|
Surmang
Surmang (or Zurmang) refers to a vast alpine nomadic and farming region, historically a duchy under the King of Nangqên, Nangchen, with vast land holdings spreading over what is today the Tibet Autonomous Region and Qinghai Province. In Tibetan the King of Nangchen's realm was called the "nyishu dza nga" or the 21 (provinces). Since 1959 it is mainly within the Yushu Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture of Qinghai province in China (historically part of Kham, eastern Tibet). Yushu Prefecture is 97% ethnic Tibetan. The Surmang region is one of the poorest regions in China ranking it among the world's highest infant and maternal mortality, almost 100% illiteracy, and personal income of less than US 14¢/day. It is part of the catchment in China of the 30 million ultra-poor. Surmang also refers to a complex of nine or ten Kagyu monasteries (gompas) in that area. These include: Surmang Namgyal Tse, Surmang Dutsi Til, Surmang Do Gompa, Surmang Doka Gompa, Surmang Kyere Gompa. The lineage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chögyam Trungpa
Chögyam Trungpa (Wylie transliteration, Wylie: ''Chos rgyam Drung pa''; March 5, 1939 – April 4, 1987), formally named the 11th Zurmang Trungpa, Chokyi Gyatso, was a Tibetan Buddhism, Tibetan Buddhist master and holder of both Kagyu and Nyingma lineages of Tibetan Buddhism. He was recognized by both Tibetan Buddhists and other spiritual practitioners and scholars as a preeminent teacher of Tibetan Buddhism. He was a major figure in the dissemination of Buddhism in the West, founding Vajradhatu and Naropa University and establishing the Shambhala Training method. The 11th of the Trungpa tülkus, he was a tertön, supreme abbot of the Surmang, Surmang monasteries, scholar, teacher, poet, artist, and originator of Shambhala Buddhist tradition. Among Trungpa's contributions are the translation of numerous Tibetan Buddhist canon, Tibetan Buddhist texts, the introduction of the Vajrayana, Vajrayana teachings to the West, and a presentation of Buddhism largely devoid of traditional tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choseng Trungpa
Choseng Trungpa Rinpoche, formally the 12th Zurmang Trungpa, Chokyi Sengye, is the 12th and current Trungpa lineage holder. He was born on February 6, 1989, in Pawo village, in Derge, eastern Tibet. He was recognized by the 12th Tai Situ Rinpoche in 1991, and enthroned a year later at Surmang Monastery at a ceremony presided over by Domkhar Rinpoche, a high Kagyu Rinpoche, and Choseng Trungpa's uncle. The monastery's late Rinpoche and Choseng Trungpa's predecessor, was Chogyam Trungpa Rinpoche. The name Choseng is a contraction of Chokyi Sengye (), which means "Lion of Dharma." Choseng Trungpa studied the traditions of Surmang under the tutelage of Lama Kenla (1932–2003) and received his early monastic education at the Shedra at Palpung Monastery. He studied at Surmang Namgyal-tse until 2008, and then began studies at Serthar Institute. In 2001, he met for the first time with Sakyong Mipham Rinpoche, the first son of his previous incarnation, Chögyam Trungpa. See also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarmoung
The Sarmoung Brotherhood was an alleged esoteric Sufi brotherhood based in Asia. The reputed existence of the brotherhood was brought to light in the writings of George Gurdjieff, a Greek-Armenian spiritual teacher. Some contemporary Sufi-related sources also claim to have made contact with the group although the earliest and primary source is Gurdjieff himself, leading most scholars to conclude the group was fictional. Name According to the author John G. Bennett, a student and aide of George Gurdjieff who first mentioned the concept, the word ''sarmoung'' uses the Armenian pronunciation of the Persian term ''sarman'', which may mean either "he who preserves the doctrine of Zoroaster" or " bee".Bennett, John G., ''Gurdjieff: Making of A New World'', pp 56-57, Bennett Pub. Co., 1992. . Regarding the meaning, Bennett writes: "The word can be interpreted in three ways. It is the word for bee, which has always been a symbol of those who collect the precious 'honey' of tradition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trungpa Tülkus
The Trungpa tülkus are a line of incarnate Tibetan lamas who traditionally head Surmang monastery complex in Kham, now Surmang. There have been twelve such Trungpa tulkus. They are members of the Karma Kagyu tradition as well as the Nyingma tradition. Line of the Trungpa tulkus # Künga Gyaltsen (15th century), student of Trungmase # Künga Sangpo (born 1464) # Künga Öser (15th and 16th centuries) # Künga Namgyal (1567–1629) # Tenpa Namgyal (1633–1712) # Tendzin Chökyi Gyatso (1715–1761) # Jampal Chökyi Gyatso (1763–1768) # Gyurme Thenphel (born 1771) # Tenpa Rabgye (19th century) # Chökyi Nyinche (1879–1939) # Chögyam Trungpa (Chökyi Gyamtso, 1940–1987) was one of the most influential teachers of Buddhism in the West. He founded Shambhala Buddhism. # Choseng Trungpa (Chökyi Sengye, born February 6, 1989) is the present Trungpa tülku. Chökyi Nyinche According to Fabrice Midal, the tenth Trungpa tulku rejected his role as fundraiser for the Surmang monaste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
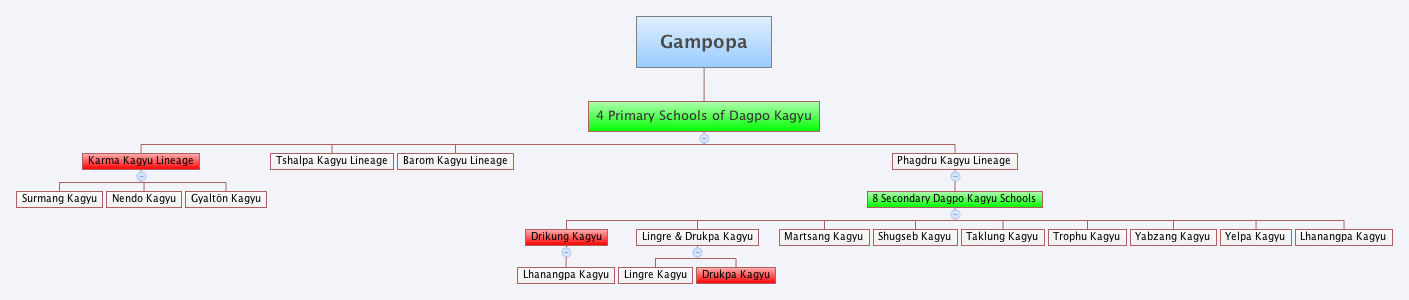
Kagyu Monasteries And Temples
The ''Kagyu'' school, also transliterated as ''Kagyü'', or ''Kagyud'' (), which translates to "Oral Lineage" or "Whispered Transmission" school, is one of the main schools (''chos lugs'') of Tibetan (or Himalayan) Buddhism. The Kagyu lineages trace themselves back to the 11th century Indian Mahasiddhas Naropa, Maitripa and the yogini Niguma, via their student Marpa Lotsawa (1012–1097), who brought their teachings to Tibet. Marpa's student Milarepa was also an influential poet and teacher. The Tibetan Kagyu tradition gave rise to a large number of independent sub-schools and lineages. The principal Kagyu lineages existing today as independent schools are those which stem from Milarepa's disciple, Gampopa (1079–1153), a monk who merged the Kagyu lineage with the Kadam tradition. The Kagyu schools which survive as independent institutions are mainly the Karma Kagyu, Drikung Kagyu, Drukpa Lineage and the Taklung Kagyu. The Karma Kagyu school is the largest of the sub-scho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tulku
A ''tulku'' (, also ''tülku'', ''trulku'') is an individual recognized as the reincarnation of a previous spiritual master (lama), and expected to be reincarnated, in turn, after death. The tulku is a distinctive and significant aspect of Tibetan Buddhism, embodying the concept of enlightened beings taking corporeal forms to continue the lineage of specific teachings. The term "tulku" is a loanword from Tibetan སྤྲུལ་སྐུ ("sprul sku"), which originally referred to an emperor or ruler taking human form on Earth, signifying a divine incarnation. Over time, it evolved within Tibetan Buddhism to denote the corporeal existence of certain highly accomplished Buddhist masters whose purpose was to ensure the preservation and transmission of a particular lineage. The tulku system originated in Tibet, particularly associated with the recognition of the second Karmapa in the 13th century. Since then, numerous tulku lineages have been established, with each tulku having a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kagyu
The ''Kagyu'' school, also transliterated as ''Kagyü'', or ''Kagyud'' (), which translates to "Oral Lineage" or "Whispered Transmission" school, is one of the main schools (''chos lugs'') of Tibetan Buddhism, Tibetan (or Himalayan) Buddhism. The Kagyu lineages trace themselves back to the 11th century Indian Mahasiddhas Naropa, Maitripa and the yogini Niguma, via their student Marpa Lotsawa (1012–1097), who brought their teachings to Tibet. Marpa's student Milarepa was also an influential poet and teacher. The Tibetan Kagyu tradition gave rise to a large number of independent sub-schools and lineages. The principal Kagyu lineages existing today as independent schools are those which stem from Milarepa's disciple, Gampopa (1079–1153), a monk who merged the Kagyu lineage with the Kadam (Tibetan Buddhism), Kadam tradition. The Kagyu schools which survive as independent institutions are mainly the Karma Kagyu, Drikung Kagyu, Drukpa Lineage and the Taklung Kagyu. The Karma Kag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gharwang
Prior to his birth on 30 June 1965, Zurmang Gharwang Rinpoche () was recognized by the 16th Karmapa, Rangjung Rigpe Dorje as the twelfth incarnation of the Gharwang Tulkus and as an emanation of Tilopa. He is the supreme lineage holder of the Zurmang Ear Whispered Lineage (zur mang snyan rgyud). The unbroken line of the Gharwang Tulkus begins in the 14th century with the siddha Trung Mase, the first Gharwang Tulku and founder of the Zurmang Kagyu tradition and Zurmang Monastery. He was identified by the 5th Karmapa, Deshin Shekpa as the omniscient emanation of the Indian mahasiddha Tilopa. This was believed to be the fulfillment of Tilopa's prediction made after he received teachings directly from Vajrayogini in the Western land of Uddiyana, in which he had pledged to return to spread these teachings widely, after they had been transmitted through thirteen successive lineage holders. Before Tilopa's return this set of teachings was to be limited to a one-to-one transmission fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhist Monasteries In Qinghai
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or 5th century Before the Common Era, BCE. It is the Major religious groups, world's fourth-largest religion, with about 500 million followers, known as Buddhists, who comprise four percent of the global population. It arose in the eastern Gangetic plain as a movement in the 5th century BCE, and gradually spread throughout much of Asia. Buddhism has subsequently played a major role in Asian culture and spirituality, eventually spreading to Western world, the West in the 20th century. According to tradition, the Buddha instructed his followers in a path of bhavana, development which leads to Enlightenment in Buddhism, awakening and moksha, full liberation from ''Duḥkha, dukkha'' (). He regarded this path as a Middle Way between extremes su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |