to give her son up to a nearby adoptive family when he was six years old. The adopting family raised Brownson under the strict confines of Calvinist Congregationalism on a small farm in Royalton, Vermont. He did not receive much schooling but enjoyed reading books. Among these were volumes by Homer and Locke and the Bible. In 1817, when he was fourteen, Brownson attended an academy briefly in New York. This was the extent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenback (money)
Greenbacks were emergency paper currency issued by the United States during the American Civil War that were printed in green on the back. They were in two forms: Demand Notes, issued in 1861–1862, and United States Notes, issued in 1862–1865. A form of fiat money, the notes were legal tender for most purposes and carried varying promises of eventual payment in coin, but were not backed by existing gold or silver reserves. History Background Before the Civil War, the United States used gold and silver coins as its official currency. Paper currency in the form of banknotes was issued by privately-owned banks, the notes being redeemable for specie at the bank's office. Such notes had value only if the bank could be counted on to redeem them; if a bank failed, its notes became worthless. The federal government sometimes issued Treasury Notes to borrow money during periods of economic distress, but proposals for a federal paper currency were politically contentious and recalle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
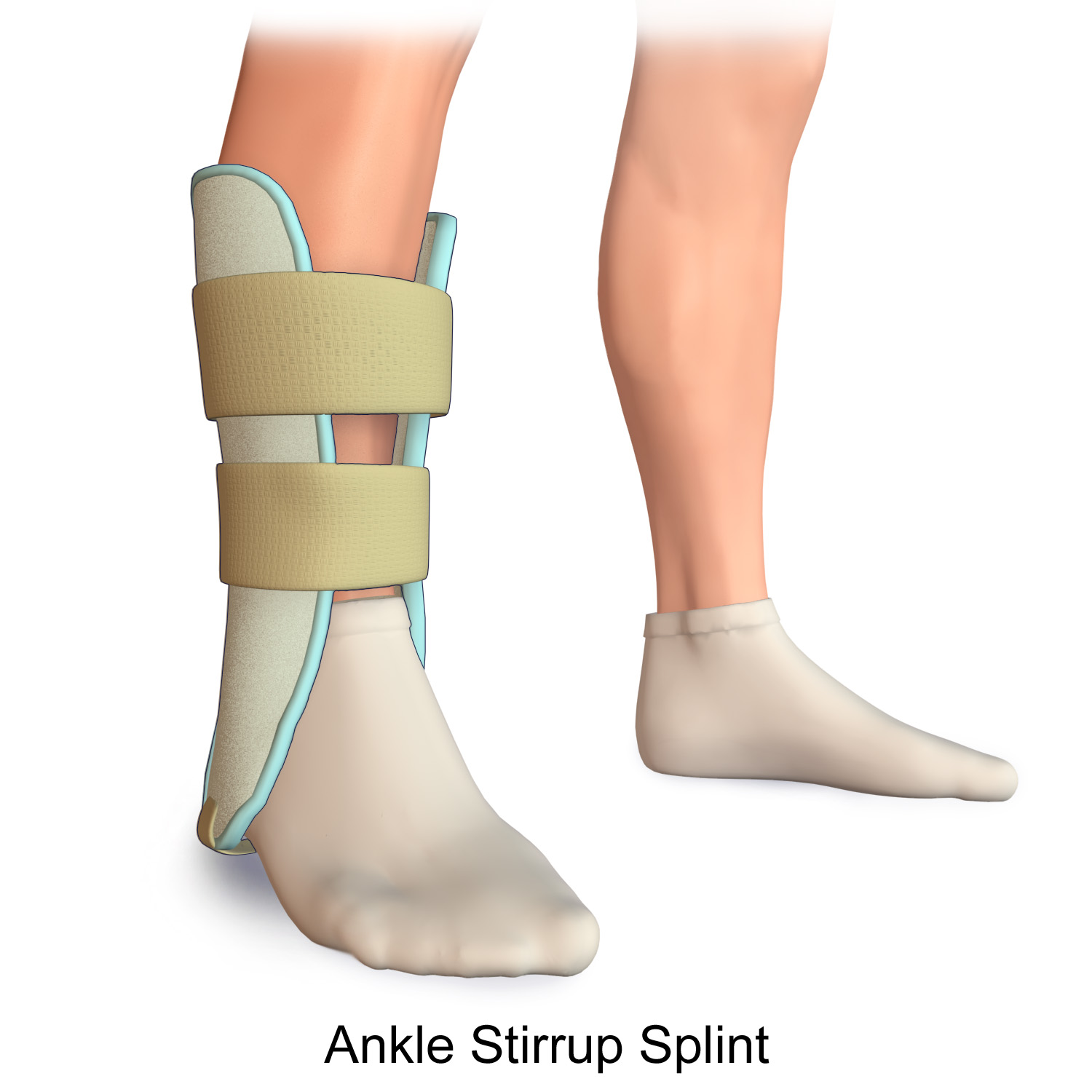
Splint (medicine)
A splint is defined as "a rigid or flexible device that maintains in position a displaced or movable part; also used to keep in place and protect an injured part" or as "a rigid or flexible material used to protect, immobilize, or restrict motion in a part". Splints can be used for injuries that are not severe enough to immobilize the entire injured structure of the body. For instance, a splint can be used for certain fractures, soft tissue sprains, tendon injuries, or injuries awaiting orthopedic treatment. A splint may be static, not allowing motion, or dynamic, allowing controlled motion. Splints can also be used to relieve pain in damaged joints. Splints are quick and easy to apply and do not require a plastering technique. Splints are often made out of some kind of flexible material and a firm pole-like structure for stability. They often buckle or Velcro together. Uses * By the emergency medical services or by volunteer first responders, to temporarily immobilize a fract ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ford's Theater
Ford's Theatre is a theater located in Washington, D.C., which opened in August 1863. The theater is infamous for being the site of the assassination of Abraham Lincoln. On the night of April 14, 1865, John Wilkes Booth entered the theater box where Lincoln and his wife were watching a performance of ''Our American Cousin'', slipped the single-shot, 5.87-inch derringer from his pocket and fired at Lincoln's head. After being shot, the fatally wounded Lincoln was carried across the street to the Petersen House, where he died the next morning. The theater was later used as a warehouse and government office building. In 1893, part of its interior flooring collapsed, causing 22 deaths, and needed repairs were made. The building became a museum in 1932, and it was renovated and re-opened as a theater in 1968. A related Center for Education and Leadership museum opened February 12, 2012, next to Petersen House. The Petersen House and the theater are preserved together as Ford's Theat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibula
The fibula or calf bone is a leg bone on the lateral side of the tibia, to which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and, in proportion to its length, the most slender of all the long bones. Its upper extremity is small, placed toward the back of the head of the tibia, below the knee joint and excluded from the formation of this joint. Its lower extremity inclines a little forward, so as to be on a plane anterior to that of the upper end; it projects below the tibia and forms the lateral part of the ankle joint. Structure The bone has the following components: * Lateral malleolus * Interosseous membrane connecting the fibula to the tibia, forming a syndesmosis joint * The superior tibiofibular articulation is an arthrodial joint between the lateral condyle of the tibia and the head of the fibula. * The inferior tibiofibular articulation (tibiofibular syndesmosis) is formed by the rough, convex surface of the medial side of the lower end of the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mary Surratt
Mary Elizabeth Jenkins SurrattCashin, p. 287.Steers, 2010, p. 516. (1820 or May 1823 – July 7, 1865) was an American boarding house owner in Washington, D.C., who was convicted of taking part in the conspiracy which led to the assassination of U.S. President Abraham Lincoln in 1865. Sentenced to death, she was hanged and became the first woman executed by the U.S. federal government. She maintained her innocence until her death, and the case against her was and remains controversial. Surratt was the mother of John Surratt, who was later tried, but due to statute of limitations, was not convicted. Born in Maryland in the 1820s, Surratt converted to Catholicism at a young age and remained a practicing Catholic for the rest of her life. She wed John Harrison Surratt in 1840 and had three children with him. An entrepreneur, John became the owner of a tavern, an inn, and a hotel. The Surratts were sympathetic to the Confederate States of America and often hosted fellow Conf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lewis Powell (conspirator)
Lewis Thornton Powell (April 22, 1844 – July 7, 1865), also known as Lewis Payne and Lewis Paine, was an American Confederate soldier who attempted to assassinate William Henry Seward as part of the Lincoln assassination plot. Wounded at the Battle of Gettysburg, he later served in Mosby's Rangers before working with the Confederate Secret Service in Maryland. John Wilkes Booth recruited him into a plot to kidnap Lincoln and turn the president over to the Confederacy, but then decided to assassinate Lincoln, Seward, and Vice President Andrew Johnson instead, and assigned Powell the task to kill Seward. Co-conspirator David Herold was to guide Powell to Seward's home, then help him escape, but fled before Powell was able to exit the Seward home. He arrived at the boarding house run by Mary Surratt, mother of co-conspirator John Surratt, three days later while the police were there conducting a search, and was arrested. Powell, Mary Surratt, Herold, and George Atzerodt were se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Atzerodt
George Andrew Atzerodt (June 12, 1835 – July 7, 1865) was a German American repairman, Confederate sympathizer, and conspirator with John Wilkes Booth in the assassination of US President Abraham Lincoln. He was assigned to assassinate Vice President Andrew Johnson, but lost his nerve and made no attempt. He was executed along with three other conspirators by hanging. Early life Atzerodt was born in in the Prussian Province of Saxony, today part of Anrode, Thuringia, Germany. He emigrated to the United States in 1843 at the age of eight. As an adult, he opened his own carriage repair business in Port Tobacco, Maryland. Despite having lived in the United States for most of his life, Atzerodt could not speak English fluently. Conspiracy In January 1865, some years after opening his failed carriage repair business, Atzerodt was introduced to John Wilkes Booth in Washington, D.C., by John Surratt. Atzerodt was willing to join in Booth's earlier conspiracy to kidnap Pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emancipation Proclamation
The Emancipation Proclamation, officially Proclamation 95, was a presidential proclamation and executive order issued by United States President Abraham Lincoln on January 1, 1863, during the Civil War. The Proclamation changed the legal status of more than 3.5 million enslaved African Americans in the secessionist Confederate states from enslaved to free. As soon as slaves escaped the control of their enslavers, either by fleeing to Union lines or through the advance of federal troops, they were permanently free. In addition, the Proclamation allowed for former slaves to "be received into the armed service of the United States." On September 22, 1862, Lincoln issued the preliminary Emancipation Proclamation. Its third paragraph reads: That on the first day of January, in the year of our Lord, one thousand eight hundred and sixty-three, all persons held as slaves within any State or designated part of a State, the people whereof shall then be in rebellion against the U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maryland In The American Civil War
During the American Civil War (1861–1865), Maryland, a slave state, was one of the border states, straddling the South and North. Despite some popular support for the cause of the Confederate States of America, Maryland did not secede during the Civil War. Governor Thomas H. Hicks, despite his early sympathies for the South, helped prevent the state from seceding. Because the state bordered the District of Columbia and the opposing factions within the state strongly desired to sway public opinion towards their respective causes, Maryland played an important role in the war. The Presidency of Abraham Lincoln (1861–1865) suspended the constitutional right of ''habeas corpus'' from Washington to Philadelphia. Lincoln ignored the ruling of Chief Justice Roger B. Taney in "Ex parte Merryman" decision in 1861 concerning freeing John Merryman, a prominent Southern sympathizer arrested by the military. The first fatalities of the war happened during the Baltimore Civil W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)