|
Single-crossing Preferences
In monotone comparative statics, the single-crossing condition or single-crossing property refers to a condition where the relationship between two or more functionsThe property need not only relate to continuous functions but can also similarly describe ordered sets or lattices. is such that they will only cross once. For example, a mean-preserving spread will result in an altered probability distribution whose cumulative distribution function will intersect with the original's only once. The single-crossing condition was posited in Samuel Karlin's 1968 monograph 'Total Positivity'. It was later used by Peter Diamond, Joseph Stiglitz, and Susan Athey, in studying the economics of uncertainty. The single-crossing condition is also used in applications where there are a few agents or types of agents that have preferences over an ordered set. Such situations appear often in information economics, contract theory, social choice and political economics, among other fields. Exampl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single Crossing Condition Example
Single may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media * Single (music), a song release Songs * "Single" (Natasha Bedingfield song), 2004 * "Single" (New Kids on the Block and Ne-Yo song), 2008 * "Single" (William Wei song), 2016 * "Single", by Meghan Trainor from the album '' Only 17'' * "Single", from the musical ''The Wedding Singer'' Film * ''#Single'' (film), an Indian Telugu-language romantic comedy film Sports * Single (baseball), the most common type of base hit * Single (cricket), point in cricket * Single (football), Canadian football point * Single-speed bicycle Transportation * Single-cylinder engine, an internal combustion engine design with one cylinder, or a motorcycle using such engine * Single (locomotive), a steam locomotive with a single pair of driving wheels * As a verb: to convert a double-track railway to a single-track railway Other uses * Single (mathematics) (1-tuple), a list or sequence with only one element * Single person, a person who is not in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Choice Theory
Social choice theory is a branch of welfare economics that extends the Decision theory, theory of rational choice to collective decision-making. Social choice studies the behavior of different mathematical procedures (social welfare function, social welfare functions) used to combine individual preferences into a coherent whole.Amartya Sen (2008). "Social Choice". ''The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics'', 2nd EditionAbstract & TOC./ref> It contrasts with political science in that it is a Normative economics, normative field that studies how a society can make good decisions, whereas political science is a Positive economics, descriptive field that observes how societies actually do make decisions. While social choice began as a branch of economics and decision theory, it has since received substantial contributions from mathematics, philosophy, political science, and game theory. Real-world examples of social choice rules include constitution, constitutions and Parliamentary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asymmetric Information
In contract theory, mechanism design, and economics, an information asymmetry is a situation where one party has more or better information than the other. Information asymmetry creates an imbalance of power in transactions, which can sometimes cause the transactions to be inefficient, causing market failure in the worst case. Examples of this problem are adverse selection, moral hazard,Dembe, Allard E. and Boden, Leslie I. (2000). "Moral Hazard: A Question of Morality?" New Solutions 2000 10(3). 257–79 and monopolies of knowledge. A common way to visualise information asymmetry is with a scale, with one side being the seller and the other the buyer. When the seller has more or better information, the transaction will more likely occur in the seller's favour ("the balance of power has shifted to the seller"). An example of this could be when a used car is sold, the seller is likely to have a much better understanding of the car's condition and hence its market value than the bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brouwer Fixed-point Theorem
Brouwer's fixed-point theorem is a fixed-point theorem in topology, named after Luitzen Egbertus Jan Brouwer, L. E. J. (Bertus) Brouwer. It states that for any continuous function f mapping a nonempty compactness, compact convex set to itself, there is a point x_0 such that f(x_0)=x_0. The simplest forms of Brouwer's theorem are for continuous functions f from a closed interval I in the real numbers to itself or from a closed Disk (mathematics), disk D to itself. A more general form than the latter is for continuous functions from a nonempty convex compact subset K of Euclidean space to itself. Among hundreds of fixed-point theorems, Brouwer's is particularly well known, due in part to its use across numerous fields of mathematics. In its original field, this result is one of the key theorems characterizing the topology of Euclidean spaces, along with the Jordan curve theorem, the hairy ball theorem, the invariance of dimension and the Borsuk–Ulam theorem. This gives it a place ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Mirrlees
Sir James Alexander Mirrlees (5 July 1936 – 29 August 2018) was a British economist and winner of the 1996 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences. He was knighted in the 1997 Birthday Honours. Early life and education Born in Minnigaff, Wigtownshire, Mirrlees was educated at Douglas Ewart High School, then at the University of Edinburgh ( MA in Mathematics and Natural Philosophy in 1957) and Trinity College, Cambridge (Mathematical Tripos and PhD in 1963 with thesis title ''Optimum Planning for a Dynamic Economy'', supervised by Richard Stone). He was a very active student debater. A contemporary, Quentin Skinner, has suggested that Mirrlees was a member of the Cambridge Apostles along with fellow Nobel Laureate Amartya Sen during the period. Economics Between 1968 and 1976, Mirrlees was a visiting professor at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology three times. He was also a visiting professor at the University of California, Berkeley (1986) and Yale Universit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Spence
Andrew Michael Spence (born November 7, 1943) is a Canadian-American economist and Nobel laureate. Spence is the William R. Berkley Professor in Economics and Business at the Stern School of Business at New York University, and the Philip H. Knight Professor of Management, Emeritus, and Dean, Emeritus, at the Stanford Graduate School of Business. Together with George A. Akerlof and Joseph E. Stiglitz, Spence is a co-recipient of the 2001 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences, "for their analyses of markets with asymmetric information." Career Spence is noted for his job-market signaling model, which inspired research into this branch of contract theory. In this model, employees signal their respective skills to employers by acquiring a certain degree of education, which is costly to them. Employers will pay higher wages to more educated employees, because they know that the proportion of employees with high abilities is higher among the educated ones, as it is less costl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
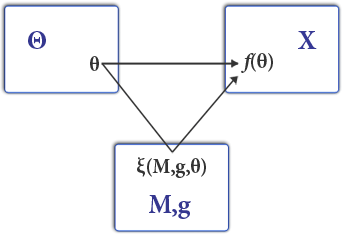
Mechanism Design
Mechanism design (sometimes implementation theory or institution design) is a branch of economics and game theory. It studies how to construct rules—called Game form, mechanisms or institutions—that produce good outcomes according to Social welfare function, some predefined metric, even when the designer does not know the players' true preferences or what information they have. Mechanism design thus focuses on the study of solution concepts for a class of private-information games. Mechanism design has broad applications, including traditional domains of economics such as market design, but also political science (through voting theory). It is a foundational component in the operation of the internet, being used in networked systems (such as inter-domain routing), e-commerce, and Sponsored search auction, advertisement auctions by Facebook and Google. Because it starts with the end of the game (a particular result), then works backwards to find a game that implements it, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Majority-preferred Candidate
A Condorcet winner (, ) is a candidate who would receive the support of more than half of the electorate in a one-on-one race against any one of their opponents. Voting systems where a majority winner will always win are said to satisfy the Condorcet winner criterion. The Condorcet winner criterion extends the principle of majority rule to elections with multiple candidates. Named after Nicolas de Condorcet, it is also called a majority winner, a majority-preferred candidate, a beats-all winner, or tournament winner (by analogy with round-robin tournaments). A Condorcet winner may not necessarily always exist in a given electorate: it is possible to have a rock, paper, scissors-style cycle, when multiple candidates defeat each other (Rock < Paper < Scissors < Rock). This is called , and is analogous to the counterintuitive [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
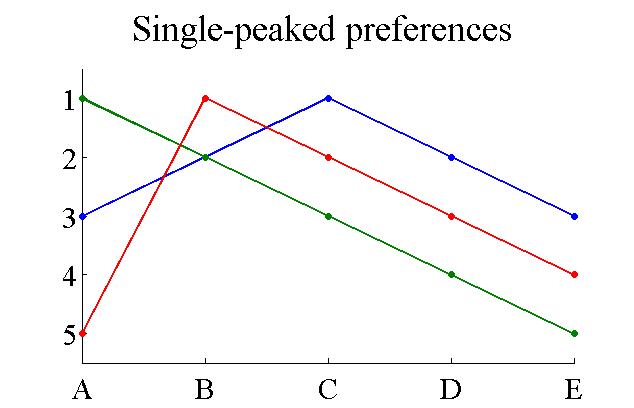
Single Peaked Preferences
Single-peaked preferences are a class of preference relations. A group has single-peaked preferences over a set of outcomes if the outcomes can be ordered along a line such that: # Each agent has a "best outcome" in the set, and # For each agent, outcomes that are further from his or her best outcome are preferred less. Single-peaked preferences are typical of one-dimensional domains. A typical example is when several consumers have to decide on the amount of Public good (economics), public good to purchase. The amount is a one-dimensional variable. Usually, each consumer decides on a certain quantity which is best for him or her, and if the actual quantity is more/less than that ideal quantity, the agent is then less satisfied. With single-peaked preferences, there is a simple truthful mechanism for selecting an outcome, which is to select the median quantity; this results in the median voter theorem. It is truthful because the median function satisfies the Monotonicity (mechani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
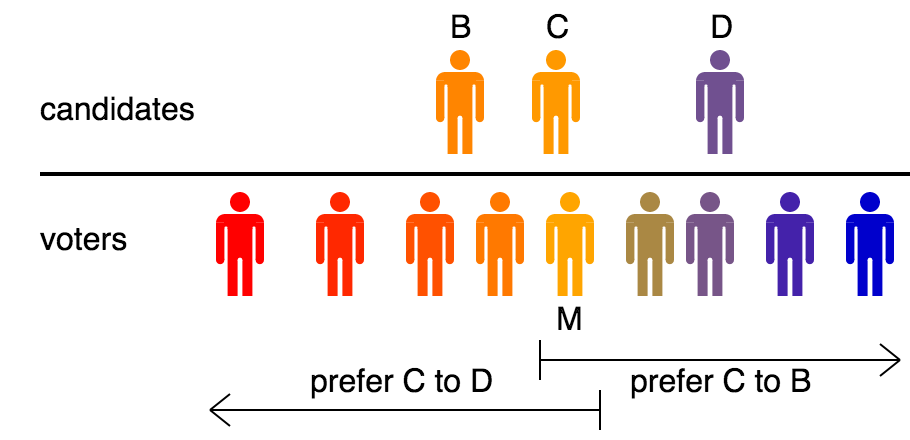
Median Voter Theorem
In political science and social choice theory, social choice, Black's median voter theorem says that if voters and candidates are distributed along a political spectrum, any voting method Condorcet criterion, compatible with majority-rule will elect the candidate preferred by the median voter. The median voter theorem thus shows that under a realistic model of voter behavior, Arrow's impossibility theorem, Arrow's theorem does not apply, and Decision theory, rational choice is possible for societies. The theorem was first derived by Duncan Black in 1948, and independently by Kenneth Arrow. Voting rules without this median voter property, like Instant-runoff voting, ranked choice voting, Plurality voting, plurality, and plurality-with-primaries have a Center-squeeze, center-squeeze effect that encourages candidates to take more extreme positions than the population would prefer. Similar median voter theorems exist for rules like score voting and approval voting when voters are either ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agent (economics)
In economics, an agent is an actor (more specifically, a decision maker) in a model of some aspect of the economy. Typically, every agent makes decisions by solving a well- or ill-defined optimization or choice problem. For example, ''buyers'' (consumers) and ''sellers'' ( producers) are two common types of agents in partial equilibrium models of a single market. Macroeconomic models, especially dynamic stochastic general equilibrium models that are explicitly based on microfoundations, often distinguish households, firms, and governments or central banks as the main types of agents in the economy. Each of these agents may play multiple roles in the economy; households, for example, might act as consumers, as workers, and as voters in the model. Some macroeconomic models distinguish even more types of agents, such as workers and shoppers or commercial banks. The term ''agent'' is also used in relation to principal–agent models; in this case, it refers specifically to someone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preference (economics)
In economics, and in other social sciences, preference refers to an order by which an Agent (economics), agent, while in search of an "optimal choice", ranks alternatives based on their respective utility. ''Preferences'' are evaluations that concern matters of value, in relation to practical reasoning. Individual preferences are determined by taste, need, ..., as opposed to price, availability or personal income. Classical economics assumes that people act in their best (rational) interest. In this context, rationality would dictate that, when given a choice, an individual will select an option that maximizes their self-interest. But preferences are not always transitive relation, transitive, both because real humans are far from always being rational and because in some situations preferences can form cycle (graph theory), cycles, in which case there exists no well-defined optimal choice. An example of this is Efron dice. The concept of preference plays a key role in many discip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |