|
Société Alsacienne De Constructions Mécaniques
The Société Alsacienne de Constructions Mécaniques (the Alsatian Corporation of Mechanical Engineering), or SACM, is an engineering company with its headquarters in Mulhouse, Alsace, which produced railway locomotives, textile and printing machinery, diesel engines, boilers, lifting equipment, firearms and mining equipment. SACM also produced the first atomic reactor at Marcoule. History Foundation The company was founded by André Koechlin in 1826 to produce textile machinery. In 1839, he opened a factory to build railway locomotives at Mulhouse in Alsace. The business grew rapidly but in 1871, the annexation of Alsace-Lorraine by Germany, brought about the transfer of some production to Belfort in France. In 1872 the company merged with the Graffenstaden company of Illkirch-Graffenstaden (a suburb of Strasbourg) to form SACM. Alsthom The new company diversified into the production of boilers, steel equipment, printing equipment, compressors, firearms and other engi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mulhouse
Mulhouse (; ; Alsatian language, Alsatian: ''Mìlhüsa'' ; , meaning "Mill (grinding), mill house") is a France, French city of the European Collectivity of Alsace (Haut-Rhin department, in the Grand Est region of France). It is near the France–Switzerland border, border with Switzerland and France–Germany border, Germany. It is the largest city in Haut-Rhin and second largest in Alsace after Strasbourg. Mulhouse is known for its museums, especially the (also known as the , 'National Museum of the Automobile') and the (also known as , 'French Museum of the Railway'), respectively the largest automobile and railway museums in the world. An industrial town nicknamed "the French Manchester", Mulhouse is also the main seat of the Upper Alsace University, where the secretariat of the European Physical Society is found. Administration Mulhouse is a Communes of France, commune with a population of 108,312 in 2019. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomson-Houston Electric Company
The Thomson-Houston Electric Company was a manufacturing company that was one of the precursors of General Electric. History The company began as the American Electric Company, founded by Elihu Thomson and Edwin Houston. In 1882, Charles Albert Coffin led a group of investors—largely shoe manufacturers from Lynn, Massachusetts—in buying American Electric from investors in New Britain, Connecticut. They renamed the company Thomson-Houston Electric Company and moved its operations to a new building on Lynn's Western Avenue. Elihu Thomson Papers at the American Philosophical Society Coffin led the company and organized its finances, marketing, and sales operations. Edwin Rice organized the manufacturing facilities, and Elihu Thomson ran the Model Room, a precursor to the industrial research lab. With their leadership, the company grew into an enterprise with sales of and 4,000 employees by 1892. In 1884, Thomson-Houston International Company was organized to promote int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of SNCF Classes
List of locomotive and multiple unit classes of SNCF. Classes in bold are in use, whilst those in ''italics'' have been withdrawn. Numbering Scheme Locomotives and Multiple Units Vehicle numbers are three to six digits long. The first (not always present) digit indicates the sector in which that vehicle operates: * 1: '' SNCF Voyages'': high-speed services, including the TGV * 2: ''Intercités'': medium-distance services * 4: '' SNCF Fret'': freight operations * 5: ''Transport Express Régional'' ( TER): urban, local and regional services * 6: '' SNCF Infra'': maintains rail infrastructure, the assets of ''Réseau ferré de France'' (RFF) * 7: Departmental use * 8: ''Transilien'': commuter services serving Île-de-France The next (possibly first) two or three digits of a vehicle's number indicate its class, in loose bands corresponding to the traction and power output of the stock: * 0-9999: DC Electric * 10000-19999: AC Electric * 20000-29999: Dual Voltage * 30000-39999: Trip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SNCF
The Société nationale des chemins de fer français (, , SNCF ) is France's national State-owned enterprise, state-owned railway company. Founded in 1938, it operates the Rail transport in France, country's national rail traffic along with that of Monaco, including the TGV, on France's high-speed rail network. Its functions include operation of railway services for passengers and freight (through its subsidiaries SNCF Voyageurs and Rail Logistics Europe), as well as maintenance and signalling of rail infrastructure (SNCF#Divisions, SNCF Réseau). The railway network consists of about of route, of which are high-speed lines and electrified. About 14,000 trains are operated daily. In 2010 the SNCF was ranked 22nd in France and 214th globally on the Fortune Global 500, ''Fortune'' Global 500 list. It is the main business of the SNCF Group, which in 2020 had €30 billion of sales in 120 countries. The SNCF Group employs more than 275,000 employees in France and around the worl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
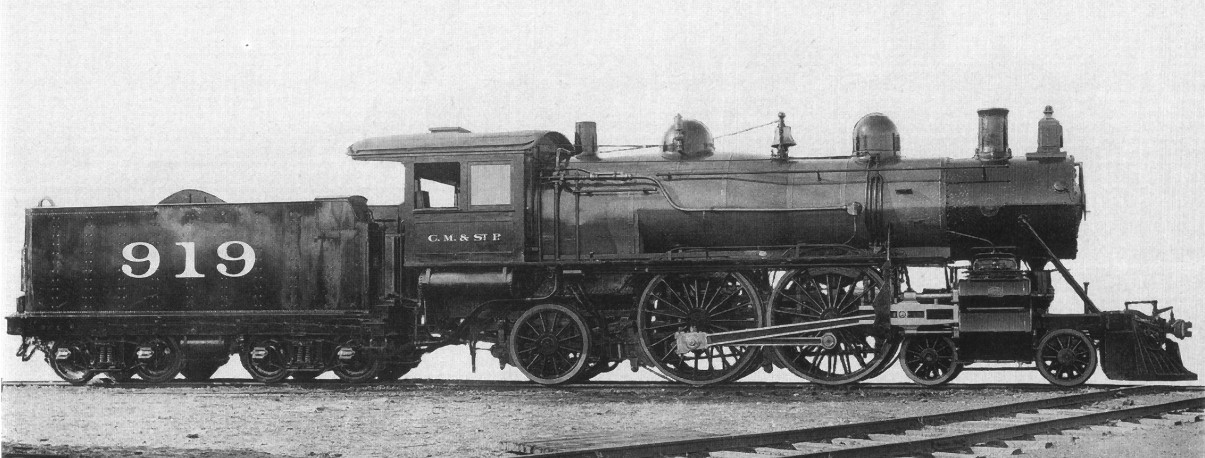
Alfred De Glehn
Alfred George de Glehn (15 September 1848 – 8 June 1936) was a notable English-born French designer of steam locomotives and an engineer with the Société Alsacienne de Constructions Mécaniques (SACM). His steam engines of the 1890s combined elegance, high speed, and efficiency. De Glehn's express locomotives were first used on the Nord Railway and on the boat trains from Calais to Paris, where they impressed passengers with their speed. He invented the Glehn system of compounding, and De Glehn types were built in large numbers in France, and were also built in smaller numbers in Belgium, Germany, New Zealand, and Russia, see Compound locomotive. Compounding lost favour from the 1900s, being replaced by superheating. However André Chapelon rebuilt many of the French De Glehn compounds from 1929 onwards. Personal life Alfred De Glehn was one of the twelve children of Robert von Glehn, a Prussian nobleman originally from the Baltic provinces, whose family had estates near Tal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compound Locomotive
A compound locomotive is a steam locomotive which is powered by a compound steam engine, compound engine, a type of steam engine where steam is expanded in two or more stages. The locomotive was only one application of compounding. Two and three stages were used in ships, for example. Compounding became popular for railway locomotives from the early 1880s and by the 1890s were becoming common. Large numbers were constructed, mostly two- and four-cylinder compounds, in Germany, Austria, Hungary, and the United States. It declined in popularity due to a perceived increased maintenance requirement. Nonetheless, compound Mallets were built by the Norfolk and Western Railway up to 1952 and more importantly, Compound locomotives continued to be designed and built in France until the end of steam in the 1970's. French compounding of railway engines became so highly developed, eventually incorporating reheaters between the high and low pressure stages as well as the initial use of superh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Europa Nostra
Europa Nostra (Latin for "Our Europe") is a pan-European Federation for cultural heritage, Cultural Heritage, representing citizens' organisations that work on safeguarding Europe's cultural and natural heritage. It is the voice of this movement to relevant international bodies, in particular the European Union, the Council of Europe and UNESCO. It has consultative status with UNESCO and is recognised as an NGO partner. Organisation and objectives Europa Nostra's network covers almost 50 countries across Europe and beyond. It is composed of over 250 member organisations (heritage associations and foundations with a combined membership of more than 5 million people), 150 associated organisations (governmental bodies, local authorities and corporations) and also 1500 individual members who directly support the mission of Europa Nostra. Europa Nostra's main goal is to place heritage and its benefits in the mainstream of public consciousness and to make heritage a higher priority for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Alsace University
University of Upper Alsace (, UHA) is a multidisciplinary teaching and research centre based in the two cities of Mulhouse and Colmar, France. Research and teaching at UHA concentrates mainly on science, technology, economics, management, arts and humanities. In 2017, UHA has more than 8000 students with about a hundred courses offered. The founding of UHA was driven by social and business players, among them was Jean-Baptiste Donnet. The special geographical situation of UHA, which lies close to the Swiss and German borders, is favourable to the emergence of single courses leading to double or triple degrees that are recognized in the neighbouring countries. Together with Albert Ludwigs University of Freiburg, University of Basel, Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, as well as University of Strasbourg, the university of Upper Alsace is a member of the EUCOR, which is a trinational cross-border alliance of five universities on the Upper Rhine in the border region between Germany, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wärtsilä
Wärtsilä Oyj Abp (), trading internationally as Wärtsilä Corporation, is a Finnish corporation, Finnish company which manufactures and services power sources and other equipment in the Marine propulsion, marine and energy markets. The core products of Wärtsilä include technologies for the energy sector, including gas, multi-fuel, liquid fuel and biofuel power plants and energy storage systems; and technologies for the marine sector, including cruise ships, ferries, fishing vessels, merchant ships, navy ships, special vessels, tugs, yachts and offshore vessels. Ship design capabilities include ferries, tugs, and vessels for the fishing, merchant, offshore and special segments. Services offerings include online services, underwater services, turbocharger services, and also services for the marine, energy, and oil and gas markets. At the end of December 2023, the company employed 17,800 workers. Wärtsilä has two main businesses; Energy Business focusing on the energy marke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcatel-Lucent
Alcatel-Lucent S.A. () was a multinational telecommunications equipment company, headquartered in Boulogne-Billancourt, Paris, France. The company focused on Fixed line telephone, fixed, Mobile phone, mobile and telecommunications convergence, converged networking hardware, Internet Protocol, IP technologies, Telecommunications convergence#Telecommunication convergence business support systems, software and services, and operated between 2006 and 2016 in more than 130 countries. The American company Lucent Technologies was acquired by the France-based Alcatel in 2006, after which the latter renamed itself to Alcatel-Lucent. Lucent was a successor of AT&T's Western Electric and a holding company of Bell Labs. In 2014, the Alcatel-Lucent group split into two: Alcatel-Lucent Enterprise, providing enterprise communication services, and Alcatel-Lucent, selling to communications operators. The enterprise business was sold to China Huaxin Post and Telecom Technologies in the same year, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |