|
Shang Commandery
Shang Commandery ( zh, c=上郡, l=Upper Commandery) was a historical commandery of China. It was located in modern-day Northern Shaanxi. The commandery was established during the reign of Marquess Wen of Wei. In 328 BC, it was annexed by the Qin state. The seat was Fushi (膚施), to the south of modern Yulin, Shaanxi. During the Chu–Han Contention, Shang was granted to Dong Yi, a Qin general who received the title "King of Di" from Xiang Yu. After Dong's defeat in 205 BC, the territory became part of Han. In late Western Han dynasty, Shang included 23 counties, namely Fushi (膚施), Dule (獨樂), Yangzhou (陽周), Muhe (木禾), Pingdu (平都), Qianshui (淺水), Jingshi (京室), Luodu (洛都), Baitu (白土), Xiangluo (襄洛), Yuandu (原都), Qiyuan (漆垣), Sheyan (奢延), Diaoyin (雕陰), Tuixie (推邪), Zhenlin (楨林), Gaowang (高望), Diaoyindao (雕陰道), Qiuci (龜茲), Dingyang (定陽), Gaonu (), Wangsong (望松) and Yidu (宜都). The populati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jun (country Subdivision)
A commandery ( zh, s=郡, p=jùn) was a historical administrative division of China that was in use from the Eastern Zhou (c. 7th century BCE) until the early Tang dynasty (c. 7th century CE). Several neighboring countries adopted Chinese commanderies as the basis for their own administrative divisions. History and development China Eastern Zhou During the Eastern Zhou's Spring and Autumn period from the 8th to 5th centuries BCE, the larger and more powerful of the Zhou dynasty, Zhou's Chinese feudalism, vassal states—including Qin (state), Qin, Jin (Chinese state), Jin and Wei (state), Wei—began annexing their smaller rivals. These new lands were not part of their original fiefs and were instead organized into Counties of the People's Republic of China#History, counties (''xiàn''). Eventually, commanderies were developed as marchlands between the Warring States period, major realms. Despite having smaller populations and ranking lower on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Han
The ''Book of Han'' is a history of China finished in 111 CE, covering the Western, or Former Han dynasty from the first emperor in 206 BCE to the fall of Wang Mang in 23 CE. The work was composed by Ban Gu (32–92 CE), an Eastern Han court official, with the help of his sister Ban Zhao, continuing the work of their father, Ban Biao. They modelled their work on the ''Records of the Grand Historian'' (), a cross-dynastic general history, but theirs was the first in this annals-biography form to cover a single dynasty. It is the best source, sometimes the only one, for many topics such as literature in this period. The ''Book of Han'' is also called the ''Book of the Former Han'' () to distinguish it from the '' Book of the Later Han'' () which covers the Eastern Han period (25–220 CE), and was composed in the fifth century by Fan Ye (398–445 CE). Contents This history developed from a continuation of Sima Qian's ''Records of the Grand Hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Book Of Tang
The ''New Book of Tang'', generally translated as the "New History of the Tang" or "New Tang History", is a work of official history covering the Tang dynasty in ten volumes and 225 chapters. The work was compiled by a team of scholars of the Song dynasty, led by Ouyang Xiu and Song Qi. It was originally simply called the ''Tangshu'' (唐書, Book of Tang) until the 18th century. History In Chinese history, it was customary for dynasties to compile histories of their immediate predecessor as a means of cementing their own legitimacy. As a result, during the Later Jin (Five Dynasties), Later Jin dynasty of the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period, a history of the preceding Tang dynasty, the ''Old Book of Tang'' () had already been compiled. In 1044, however, Emperor Renzong of Song ordered a new compilation of Tang history, based on his belief that the original ''Old Book of Tang'' lacked organization and clarity. The process took 17 years, being finally completed in 1060. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Sui
The ''Book of Sui'' () is the official history of the Sui dynasty, which ruled China in the years AD 581–618. It ranks among the official Twenty-Four Histories of imperial China. It was written by Yan Shigu, Kong Yingda, and Zhangsun Wuji, with Wei Zheng as the lead author. In the third year of Zhenguan of the Tang dynasty (629), Emperor Taizong of Tang ordered Fang Xuanling to supervise the completion of the Book of Sui, which was being compiled around the same time as other official histories were being written. The Book of Sui was completed in 636 AD, the same year as the ''Book of Chen'' was completed. Contents The format used in the text follows the composite historical biography format (斷代紀傳體) established by Ban Gu in the ''Book of the Later Han'' with three sections: annals (紀), treatises (志), and biographies (傳). The extensive set of 30 treatises, sometimes translated as "monographs", in the ''Book of Sui'' was completed by a separate set of au ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tang Dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, c=唐朝), or the Tang Empire, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907, with an Wu Zhou, interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. Historians generally regard the Tang as a high point in Chinese civilisation, and a Golden age (metaphor), golden age of cosmopolitan culture. Tang territory, acquired through the military campaigns of its early rulers, rivalled that of the Han dynasty. The House of Li, Li family founded the dynasty after taking advantage of a period of Sui decline and precipitating their final collapse, in turn inaugurating a period of progress and stability in the first half of the dynasty's rule. The dynasty was formally interrupted during 690–705 when Empress Wu Zetian seized the throne, proclaiming the Wu Zhou dynasty and becoming the only legitimate Chinese empress regnant. The An Lushan rebellion (755 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sui Dynasty
The Sui dynasty ( ) was a short-lived Dynasties of China, Chinese imperial dynasty that ruled from 581 to 618. The re-unification of China proper under the Sui brought the Northern and Southern dynasties era to a close, ending a prolonged period of political division since the War of the Eight Princes. The Sui endeavoured to rebuild the country, re-establishing and reforming many imperial institutions; in so doing, the Sui laid much of the foundation for the subsequent Tang dynasty, who after toppling the Sui would ultimately preside over golden ages of China, a new golden age in Chinese history. Often compared to the Qin dynasty (221–206 BC), the Sui likewise unified China after a prolonged period of division, undertook wide-ranging reforms and construction projects to consolidate state power, and collapsed after a brief period. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Wen of Sui, Yang Jian (Emperor Wen), who had been a member of the military aristocracy that had developed in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Jin
The ''Book of Jin'' is an official Chinese historical text covering the history of the Jin dynasty (266–420), Jin dynasty from 266 to 420. It was compiled in 648 by a number of officials commissioned by the imperial court of the Tang dynasty, with Chancellor (China), chancellor Fang Xuanling as the lead editor, drawing mostly from official documents left from earlier archives. A few essays in volumes 1, 3, 54 and 80 were composed by the Tang dynasty's Emperor Taizong of Tang, Emperor Taizong himself. However, the contents of the ''Book of Jin'' included not only the history of the Jin dynasty, but also that of the Sixteen Kingdoms period, which was contemporaneous with the Eastern Jin dynasty. Compilation Over 20 histories of the Jin had been written during the Jin era itself and the subsequent Northern and Southern dynasties, of which Eighteen History Books of Jin, 18 were still extant at the beginning of the Tang dynasty. Yet Emperor Taizong of Tang, Emperor Taizong deemed t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Later Han
The ''Book of the Later Han'', also known as the ''History of the Later Han'' and by its Chinese name ''Hou Hanshu'' (), is one of the Twenty-Four Histories and covers the history of the Han dynasty from 6 to 189 CE, a period known as the Later or Eastern Han. The book was compiled by Fan Ye and others in the 5th century during the Liu Song dynasty, using a number of earlier histories and documents as sources. Background In 23 CE, Han dynasty official Wang Mang was overthrown by a peasants' revolt known as the Red Eyebrows. His fall separates the Early (or Western) Han dynasty from the Later (or Eastern) Han dynasty. As an orthodox history, the book is unusual in being completed over two hundred years after the fall of the dynasty. Fan Ye's primary source was the '' Dongguan Hanji'' (東觀漢記; "Han Records of the Eastern Lodge"), which was written during the Han dynasty itself. Contents References Citations Sources ; General * Chavannes, Édouard (1906) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaonu County
Gaonu County () was an ancient Chinese county under the jurisdiction of Shang Commandery in present-day northern Shaanxi. The county was established in the Qin dynasty, during the reign of Qin Shi Huang. Iterations of Gaonu County continued until the latter Eastern Han period, albeit interrupted by rebellions and invasions. The location of Gaonu County corresponds to present-day Baota District and Ansai District within Yan'an. During the Qin dynasty and the Han dynasty, Gaonu County served as an important regional center within present-day Yan'an. History In 328 BCE, the Qin state took land corresponding to present-day Baota District from the Wei state. Subsequently, during the rule of Emperor Qin Shihuang, the area was organized as Gaonu County beginning in 221 BCE, and was placed under the jurisdiction of the Shang Commandery. In 206 BCE, following the collapse of the Qin, Gaonu County was taken by forces belonging to Xiang Yu during the Chu–Han Contention. However, just six ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Shaanxi
Northern Shaanxi or Shaanbei () is the portion of China's Shaanxi province north of the Huanglong Mountain and the Meridian Ridge (the so-called "Guanzhong north mountains"), and is both a geographic as well as a cultural area. It makes up the southeastern portion of the Ordos Basin and forms the northern part of the Loess Plateau. The region includes two prefecture-level cities: Yulin, which is known for the Ming Great Wall traversing through its northern part; and Yan'an, which is known as the birthplace of the Chinese Communist Revolution. Geography Shaanbei, referring to the northern portion of Shaanxi, includes the prefecture-level cities of Yulin and Yan'an. The region's physical geography is largely characterized by the presence of the Loess Plateau. Shaanbei is located in the northern edge of the Loess Plateau with a general elevation range of , occupying approximately 45% of the total area of Shaanxi. Elevation tends to increase from northwest to southeast. The north ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han Dynasty
The Han dynasty was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC9 AD, 25–220 AD) established by Liu Bang and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–206 BC) and a warring interregnum known as the Chu–Han Contention (206–202 BC), and it was succeeded by the Three Kingdoms period (220–280 AD). The dynasty was briefly interrupted by the Xin dynasty (9–23 AD) established by the usurping regent Wang Mang, and is thus separated into two periods—the #Western Han (202 BC – 9 AD), Western Han (202 BC9 AD) and the #Eastern Han (25–220 AD), Eastern Han (25–220 AD). Spanning over four centuries, the Han dynasty is considered a Golden ages of China, golden age in Chinese history, and had a permanent impact on Chinese identity in later periods. The majority ethnic group of modern China refer to themselves as the "Han people" or "Han Chinese". The spoken Chinese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
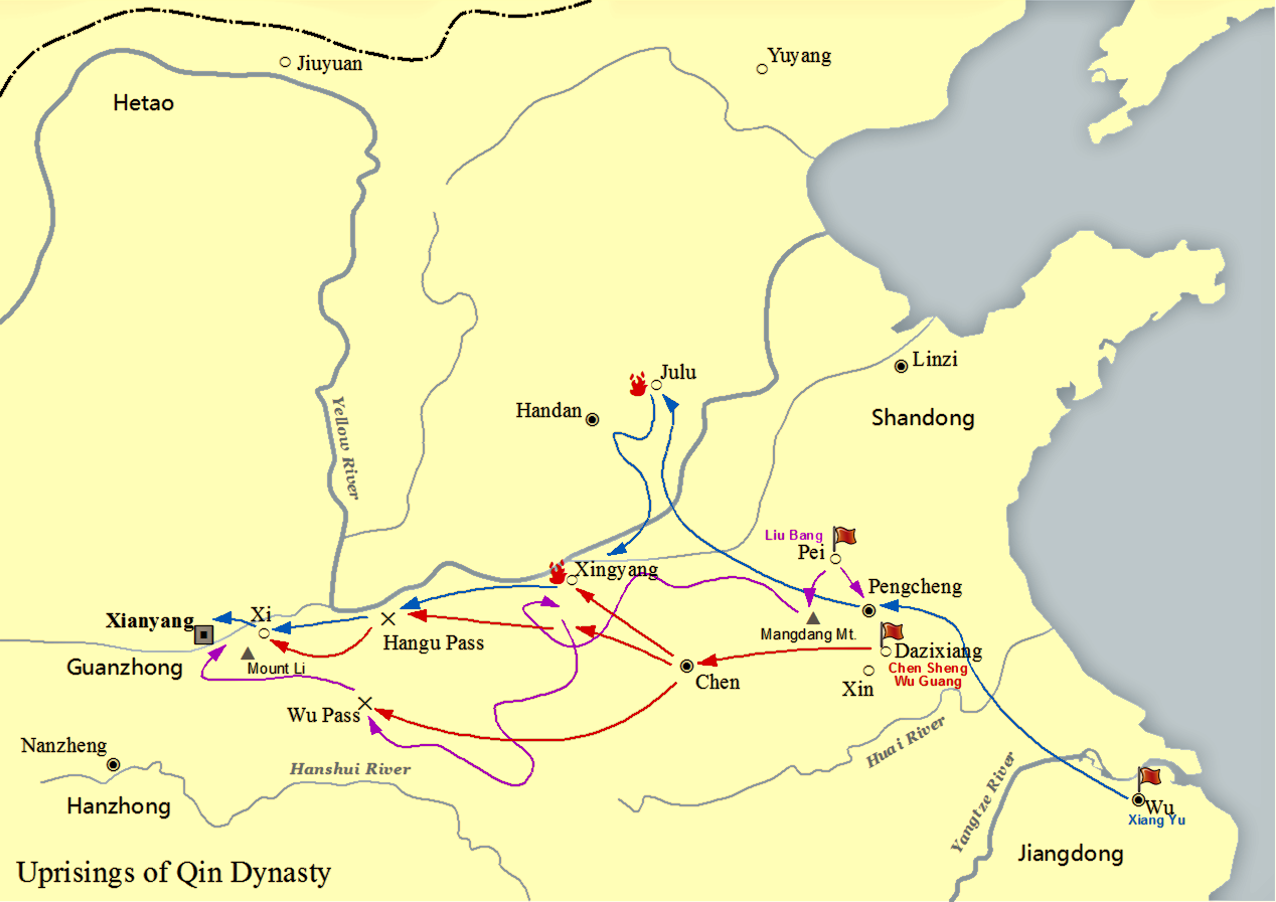
Xiang Yu
Xiang Yu (), born Xiang Ji, was a Chinese warlord who founded and led the short-lived ancient Chinese states, kingdom-state of Western Chu during the interregnum period between the Qin dynasty, Qin and Han dynasty, Han dynasties of China, dynasties known as the Chu–Han Contention (206–202 BC). A nobleman of the former state of Chu, Xiang Yu rebelled against the Qin dynasty under the command of his uncle Xiang Liang, and was granted the title of "Duke of Lu" () by Emperor Yi of Chu, King Huai II of the restoring Chu state in 208 BC. The following year, he led an outnumbered Chu army to victory at the Battle of Julu against the Qin armies led by Zhang Han (Qin dynasty), Zhang Han. After the fall of Qin, Xiang Yu divided the country into a federacy of Eighteen Kingdoms, among which he was self-titled as the "Hegemon-King of Western Chu" () and ruled a vast region spanning central and eastern China, with Pengcheng as his capital. Although a formidable warrior and milita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |