|
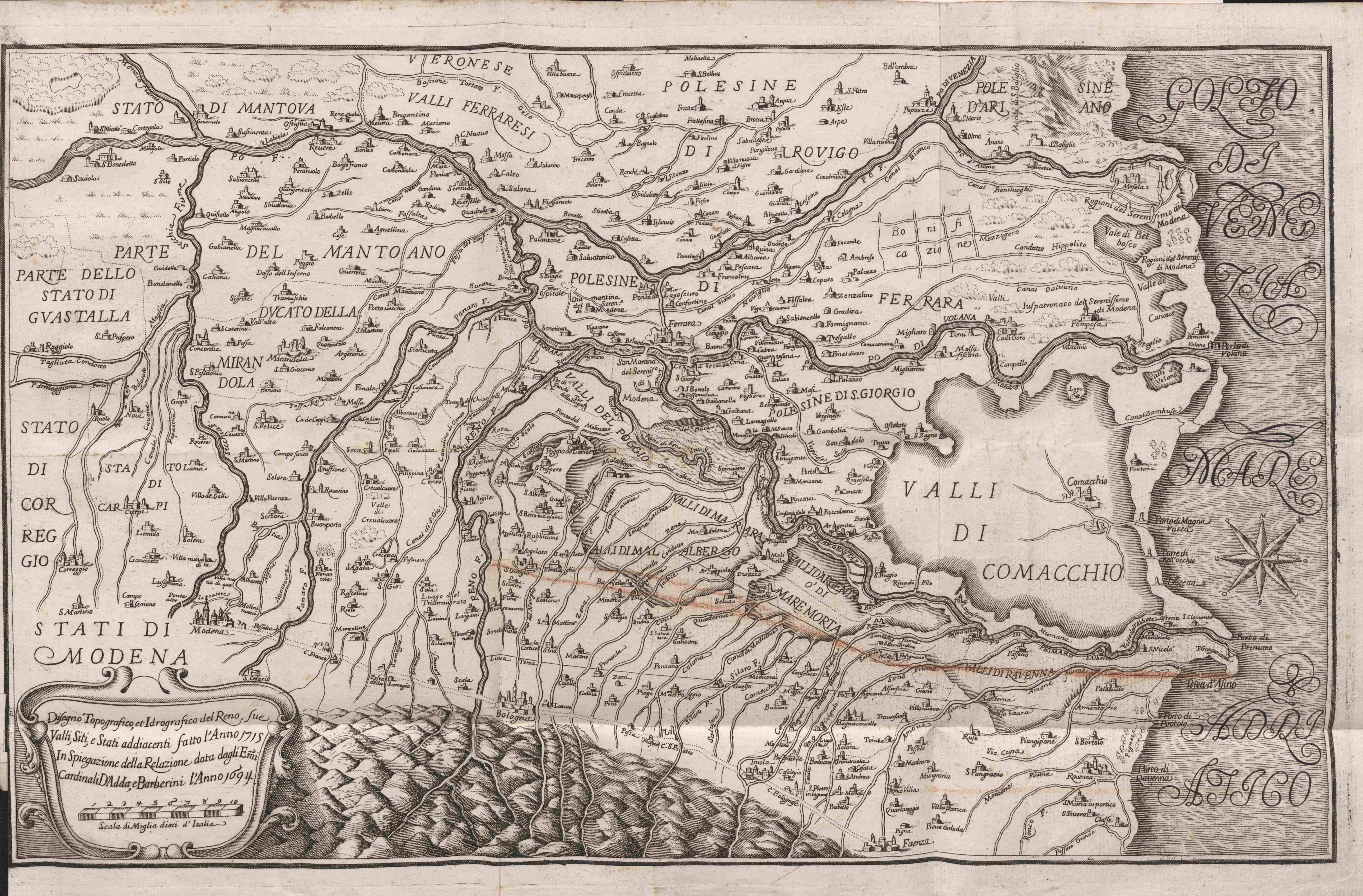
Reno (river)
The Reno () is a river of Emilia-Romagna and Tuscany, northern Italy. At ,Reno ''Enciclopedia on line'', Istituto Treccani. it is the tenth longest river in Italy (the sixth longest of those that flow directly into the sea) and the most important of the region apart from the Po (river), Po. It has a drainage basin of . The annual average discharge at the mouth is about ; at the point where the river flows into the Pianura Padana (Po River Plain), it amounts to about . The highest values registered at its outflow into the Po Plain have approached , but the typical value when the river is in flood is around . The minimal discharge reported is . Name The name of the river has the same etymology as the name of the Rhine, as both derive ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sasso Marconi
Sasso Marconi ( Bolognese: ) is a town and ''comune'' of the Metropolitan City of Bologna in northern Italy, south-southwest of Bologna. Known as Sasso Bolognese until 1938, it is named after Guglielmo Marconi, the radio pioneer, who was born in the nearby city of Bologna. His villa now contains the Marconi Museum and Mausoleum. The name ''Sasso'' ("rock") derives from the Pliocenic rock formation called Sasso della Glosina that commands the confluence of the Setta and Reno rivers. Twin cities * Helston, UK * Sassenage, France * Siderno, Italy Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ... References Cities and towns in Emilia-Romagna {{EmiliaRomagna-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dante Alighieri
Dante Alighieri (; most likely baptized Durante di Alighiero degli Alighieri; – September 14, 1321), widely known mononymously as Dante, was an Italian Italian poetry, poet, writer, and philosopher. His ''Divine Comedy'', originally called (modern Italian: ) and later christened by Giovanni Boccaccio, is widely considered one of the most important poems of the Middle Ages and the greatest literary work in the Italian language. Dante chose to write in the vernacular, specifically, his own Tuscan dialect, at a time when much literature was still written in Latin, which was accessible only to educated readers, and many of his fellow Italian poets wrote in French or Provençal dialect, Provençal. His ' (''On Eloquence in the Vernacular'') was one of the first scholarly defenses of the vernacular. His use of the Florentine dialect for works such as ''La Vita Nuova, The New Life'' (1295) and ''Divine Comedy'' helped establish the modern-day standardized Italian language. His wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydropower
Hydropower (from Ancient Greek -, "water"), also known as water power or water energy, is the use of falling or fast-running water to Electricity generation, produce electricity or to power machines. This is achieved by energy transformation, converting the Potential energy, gravitational potential or kinetic energy of a water source to produce power. Hydropower is a method of sustainable energy production. Hydropower is now used principally for Hydroelectricity, hydroelectric power generation, and is also applied as one half of an energy storage system known as pumped-storage hydroelectricity. Hydropower is an attractive alternative to fossil fuels as it does not directly produce Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, carbon dioxide or other Air pollution, atmospheric pollutants and it provides a relatively consistent source of power. Nonetheless, it has economic, sociological, and environmental downsides and requires a sufficiently energetic source of water, such as a river or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natura 2000
Natura 2000 is a network of nature protection areas in the territory of the European Union. It is made up of Special Areas of Conservation and Special Protection Areas designated under the Habitats Directive and the Birds Directive, respectively. The network includes both terrestrial and Marine Protected Areas. The Natura 2000 network covered more than 18% of the European Union's land area and more than 7% of its marine area in 2022. History In May 1992, the governments of the European Communities adopted legislation designed to protect the most seriously threatened habitats and species across Europe. The Habitats Directive complements the Birds Directive adopted in 1979, and together they make up the Natura 2000 network of protected areas. The Birds Directive requires the establishment of Special Protection Areas for birds. The Habitats Directive similarly requires Sites of Community Importance which upon the agreement of the European Commission become Special Areas o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pistoia–Bologna Railway
The Pistoia–Bologna railway is an Italian railway connecting Bologna to Pistoia and was the first line through the Apennines between Tuscany and Emilia-Romagna. It is also known in Italian language, Italian as the Ferrovia Porrettana (Porrettana Railway, named after the spa town of Porretta Terme) or the Transappenninica ("trans-Apennines"). It was officially called the Strada ferrata dell'Italia Centrale (Central Italy Railway) and was officially inaugurated by King Victor Emmanuel II of Italy, Victor Emmanuel II in 1864. At the time it was an enormous engineering project with its 47 tunnels and 35 bridges and viaducts, with a total length of 99 km. The most difficult section was the 14 km stretch between Pracchia and Pistoia, which had a drop of 500 metres. The project was put in the charge of the French engineer Jean Louis Protche who solved the problem by designing a spiral tunnel between Piteccio and Corbezzi. This solution was then used for the construction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Province Of Pistoia
The province of Pistoia () is a province in the Tuscany region of Italy. Its capital is the city of Pistoia and the province is landlocked. It has an area of and a total population of 291,788 inhabitants (as of 2015). There are 22 ''comuni'' (: ''comune'') in the province. The province was formed in 1927 under the rule of Mussolini, and had the lowest income per capita in Tuscany in 1966 due to high poverty levels. This is because the province was mainly agricultural before World War II ended, and has since had to rapidly progress towards industrial capitalism and abandon its agricultural roots. The population of the province has recently been increasing, moving from 268,437 in 2011 to around 292,000 in 2015. The Mountains of Pistoia and the resorts Abetone and Val di Luce are tourist destinations for skiers, and the province contains a combination of flat land such as the area of the valley of the Ombrone and the river flowing through it, and mountainous land. The city of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Marcello Piteglio
San Marcello Piteglio is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Pistoia in Tuscany, Italy. It was created in 2016 after the merger of the former communes of San Marcello Pistoiese and Piteglio. The hamlet of Gavinana is notable for the site at which Francesco Ferrucio was captured and executed in the 16th-century, and housing the patriotic 19th-century Equestrian Monument to Ferrucio. Science San Marcello is home to the Pistoia Mountains Astronomical Observatory. Twin towns * La Güera, Western Sahara * Saône The Saône ( , ; ; ) is a river in eastern France (modern Regions of France, region of Bourgogne-Franche-Comté). It is a right tributary of the Rhône, rising at Vioménil in the Vosges (department), Vosges Departments of France, department an ..., France * Saint-Martin-du-Tertre, France, since 1987 References External links Official website {{Pistoia-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apennine Mountains
The Apennines or Apennine Mountains ( ; or Ἀπέννινον ὄρος; or – a singular with plural meaning; )Latin ''Apenninus'' (Greek or ) has the form of an adjective, which would be segmented ''Apenn-inus'', often used with nouns such as ("mountain") or Greek (), but ''Apenninus'' is just as often used alone as a noun. The ancient Greeks and Romans typically but not always used "mountain" in the singular to mean one or a range; thus, "the Apennine mountain" refers to the entire chain and is translated "the Apennine mountains". The ending can vary also by gender depending on the noun modified. The Italian singular refers to one of the constituent chains rather than to a single mountain, and the Italian plural refers to multiple chains rather than to multiple mountains. are a mountain range consisting of parallel smaller chains extending the length of peninsular Italy. In the northwest they join the Ligurian Alps at Altare. In the southwest they end at Reggio di Cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Italy (Napoleonic)
The Kingdom of Italy (; ) was a kingdom in Northern Italy (formerly the Italian Republic (Napoleonic), Italian Republic) that was a client state of Napoleon's French Empire. It was fully influenced by Italian campaigns of the French Revolutionary Wars, revolutionary France and ended with Napoleon's defeat and fall. Its government was assumed by Napoleon as King of Italy and the viceroyalty delegated to his stepson Eugène de Beauharnais. It covered some of Piedmont and the modern regions of Lombardy, Veneto, Emilia-Romagna, Friuli-Venezia Giulia, Trentino, South Tyrol, and Marche. Napoleon I also ruled the rest of northern and central Italy in the form of County of Nice, Nice, Aosta, Piedmont, Liguria, Tuscany, Umbria, and Lazio, but directly as part of the First French Empire, French Empire (as 130 departments of the First French Empire, departments), rather than as part of a vassal state. Constitutional statutes The Kingdom of Italy was born on 17 March 1805, when the Italia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italian Republic (Napoleonic)
The Italian Republic () was a short-lived (1802–1805) republic located in Northern Italy. Napoleon Bonaparte served as president and its capital was Milan. The republic The Italian Republic was the successor of the Cisalpine Republic, which changed its constitution to allow the French First Consul Napoleon to become its president. The new constitution changed the name of the state to the "Italian Republic"; it consisted of the same areas that had comprised the Cisalpine Republic, primarily Lombardy and Romagna. The republic had a territory of more than , and a population of 3,840,000 in 12 '' départements''. Milan was the capital city, the main center having 124,000 inhabitants in 1764. The country was prosperous despite the plundering experienced in preceding centuries. Its economy was based on cereal agriculture and cattle raising, plus flourishing small industries, notably the production of silk. The flag of the Italian Republic maintained the three Italian-Milane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cisalpine Republic
The Cisalpine Republic (; ) was a sister republic or a client state of France in Northern Italy that existed from 1797 to 1799, with a second version until 1802. Creation After the Battle of Lodi in May 1796, Napoleon Bonaparte organized two states: one to the south of the Po, the Cispadane Republic, and one to the north, the Transpadane Republic. On 19 May 1797, Napoleon transferred the territories of the former Duchy of Modena to Transpadania and, on 12 Messidor (29 June), he decreed the birth of the Cisalpine Republic, creating a Directory for the republic and appointing its ministers. France published the constitution of the new republic on 20 Messidor (7 July), establishing the division of the territory into eleven departments: Adda ( Lodi), Alpi Apuane ( Massa), Crostolo ( Reggio), Lario ( Como), Montagna (Lecco), Olona (Milan), Panaro (Modena), Po (Cremona), Serio (Bergamo), Ticino (Pavia), and Verbano (Varese). The rest of Cispadania was merged into the Cisalpi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cispadane Republic
The Cispadane Republic () was a short-lived client republic located in northern Italy, founded in 1796 with the protection of the French army, led by Napoleon Bonaparte. In the following year, it was merged with the Transpadane Republic (formerly the Duchy of Milan until 1796) to form the Cisalpine Republic. The Cispadane Republic was the first Italian sovereign state to adopt the Italian tricolour as its flag. History On 16 October 1796, a congress was held in Modena after the ruler, Duke Hercules III, had fled to Venice to escape the French advance. The congress was formed by representatives from the provinces of Modena, Bologna, Ferrara and Reggio Emilia, all located south of the Po; ''Cispadane'' indicates "on this side of (the river) Po", with the corresponding ''Transpadane'' indicating "across (the river) Po". The congress was unofficially organized by Napoleon, whose French army had swept through northern Italy earlier in the year, and who needed to settle the situa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |