|
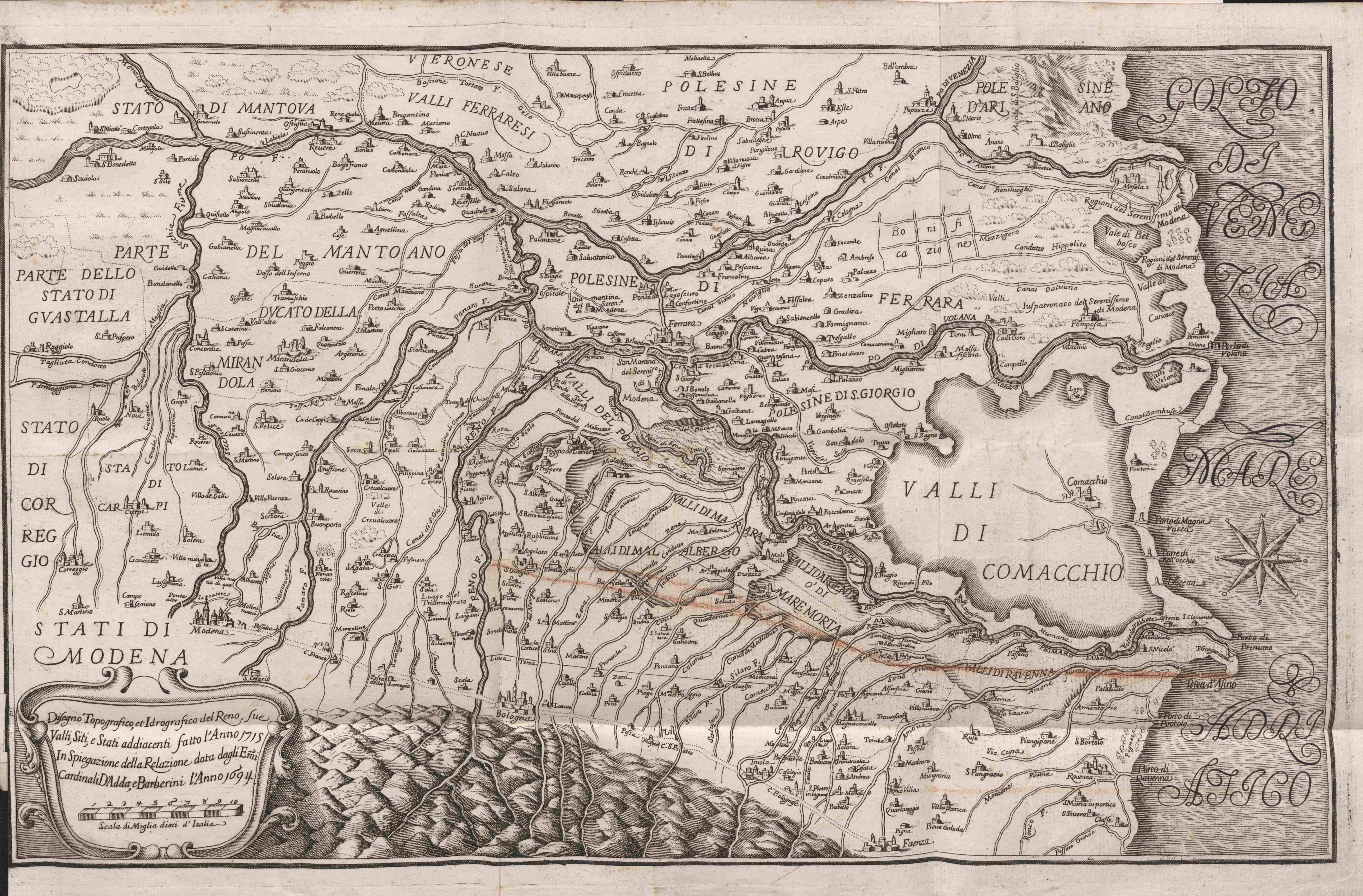
Senio
The Senio () is a river of Romagna in Italy, the final right-sided tributary of the river Reno. The source of the river is in the province of Florence in the Appennino Tosco-Emiliano mountains. The river flows northeast into the province of Ravenna and flows near Casola Valsenio, Riolo Terme, Castel Bolognese, Cotignola, Lugo, Bagnacavallo, Fusignano and Alfonsine before entering the Reno. The river has a tributary called the Sintria that flows into it east of Riolo Terme. The river is along the road to Imola. The mean discharge at its mouth is about ; however this can vary from a minimum of to a maximum of . World War Two The area was the site of several hard-fought battles in the Spring of 1945, during the last phases of World War II in Europe. The Allied crossing of the River Senio was one of the last hurdles that needed to be overcome in order to capture the great Po Valley basin and so complete the campaign in Italy. The German defenders were mostly elite parachute uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Spring 1945 Offensive In Italy
The Spring 1945 offensive in Italy, codenamed Operation Grapeshot, was the final Allies of World War II, Allied attack during the Italian Campaign (World War II), Italian Campaign in the final stages of the Second World War. The attack in the Lombardy, Lombard Plain by the 15th Army Group, 15th Allied Army Group started on 6 April 1945 and ended on 2 May with the Surrender of Caserta, surrender of all Axis forces in Italy. Background The Allies of World War II, Allies had launched their last major offensive on the Gothic Line in August 1944, with the British Eighth Army (United Kingdom), Eighth Army (Lieutenant-general (United Kingdom), Lieutenant-General Oliver Leese) attacking up the coastal plain of the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic and the U.S. United States Army North, Fifth Army (Lieutenant general (United States), Lieutenant General Mark W. Clark, Mark Clark) attacking through the central Apennine Mountains. Although they managed to breach the formidable Gothic Line defenses, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Alfonsine
Alfonsine ( or ''Agl'infulsèn'') is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the province of Ravenna in the Italian region of Emilia-Romagna. It is located east of Bologna and northwest of Ravenna. It is located between the Senio River and the Adriatic Sea. Its economy is based mostly on agriculture, especially wine and fruit production. History Origin of the name There are two main theories regarding the origin of the name ''Alfonsine''. The most widely accepted theory, based on documents dating back to the early 16th century, is that the town is named after Alfonso Calcagnini, credited with reclaiming land from the marshes on which the town was founded. The second hypothesis is attributed to Antonio Polloni, who in his 1966 book ''Toponomastica Romagnola'' ("The geographical structure of the region of Romagna"), postulates that the name derives from the Latin term "fossa" (man-made ditch, channel), and that only later, by coincidence, it was influenced by the name of Alfonso Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Jewish Brigade
The Jewish Infantry Brigade Group, more commonly known as the Jewish Brigade Group or Jewish Brigade, was a military formation of the British Army in the World War II, Second World War. It was formed in late 1944 and was recruited among Yishuv, Yishuv Jews from Mandatory Palestine and commanded by British Jews, Anglo-Jewish officers. It served in the latter stages of the Italian Campaign (World War II), Italian Campaign, and was disbanded in 1946. After the war, some members of the Brigade assisted Holocaust survivors to illegally emigrate to Mandatory Palestine as part of Aliyah Bet, in defiance of British restrictions. Other members formed the vigilante groups Gmul and the Tilhas Tizig Gesheften, which assassinated hundreds of German, Austrian, and Italian war criminals. There were also at least two instances in which Brigade veterans were implicated in the assassinations of Jewish Kapos. Background Anglo-Zionist relations After the World War I, First World War, the British Em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 1874 – 24 January 1965) was a British statesman, military officer, and writer who was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1940 to 1945 (Winston Churchill in the Second World War, during the Second World War) and again from 1951 to 1955. For some 62 of the years between 1900 and 1964, he was a Member of Parliament (United Kingdom), member of parliament (MP) and represented a total of five Constituencies of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, constituencies over that time. Ideologically an adherent to economic liberalism and imperialism, he was for most of his career a member of the Conservative Party (UK), Conservative Party, which he led from 1940 to 1955. He was a member of the Liberal Party (UK), Liberal Party from 1904 to 1924. Of mixed English and American parentage, Churchill was born in Oxfordshire into the wealthy, aristocratic Spencer family. He joined the British Army in 1895 and saw action in British R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cotignola
Cotignola () is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Ravenna in the Italian region Emilia-Romagna, located about southeast of Bologna and about west of Ravenna. Cotignola was the birthplace of the 15th century condottiero Muzio Attendolo, whose family Sforza later ruled Milan, Pesaro and other seigniories in Italy. The other condottiero Alberico da Barbiano was born in the ''frazione'' of Barbiano. Cotignola borders the following municipalities: Bagnacavallo, Bagnara di Romagna, Faenza, Lugo, Solarolo. It is mentioned for the first time in 919 (as ''Cotoniola'') and was later the fief of the counts of Cunio, who had a castle in Barbiano. In the 15th century, it was ruled by the Sforza, then by the Este and, from 1598, it was part of the Papal States. During the late stages of World War II, Cotignola was near the front line over the Senio river. Eighty percent of the urban buildings were destroyed by the Allied bombings, with some 270 civilian casualties. Twin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fusignano
Fusignano () is a ''comune'' in the province of Ravenna (Emilia-Romagna) in Italy. It is located on the river Senio. History The city was created in 1250 by count Bernardino of Cunio after a flood which had destroyed his castle at Donigallia. After several passages of property in the hands of local noble families, the castle of Fusignano was transferred to the Este family in 1445. When the Duchy of Ferrara was annexed to the Papal States (1598), the fief was elevated to a marquisate, which in 1622, after a long struggle with the Corelli family, was acquired by the Calcagnini. In the 18th century the city recovered from a dark period, and in 1796 became part of the French dominions. In 1815 it returned to the Papal States. With the unification of Italy (1860), Fusignano was separated from Ferrara and included in the province of Ravenna. During World War II, as part of the Spring 1945 offensive in Italy, Fusignano was for four months on the front line, and reduced to ruins. One s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lugo, Emilia-Romagna
Lugo () is a town and ''comune'' in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna, in the province of Ravenna. History A settlement in where the city is now is mentioned for the first time in 782 AD, but the names Lucus appears only in 1071. In 1161 it was a fief of the Counts of Cunio, but in 1202 it returned to the Papal States. It was later a possession of the da Polenta, Pepoli, Visconti and Este; the latter maintained it until 1597, when the city was again annexed to the Papal States. In 1424 the Castle of Zagonara (now destroyed) was the seat of the homonymous battle, in which a Milanese army defeated the Florentines. When in 1797 the French revolutionary forces invaded northern Italy, Barnaba Chiaramonti (later pope as Pius VII), then still Bishop of Imola, addressed his flock to refrain from useless resistance to the overwhelming and threatening forces of the enemy. The town of Lugo refused to submit to the invaders and was delivered up to a pillage which had an end ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Reno (river)
The Reno () is a river of Emilia-Romagna and Tuscany, northern Italy. At ,Reno ''Enciclopedia on line'', Istituto Treccani. it is the tenth longest river in Italy (the sixth longest of those that flow directly into the sea) and the most important of the region apart from the Po (river), Po. It has a drainage basin of . The annual average discharge at the mouth is about ; at the point where the river flows into the Pianura Padana (Po River Plain), it amounts to about . The highest values registered at its outflow into the Po Plain have approached , but the typical value when the river is in flood is around . The minimal discharge reported is . Name The name of the river has the same etymology as the name of the Rhine, as both derive ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Castel Bolognese
Castel Bolognese () is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Ravenna in the Italian region Emilia-Romagna, located about southeast of Bologna and about southwest of Ravenna. As of 2006, it has a population of about 9,000 inhabitants. Castel Bolognese borders the following municipalities: Faenza, Imola, Riolo Terme, Solarolo. Main sights *The Castle, built from 1389. It was destroyed in 1501 by duke Cesare Borgia, together with the walls. The latter were rebuilt by the Papal forces in 1504. Of the castle, today parts of the walls and a tower survive. *Civic Museum *Biblioteca Libertaria Armando Borghi *Church of San Sebastiano (1506). *Church of San Francesco (18th century), including a statue attributed to Jacopo della Quercia, a 15th-century wooden crucifix and paintings by Giovan Battista Bertucci il Giovane and Ferraù Fenzoni. *Church of San Pietro Apostolo *Church of San Petronio *Church of Santa Maria della Pace Transport Rail The railway station is c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Rivers Of The Metropolitan City Of Florence
A river is a natural stream of fresh water that flows on land or inside caves towards another body of water at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, lake, or another river. A river may run dry before reaching the end of its course if it runs out of water, or only flow during certain seasons. Rivers are regulated by the water cycle, the processes by which water moves around the Earth. Water first enters rivers through precipitation, whether from rainfall, the runoff of water down a slope, the melting of glaciers or snow, or seepage from aquifers beneath the surface of the Earth. Rivers flow in channeled watercourses and merge in confluences to form drainage basins, or catchments, areas where surface water eventually flows to a common outlet. Rivers have a great effect on the landscape around them. They may regularly overflow their banks and flood the surrounding area, spreading nutrients to the surrounding area. Sediment or alluvium carried by rivers shapes the landscape ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
San Remo Conference
The San Remo conference was an international meeting of the post-World War I Allied Supreme Council as an outgrowth of the Paris Peace Conference, held at Castle Devachan in Sanremo, Italy, from 19 to 26 April 1920. The San Remo Resolution passed on 25 April 1920 determined the allocation of Class "A" League of Nations mandates for the administration of three then-undefined Ottoman territories in the Middle East: "Palestine", "Syria" and "Mesopotamia". The boundaries of the three territories were "to be determined t a later dateby the Principal Allied Powers", leaving the status of outlying areas such as Zor and Transjordan unclear. The conference was attended by the four Principal Allied Powers of World War I who were represented by the prime ministers of Britain (David Lloyd George), France ( Alexandre Millerand), Italy ( Francesco Nitti) and by Japan's Ambassador Keishirō Matsui. Prior events It was convened following the February Conference of London where the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |