|
Xiang Yu
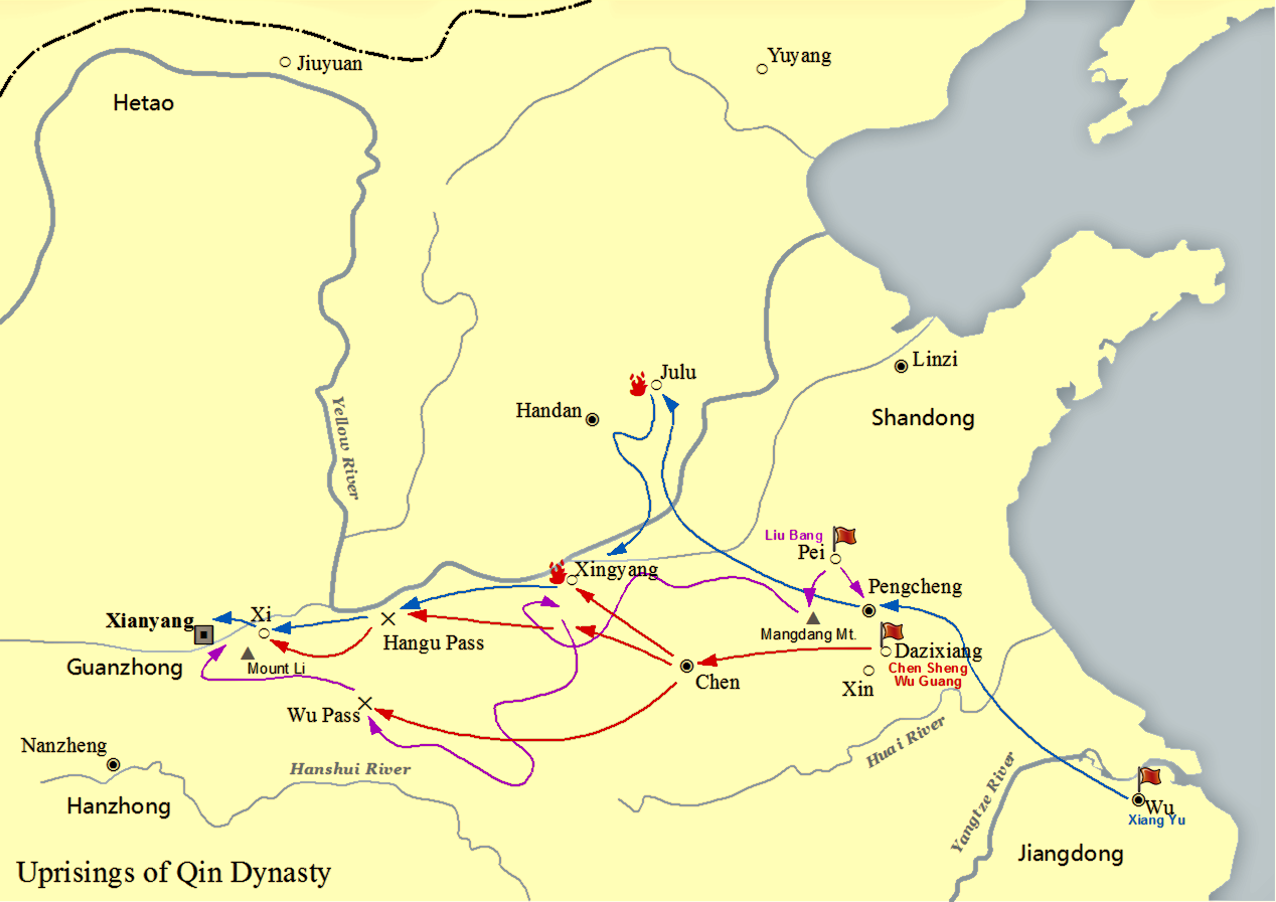
Xiang Yu (), born Xiang Ji, was a Chinese warlord who founded and led the short-lived ancient Chinese states, kingdom-state of Western Chu during the interregnum period between the Qin dynasty, Qin and Han dynasty, Han dynasties of China, dynasties known as the Chu–Han Contention (206–202 BC). A nobleman of the former state of Chu, Xiang Yu rebelled against the Qin dynasty under the command of his uncle Xiang Liang, and was granted the title of "Duke of Lu" () by Emperor Yi of Chu, King Huai II of the restoring Chu state in 208 BC. The following year, he led an outnumbered Chu army to victory at the Battle of Julu against the Qin armies led by Zhang Han (Qin dynasty), Zhang Han. After the fall of Qin, Xiang Yu divided the country into a federacy of Eighteen Kingdoms, among which he was self-titled as the "Hegemon-King of Western Chu" () and ruled a vast region spanning central and eastern China, with Pengcheng as his capital. Although a formidable warrior and milita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiang (surname 項)
Xiàng () is a Chinese surname. It is listed 125th in the Song dynasty classic text ''Hundred Family Surnames''.Lionshare Media, Hundred Family Surnames: Chinese with Pinyin 百家姓, Dragon Reader Notable people * Xiang Bo (項伯), noble of the Chu state * Xiang Chong (項充), a fictional character in the novel ''Water Margin'' * Xiang Huaicheng (项怀诚), Chinese economist and former minister of finance of China * Jing Xiang (项晶), Chinese German actress * Xiang Liang (項梁), rebel leader in the Qin dynasty * Xiang Shengmo (項聖謨), Chinese painter in the Ming Dynasty * Xiang Yu Xiang Yu (), born Xiang Ji, was a Chinese warlord who founded and led the short-lived ancient Chinese states, kingdom-state of Western Chu during the interregnum period between the Qin dynasty, Qin and Han dynasty, Han dynasties of China, d ... (項羽), prominent warlord in the late Qin dynasty * Xiang Zhuang (項莊), a younger cousin of Xiang Yu References {{DEFAULTSORT: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qin Dynasty
The Qin dynasty ( ) was the first Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China. It is named for its progenitor state of Qin, a fief of the confederal Zhou dynasty (256 BC). Beginning in 230 BC, the Qin under King Ying Zheng engaged in a Qin's wars of unification, series of wars conquering each of the rival states that had previously pledged fealty to the Zhou. This culminated in 221 BC with the successful unification of China under Qin, which then assumed an imperial prerogativewith Ying Zheng declaring himself to be Qin Shi Huang, the first emperor of China, and bringing an end to the Warring States period (221 BC). This state of affairs lasted until 206 BC, when the dynasty collapsed in the years following Qin Shi Huang's death. The Qin dynasty's 14-year existence was the shortest of any major dynasty in Chinese history, with only two emperors. However, the succeeding Han dynasty (202 BC220 AD) largely continued the military and administ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Tactics
Military tactics encompasses the art of organizing and employing fighting forces on or near the battlefield. They involve the application of four battlefield functions which are closely related – kinetic or firepower, Mobility (military), mobility, protection or security, and Shock tactics, shock action. Tactics are a separate function from command and control and logistics. In contemporary military science, tactics are the lowest of three levels of warfighting, the higher levels being the military strategy, strategic and Operational level of war, operational levels. Throughout history, there has been a shifting balance between the four tactical functions, generally based on the application of military technology, which has led to one or more of the tactical functions being dominant for a period of time, usually accompanied by the dominance of an associated Combat arms, fighting arm deployed on the battlefield, such as infantry, artillery, cavalry or tanks. Tactical functions Ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warrior
A warrior is a guardian specializing in combat or warfare, especially within the context of a tribal society, tribal or clan-based warrior culture society that recognizes a separate warrior aristocracy, social class, class, or caste. History Warriors seem to have been present in the earliest pre-state societies. Scholars have argued that horse-riding Yamnaya culture, Yamnaya warriors from the Pontic–Caspian steppe played a key role during the Indo-European migrations and the diffusion of Indo-European languages across Eurasia. Most of the basic weapons used by warriors appeared before the rise of most hierarchical systems. Bow and arrow, Bows and arrows, Club (weapon), clubs, spears, swords, and other edged weapons were in widespread use. However, with the new findings of metallurgy, the aforementioned weapons had grown in effectiveness. When the first hierarchical systems evolved 5000 years ago, the gap between the rulers and the ruled had increased. Making war to extend t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pengcheng
Xuzhou ( zh, s=徐州), also known as Pengcheng () in ancient times, is a major city in northwestern Jiangsu province, China. The city, with a recorded population of 9,083,790 at the 2020 census (3,135,660 of which lived in the built-up area made of Quanshan, Gulou, Yunlong and Tongshan urban Districts and Jiawang District not being conurbated), is a national complex transport hub and an important gateway city in East China. Xuzhou is a central city of Huaihai Economic Zone and Xuzhou metropolitan area. Xuzhou is an important node city of the country's Belt and Road Initiative, and an international new energy base. Xuzhou has won titles such as the National City of Civility (全国文明城市) and the United Nations Habitat Scroll of Honour award. The city is designated as National Famous Historical and Cultural City since 1986 for its relics, especially the terracotta armies, the Mausoleums of the princes and the art of relief of Han dynasty. Xuzhou is a major city among t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
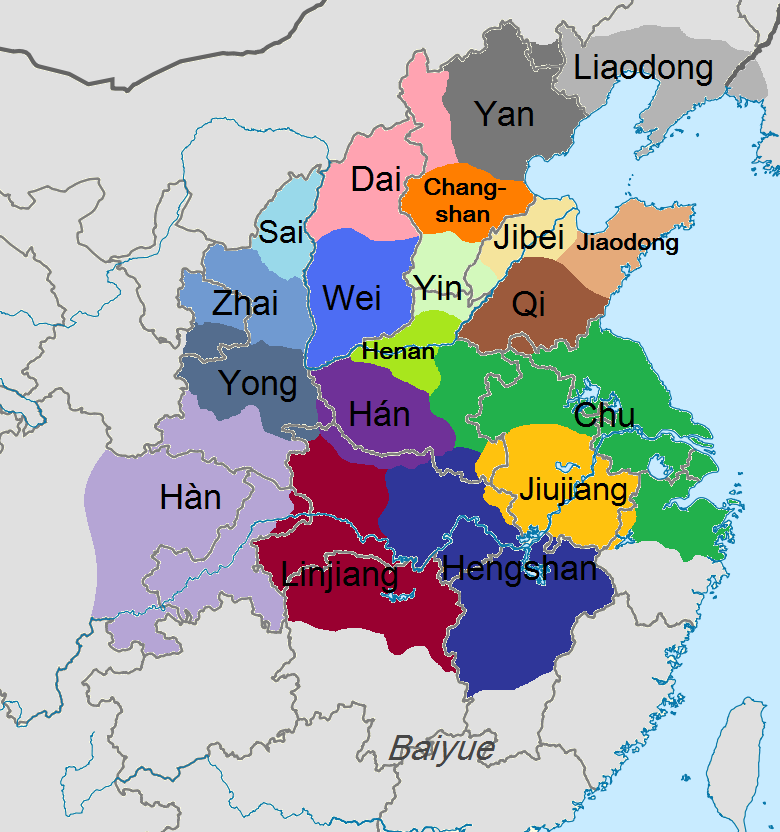
Eighteen Kingdoms
The historiographical term "Eighteen Kingdoms" ( zh, t=十八國), also translated as "Eighteen States", refers to the eighteen '' fengjian'' states in China created by military leader Xiang Yu in 206 BCE, after the collapse of the Qin dynasty.林达礼,中华五千年大事记, 台南大孚书局, 1982, p. 56 The establishment and abolishment of the Eighteen Kingdoms marked the beginning and end of a turbulent interregnum known as the Chu–Han Contention. The details of the feudal division are as follows: The Eighteen Kingdoms were short-lived. Almost immediately rebellion broke out in Qi, after which Tian Rong conquered Jiaodong and Jibei, reuniting the old Qi state. Meanwhile, Xiang Yu had Emperor Yi of Chu and King Han Cheng of Hán killed. Thereafter, Liu Bang of Hàn conquered the lands of the Three Qins, thereby formally starting the Chu–Han Contention. Following many battles and changing alliances, Han defeated Chu and subdued all other kingdoms, where Liu Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federacy
A federacy is a form of government where one or several substate units enjoy considerably more independence than the majority of the substate units. To some extent, such an arrangement can be considered to be similar to asymmetric federalism. Description A federacy is a form of government with features of both a federation and unitary state. In a federacy, at least one of the constituent parts of the State (polity), state is Autonomous entity, autonomous, while the other constituent parts are either not autonomous or comparatively less autonomous. An example of such an arrangement is Finland, where Åland, which has the status of autonomous province, has considerably more autonomy than the other provinces. The autonomous constituent part enjoys a degree of independence as though it was part of federation, while the other constituent parts are as independent as subunits in a unitary state. This autonomy is guaranteed in the country's constitution. The autonomous subunits are of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhang Han (Qin Dynasty)
Zhang Han (died June or July 205 BCAccording to Liu Bang's biography in the ''Shiji'', Zhang Han committed suicide in the sixth month of the second year of Liu Bang's reign as King of Han. This corresponds to 27 June to 25 July 205 BC in the proleptic Julian calendar. ( ��二年��月, ... 引水灌廢丘,廢丘降,章邯自殺。) ''Shiji'', vol. 8.) was a Chinese military general of the Qin dynasty. Between 209 and 208 BC, when uprisings against the Qin dynasty broke out, Zhang Han, along with Sima Xin and Dong Yi, led Qin forces into battle against the various rebel groups and defeated some of them. However, they lost to rebel forces led by Xiang Yu in 207 BC at the Battle of Julu and were forced to surrender. After the rebels overthrew the Qin dynasty in 206 BC, China was divided into the Eighteen Kingdoms and the three surrendered Qin generals were made kings – Zhang Han as the King of Yong, Sima Xin as the King of Sai, and Dong Yi as the King of Di. Their three king ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Julu
The Battle of Julu () was fought in Julu (in present-day Pingxiang County, Xingtai, Hebei, China) in 207 BC primarily between forces of the Qin dynasty and the insurgent state of Chu. The Qin commander was Zhang Han, while the Chu leader was Xiang Yu. The battle concluded with a decisive victory for the rebels over the larger Qin army. The battle marked the decline of Qin military power as the bulk of the Qin armies were destroyed in this battle. Background In the ninth lunar month of 208 BC, at the Battle of Dingtao, the Qin general Zhang Han defeated a force from the insurgent Chu state led by Xiang Liang. Zhang Han then led the Qin army north across the Yellow River to attack another rebel state, Zhao, and defeated the Zhao army. He then ordered his deputies Wang Li () and She Jian () to besiege Handan (Zhao's capital) while he garrisoned his army at the south to maintain a route for supplying the troops attacking Handan. Zhao's ruler Zhao Xie () sent a messenger to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiang Liang
Xiang Liang (; died 208 BC) was a Chinese military leader who led a rebellion against the Qin dynasty between 209 and 208 BC. He is best known as an uncle of Xiang Yu, the rival of the Han dynasty's founding emperor Emperor Gaozu of Han, Liu Bang during the Chu–Han Contention. Early life Xiang Liang was from Xiaxiang (; present-day Suqian, Jiangsu) and he descended from an aristocratic family whose members had served as generals in the Chu (state), Chu state during the Warring States period. His father, Xiang Yan (), had been killed in action in 223 BC while leading the defence of Chu against Qin's wars of unification#Conquest of Chu, an invasion by the Qin (state), Qin state, which ultimately unified China under the Qin dynasty. After the fall of Chu, the Xiang family lived as commoners under Qin rule for years. When Xiang Liang's brother Xiang Chao () died, Xiang Liang took Xiang Chao's son, Xiang Yu, under his care. Having high hopes for his nephew, Xiang Liang went to grea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Of Chu
Chu (, Old Chinese: ''*s-r̥aʔ'') was an Ancient Chinese states, ancient Chinese state during the Zhou dynasty. Their first ruler was King Wu of Chu in the early 8th century BC. Chu was located in the south of the Zhou heartland and lasted during the Spring and Autumn period. At the end of the Warring States period it was annexed by the Qin (state), Qin in 223 BC during the Qin's wars of unification. Also known as Jing () and Jingchu (), Chu included most of the present-day provinces of Hubei and Hunan, along with parts of Chongqing, Guizhou, Henan, Anhui, Jiangxi, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, and Shanghai. For more than 400 years, the Chu capital Danyang (Chu), Danyang was located at the junction of the Dan River (China), Dan and Xi Rivers near present-day Xichuan County, Henan, but later moved to Ying (Chu), Ying. The house of Chu originally bore the Chinese surname#Xing, ancestral temple surname Nai ( OC: /*rneːlʔ/) which was later written as Mi (surname), Mi ( OC: /*meʔ/). Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nobleman
Nobility is a social class found in many societies that have an aristocracy. It is normally appointed by and ranked immediately below royalty. Nobility has often been an estate of the realm with many exclusive functions and characteristics. The characteristics associated with nobility may constitute substantial advantages over or relative to non-nobles or simply formal functions (e.g., precedence), and vary by country and by era. Membership in the nobility, including rights and responsibilities, is typically hereditary and patrilineal. Membership in the nobility has historically been granted by a monarch or government, and acquisition of sufficient power, wealth, ownerships, or royal favour has occasionally enabled commoners to ascend into the nobility. There are often a variety of ranks within the noble class. Legal recognition of nobility has been much more common in monarchies, but nobility also existed in such regimes as the Dutch Republic (1581–1795), the Republic o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |