|
Smolarnia, Opole Voivodeship
Smolarnia is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Strzeleczki, within Krapkowice County, Opole Voivodeship, in Upper Silesia in southern Poland. It lies approximately west of Strzeleczki, west of Krapkowice, and south-west of the regional capital Opole. The nearby hamlet of Serwitut, Opole Voivodeship, Serwitut is administered as part of this village. History In the 10th century, the territory became part of the emerging Polish state under its first historic ruler Mieszko I. Following the fragmentation of Poland, it formed part of several provincial duchies ruled by the Piast dynasty, and later on it passed to the Kingdom of Bohemia. The village itself can trace its history back to 12 November 1663, when a large estate was granted to a nobleman which later became the center of the village, attracting settlers from nearby villages. The village's name was first recorded as Dziedzützer Pechhüte, indicating it was a hamlet of Dziedzice, Krapkowice County, Dziedzice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Sovereign States
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 205 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 member states of the United Nations, UN member states, two United Nations General Assembly observers#Current non-member observers, UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and ten other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and one UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (15 states, of which there are six UN member states, one UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and eight de facto states), and states having a political status of the Cook Islands and Niue, special political status (two states, both in associated state, free association with New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landkreis Neustadt O
In 13 German states, the primary administrative subdivision higher than a '' Gemeinde'' (municipality) is the () or (). Most major cities in Germany are not part of any ''Kreis'', but instead combine the functions of a municipality and a ''Kreis''; such a city is referred to as a () or (). ''(Land-)Kreise'' stand at an intermediate level of administration between each state () and the municipalities () within it. These correspond to level-3 administrative units in the Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics (NUTS 3). Previously, the similar title Imperial Circle () referred to groups of states in the Holy Roman Empire. The related term was used for similar administrative divisions in some German territories until the 19th century. Types of districts The majority of German districts are "rural districts" (German: , ), of which there are 294 . Cities with more than 100,000 inhabitants (and smaller towns in some states) do not usually belong to a district, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
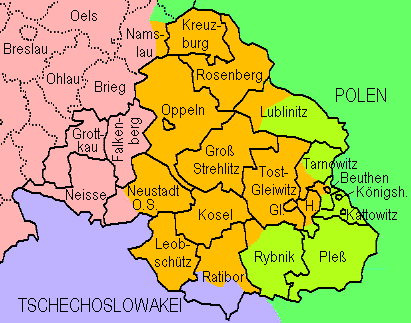
Upper Silesia Plebiscite
The Upper Silesia plebiscite was a plebiscite mandated by the Versailles Treaty and carried out on 20 March 1921 to determine ownership of the province of Upper Silesia between Weimar Germany and the Second Polish Republic. The region was ethnically mixed with both Germans and Polish people, Poles. According to prewar statistics, ethnic Poles formed 60 percent of the population. Under the previous rule by the German Empire, Poles claimed they had faced discrimination and had been effectively second-class citizens. The period of the plebiscite campaign and the Allies of World War I, Allied occupation was marked by violence. Silesian Uprisings, Three Polish uprisings occurred, and German volunteer paramilitary units came to the region. The area was policed by French, British and Italian troops and overseen by an Interallied Commission. The Allies planned a partition of the region, but a Polish insurgency took control of over half the area. The Germans responded with the Freikorps ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Głogówek
Głogówek (, , , ) is a small historic town in southern Poland. It is situated on the Osobloga River, in Opole Voivodeship of the greater Silesian region. The city lies approximately from Opole, the capital of the voivodeship, and is about from the Czech border. The name of the city comes from the Polish word , meaning ' hawthorn'. The plant was abundant in the area when the city was founded. The town is well known for its preserved medieval core, market square and many architectural monuments. Since 2009, the town has been bilingual in Polish and German, a substantial German minority having remained in the area after the bulk of Silesia was ceded to Poland at the end of World War II. History Previously, it was believed that the first historical mention of Głogówek was in the year 1076, however this is now known to be false. The sources which frequently cited the city's 11th-century founding were misinterpreted, and referred instead to the Lower Silesian town of Głogów. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Easement
An easement is a Nonpossessory interest in land, nonpossessory right to use or enter onto the real property of another without possessing it. It is "best typified in the right of way which one landowner, A, may enjoy over the land of another, B". An easement is a property right and type of Incorporeality, incorporeal property in itself at common law in most jurisdictions. An easement is similar to covenant (law), real covenants and equitable servitudes. In the United States, the Restatements of the Law, Restatement (Third) of Property takes steps to merge these concepts as servitudes. Easements are helpful for providing a 'limited right to use another person's land for a stated purpose. For example, an easement may allow someone to use a road on their neighbor’s land to get to their own.' Another example is someone's right to fish in a privately owned pond, or to have access to a public beach. The rights of an easement holder vary substantially among jurisdictions. Types ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Empire
The German Empire (),; ; World Book, Inc. ''The World Book dictionary, Volume 1''. World Book, Inc., 2003. p. 572. States that Deutsches Reich translates as "German Realm" and was a former official name of Germany. also referred to as Imperial Germany, the Second Reich or simply Germany, was the period of the German Reich; . from the unification of Germany in 1871 until the German revolution of 1918–1919, November Revolution in 1918, when the German Reich changed its form of government from a monarchy to a Weimar Republic, republic. The German Empire consisted of States of the German Empire, 25 states, each with its own nobility: four constituent Monarchy, kingdoms, six Grand duchy, grand duchies, five Duchy, duchies (six before 1876), seven Principality, principalities, three Free imperial city, free Hanseatic League, Hanseatic City-state, cities, and Alsace–Lorraine, one imperial territory. While Prussia was one of four kingdoms in the realm, it contained about two-thirds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (, ) was a German state that existed from 1701 to 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Rev. ed. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1946. It played a significant role in the unification of Germany in 1871 and was a major constituent of the German Empire until its German Revolution of 1918–1919, dissolution in 1918. Although it took its name from the Prussia (region), region called Prussia, it was based in the Margraviate of Brandenburg. Its capital was Berlin. The list of monarchs of Prussia, kings of Prussia were from the House of Hohenzollern. The polity of Brandenburg-Prussia, predecessor of the kingdom, became a military power under Frederick William, Elector of Brandenburg, known as "The Great Elector". As a kingdom, Prussia continued its rise to power, especially during the reign of Frederick the Great, Frederick II "the Great".Horn, D. B. "The Youth of Frederick the Great 1712–30." ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Racławiczki
Racławiczki is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Strzeleczki, within Krapkowice County, Opole Voivodeship, in south-western Poland. It lies approximately west of Strzeleczki, west of Krapkowice, and south-west of the regional capital Opole. See also * Prudnik Land Prudnik Land (, , ) is a part of the historical region of Upper Silesia, in southern Poland. It is named after the town of Prudnik, the largest town in the region. Towns located in the region are: Prudnik, Biała, Opole Voivodeship, Biała, Głog ... References Villages in Krapkowice County Populated riverside places in Poland {{Krapkowice-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pitch (resin)
Pitch is a viscoelastic polymer which can be natural or manufactured, derived from petroleum, coal tar, or plants. Pitch produced from petroleum may be called bitumen or asphalt, while plant-derived pitch, a resin, is known as rosin in its solid form. Tar is sometimes used interchangeably with pitch, but generally refers to a more liquid substance derived from coal production, including coal tar, or from plants, as in pine tar. Uses Pitch, a traditional naval store, was traditionally used to help caulk the seams of wooden sailing vessels (see shipbuilding). Other important historic uses included coating earthenware vessels for the preservation of wine, waterproofing wooden containers, and making torches. It was also used to make patent fuel from coal slack around the turn of the 19th century. Petroleum-derived pitch is black in colour, hence the adjectival phrase "pitch-black". The viscoelastic properties of pitch make it well suited for the polishing of high-quali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dziedzice, Krapkowice County
Dziedzice () is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Strzeleczki, within Krapkowice County, Opole Voivodeship, in southern Poland. It lies approximately west of Strzeleczki, west of Krapkowice, and south-west of the regional capital Opole. History The settlement dates back to the Early Middle Ages, to the 5th or 8th century, and in the 10th century it became part of the emerging Polish state. Within medieval Piast-ruled Poland, it was the location of a motte-and-bailey castle, which existed until the 15th century, and is now an archaeological site. It was first mentioned in 1531, and its name is believed to derive from the name of its founder. In 1783 the town was bought by King Frederick the Great of Prussia. From 1871 it was also part of Germany. In 1921 the Upper Silesia plebiscite on 20 March 1921, 862 votes were cast, with 541 villagers voting to remain with Germany, and 321 voting to join the newly restored state of Poland. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |