|
Squares
In geometry, a square is a regular polygon, regular quadrilateral. It has four straight sides of equal length and four equal angles. Squares are special cases of rectangles, which have four equal angles, and of rhombuses, which have four equal sides. As with all rectangles, a square's angles are right angles (90 degree (angle), degrees, or Pi, /2 radians), making adjacent sides perpendicular. The area of a square is the side length multiplied by itself, and so in algebra, multiplying a number by itself is called square (algebra), squaring. Equal squares can tile the plane edge-to-edge in the square tiling. Square tilings are ubiquitous in tiled floors and walls, graph paper, image pixels, and game boards. Square shapes are also often seen in building floor plans, origami paper, food servings, in graphic design and heraldry, and in instant photos and fine art. The formula for the area of a square forms the basis of the calculation of area and motivates the search for methods for s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squaring The Square
Squaring the square is the problem of tessellation, tiling an integral square using only other integral squares. (An integral square is a square (geometry), square whose sides have integer length.) The name was coined in a humorous analogy with squaring the circle. Squaring the square is an easy task unless additional conditions are set. The most studied restriction is that the squaring be perfect, meaning the sizes of the smaller squares are all different. A related problem is squaring the plane, which can be done even with the restriction that each natural number occurs exactly once as a size of a square in the tiling. The order of a squared square is its number of constituent squares. Perfect squared squares A "perfect" squared square is a square such that each of the smaller squares has a different size. Perfect squared squares were studied by R. Leonard Brooks, R. L. Brooks, Cedric Smith (statistician), C. A. B. Smith, Arthur Harold Stone, A. H. Stone and W. T. Tutte (wr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inscribed Square Problem
The inscribed square problem, also known as the square peg problem or the Toeplitz conjecture, is an unsolved question in geometry: ''Does every plane simple closed curve contain all four vertices of some square?'' This is true if the curve is convex or piecewise smooth and in other special cases. The problem was proposed by Otto Toeplitz in 1911. Some early positive results were obtained by Arnold Emch and Lev Schnirelmann. The general case remains open. Problem statement Let C be a Jordan curve. A polygon P is inscribed in C if all vertices of P belong to C. The inscribed square problem asks: : ''Does every Jordan curve admit an inscribed square?'' It is ''not'' required that the vertices of the square appear along the curve in any particular order. Examples Some figures, such as circles and squares, admit infinitely many inscribed squares. There is one inscribed square in a triangle for any obtuse triangle, two squares for any right triangle, and three squares ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Square (algebra)
In mathematics, a square is the result of multiplying a number by itself. The verb "to square" is used to denote this operation. Squaring is the same as raising to the power 2, and is denoted by a superscript 2; for instance, the square of 3 may be written as 32, which is the number 9. In some cases when superscripts are not available, as for instance in programming languages or plain text files, the notations ''x''^2 ( caret) or ''x''**2 may be used in place of ''x''2. The adjective which corresponds to squaring is '' quadratic''. The square of an integer may also be called a '' square number'' or a ''perfect square''. In algebra, the operation of squaring is often generalized to polynomials, other expressions, or values in systems of mathematical values other than the numbers. For instance, the square of the linear polynomial is the quadratic polynomial . One of the important properties of squaring, for numbers as well as in many other mathematical systems, is that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graph Paper
Graph paper, coordinate paper, grid paper, or squared paper is writing paper that is printed with fine lines making up a regular grid. It is available either as loose leaf paper or bound in notebooks or graph books. It is commonly found in mathematics and engineering education settings, exercise books, and in laboratory notebooks. The lines are often used as guides for mathematical notation, plotting graph of a function, graphs of functions or experimental data, and drawing curves. History The Metropolitan Museum of Art owns a pattern book dated to around 1596 in which each page bears a grid woodblock printing, printed with a woodblock. The owner has used these grids to create block pictures in black and white and in colour. The first commercially published "coordinate paper" is usually attributed to a Dr. Buxton of England, who patented paper printed with a rectangular coordinate grid, in 1794. A century later, E. H. Moore, a distinguished mathematician at the University of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rectangle
In Euclidean geometry, Euclidean plane geometry, a rectangle is a Rectilinear polygon, rectilinear convex polygon or a quadrilateral with four right angles. It can also be defined as: an equiangular quadrilateral, since equiangular means that all of its angles are equal (360°/4 = 90°); or a parallelogram containing a right angle. A rectangle with four sides of equal length is a ''square''. The term "wikt:oblong, oblong" is used to refer to a non-square rectangle. A rectangle with Vertex (geometry), vertices ''ABCD'' would be denoted as . The word rectangle comes from the Latin ''rectangulus'', which is a combination of ''rectus'' (as an adjective, right, proper) and ''angulus'' (angle). A #Crossed rectangles, crossed rectangle is a crossed (self-intersecting) quadrilateral which consists of two opposite sides of a rectangle along with the two diagonals (therefore only two sides are parallel). It is a special case of an antiparallelogram, and its angles are not right angles an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadrilateral
In Euclidean geometry, geometry a quadrilateral is a four-sided polygon, having four Edge (geometry), edges (sides) and four Vertex (geometry), corners (vertices). The word is derived from the Latin words ''quadri'', a variant of four, and ''latus'', meaning "side". It is also called a tetragon, derived from Greek "tetra" meaning "four" and "gon" meaning "corner" or "angle", in analogy to other polygons (e.g. pentagon). Since "gon" means "angle", it is analogously called a quadrangle, or 4-angle. A quadrilateral with vertices A, B, C and D is sometimes denoted as \square ABCD. Quadrilaterals are either simple polygon, simple (not self-intersecting), or complex polygon, complex (self-intersecting, or crossed). Simple quadrilaterals are either convex polygon, convex or concave polygon, concave. The Internal and external angle, interior angles of a simple (and Plane (geometry), planar) quadrilateral ''ABCD'' add up to 360 Degree (angle), degrees, that is :\angle A+\angle B+\angle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhombus
In plane Euclidean geometry, a rhombus (: rhombi or rhombuses) is a quadrilateral whose four sides all have the same length. Another name is equilateral quadrilateral, since equilateral means that all of its sides are equal in length. The rhombus is often called a "diamond", after the Diamonds (suit), diamonds suit in playing cards which resembles the projection of an Octahedron#Orthogonal projections, octahedral diamond, or a lozenge (shape), lozenge, though the former sometimes refers specifically to a rhombus with a 60° angle (which some authors call a calisson after calisson, the French sweet—also see Polyiamond), and the latter sometimes refers specifically to a rhombus with a 45° angle. Every rhombus is simple polygon, simple (non-self-intersecting), and is a special case of a parallelogram and a Kite (geometry), kite. A rhombus with right angles is a square. Etymology The word "rhombus" comes from , meaning something that spins, which derives from the verb , roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Square Tiling
In geometry, the square tiling, square tessellation or square grid is a regular tiling of the Euclidean plane consisting of four squares around every vertex. John Horton Conway called it a quadrille. Structure and properties The square tiling has a structure consisting of one type of congruent prototile, the square, sharing two vertices with other identical ones. This is an example of monohedral tiling. Each vertex at the tiling is surrounded by four squares, which denotes in a vertex configuration as 4.4.4.4 or 4^4 . The vertices of a square can be considered as the lattice, so the square tiling can be formed through the square lattice. This tiling is commonly familiar with the flooring and game boards. It is self-dual, meaning the center of each square connects to another of the adjacent tile, forming square tiling itself. The square tiling acts transitively on the ''flags'' of the tiling. In this case, the flag consists of a mutually incident vertex, edge, and tile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Origami Paper
Origami paper is the paper used for ''origami'', the art of Japanese paper folding. The only real requirement of the folding medium is that it must be able to hold a crease, but should ideally also be thinner than regular paper for convenience when multiple folds over the same small paper area are required (e.g. such as would be the case if creating an origami bird's "legs", "feet", and "beak"). Kami Kami, or koiy paper, is the cheapest paper made specifically for origami, and the most widely available. It was developed for use in schools. The word ''kami'' is simply Japanese for ''paper'', but it has acquired this specific meaning. Kami is thin and easy to fold. It is usually printed only on one side, with a solid color or pattern. These patterns can be as simple as a gradation from red to blue, or as complex as a multi-colored kimono pattern of flowers and cranes with gold foil embellishments. Kami comes in several sizes, but standard sizes include 75 × 75 mm ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perpendicular
In geometry, two geometric objects are perpendicular if they intersect at right angles, i.e. at an angle of 90 degrees or π/2 radians. The condition of perpendicularity may be represented graphically using the '' perpendicular symbol'', ⟂. Perpendicular intersections can happen between two lines (or two line segments), between a line and a plane, and between two planes. ''Perpendicular'' is also used as a noun: a perpendicular is a line which is perpendicular to a given line or plane. Perpendicularity is one particular instance of the more general mathematical concept of '' orthogonality''; perpendicularity is the orthogonality of classical geometric objects. Thus, in advanced mathematics, the word "perpendicular" is sometimes used to describe much more complicated geometric orthogonality conditions, such as that between a surface and its '' normal vector''. A line is said to be perpendicular to another line if the two lines intersect at a right angle. Explicitly, a fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Area
Area is the measure of a region's size on a surface. The area of a plane region or ''plane area'' refers to the area of a shape or planar lamina, while '' surface area'' refers to the area of an open surface or the boundary of a three-dimensional object. Area can be understood as the amount of material with a given thickness that would be necessary to fashion a model of the shape, or the amount of paint necessary to cover the surface with a single coat. It is the two-dimensional analogue of the length of a curve (a one-dimensional concept) or the volume of a solid (a three-dimensional concept). Two different regions may have the same area (as in squaring the circle); by synecdoche, "area" sometimes is used to refer to the region, as in a " polygonal area". The area of a shape can be measured by comparing the shape to squares of a fixed size. In the International System of Units (SI), the standard unit of area is the square metre (written as m2), which is the area o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
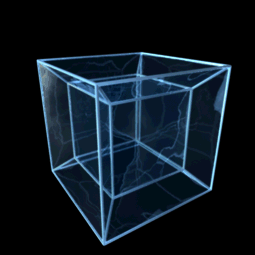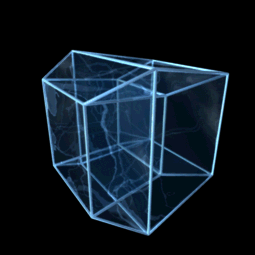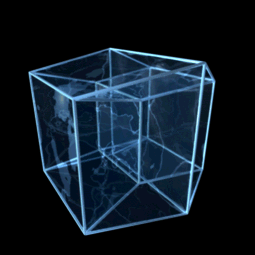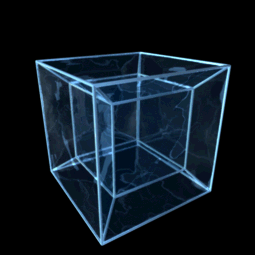
Hypercube
In geometry, a hypercube is an ''n''-dimensional analogue of a square ( ) and a cube ( ); the special case for is known as a ''tesseract''. It is a closed, compact, convex figure whose 1- skeleton consists of groups of opposite parallel line segments aligned in each of the space's dimensions, perpendicular to each other and of the same length. A unit hypercube's longest diagonal in ''n'' dimensions is equal to \sqrt. An ''n''-dimensional hypercube is more commonly referred to as an ''n''-cube or sometimes as an ''n''-dimensional cube. The term measure polytope (originally from Elte, 1912) is also used, notably in the work of H. S. M. Coxeter who also labels the hypercubes the γn polytopes. The hypercube is the special case of a hyperrectangle (also called an ''n-orthotope''). A ''unit hypercube'' is a hypercube whose side has length one unit. Often, the hypercube whose corners (or ''vertices'') are the 2''n'' points in R''n'' with each coordinate equal to 0 or 1 i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |