|
Solubility Equilibrium
Solubility equilibrium is a type of dynamic equilibrium that exists when a chemical compound in the solid state is in chemical equilibrium with a solution of that compound. The solid may dissolve unchanged, with dissociation, or with chemical reaction with another constituent of the solution, such as acid or alkali. Each solubility equilibrium is characterized by a temperature-dependent ''solubility product'' which functions like an equilibrium constant. Solubility equilibria are important in pharmaceutical, environmental and many other scenarios. Definitions A solubility equilibrium exists when a chemical compound in the solid state is in chemical equilibrium with a solution containing the compound. This type of equilibrium is an example of dynamic equilibrium in that some individual molecules migrate between the solid and solution phases such that the rates of dissolution and precipitation are equal to one another. When equilibrium is established and the solid has not al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamic Equilibrium
In chemistry, a dynamic equilibrium exists once a reversible reaction occurs. Substances initially transition between the reactants and products at different rates until the forward and backward reaction rates eventually equalize, meaning there is no net change. Reactants and products are formed at such a rate that the concentration of neither changes. It is a particular example of a system in a steady state. Examples In a new bottle of soda, the concentration of carbon dioxide in the liquid phase has a particular value. If half of the liquid is poured out and the bottle is sealed, carbon dioxide will leave the liquid phase at an ever-decreasing rate, and the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the gas phase will increase until equilibrium is reached. At that point, due to thermal motion, a molecule of CO2 may leave the liquid phase, but within a very short time another molecule of CO2 will pass from the gas to the liquid, and vice versa. At equilibrium, the rate of tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadratic Equation
In mathematics, a quadratic equation () is an equation that can be rearranged in standard form as ax^2 + bx + c = 0\,, where the variable (mathematics), variable represents an unknown number, and , , and represent known numbers, where . (If and then the equation is linear equation, linear, not quadratic.) The numbers , , and are the ''coefficients'' of the equation and may be distinguished by respectively calling them, the ''quadratic coefficient'', the ''linear coefficient'' and the ''constant coefficient'' or ''free term''. The values of that satisfy the equation are called ''solution (mathematics), solutions'' of the equation, and ''zero of a function, roots'' or ''zero of a function, zeros'' of the quadratic function on its left-hand side. A quadratic equation has at most two solutions. If there is only one solution, one says that it is a double root. If all the coefficients are real numbers, there are either two real solutions, or a single real double root, or two comple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver Chloride
Silver chloride is an inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula Ag Cl. This white crystalline solid is well known for its low solubility in water and its sensitivity to light. Upon illumination or heating, silver chloride converts to silver (and chlorine), which is signaled by grey to black or purplish coloration in some samples. AgCl occurs naturally as the mineral chlorargyrite. It is produced by a metathesis reaction for use in photography and in pH meters as electrodes. Preparation Silver chloride is unusual in that, unlike most chloride salts, it has very low solubility. It is easily synthesized by metathesis: combining an aqueous solution of silver nitrate (which is soluble) with a soluble chloride salt, such as sodium chloride (which is used industrially as a method of producing AgCl), or cobalt(II) chloride. The silver chloride that forms will precipitate immediately. : : It can also be produced by the reaction of silver metal and aqua regia; howev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common-ion Effect
In chemistry, the common-ion effect refers to the decrease in solubility of an ionic precipitate by the addition to the solution of a soluble compound with an ion in common with the precipitate. This behaviour is a consequence of Le Chatelier's principle for the equilibrium reaction of the ionic association/ dissociation. The effect is commonly seen as an effect on the solubility of salts and other weak electrolytes. Adding an additional amount of one of the ions of the salt generally leads to increased precipitation of the salt, which reduces the concentration of both ions of the salt until the solubility equilibrium is reached. The effect is based on the fact that both the original salt and the other added chemical have one ion in common with each other. Examples of the common-ion effect Dissociation of hydrogen sulfide in presence of hydrochloric acid Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is a weak electrolyte. It is partially ionized when in aqueous solution, therefore there exists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mole Fraction
In chemistry, the mole fraction or molar fraction, also called mole proportion or molar proportion, is a quantity defined as the ratio between the amount of a constituent substance, ''ni'' (expressed in unit of moles, symbol mol), and the total amount of all constituents in a mixture, ''n''tot (also expressed in moles): :x_i = \frac It is denoted ''xi'' (lowercase Roman letter '' x''), sometimes (lowercase Greek letter chi). (For mixtures of gases, the letter ''y'' is recommended.) It is a dimensionless quantity with dimension of \mathsf/\mathsf and dimensionless unit of moles per mole (mol/mol or molmol−1) or simply 1; metric prefixes may also be used (e.g., nmol/mol for 10−9). When expressed in percent, it is known as the mole percent or molar percentage (unit symbol %, sometimes "mol%", equivalent to cmol/mol for 10−2). The mole fraction is called amount fraction by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) and amount-of-substance fractio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Atkins
Peter William Atkins (born 10 August 1940) is an English chemist and a Fellow of Lincoln College at the University of Oxford. He retired in 2007. He is a prolific writer of popular chemistry textbooks, including ''Physical Chemistry'', ''Inorganic Chemistry'', and ''Molecular Quantum Mechanics''. Atkins is also the author of a number of popular science books, including ''Atkins' Molecules'', ''Galileo's Finger: The Ten Great Ideas of Science'' and ''On Being''. Career Atkins left school ( Dr Challoner's Grammar School, Amersham) at fifteen and took a job at Monsanto as a laboratory assistant. He studied for A-levels by himself and gained a place, following a last-minute interview, at the University of Leicester. Atkins studied chemistry there, obtaining a BSc degree in chemistry, and a PhD degree in 1964 for research into electron spin resonance spectroscopy, and other aspects of theoretical chemistry. Atkins then took a postdoctoral position at UCLA as a Harkness Fell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kenneth Denbigh
Kenneth George Denbigh FRS (30 May 1911 – 23 January 2004) was an English Chemist and scientific philosopher. He wrote much on the issue of time in relation to thermodynamics. He was an associate of the Russian chemist Georgi Gladyshev. The University of Edinburgh named the Kenneth Denbigh Building at King's Buildings in his honour. They also offer a Kenneth Denbigh Scholarship to science students. ThSchool of Engineering of The University of Edinburghawards the Kenneth Denbigh Medal in support of his scientific legacy. The Medal has been first established in 2023 and awarded during th10th Heat Powered Cycles Conference Life He was born in Luton on 30 May 1911 the son of George Denbigh, manager of Brothertons Chemical Works in Wakefield. He attended the University of Leeds graduating with a BSc in 1932. He then undertook his doctorate under Robert Whytlaw-Gray gaining a PhD in 1934. He worked for Imperial Chemical Industries (ICI) until 1938 when obtained a post of Lectu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
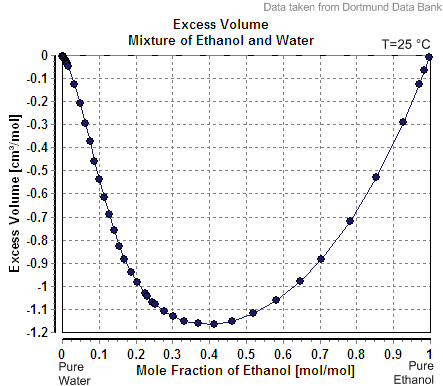
Partial Molar Enthalpy
In thermodynamics, a partial molar property is a quantity which describes the variation of an extensive property of a solution or mixture with changes in the molar composition of the mixture at constant temperature and pressure. It is the partial derivative of the extensive property with respect to the amount (number of moles) of the component of interest. Every extensive property of a mixture has a corresponding partial molar property. Definition The partial molar volume is broadly understood as the contribution that a component of a mixture makes to the overall volume of the solution. However, there is more to it than this: When one mole of water is added to a large volume of water at 25 °C, the volume increases by 18 cm3. The molar volume of pure water would thus be reported as 18 cm3 mol−1. However, addition of one mole of water to a large volume of pure ethanol results in an increase in volume of only 14 cm3. The reason that the increase is differe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Sulfate
Sodium sulfate (also known as sodium sulphate or sulfate of soda) is the inorganic compound with formula Na2SO4 as well as several related hydrates. All forms are white solids that are highly soluble in water. With an annual production of 6 million tonnes, the decahydrate is a major commodity chemical product. It is mainly used as a filler in the manufacture of powdered home laundry detergents and in the Kraft process of paper pulping for making highly alkaline sulfides. Forms *Anhydrous sodium sulfate, known as the rare mineral thénardite, used as a drying agent in organic synthesis. *Heptahydrate sodium sulfate, a very rare form. *Decahydrate sodium sulfate, known as the mineral mirabilite, widely used by chemical industry. It is also known as Glauber's salt. History The decahydrate of sodium sulfate is known as Glauber's salt after the Netherlands, Dutch–Germany, German chemist and apothecary Johann Rudolf Glauber (1604–1670), who discovered it in Austrian spring water i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exothermic
In thermodynamics, an exothermic process () is a thermodynamic process or reaction that releases energy from the system to its surroundings, usually in the form of heat, but also in a form of light (e.g. a spark, flame, or flash), electricity (e.g. a battery), or sound (e.g. explosion heard when burning hydrogen). The term ''exothermic'' was first coined by 19th-century French chemist Marcellin Berthelot. The opposite of an exothermic process is an endothermic process, one that absorbs energy, usually in the form of heat. The concept is frequently applied in the physical sciences to chemical reactions where chemical bond energy is converted to thermal energy (heat). Two types of chemical reactions Exothermic and endothermic describe two types of chemical reactions or systems found in nature, as follows: Exothermic An exothermic reaction occurs when heat is released to the surroundings. According to the IUPAC, an exothermic reaction is "a reaction for which the overall stand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recrystallization (chemistry)
Recrystallization is a broad class of List of purification methods in chemistry , chemical purification techniques characterized by the dissolution of an impure sample in a solvent or solvent mixture, followed by some change in conditions that encourages the formation of pure isolate as solid crystals. Recrystallization as a purification technique is driven by spontaneous process , spontaneous processes of molecular self-assembly , self-assembly that leverage the highly ordered (i.e. low-entropy) and periodic characteristics of a crystal's molecular structure to produce purification. Basic principles The driving force of this purification emerges from the difference in molecular interactions between the isolate and the impurities: if a molecule of the desired isolate interacts with any isolate crystal present, it is likely the molecule Deposition (chemistry) , deposits on the crystal's ordered surface and contributes to the crystal's growth; if a molecule of the impurity inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |