|
Suldaan
This is a list of Somali aristocratic and court titles that were historically used by the Somali people's various sultanates, kingdoms and empires. Also included are the honorifics reserved for Islamic notables as well as traditional leaders and officials within Somali customary law (''xeer''), in addition to the nobiliary particles set aside for distinguished individuals. Monarchs and aristocrats Below is a list of the royal court titles historically retained by the Somali monarchies and aristocracies. Male titles Kings or Rulers *Suldaan: From the Arabic for Sultan or English "Ruler". Very common title for rulers in the pre-colonial and colonial periods; used throughout the Somali territories, particularly by the Isaaq. Famous Sultans include Fakr ad-Din, the first Sultan of the Sultanate of Mogadishu, who built the 13th-century Fakr ad-Din Mosque; Nur Ahmed Aman, Maryam Abdi the queen of Galmudug, 5th Sultan of the Habr Yunis and one of the founders of the Dervish state; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isaaq Sultanate
The Isaaq Sultanate (, Wadaad's writing, Wadaad: , ) was a Muslims, Muslim sultanate that ruled parts of the Horn of Africa in the 18th and 19th centuries. The kingdom spanned the territories of the Isaaq clan in modern-day Somaliland and Ethiopia. It was governed by the Guled Dynasty, Rer Guled Eidagale branch of the Garhajis clan and is the pre-colonial predecessor to the Republic of Somaliland. History Origins Somali genealogical tradition places the origin of the Isaaq tribe in the 12th or 13th century with the arrival of Sheikh Ishaaq bin Ahmed, Ishaaq Bin Ahmed (Sheikh Ishaaq) was one of the scholars who crossed the sea from Arabia to the Horn of Africa.Rima Berns McGown, ''Muslims in the diaspora'', (University of Toronto Press: 1999), pp. 27–28I.M. Lewis, ''A Modern History of the Somali'', fourth edition (Oxford: James Currey, 2002), p. 22 Sheikh Ishaaq settled in the coastal town of Maydh in modern-day northeastern Somaliland. Hence, Sheikh Ishaaq married two local wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
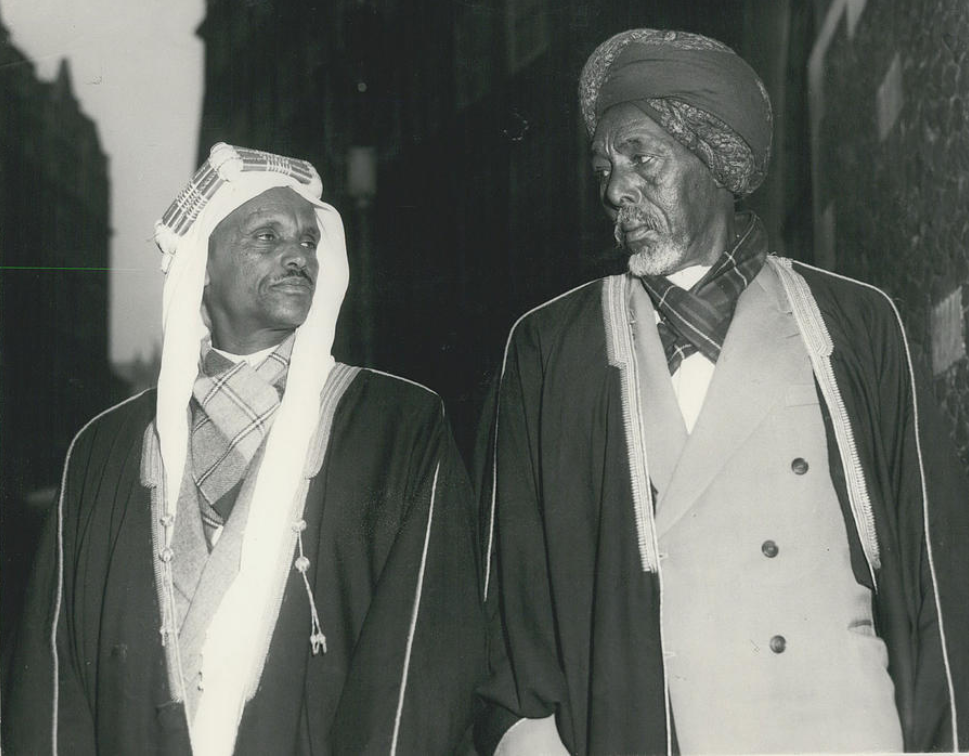
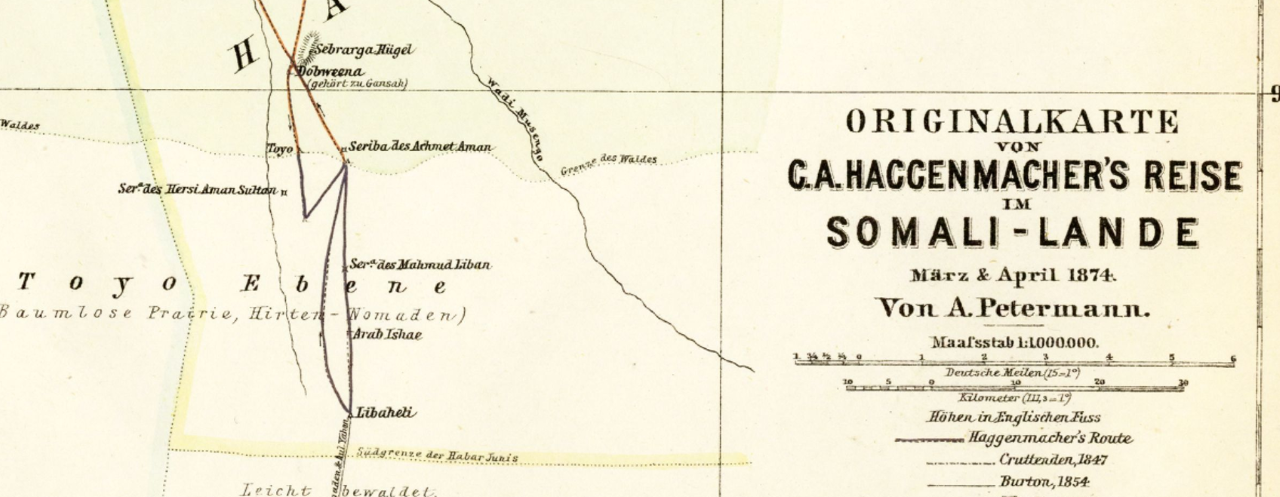
Nur Ahmed Aman
Sultan Nur Ahmed Aman (; (1841–1907); Somali nickname Nuur Dheere), was a learned religious leader and the 5th Sultan of the Habr Yunis Sultanate and later also one of the leaders behind the Dervish movement (Somali), Somali Dervish movement and Somaliland campaign, revolt (1899–1920). He was the principal agitator rallying the followers of the Kob Fardod Tariqa behind his anti- French Roman Catholic missions, Catholic Mission campaign that would become the cause of the Dervish uprising. He assisted in assembling men and arms and hosted the revolting tribesmen in his quarter at Burao in August 1899, declaring the Dervish rebellion. He fought and led the war throughout the years 1899–1904. He and his brother Geleh Ahmed (Kila Ahmed) were the main signatories of the Dervish peace treaty with the British, Ethiopians and Italian colonial powers on March 5, 1905, known as the Ilig Treaty or the Pestalozza agreement. Sultan Nur is entombed in a white-domed shrine in Taleh, the loc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habr Yunis Sultanate
The Habr Yunis Sultanate (, ) was a Somali kingdom that ruled parts of the Horn of Africa during the 18th century. It spanned the territories of the Habr Yunis clan which is part of the wider Isaaq in modern day Somaliland and Ethiopia. The sultanate was governed by the Rer Ainanshe branch of the Habr Yunis clan. History Establishment The Habr Yunis Sultanate finds its roots in the Isaaq Sultanate which was established by the Rer Guled branch of the Eidagale after the Isaaq successfully defeated the Absame clan at Lafaruug in the 17th century. With time the Habr Yunis and later the Habr Awal and Habr Je'lo would break from the Isaaq Sultanate with the Habr Yunis forming their own Sultanate led by Sugulle the son of the previous Habr Yunis Chieftain, Ainanshe Hersi. The Sultan Deria Sugulleh would establish his capital at Wadhan (Waram) near the Sheikh pass and tax and administer the affairs of the Habr Yunis from the town. Expansion and Rayyad War Following Sultan Der ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isaaq
The Isaaq (, , ''Banu Ishaq'') is a major Somali clans, Somali clan. It is one of the largest Somali clan families in the Horn of Africa, with a large and densely populated traditional territory. The Isaaq people claim in a traditional legend to have descended from Ishaaq bin Ahmed, Sheikh Ishaaq bin Ahmed, an Ulama, Islamic scholar who purportedly traveled to Somaliland in the 12th or 13th century and married two women; one from the local Dir (clan), Dir clan.I.M. Lewis, ''A Modern History of the Somali'', fourth edition (Oxford: James Currey, 2002), pp. 22–23. He is said to have sired eight sons who are the common ancestors of the clans of the Isaaq clan-family. He remained in Maydh until his death. Overview Somali genealogical tradition places the origin of the Isaaq tribe in the 12th or 13th century with the arrival of the Sheikh Ishaaq bin Ahmed, Ishaaq Bin Ahmed (Sheikh Ishaaq) from Arabian Peninsula, Arabia. Sheikh Ishaaq settled in the coastal town of Maydh in mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdillahi Deria
Abdillahi Deria (, ; died January 1967) was the fifth Grand Sultan of the Isaaq Sultanate and a notable Somali anti-colonial figure. Biography Abdillahi was the son of Sultan Deria Hassan whom he succeeded in 1943 after his death. Abdillahi was described as a religious man, and was educated in Aden before returning to Somaliland in 1920. A member of the Eidagale sub-division of the Garhajis subclan, Reer Guuled his reign covered the later years of British Somaliland and most of the subsequent Somali Republic. Somali National League Sultan Abdillahi was a vehement anti-colonialist and was a prominent member of the ''Somali National League'' the dominant party in the protectorate. He directly encouraged agitation and petitions by local British Somaliland communities to file with authorities. He would soon become the secretary general of the party and one of its critical tasks was resolving the Haud dispute. Haud Delegation In response to the cessation of Haud Reserve and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sultanate Of Geledi
The Sultanate of the Geledi (, ) also known as the Gobroon dynasty,Somali Sultanate: The Geledi City-state Over 150 Years - Virginia Luling (2002) Page 229 was a Somali people, Somali kingdom that ruled parts of the Horn of Africa during the late-17th century to the early 20th century. The Sultanate was governed by the Gobroon dynasty. It was established by the Geledi soldier Ibrahim Adeer, who had defeated various vassals of the Ajuran Sultanate and elevated the Gobroon to wield significant political power. Following Mahamud Ibrahim's consolidation, the dynasty reached its apex under Yusuf Mahamud Ibrahim, who successfully modernized the Geledi economy and eliminated regional threats with the Yusuf Mahamud Ibrahim#Conquest of Bardera, Conquest of Bardera in 1843, and would go on to receive tribute from Said bin Sultan, the ruler of the Omani Empire. Geledi Sultans had strong regional ties and built alliances with the Pate Island#Pate Town, Pate and Wituland, Witu Sultanates on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sultanate Of Hobyo
The Sultanate of Hobyo (, ), also known as the Sultanate of Obbia,''New International Encyclopedia'', Volume 21, (Dodd, Mead: 1916), p.283. was a 19th-century Somali Sultanate in present-day northeastern and central Somalia and eastern Ethiopia. It was established in 1878 by Yusuf Ali Kenadid. In 1888, it became a protectorate of Italy and was eventually integrated in the colony of Italian Somaliland. Administration As with the Majeerteen Sultanate, the Sultanate of Hobyo exerted a strong centralised authority during its existence and possessed all of the organs and trappings of an integrated modern state: a functioning bureaucracy, a hereditary nobility, titled aristocrats, a state flag, and a professional army.''Horn of Africa'', Volume 15, Issues 1-4, (Horn of Africa Journal: 1997), p.130.Michigan State University. African Studies Center, Northeast African studies, Volumes 11-12, (Michigan State University Press: 1989), p.32. Like the Majeerteen Sultanate, it was another e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yusuf Ali Kenadid
Yusuf Ali Kenadid (; 1837 – 14 August 1911) was a Somali Sultan and the founder of the Sultanate of Hobyo. He was succeeded to the throne by his son Ali Yusuf Kenadid. Family Yusuf Ali Kenadid was born into the Bah Yaaqub (part of the larger Bah Dirooble) branch of the Osman Mahamuud, Majeerteen Darod family. He is the father of Osman Yusuf Kenadid, who would go on to create the Osmanya writing script for the Somali language. Yusuf Ali's grandson, Yasin Osman Kenadid, would later help found the Society for Somali Language and Literature. Yusuf Ali was not a lineal descendant of the previous dynasties that governed over northeastern Somalia. He independently amassed his own fortune, and would later evolve into a skilled military leader commanding more senior troops. "Kenadid" was not his surname, but rather a title given to him by his rivals. As per custom among the period's prominent urban traders, to ensure commercial success in the interior, Kenadid married a local wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mohamoud Ali Shire
Mohamoud Ali Shire MBE (, ; died 1960) was a Somali Sultan of the Warsengali Sultanate. He bore the title Sultan * (also referred to as Senior Akil) of the Warsangali. He was centered at Las Khorey. Reign Mohamoud Ali Shire served as Sultan of the Warsengali Sultanate during the late 19th century and early 20th century. Dervish movement Shire was the father-in-law of Sayyid Mohammed Abdullah Hassan, whose Dervish movement fought a two-decade long war against British, Italian and Ethiopian forces. Shire already had four wives of his own. He sought to marry Hassan's daughter Faṭmah, offering a bride-price (''yarad'') of ten camels loaded with draperies and silk, but Hassan refused to give her hand in marriage to Shire. The two leaders regularly engaged in trade and political intrigue. In 1886, Shire and other elders of the Warsangali clan signed a treaty with the British Empire establishing a protectorate in his territory. This came following other protectorate treaties ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ajuran Sultanate
The Ajuran Sultanate (, ), natively referred to as Ajuuraan, and often simply Ajuran/Ajur, was a Muslims, Muslim empire in the Horn of Africa that thrived from the Late Middle Ages, late medieval and Early modern period, early modern period. Founded by Somali people, Somali Sultans its rise to prominence began during the 13th century, 13th and 14th century, 14th centuries and by the 15th century, it was Africa, Africa's only 'hydraulic empire'. Through a strong centralized administration and an aggressive military stance towards invaders, the Ajuran Empire successfully resisted Oromo expansion, Oromo invasions from the west and fought against Somali–Portuguese conflicts, Portuguese incursions from the east. The Ajuran were among the great centres of commerce in the contemporary African world. Trading routes dating from ancient and early medieval periods of Maritime history of Somalia, Somali maritime enterprise were strengthened and re-established, foreign trade and commerce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Court (royal)
A royal court, often called simply a court when the royal context is clear, is an extended royal household in a monarchy, including all those who regularly attend on a monarch, or another central figure. Hence, the word ''court'' may also be applied to the coterie of a senior member of the nobility. Royal courts may have their seat in a designated place, several specific places, or be a mobile, itinerant court. In the largest courts, the royal households, many thousands of individuals constituted the court. These courtiers included the monarch or noble's camarilla and retinue, household, nobility, clergy, those with court appointments, bodyguards, and may also include emissaries from other kingdoms or visitors to the court. Foreign princes and foreign nobility in exile may also seek refuge at a court. Near Eastern and Far Eastern courts often included the harem and concubines as well as eunuchs who fulfilled a variety of functions. At times, the harem was walled off and se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Customary Law
A legal custom is the established pattern of behavior within a particular social setting. A claim can be carried out in defense of "what has always been done and accepted by law". Customary law (also, consuetudinary or unofficial law) exists where: #a certain legal practice is observed and #the relevant actors consider it to be an opinion of law or necessity ('' opinio juris''). Most customary laws deal with ''standards of the community'' that have been long-established in a given locale. However, the term can also apply to areas of international law where certain standards have been nearly universal in their acceptance as correct bases of action – for example, laws against piracy or slavery (see '' hostis humani generis''). In many, though not all instances, customary laws will have supportive court rulings and case law that have evolved over time to give additional weight to their rule as law and also to demonstrate the trajectory of evolution (if any) in the judicial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |