|
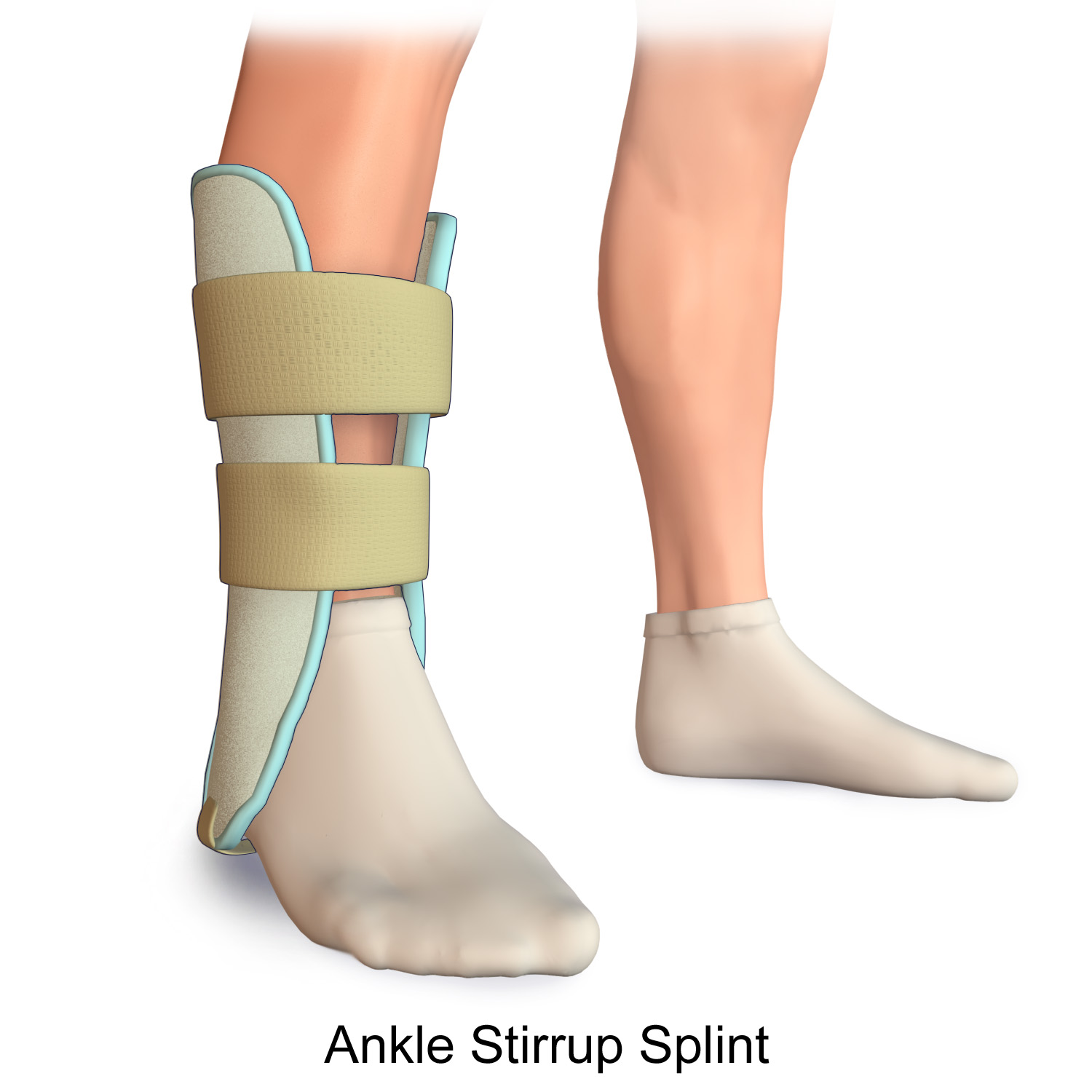
Splint (medicine)
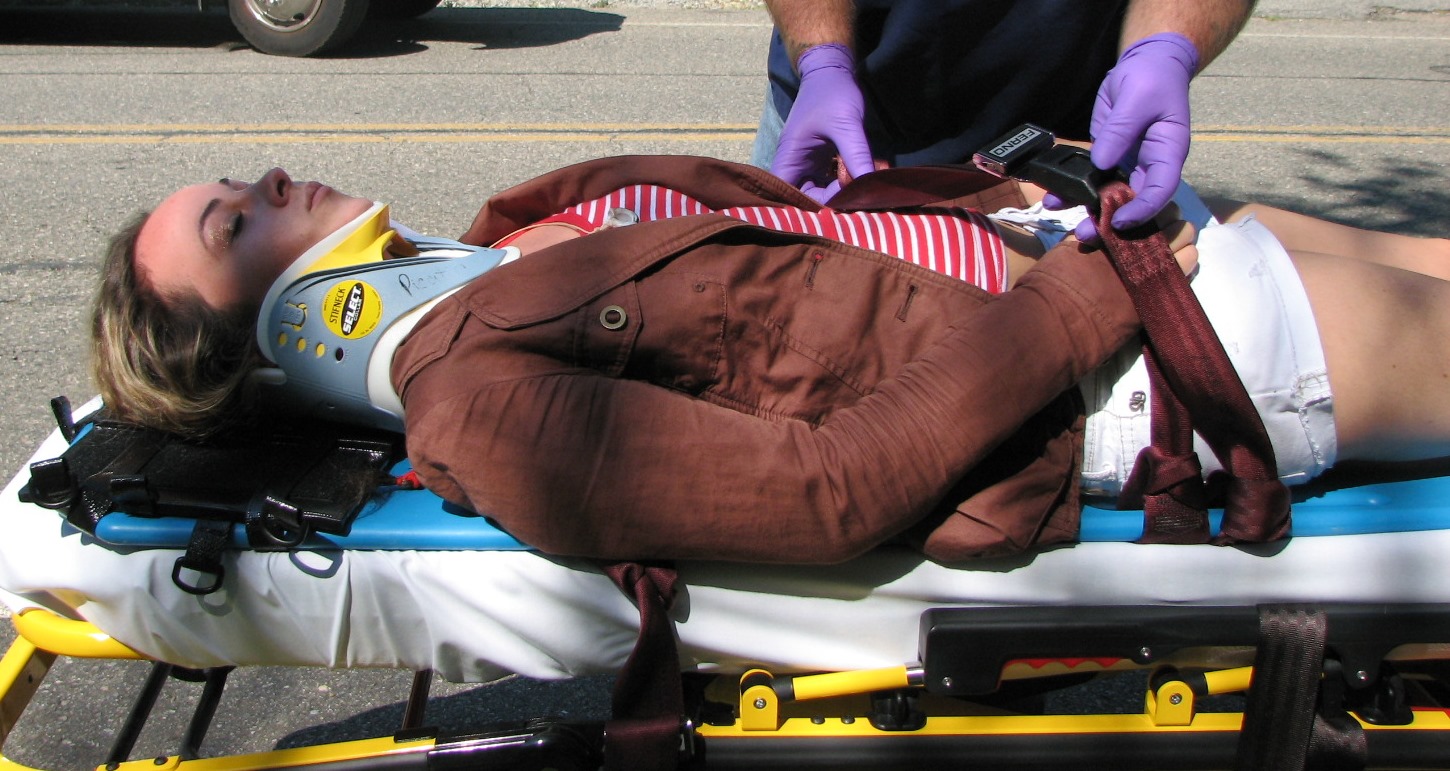
A splint is defined as "a rigid or flexible device that maintains in position a displaced or movable part; also used to keep in place and protect an injured part" or as "a rigid or flexible material used to protect, immobilize, or restrict motion in a part". Splints can be used for injuries that are not severe enough to immobilize the entire injured structure of the body. For instance, a splint can be used for certain fractures, soft tissue sprains, tendon injuries, or injuries awaiting orthopedic treatment. A splint may be static, not allowing motion, or dynamic, allowing controlled motion. Splints can also be used to relieve pain in damaged joints. Splints are quick and easy to apply and do not require a plastering technique. Splints are often made out of some kind of flexible material and a firm pole-like structure for stability. They often buckle or Velcro together. Uses * By the emergency medical services or by volunteer first responders, to temporarily immobilize a fractu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthopedics
Orthopedic surgery or orthopedics ( alternatively spelt orthopaedics), is the branch of surgery concerned with conditions involving the musculoskeletal system. Orthopedic surgeons use both surgical and nonsurgical means to treat musculoskeletal trauma, spine diseases, sports injuries, degenerative diseases, infections, tumors, and congenital disorders. Etymology Nicholas Andry coined the word in French as ', derived from the Ancient Greek words ὀρθός ''orthos'' ("correct", "straight") and παιδίον ''paidion'' ("child"), and published ''Orthopedie'' (translated as ''Orthopædia: Or the Art of Correcting and Preventing Deformities in Children'') in 1741. The word was assimilated into English as ''orthopædics''; the ligature ''æ'' was common in that era for ''ae'' in Greek- and Latin-based words. As the name implies, the discipline was initially developed with attention to children, but the correction of spinal and bone deformities in all stages of life eventu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippocrates
Hippocrates of Kos (; grc-gre, Ἱπποκράτης ὁ Κῷος, Hippokrátēs ho Kôios; ), also known as Hippocrates II, was a Greek physician of the classical period who is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history of medicine. He is traditionally referred to as the "Father of Medicine" in recognition of his lasting contributions to the field, such as the use of prognosis and clinical observation, the systematic categorization of diseases, or the formulation of humoral theory. The Hippocratic school of medicine revolutionized ancient Greek medicine, establishing it as a discipline distinct from other fields with which it had traditionally been associated (theurgy and philosophy), thus establishing medicine as a profession. However, the achievements of the writers of the Hippocratic Corpus, the practitioners of Hippocratic medicine, and the actions of Hippocrates himself were often conflated; thus very little is known about what Hippocrates actually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervical Collar
A cervical collar, also known as a neck brace, is a medical device used to support and immobilize a person's neck. It is also applied by emergency personnel to those who have had traumatic head or neck injuries, and can be used to treat chronic medical conditions. Whenever people have a traumatic head or neck injury, they may have a cervical fracture. This makes them at high risk for spinal cord injury, which could be exacerbated by movement of the person and could lead to paralysis or death. A common scenario for this injury would be a person suspected of having whiplash because of a car accident. In order to prevent further injury, such people may have a collar placed by medical professionals until X-rays can be taken to determine if a cervical spine fracture exists. Medical professionals will often use the NEXUS criteria and/or the Canadian C-spine rules to clear a cervical collar and determine the need for imaging. The cervical collar only stabilizes the top seven verte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuum Splint
A vacuum splint is a device like a small vacuum mattress that is used in emergency medicine as a temporary splint. Vacuum splints operate by extracting air from the splint itself to enable the thousands of polystyrene balls inside the splint to mold around the injured body part similar to an orthopedic cast. Vacuum splints are primarily used by paramedics to splint trauma-related injuries, joint dislocation, subluxation, and extremity fractures. Advantages of the vacuum splint include the ability to provide support whilst relieving pressure at the injury site and the ability to conform to any shape. The limb may also be X-ray An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nb ...ed with the splint on. References Emergency medical equipment {{Treatment-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traction Splint
A traction splint most commonly refers to a splinting device that uses straps attaching over the pelvis or hip as an anchor, a metal rod(s) to mimic normal bone stability and limb length, and a mechanical device to apply traction (used in an attempt to reduce pain, realign the limb, and minimize vascular and neurological complication) to the limb. The use of traction splints to treat complete long bone fractures of the femur is common in prehospital care. Evidence to support their usage, however, is poor. A dynamic traction splint has also been developed for intra-articular fractures of the phalanges of the hand. Medical uses Traction splints are most commonly used for fractures of the femur (or upper leg bone). For these fractures they may reduce pain and decrease the amount of bleeding which occurs into the soft tissues of the leg. Some state that they are appropriate for middle tibia fractures which are displaced or bent. Others state they should not be used for lower l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alessandro Codivilla
Alessandro Codivilla (21 March 1861 – 28 February 1912) was an Italian surgeon from Bologna and head of the surgical department of the hospital of Castiglion Fiorentino, known for his work in orthopaedics and first describing the pancreaticoduodenectomy. Life Early years and degree He was born in Bologna, Italy, on 21 March 1861 and belonged to a humble family. His father was a pawnbroker at the financial institution of Monte di Pietà. He was a very bright student, first of his class in high school, and had a particular attitude towards scientific subjects. Codivilla obtained a degree in medicine and surgery in 1886, and, right after that, became assistant to professor Pietro Loreta, the man whose death shot down Codivilla's possibilities for a career in teaching. Despite this, he did not let himself get discouraged and started to work at various hospitals. As noted by physician and writer , Codivilla had a tough apprenticeship in the hospitals of Castiglione Fiorenti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugh Owen Thomas
Hugh Owen Thomas (23 August 1834 – 6 January 1891) was a Welsh orthopaedic surgeon. He and his nephew Robert Jones have been called "the Fathers of orthopaedic surgery". Thomas was descended from a line of Welsh bone setters and placed great importance on rest in treatment of fractures. He is responsible for a number of contributions to orthopaedic treatment and surgery, producing a number of books and methods that revolutionised orthopaedic practice. He is particularly known for the Thomas splint, which was widely used during World War I, reducing mortality from 80% to just 8% by the end of the war. His principles of practice were also spread to the USA by John Ridlon, amongst others. Family background Hugh Owen Thomas was the great-grandson of a young boy who had been shipwrecked on Ynys Môn/Anglesey between 1743 and 1745 with his brother. One of the young brothers died a few days later bur the survivor was given the name Evan Thomas by the family that adopted and raised hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plaster-of-Paris
Plaster is a building material used for the protective or decorative coating of walls and ceilings and for moulding and casting decorative elements. In English, "plaster" usually means a material used for the interiors of buildings, while "render" commonly refers to external applications. Another imprecise term used for the material is stucco, which is also often used for plasterwork that is worked in some way to produce relief decoration, rather than flat surfaces. The most common types of plaster mainly contain either gypsum, lime, or cement,Franz Wirsching "Calcium Sulfate" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2012 Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. but all work in a similar way. The plaster is manufactured as a dry powder and is mixed with water to form a stiff but workable paste immediately before it is applied to the surface. The reaction with water liberates heat through crystallization and the hydrated plaster then hardens. Plaster can be relatively easily worked w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hieronymus Fabricius
Girolamo Fabrici d'Acquapendente, also known as Girolamo Fabrizio or Hieronymus Fabricius (20 May 1533 – 21 May 1619), was a pioneering anatomist and surgeon known in medical science as "The Father of Embryology." Life and accomplishments Born in Acquapendente, Latium, Fabricius studied at the University of Padua, receiving a Doctor of Medicine degree in 1559 under the guidance of Gabriele Falloppio. He was a private teacher of anatomy in Padua, 1562–1565, and in 1565, became professor of surgery and anatomy at the university, succeeding Falloppio. In 1594 he revolutionized the teaching of anatomy when he designed the first permanent theater for public anatomical dissections. Julius Casserius (1552–1616) of Piacenza was among Fabricius' students. William Harvey (1578–1657) and Adriaan van den Spiegel (1578–1625) also studied under Fabricius, beginning around 1598. Julius Casserius would later succeed Fabricius as Professor of Anatomy at the University of Padua i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthopedic Brace
Orthotics ( el, Ορθός, translit=ortho, lit=to straighten, to align) is a medical specialty that focuses on the design and application of orthoses, or braces. An is "an externally applied device used to influence the structural and functional characteristics of the neuromuscular and skeletal system". Orthotists are professionals who specialize in the provision of orthoses. Classification Orthotic devices are classified into four areas of the body according to the international classification system (ICS): orthotics of the lower extremities, orthotics of the upper extremities, orthotics for the trunk, and orthotics for the head. Orthoses are also classified by function: paralysis orthoses, relief orthoses, and soft braces. Under the International Standard terminology, orthoses are classified by an acronym describing the anatomical joints which they contain. For example, a knee-ankle-foot orthosis (English abbreviation: KAFO for Knee-ankle-foot orthoses) spans the knee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomy
Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having its beginnings in prehistoric times. Anatomy is inherently tied to developmental biology, embryology, comparative anatomy, evolutionary biology, and phylogeny, as these are the processes by which anatomy is generated, both over immediate and long-term timescales. Anatomy and physiology, which study the structure and function of organisms and their parts respectively, make a natural pair of related disciplines, and are often studied together. Human anatomy is one of the essential basic sciences that are applied in medicine. The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal's body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)



