|
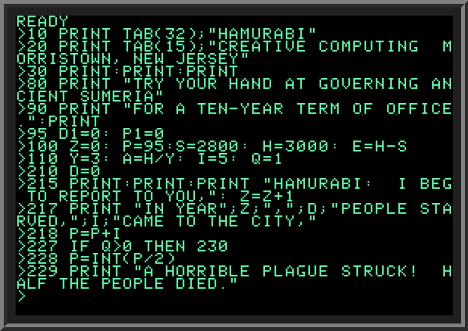
SuperBASIC
SuperBASIC is an advanced variant of the BASIC programming language with many structured programming additions. It was developed at Sinclair Research by Jan Jones during the early 1980s. Originally SuperBASIC was intended as the BASIC interpreter for a home computer code-named ''SuperSpectrum'', then under development. This project was later cancelled; however, SuperBASIC was subsequently included in the ROM firmware of the Sinclair QL microcomputer (announced in January 1984), also serving as the command line interpreter for the QL's QDOS operating system An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs. Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for .... It was one of the first second-generation BASICs to be integrated into a microcomputer's operating system (unlike BBC BASIC which preceded it in 1981), making the OS user-e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinclair QL
The Sinclair QL (for ''Quantum Leap'') is a personal computer launched by Sinclair Research in 1984, as an upper-end counterpart to the ZX Spectrum. The QL was the last desktop microcomputer from Sinclair Research aimed at the serious home user and professional and executive users markets from small to medium-sized businesses and higher educational establishments, but failed to achieve commercial success. While the ZX Spectrum has an 8-bit Zilog Z80 as the CPU, the QL uses a Motorola 68008. The 68008 is a member of the Motorola 68000 family with 32-bit internal data registers, but an 8-bit external data bus characteristic of microcomputers. History Development The QL was conceived in 1981 under the code name ''ZX83'', as a portable computer for business users, with a built-in ultra-thin flat-screen CRT display similar to the later TV80 pocket TV, printer and modem. As development progressed it eventually became clear that the portability features were over-ambitious ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinclair QDOS
QDOS is the multitasking operating system found on the Sinclair QL personal computer and its clones. It was designed by Tony Tebby whilst working at Sinclair Research, as an in-house alternative to 68K/OS, which was later cancelled by Sinclair, but released by original authors GST Computer Systems. Its name is not regarded as an acronym and sometimes written as Qdos in official literature. QDOS was implemented in Motorola 68000 assembly language, and on the QL, resided in 48 KB of ROM, consisting of either three 16 KB EPROM chips or one 32 KB and one 16 KB ROM chip. These ROMs also held the SuperBASIC interpreter, an advanced variant of BASIC programming language with structured programming additions. This also acted as the QDOS command-line interpreter.1 KB = 1024 bytes Facilities provided by QDOS included management of processes (or "jobs" in QDOS terminology), memory allocation, and an extensible "redirectable I/O system", providing a generic framew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinclair BASIC
Sinclair BASIC is a dialect of the programming language BASIC used in the 8-bit home computers from Sinclair Research, Timex Sinclair and Amstrad. The Sinclair BASIC interpreter was written by Nine Tiles Networks Ltd. Designed to run in only 1 KB of RAM, the system makes a number of decisions to lower memory usage. This led to one of Sinclair BASIC's most notable features, that the keywords were entered using single keystrokes; each of the possible keywords was mapped to a key on the keyboard, when pressed, the token would be placed into memory while the entire keyword was printed out on-screen. This made code entry easier whilst simplifying the parser. The original ZX80 version supported only integer mathematics, which partially made up for some of the memory-saving design notes which had negative impact on performance. When the system was ported to the ZX81 in 1981, a full floating point implementation was added. This version was very slow, among the slowest BASICs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinclair Research
Sinclair Research Ltd is a British consumer electronics company founded by Clive Sinclair in Cambridge in the 1970s. In 1980, the company entered the home computer market with the ZX80 at £99.95, at that time the cheapest personal computer for sale in the United Kingdom. A year later, the ZX81 became available through retailers, introducing home computing to a generation, with more that 1.5 million sold. In 1982 the ZX Spectrum was released, becoming the UK's best selling computer, and competing aggressively against Commodore and Amstrad. A combination of the failures of the Sinclair QL computer and the TV80 pocket television led to financial difficulties in 1985, and a year later Sinclair sold the rights to its computer products and brand name to Amstrad. Sinclair Research Ltd continued to exist as a one-man company, marketing Clive Sinclair's inventions. History Founding and early years On 25 July 1961, Clive Sinclair founded his first company, Sinclair Radi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jan Jones (novelist)
Janice Rosemary Jones (known as Jan Jones) (born 24 December 1955) is a British former software engineer, now a writer of romantic fiction and short stories. Her debut novel, ''Stage By Stage'', was published in July 2005 and won the Romantic Novelists' Association Joan Hessayon Award the same year. In her first career as software engineer, she was the architect of the SuperBASIC programming language for the Sinclair QL personal computer while working at Sinclair Research in the early 1980s. Before joining Sinclair Research, she worked at British Gas and the Royal School of Mines as a programmer and lecturer. Bibliography Source: Technical * ''QL SuperBasic: The Definitive Handbook''. McGraw-Hill, 1984 (e-book An ebook (short for electronic book), also spelled as e-book or eBook, is a book publication made available in electronic form, consisting of text, images, or both, readable on the flat-panel display of computers or other electronic devices. Al ... reissue 201 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BASIC Interpreter
A BASIC interpreter is an Interpreter (computing), interpreter that enables users to enter and run programs in the BASIC programming language, language and was, for the first part of the microcomputer era, the default Application software, application that computers would launch. Users were expected to use the BASIC interpreter to type-in programs, type in programs or to load programs from storage (initially cassette tapes then floppy disks). BASIC interpreters are of historical importance. Microsoft's first product for sale was a BASIC interpreter (Altair BASIC), which paved the way for the company's success. Before Altair BASIC, microcomputers were sold as kits that needed to be programmed in machine code (for instance, the Apple I). During the Altair period, BASIC interpreters were sold separately, becoming the first software sold to individuals rather than to organizations; Apple BASIC was Apple's first software product. After the Altair 8800, MITS Altair 8800, microcomputers w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
E-book
An ebook (short for electronic book), also spelled as e-book or eBook, is a book publication made available in electronic form, consisting of text, images, or both, readable on the flat-panel display of computers or other electronic devices. Although sometimes defined as "an electronic version of a printed book", some e-books exist without a printed equivalent. E-books can be read on dedicated e-reader devices, also on any computer device that features a controllable viewing screen, including desktop computers, laptops, tablet computer, tablets and smartphones. In the 2000s, there was a trend of print and e-book sales moving to the Internet, where readers buy traditional paper books and e-books on websites using e-commerce systems. With print books, readers are increasingly browsing through images of the covers of books on publisher or bookstore websites and selecting and ordering titles online. The paper books are then delivered to the reader by mail or any other delivery servi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Determination Of The Day Of The Week
The determination of the day of the week for any date may be performed with a variety of algorithms. In addition, perpetual calendars require no calculation by the user, and are essentially lookup tables. A typical application is to calculate the day of the week on which someone was born or a specific event occurred. Concepts In numerical calculation, the days of the week are represented as weekday numbers. If Monday is the first day of the week, the days may be coded 1 to 7, for Monday through Sunday, as is practiced in ISO 8601. The day designated with 7 may also be counted as ''0'', by applying the arithmetic modulo 7, which calculates the remainder of a number after division by 7. Thus, the number 7 is treated as 0, the number 8 as 1, the number 9 as 2, the number 18 as 4, and so on. If Sunday is counted as day 1, then 7 days later (''i.e.''day 8) is also a Sunday, and day 18 is the same as day 4, which is a Wednesday since this falls three days after Sunday (''i.e.''). Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BASIC Interpreters
Basic or BASIC may refer to: Science and technology * BASIC, a computer programming language * Basic (chemistry), having the properties of a base * Basic access authentication, in HTTP Entertainment * ''Basic'' (film), a 2003 film * Basic, one of the languages in ''Star Wars'' Music * ''Basic'' (Glen Campbell album), 1978 * ''Basic'' (Robert Quine and Fred Maher album), 1984 * ''B.A.S.I.C.'' (Alpinestars album), 2000 * ''Basic'' (Brown Eyed Girls album), 2015 * ''B.A.S.I.C.'' (The Basics album), 2019 Places * Basic, Mississippi, a community in the US * BASIC countries, Brazil, South Africa, India and China in climate change negotiations Organizations * BASIC Bank Limited, government owned bank in Bangladesh * Basic Books, an American publisher Other uses * Basic (cigarette), a brand of cigarettes manufactured by the Altria Group (Philip Morris Company) * Basic (dance move), the dance move that defines the character of a particular dance * Basic (slang), a pejorative t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Array (data Structure)
In computer science, an array is a data structure consisting of a collection of ''elements'' (value (computer science), values or variable (programming), variables), of same memory size, each identified by at least one ''array index'' or ''key'', a collection of which may be a tuple, known as an index tuple. An array is stored such that the position (memory address) of each element can be computed from its index tuple by a mathematical formula. The simplest type of data structure is a linear array, also called a one-dimensional array. For example, an array of ten 32-bit (4-byte) integer variables, with indices 0 through 9, may be stored as ten Word (data type), words at memory addresses 2000, 2004, 2008, ..., 2036, (in hexadecimal: 0x7D0, 0x7D4, 0x7D8, ..., 0x7F4) so that the element with index ''i'' has the address 2000 + (''i'' × 4). The memory address of the first element of an array is called first address, foundation address, or base address. Because the mathematical conc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
String (computer Science)
In computer programming, a string is traditionally a sequence of character (computing), characters, either as a literal (computer programming), literal constant or as some kind of Variable (computer science), variable. The latter may allow its elements to be Immutable object, mutated and the length changed, or it may be fixed (after creation). A string is often implemented as an array data structure of bytes (or word (computer architecture), words) that stores a sequence of elements, typically characters, using some character encoding. More general, ''string'' may also denote a sequence (or List (abstract data type), list) of data other than just characters. Depending on the programming language and precise data type used, a variable (programming), variable declared to be a string may either cause storage in memory to be statically allocated for a predetermined maximum length or employ dynamic allocation to allow it to hold a variable number of elements. When a string appears lit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variable (computer Science)
In computer programming, a variable is an abstract storage location paired with an associated symbolic name, which contains some known or unknown quantity of data or object referred to as a '' value''; or in simpler terms, a variable is a named container for a particular set of bits or type of data (like integer, float, string, etc...). A variable can eventually be associated with or identified by a memory address. The variable name is the usual way to reference the stored value, in addition to referring to the variable itself, depending on the context. This separation of name and content allows the name to be used independently of the exact information it represents. The identifier in computer source code can be bound to a value during run time, and the value of the variable may thus change during the course of program execution. Variables in programming may not directly correspond to the concept of variables in mathematics. The latter is abstract, having no reference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |