|
Supersaturated
In physical chemistry, supersaturation occurs with a solution when the concentration of a solute exceeds the concentration specified by the value of solubility at equilibrium. Most commonly the term is applied to a solution of a solid in a liquid, but it can also be applied to liquids and gases dissolved in a liquid. A supersaturated solution is in a metastable state; it may return to equilibrium by separation of the excess of solute from the solution, by dilution of the solution by adding solvent, or by increasing the solubility of the solute in the solvent. History Early studies of the phenomenon were conducted with sodium sulfate, also known as Glauber's Salt because, unusually, the solubility of this salt in water may decrease with increasing temperature. Early studies have been summarised by Tomlinson. It was shown that the crystallization of a supersaturated solution does not simply come from its agitation, (the previous belief) but from solid matter entering and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleation
In thermodynamics, nucleation is the first step in the formation of either a new Phase (matter), thermodynamic phase or Crystal structure, structure via self-assembly or self-organization within a substance or mixture. Nucleation is typically defined to be the process that determines how long an observer has to wait before the new phase or self-organized structure appears. For example, if a volume of water is cooled (at atmospheric pressure) significantly below 0°C, it will tend to Freezing, freeze into ice, but volumes of water cooled only a few degrees below 0°C often stay completely free of ice for long periods (supercooling). At these conditions, nucleation of ice is either slow or does not occur at all. However, at lower temperatures nucleation is fast, and ice crystals appear after little or no delay. Nucleation is a common mechanism which generates first-order phase transitions, and it is the start of the process of forming a new thermodynamic phase. In contrast, new phas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solubility Equilibrium
Solubility equilibrium is a type of dynamic equilibrium that exists when a chemical compound in the solid state is in chemical equilibrium with a solution of that compound. The solid may dissolve unchanged, with dissociation, or with chemical reaction with another constituent of the solution, such as acid or alkali. Each solubility equilibrium is characterized by a temperature-dependent ''solubility product'' which functions like an equilibrium constant. Solubility equilibria are important in pharmaceutical, environmental and many other scenarios. Definitions A solubility equilibrium exists when a chemical compound in the solid state is in chemical equilibrium with a solution containing the compound. This type of equilibrium is an example of dynamic equilibrium in that some individual molecules migrate between the solid and solution phases such that the rates of dissolution and precipitation are equal to one another. When equilibrium is established and the solid has not al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
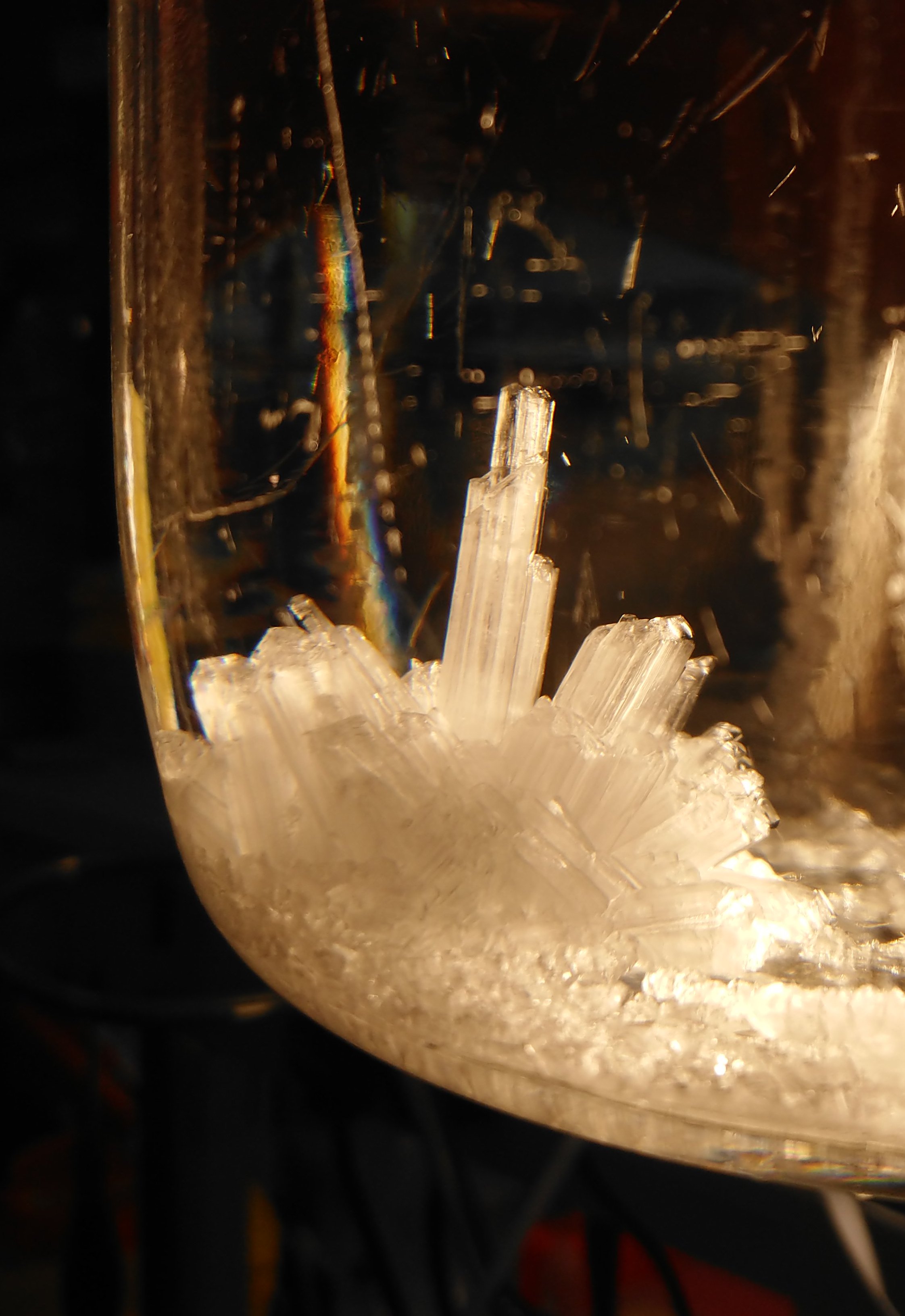
Crystallized Sugar, Multiple Crystals And A Single Crystal Grown From Seed
Crystallization is a process that leads to solids with highly organized atoms or molecules, i.e. a crystal. The ordered nature of a crystalline solid can be contrasted with amorphous solids in which atoms or molecules lack regular organization. Crystallization can occur by various routes including precipitation from solution, freezing of a liquid, or deposition from a gas. Attributes of the resulting crystal can depend largely on factors such as temperature, air pressure, cooling rate, or solute concentration. Crystallization occurs in two major steps. The first is nucleation, the appearance of a crystalline phase from either a supercooled liquid or a supersaturated solvent. The second step is known as crystal growth, which is the increase in the size of particles and leads to a crystal state. An important feature of this step is that loose particles form layers at the crystal's surface and lodge themselves into open inconsistencies such as pores, cracks, etc. Crystallizatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solute
In chemistry, a solution is defined by IUPAC as "A liquid or solid phase containing more than one substance, when for convenience one (or more) substance, which is called the solvent, is treated differently from the other substances, which are called solutes. When, as is often but not necessarily the case, the sum of the mole fractions of solutes is small compared with unity, the solution is called a dilute solution. A superscript attached to the ∞ symbol for a property of a solution denotes the property in the limit of infinite dilution." One important parameter of a solution is the concentration, which is a measure of the amount of solute in a given amount of solution or solvent. The term "aqueous solution" is used when one of the solvents is water. Types ''Homogeneous'' means that the components of the mixture form a single phase. ''Heterogeneous'' means that the components of the mixture are of different phase. The properties of the mixture (such as concentration, tempe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solubility
In chemistry, solubility is the ability of a chemical substance, substance, the solute, to form a solution (chemistry), solution with another substance, the solvent. Insolubility is the opposite property, the inability of the solute to form such a solution. The extent of the solubility of a substance in a specific solvent is generally measured as the concentration of the solute in a wikt:saturated#Chemistry, saturated solution, one in which no more solute can be dissolved. At this point, the two substances are said to be at the solubility equilibrium. For some solutes and solvents, there may be no such limit, in which case the two substances are said to be "miscibility, miscible in all proportions" (or just "miscible"). The solute can be a solid, a liquid, or a gas, while the solvent is usually solid or liquid. Both may be pure substances, or may themselves be solutions. Gases are always miscible in all proportions, except in very extreme situations,J. de Swaan Arons and G. A. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saturated Solution
In chemistry, solubility is the ability of a substance, the solute, to form a solution with another substance, the solvent. Insolubility is the opposite property, the inability of the solute to form such a solution. The extent of the solubility of a substance in a specific solvent is generally measured as the concentration of the solute in a saturated solution, one in which no more solute can be dissolved. At this point, the two substances are said to be at the solubility equilibrium. For some solutes and solvents, there may be no such limit, in which case the two substances are said to be " miscible in all proportions" (or just "miscible"). The solute can be a solid, a liquid, or a gas, while the solvent is usually solid or liquid. Both may be pure substances, or may themselves be solutions. Gases are always miscible in all proportions, except in very extreme situations,J. de Swaan Arons and G. A. M. Diepen (1966): "Gas—Gas Equilibria". ''Journal of Chemical Physics'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supernatant
In an aqueous solution, precipitation is the "sedimentation of a solid material (a precipitate) from a liquid solution". The solid formed is called the precipitate. In case of an inorganic chemical reaction leading to precipitation, the chemical reagent causing the solid to form is called the precipitant. The clear liquid remaining above the precipitated or the centrifuged solid phase is also called the supernate or supernatant. The notion of precipitation can also be extended to other domains of chemistry (organic chemistry and biochemistry) and even be applied to the solid phases (e.g. metallurgy and alloys) when solid impurities segregate from a solid phase. Supersaturation The precipitation of a compound may occur when its concentration exceeds its solubility. This can be due to temperature changes, solvent evaporation, or by mixing solvents. Precipitation occurs more rapidly from a strongly supersaturated solution. The formation of a precipitate can be caused by a che ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystals
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macroscopic single crystals are usually identifiable by their geometrical shape, consisting of flat faces with specific, characteristic orientations. The scientific study of crystals and crystal formation is known as crystallography. The process of crystal formation via mechanisms of crystal growth is called crystallization or solidification. The word ''crystal'' derives from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning both "ice" and " rock crystal", from (), "icy cold, frost". Examples of large crystals include snowflakes, diamonds, and table salt. Most inorganic solids are not crystals but polycrystals, i.e. many microscopic crystals fused together into a single solid. Polycrystals include most metals, rocks, ceramics, and ice. A third category of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recrystallization (chemistry)
Recrystallization is a broad class of List of purification methods in chemistry , chemical purification techniques characterized by the dissolution of an impure sample in a solvent or solvent mixture, followed by some change in conditions that encourages the formation of pure isolate as solid crystals. Recrystallization as a purification technique is driven by spontaneous process , spontaneous processes of molecular self-assembly , self-assembly that leverage the highly ordered (i.e. low-entropy) and periodic characteristics of a crystal's molecular structure to produce purification. Basic principles The driving force of this purification emerges from the difference in molecular interactions between the isolate and the impurities: if a molecule of the desired isolate interacts with any isolate crystal present, it is likely the molecule Deposition (chemistry) , deposits on the crystal's ordered surface and contributes to the crystal's growth; if a molecule of the impurity inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Chemistry
Physical chemistry is the study of macroscopic and microscopic phenomena in chemical systems in terms of the principles, practices, and concepts of physics such as motion, energy, force, time, thermodynamics, quantum chemistry, statistical mechanics, analytical dynamics and chemical equilibria. Physical chemistry, in contrast to chemical physics, is predominantly (but not always) a supra-molecular science, as the majority of the principles on which it was founded relate to the bulk rather than the molecular or atomic structure alone (for example, chemical equilibrium and colloids). Some of the relationships that physical chemistry strives to understand include the effects of: # Intermolecular forces that act upon the physical properties of materials ( plasticity, tensile strength, surface tension in liquids). # Reaction kinetics on the rate of a reaction. # The identity of ions and the electrical conductivity of materials. # Surface science and electrochemistry of cell m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Filtration
Filtration is a physical separation process that separates solid matter and fluid from a mixture using a ''filter medium'' that has a complex structure through which only the fluid can pass. Solid particles that cannot pass through the filter medium are described as ''oversize'' and the fluid that passes through is called the ''filtrate''. Oversize particles may form a filter cake on top of the filter and may also block the filter lattice, preventing the fluid phase from crossing the filter, known as ''blinding''. The size of the largest particles that can successfully pass through a filter is called the effective ''pore size'' of that filter. The separation of solid and fluid is imperfect; solids will be contaminated with some fluid and filtrate will contain fine particles (depending on the pore size, filter thickness and biological activity). Filtration occurs both in nature and in engineered systems; there are biological, geological, and industrial forms. In everyday us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |