|
Suzhou, Gansu
Suzhou District is a district of the city of Jiuquan, Gansu Province, China. It was an important city in its own right. Today, as the seat of Jiuquan's administration, it is usually marked Jiuquan on maps. Name Suzhou is named for the former Su Prefecture of imperial China. History Su Prefecture was established under the Sui and renamed Jiuquan Commandery under the Tang. Its seat was established just within the extreme northwest angle of the Great Wall near the Jade Gate. It sometimes served as the capital of the province of Gansu. Along with its role protecting trade along the Silk Road, Suzhou was the great center of the rhubarb trade. The old town was completely destroyed in the First Dungan Revolt but was recovered by the Qing in 1873 and was swiftly rebuilt. Administrative divisions Suzhou District is divided to 7 Subdistricts, 14 towns, 1 townships and 3 other. ;Subdistricts ;Towns ;Townships * Huangnipu Township() ;Others * State-owned Xiaheqing Farm() * Ji ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postal Code Of China
Postal codes in the People's Republic of China () are postal codes used by China Post for the delivery of letters and goods within mainland China. China Post uses a six-digit all-numerical system with four tiers: the first tier, composed of the first two digits, show the province, province-equivalent municipality, or autonomous region; the second tier, composed of the third digit, shows the postal zone within the province, municipality or autonomous region; the fourth digit serves as the third tier, which shows the postal office within prefectures or prefecture-level cities; the last two digits are the fourth tier, which indicates the specific mailing area for delivery. The range 000000–009999 was originally marked for Taiwan (The Republic of China) but is not used because it not under the control of the People's Republic of China. Mail to ROC is treated as international mail, and uses postal codes set forth by Chunghwa Post. Codes starting from 999 are the internal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial China
The earliest known written records of the history of China date from as early as 1250 BC, from the Shang dynasty (c. 1600–1046 BC), during the reign of king Wu Ding. Ancient historical texts such as the ''Book of Documents'' (early chapters, 11th century BC), the ''Bamboo Annals'' (c. 296 BC) and the ''Records of the Grand Historian'' (c. 91 BC) describe a Xia dynasty before the Shang, but no writing is known from the period, and Oracle Bone script, Shang writings do not indicate the existence of the Xia. The Shang ruled in the Yellow River valley, which is commonly held to be the cradle of Chinese civilization. However, Neolithic civilizations originated at various cultural centers along both the Yellow River and Yangtze, Yangtze River. These Yellow river civilization, Yellow River and Yangtze civilizations arose millennia before the Shang. With thousands of years of continuous history, China is among the world's oldest civilizations and is regarded as one of the Cradle of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Administrative Divisions Of Gansu
Gansu, a province of the People's Republic of China China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, sli ..., is made up of the following administrative divisions. Administrative divisions These administrative divisions are explained in greater detail at Administrative divisions of the People's Republic of China. The following table lists only the prefecture-level and county-level divisions of Gansu. Recent changes in administrative divisions Population composition Prefectures Counties References {{Counties of China Gansu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suzhou (other)
Suzhou, Jiangsu (江苏苏州), is a prefecture-level city of Jiangsu Province, China. Suzhou may also refer to: *Suzhou, Anhui (安徽宿州), a prefecture-level city of Anhui Province. *Suzhou District (肃州区), a district of Jiuquan City, Gansu Province. *Suzhou Creek (苏州河), a tributary of Huangpu River passing through Shanghai, with its principal outlet in Suzhou, Jiangsu Other uses * ''Suzhou River'' (film), a film by Lou Ye * 2719 Suzhou, an asteroid named after Suzhou, Jiangsu *Suzhou dialect *Suzhou embroidery *Suzhou numerals The Suzhou numerals, also known as ' (), is a numeral system used in China before the introduction of Arabic numerals. The Suzhou numerals are also known as ' (), ' (), ' (), ' () and ' (). History The Suzhou numeral system is the only survivin ... See also * Xuzhou (other) * Suchow (other) {{geodis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qing Dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speaking ethnic group who unified other Jurchen tribes to form a new "Manchu" ethnic identity. The dynasty was officially proclaimed in 1636 in Manchuria (modern-day Northeast China and Outer Manchuria). It seized control of Beijing in 1644, then later expanded its rule over the whole of China proper and Taiwan, and finally expanded into Inner Asia. The dynasty lasted until 1912 when it was overthrown in the Xinhai Revolution. In orthodox Chinese historiography, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the Ming dynasty and succeeded by the Republic of China. The multiethnic Qing dynasty lasted for almost three centuries and assembled the territorial base for modern China. It was the largest imperial dynasty in the history of China and in 1790 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
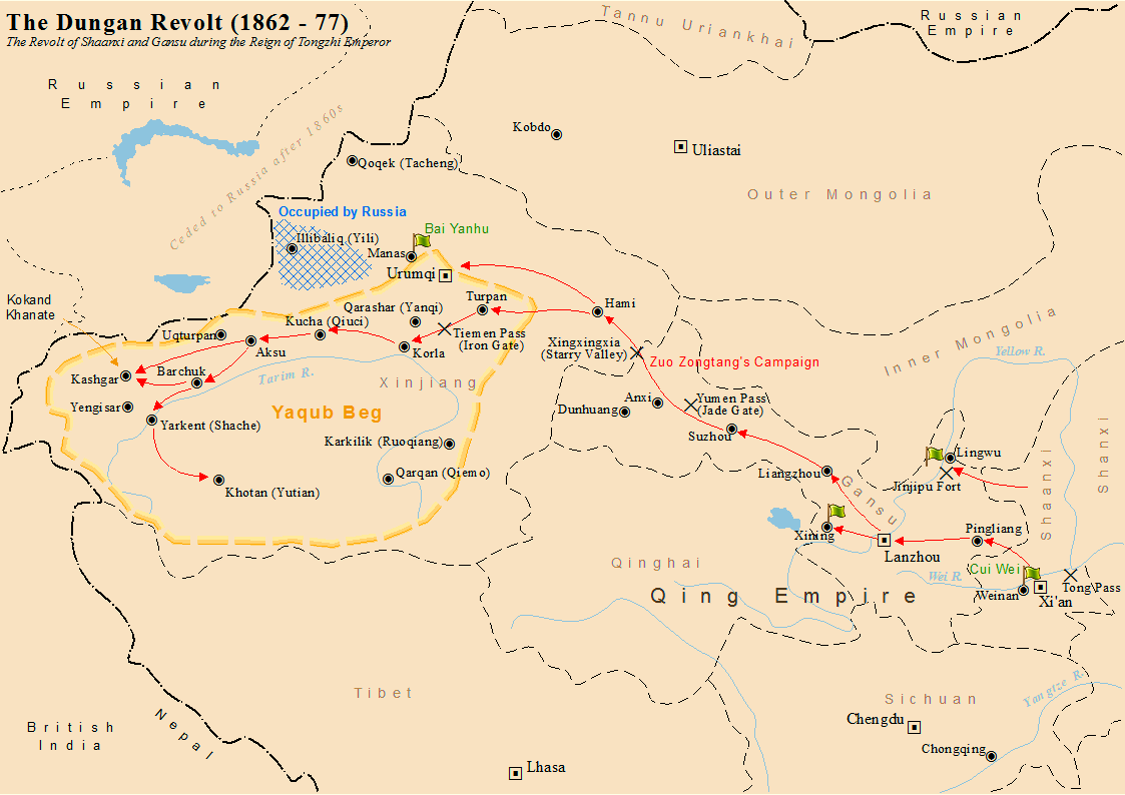
Dungan Revolt (1862–1877)
The Dungan Revolt (1862–1877) or Tongzhi Hui Revolt (, Xiao'erjing: تُجِ خُوِ لُوًا, dng, Тунҗы Хуэй Луан) or Hui (Muslim) Minorities War was a war fought in 19th-century western China, mostly during the reign of the Tongzhi Emperor (r. 1861–1875) of the Qing dynasty. The term sometimes includes the Panthay Rebellion in Yunnan, which occurred during the same period. However, this article refers specifically to two waves of uprising by various Chinese Muslims, mostly Hui people, in Shaanxi, Gansu and Ningxia provinces in the first wave, and then in Xinjiang in the second wave, between 1862 and 1877. The uprising was eventually suppressed by Qing forces led by Zuo Zongtang. The conflict began with riots by the Hui and massacres of the Han Chinese, followed by the revenge massacres of the Hui by the Han. It resulted in massive demographic shifts in Northwest China, and led to a population loss of 21 million people from a combination of mas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhubarb
Rhubarb is the fleshy, edible stalks ( petioles) of species and hybrids (culinary rhubarb) of '' Rheum'' in the family Polygonaceae, which are cooked and used for food. The whole plant – a herbaceous perennial growing from short, thick rhizomes – is also called rhubarb. Historically, different plants have been called "rhubarb" in English. The large, triangular leaves contain high levels of oxalic acid and anthrone glycosides, making them inedible. The small flowers are grouped in large compound leafy greenish-white to rose-red inflorescences. The precise origin of culinary rhubarb is unknown. The species '' Rheum rhabarbarum'' (syn. ''R. undulatum'') and '' R. rhaponticum'' were grown in Europe before the 18th century and used for medicinal purposes. By the early 18th century, these two species and a possible hybrid of unknown origin, ''R.'' × ''hybridum'', were grown as vegetable crops in England and Scandinavia. They readily hybridize, and cul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and religious interactions between the East and West. The name "Silk Road", first coined in the late 19th century, has fallen into disuse among some modern historians in favor of Silk Routes, on the grounds that it more accurately describes the intricate web of land and sea routes connecting East and Southeast Asia, the Indian subcontinent, Central Asia, the Middle East, East Africa and Europe. The Silk Road derives its name from the highly lucrative trade of silk textiles that were produced almost exclusively in China. The network began with the Han dynasty's expansion into Central Asia around 114 BCE, which largely pacified the once untamed region. Imperial envoy Zhang Qian was commissioned to explore the unknown lands beyond the re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yumen Pass
Yumen Pass (; Uyghur: قاش قوۋۇق), or Jade Gate or Pass of the Jade Gate, is the name of a pass of the Great Wall located west of Dunhuang in today's Gansu Province of China. During the Han dynasty (202 BC – AD 220), this was a pass through which the Silk Road passed, and was the one road connecting Central Asia with East Asia (China), the former called the Western Regions. Just to the south was the Yangguan pass, which was also an important point on the Silk Road. These passes, along with other sites along the Silk Road, were inscribed in 2014 on the UNESCO World Heritage List as the Silk Roads: the Routes Network of Chang'an-Tianshan Corridor World Heritage Site. The pass is at an elevation of 1400 meters. Etymology Although the Chinese ''guan'' is usually translated simply as "pass", its more specific meaning is a "frontier pass" to distinguish it from an ordinary pass through the mountains. ''Yumen guan'' 玉門關 and ''Yang guan'' 陽關 are derived fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Wall Of China
The Great Wall of China (, literally "ten thousand ''li'' wall") is a series of fortifications that were built across the historical northern borders of ancient Chinese states and Imperial China as protection against various nomadic groups from the Eurasian Steppe. Several walls were built from as early as the 7th century BC, with selective stretches later joined by Qin Shi Huang (220–206 BC), the first emperor of China. Little of the Qin wall remains. Later on, many successive dynasties built and maintained multiple stretches of border walls. The best-known sections of the wall were built by the Ming dynasty (1368–1644). Apart from defense, other purposes of the Great Wall have included border controls, allowing the imposition of duties on goods transported along the Silk Road, regulation or encouragement of trade and the control of immigration and emigration. Furthermore, the defensive characteristics of the Great Wall were enhanced by the construction of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tang Dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. Historians generally regard the Tang as a high point in Chinese civilization, and a golden age of cosmopolitan culture. Tang territory, acquired through the military campaigns of its early rulers, rivaled that of the Han dynasty. The Lǐ family () founded the dynasty, seizing power during the decline and collapse of the Sui Empire and inaugurating a period of progress and stability in the first half of the dynasty's rule. The dynasty was formally interrupted during 690–705 when Empress Wu Zetian seized the throne, proclaiming the Wu Zhou dynasty and becoming the only legitimate Chinese empress regnant. The devastating An Lushan Rebellion (755–763) shook the nation and led to the decline of central authority in the dynas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jiuquan Commandery
Jiuquan, formerly known as Suzhou, is a prefecture-level city in the northwesternmost part of Gansu Province in the People's Republic of China. It is more than wide from east to west, occupying , although its built-up area is mostly located in its Suzhou District. At the end of 2021, the province's resident population was 24.9002 million, a decrease of 110,000 compared with the end of the previous year, of which: male population was 12.6601 million, female population was 12.2401 million, and the population sex ratio was 103.43 (females were 100). Name The city was formerly known as Fulu, which became known as Suzhou (Suchow, Su-chow, &c.) after it became the seat of Su Prefecture under the Sui.485 As the seat of |


_Frambozenrood_bloeiwijze.jpg)



