|
Szikszó
Szikszó is a small town in Borsod-Abaúj-Zemplén county, Northern Hungary, from county capital Miskolc. It is also the home of the Hell Energy Magyarország Kft. main factory. History Szikszó was first mentioned in documents in 1280. It belonged to the estate of the Aba clan. After 1370 Aba Estates in the area became the property of King Sigismund and then of Queen Mary. At this time Szikszó was already a royal town. The Gothic church of the town was also built around this time. In the 16th century Szikszó and its landowners converted to the Protestant faith and its church became a Protestant one. During the Ottoman occupation of Hungary the town was ransacked and burnt down several times. The citizens fortified the strongest building of the town, the church. Several battles of the Ottoman–Habsburg wars were fought in and around the town. In 1588 there was a battle near the town, where the Hungarian army defeated the Turks. In 1679 the town witnessed another battle, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Szikszó District
Szikszó () is a district in central-northern part of Borsod-Abaúj-Zemplén County. ''Szikszó'' is also the name of the town where the district seat is found. The district is located in the Northern Hungary Statistical Region. Geography Szikszó District borders with Encs District northeast, Szerencs District to the southeast, Miskolc District to the southwest, Edelény District to the west. The number of the inhabited places in Szikszó District is 24. Municipalities The district has 1 town and 23 villages. (ordered by population, as of 1 January 2012) The bolded municipality is the city. Demographics In 2011, it had a population of 17,507 and the population density was 57/km². Ethnicity Besides the Hungarian majority, the main minorities are the Roma (approx. 3,500) and Rusyn (100). Total population (2011 census): 17,507 Ethnic groups (2011 census): Identified themselves: 20,043 persons: *Hungarians: 16,316 (81.40%) * Gypsies: 3,434 (17.13%) *Others and indefina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Szepsi Csombor Márton High School
Szepsi Csombor Márton High School is located in Szikszó, the North-Eastern part of Hungary Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and .... It is a standard school that consists of two main institutions: elementary school and high school. Szepsi Csombor Márton High School also functions as a Training School, Library, Combined Pedagogical Service and Elementary School. History Beginnings The high school was established as a part of the Parish School of Sárospatak in the 1520s. From 1526, the first teacher was György Baccalaureus and after him came András Batizi. From 1538, István Székely Benczédi's and from 1540 Mátyás Bíró Dévai's names were remarkable in the school's history. The school fulfilled a secondary school function from the beginning. Szikszó developed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Districts Of Hungary
Districts of Hungary are the second-level divisions of Hungary after counties. They replaced the 175 subregions of Hungary in 2013. There are 174 districts in the 19 counties, and there are 23 districts in Budapest. Districts of the 19 counties are numbered by Arabic numerals and named after the district seat, while districts of Budapest are numbered by Roman numerals and named after the historical towns and neighbourhoods. In Hungarian, the districts of the capital and the rest of the country hold different titles. The districts of Budapest are called ''kerületek'' (lit. district, pl.) and the districts of the country are called ''járások.'' By county Baranya County Bács-Kiskun County Békés County Borsod-Abaúj-Zemplén County Csongrád-Csanád County Fejér County Győr-Moson-Sopron County Hajdú-Bihar County Heves County Jász-Nagykun-Szolnok County Komárom-Esztergom County Nógrád County Pest County Somogy C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cities And Towns Of Hungary
Hungary has 3,152 Municipality, municipalities as of July 15, 2013: 346 towns (Hungarian term: , plural: ; the terminology does not distinguish between city, cities and towns – the term town is used in official translations) and 2,806 villages (Hungarian: , plural: ) of which 126 are classified as large villages (Hungarian: , plural: ). The number of towns can change, since villages can be elevated to town status by act of the President. The capital Budapest has a special status and is not included in any county while 25 of the towns are so-called City with county rights, cities with county rights. All county seats except Budapest are cities with county rights. Four of the cities (Budapest, Miskolc, Győr, and Pécs) have agglomerations, and the Hungarian Statistical Office distinguishes seventeen other areas in earlier stages of agglomeration development. The largest city is the capital, Budapest, while the smallest town is Pálháza with 1038 inhabitants (2010). The larg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
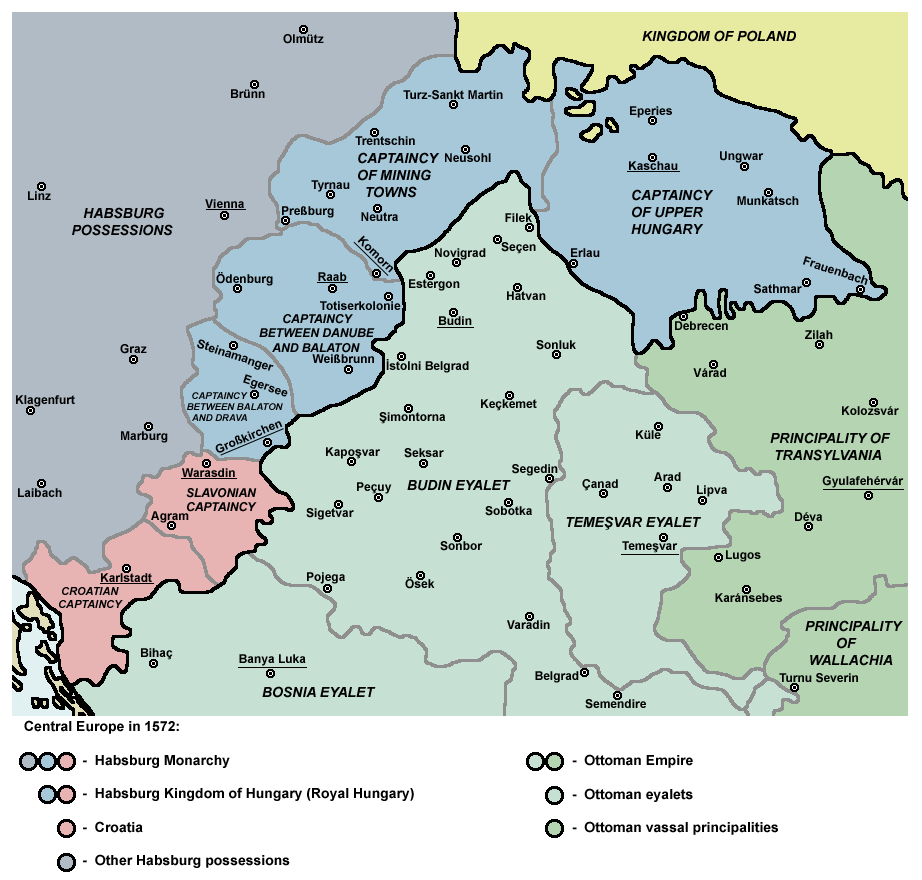
Ottoman–Habsburg Wars
The Ottoman–Habsburg wars were fought from the 16th to the 18th centuries between the Ottoman Empire and the Habsburg monarchy, which was at times supported by the Kingdom of Hungary, Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Holy Roman Empire, The Holy Roman Empire, and Habsburg Spain. The wars were dominated by land campaigns in Hungary, including Transylvania (today in Romania) and Vojvodina (today in Serbia), Kingdom of Croatia (Habsburg), Croatia, and central Serbia. By the 16th century, the Ottomans had become a serious threat to European powers, with Ottoman ships sweeping away Republic of Venice, Venetian possessions in the Aegean Sea, Aegean and Ionian Sea, Ionian seas and Ottoman-supported Barbary pirates seizing Spanish possessions in the Maghreb. The Protestant Reformation, French–Habsburg rivalry and the numerous civil conflicts of the Holy Roman Empire distracted Christians from their conflict with the Ottomans. Meanwhile, the Ottomans had to contend with Safavid Iran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Hungary
Ottoman Hungary () encompassed the parts of the Kingdom of Hungary which were under the rule of the Ottoman Empire from the occupation of Buda in 1541 until the Treaty of Karlowitz in 1699. The territory was incorporated into the empire, under the name ''Macaristan.'' For most of its duration, Ottoman Hungary covered Southern Transdanubia and almost the entire region of the Great Hungarian Plain. Ottoman Hungary was divided for administrative purposes into Eyalets (provinces), which were further divided into Sanjaks. Ownership of much of the land was distributed to Ottoman soldiers and officials with the remaining territory being retained by the Ottoman state. As a border territory, much of Ottoman Hungary was heavily fortified with troop garrisons. Remaining economically under-developed, it became a drain on Ottoman resources. During the centuries long three-way Hungarian–Habsburg–Ottoman wars the Hungarian population was highly decimated. Although there was some immigr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steppe Front
The Steppe Front () was a front of the Red Army during the Second World War which existed from July to October 1943. History On 9 July 1943, Stavka designated a new Reserve Front in the Voronezh region, that had been effective since 30 April.Great Patriotic War 1941–1945, Moscow 1977 It consisted of the command component of the 2nd Reserve Army (augmented by several officer and NCO courses), the 27th, 52nd, 53rd, 46th, 47th, 4th Guards Tank, 5th Air Army and eight mobile corps (Tank, Guards Tank, and Mechanised). Most of these armies had been reassigned from the Northwestern Front, North Caucasus Front, or the Reserve of the Supreme High Command (''Stavka'' reserve, or the RVGK). On 13 April 1943 the Front was renamed the Steppe Military District, to be effective 15 April. The Steppe Military District was redesignated the Steppe Front on July 9, 1943. It incorporated forces from the Soviet rear areas to the West of Kursk salient along the line Tula- Yelets-Stary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army, often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Republic and, from 1922, the Soviet Union. The army was established in January 1918 by a decree of the Council of People's Commissars to oppose the military forces of the new nation's adversaries during the Russian Civil War, especially the various groups collectively known as the White Army. In February 1946, the Red Army (which embodied the main component of the Soviet Armed Forces alongside the Soviet Navy) was renamed the "Soviet Army". Following the dissolution of the Soviet Union it was split between the post-Soviet states, with its bulk becoming the Russian Ground Forces, commonly considered to be the successor of the Soviet Army. The Red Army provided the largest land warfare, ground force in the Allies of World War II, Allied victory in the European theatre of World War II, and its Soviet invasion of Manchuria, invasion of Manchuria assisted the un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungary In World War II
During World War II, the Kingdom of Hungary was a member of the Axis powers. Berlin was already suspicious of the Kállay government, and in September 1943, the German General Staff prepared a project to invade and occupy Hungary. In March 1944, German forces occupied Hungary. When Soviet forces began threatening Hungary, an armistice was signed between Hungary and the USSR by Regent Miklós Horthy. Soon afterward, Horthy's son was kidnapped by German commandos and Horthy was forced to revoke the armistice. The Regent was then deposed from power, while Hungarian fascist leader Ferenc Szálasi established a new government, with German backing. In 1945, Hungarian and German forces in Hungary were defeated by advancing Soviet armies. Approximately 300,000 Hungarian soldiers and more than 600,000 civilians died during World War II, including between 450,000 and 606,000 Jews and 28,000 Roma. Many cities were damaged, most notably the capital Budapest. Most Jews in Hungary were prote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia ( ; Czech language, Czech and , ''Česko-Slovensko'') was a landlocked country in Central Europe, created in 1918, when it declared its independence from Austria-Hungary. In 1938, after the Munich Agreement, the Sudetenland became part of Nazi Germany, while the country lost further territories to First Vienna Award, Hungary and Trans-Olza, Poland (the territories of southern Slovakia with a predominantly Hungarian population to Hungary and Zaolzie with a predominantly Polish population to Poland). Between 1939 and 1945, the state ceased to exist, as Slovak state, Slovakia proclaimed its independence and Carpathian Ruthenia became part of Kingdom of Hungary (1920–1946), Hungary, while the German Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia was proclaimed in the remainder of the Czech Lands. In 1939, after the outbreak of World War II, former Czechoslovak President Edvard Beneš formed Czechoslovak government-in-exile, a government-in-exile and sought recognition from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |