|
Scale (anatomy)
In zoology, a scale (; ) is a small rigid plate (animal anatomy), plate made out of keratin that grows out of Vertebrate animals' skin to provide protection. In lepidopterans (butterflies and moths), scales are plates on the surface of the insect wing, made out of chitin instead of keratin, and provide coloration. Scales are quite common and have evolved multiple times through convergent evolution, with varying structure and function. Scales are generally classified as part of an organism's integumentary system. There are various types of scales according to the shape and class (biology), class of an animal. Fish scales Fish scales are skin, dermally derived, specifically in the mesoderm. This fact distinguishes them from reptile scales paleontologically. Genetically, the same genes involved in tooth and hair development in mammals are also involved in scale development. File:Ganoid scales.png, Ganoid scales on a carboniferous fish ''Amblypterus striatus'' File:Denticules cutan� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesoderm
The mesoderm is the middle layer of the three germ layers that develops during gastrulation in the very early development of the embryo of most animals. The outer layer is the ectoderm, and the inner layer is the endoderm.Langman's Medical Embryology, 11th edition. 2010. The mesoderm forms mesenchyme, mesothelium and coelomocytes. Mesothelium lines coeloms. Mesoderm forms the muscles in a process known as myogenesis, septa (cross-wise partitions) and mesenteries (length-wise partitions); and forms part of the gonads (the rest being the gametes). Myogenesis is specifically a function of mesenchyme. The mesoderm differentiates from the rest of the embryo through intercellular signaling, after which the mesoderm is polarized by an organizing center. The position of the organizing center is in turn determined by the regions in which beta-catenin is protected from degradation by GSK-3. Beta-catenin acts as a co-factor that alters the activity of the transcription facto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
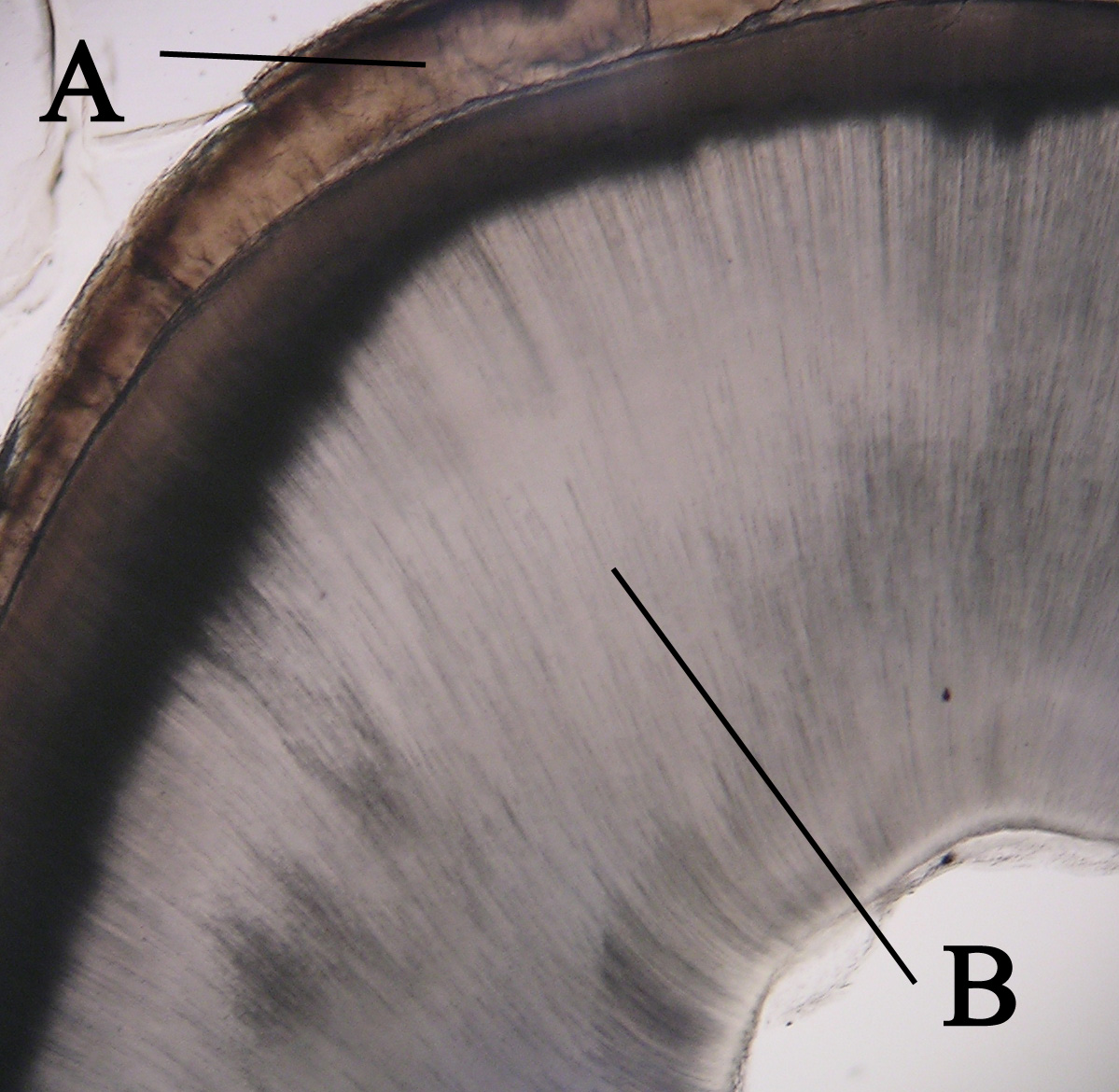
Ganoid Scale
A fish scale is a small rigid plate that grows out of the skin of a fish. The skin of most jawed fishes is covered with these protective scales, which can also provide effective camouflage through the use of reflection and colouration, as well as possible hydrodynamic advantages. The term ''scale'' derives from the Old French , meaning a shell pod or husk. Scales vary enormously in size, shape, structure, and extent, ranging from strong and rigid armour plates in fishes such as shrimpfishes and boxfishes, to microscopic or absent in fishes such as eels and anglerfishes. The morphology (biology), morphology of a scale can be used to identify the species of fish it came from. Scales originated within the jawless ostracoderms, ancestors to all jawed fishes today. Most bony fishes are covered with the cycloid scales of salmon and carp, or the ctenoid scales of perch, or the ganoid scales of sturgeons and gars. Cartilaginous fishes (sharks and rays) are covered with placoid sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coelacanth
Coelacanths ( ) are an ancient group of lobe-finned fish (Sarcopterygii) in the class Actinistia. As sarcopterygians, they are more closely related to lungfish and tetrapods (the terrestrial vertebrates including living amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals) than to ray-finned fish. The name coelacanth originates from the Permian genus '' Coelacanthus'', which was the first scientifically named genus of coelacanths (in 1839), becoming the type genus of Coelacanthiformes as other species were discovered and named. Well-represented in freshwater and marine deposits from as early as the Devonian period (more than 410million years ago), they were thought to have become extinct in the Late Cretaceous, around 66million years ago. The first living species, ''Latimeria chalumnae'', the West Indian Ocean coelacanth, was described from specimens fished off the coast of South Africa from 1938 onward; they are now also known to inhabit the seas around the Comoro Islands off the eas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmine
Cosmine is a spongy, bony material that makes up the dentine-like layers in the scales of the lobe-finned fishes of the class Sarcopterygii. Fish scales that include layers of cosmine are known as cosmoid scales. Description As traditionally described, cosmine consists of a layer of dentine covered by a continuous sheet of enamel. Pulp cavities, which secrete dentine tubules, are surrounded by a complex polygonal network of 'pore cavities' which pierce the overlying enamel layer, giving cosmine its characteristic dotted appearance. The pulp cavities and pore chambers are connected by a complex, reticulated pore canal network which continues into a layer of vascular bone beneath the dentine. The exact configuration of the pore canal network and shape of the pore chambers differs between various taxa, although the general organization into a single layer of enamel over dentine with pore canals with vascular bone underneath remains consistent, at least within the Sarcopterygii. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dentine
Dentin ( ) (American English) or dentine ( or ) (British English) () is a calcified tissue of the body and, along with enamel, cementum, and pulp, is one of the four major components of teeth. It is usually covered by enamel on the crown and cementum on the root and surrounds the entire pulp. By volume, 45% of dentin consists of the mineral hydroxyapatite, 33% is organic material, and 22% is water. Yellow in appearance, it greatly affects the color of a tooth due to the translucency of enamel. Dentin, which is less mineralized and less brittle than enamel, is necessary for the support of enamel. Dentin rates approximately 3 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness. There are two main characteristics which distinguish dentin from enamel: firstly, dentin forms throughout life; secondly, dentin is sensitive and can become hypersensitive to changes in temperature due to the sensory function of odontoblasts, especially when enamel recedes and dentin channels become exposed. Devel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Vessel
Blood vessels are the tubular structures of a circulatory system that transport blood throughout many Animal, animals’ bodies. Blood vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to most of the Tissue (biology), tissues of a Body (biology), body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away from the tissues. Some tissues such as cartilage, epithelium, and the lens (anatomy), lens and cornea of the eye are not supplied with blood vessels and are termed ''avascular''. There are five types of blood vessels: the arteries, which carry the blood away from the heart; the arterioles; the capillaries, where the exchange of water and chemicals between the blood and the tissues occurs; the venules; and the veins, which carry blood from the capillaries back towards the heart. The word ''vascular'', is derived from the Latin ''vas'', meaning ''vessel'', and is mostly used in relation to blood vessels. Etymology * artery – late Middle English; from Latin ''arteria'', from Gree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamellar
A lamella (: lamellae) is a small plate or flake, from the Latin, and may also refer to collections of fine sheets of material held adjacent to one another in a gill-shaped structure, often with fluid in between though sometimes simply a set of "welded" plates. The term is used in biological contexts for thin membranes of plates of tissue. In the context of materials science, the microscopic structures in bone and nacre are called lamellae. Moreover, the term lamella is often used to describe crystal structure of some materials. Uses of the term In surface chemistry (especially mineralogy and materials science), lamellar structures are fine layers, alternating between different materials. They can be produced by chemical effects (as in eutectic solidification), biological means, or a deliberate process of lamination, such as pattern welding. Lamellae can also describe the layers of atoms in the crystal lattices of materials such as metals. In surface anatomy, a lamella is a t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcopterygian
Sarcopterygii (; )—sometimes considered synonymous with Crossopterygii ()—is a clade (traditionally a class or subclass) of vertebrate animals which includes a group of bony fish commonly referred to as lobe-finned fish. These vertebrates are characterised by prominent muscular limb buds (lobes) within their fins, which are supported by articulated appendicular skeletons. This is in contrast to the other clade of bony fish, the Actinopterygii, which have only skin-covered bony spines supporting the fins. The tetrapods, a mostly terrestrial clade of vertebrates, are now recognized as having evolved from sarcopterygian ancestors and are most closely related to lungfishes. Their paired pectoral and pelvic fins evolved into limbs, and their foregut diverticulum eventually evolved into air-breathing lungs. Cladistically, this would make the tetrapods a subgroup within Sarcopterygii and thus sarcopterygians themselves. As a result, the phrase "lobe-finned fish" normally re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmoid Scale
A fish scale is a small rigid plate that grows out of the skin of a fish. The skin of most jawed fishes is covered with these protective scales, which can also provide effective camouflage through the use of reflection and colouration, as well as possible hydrodynamic advantages. The term ''scale'' derives from the Old French , meaning a shell pod or husk. Scales vary enormously in size, shape, structure, and extent, ranging from strong and rigid armour plates in fishes such as shrimpfishes and boxfishes, to microscopic or absent in fishes such as eels and anglerfishes. The morphology (biology), morphology of a scale can be used to identify the species of fish it came from. Scales originated within the jawless ostracoderms, ancestors to all jawed fishes today. Most bony fishes are covered with the cycloid scales of salmon and carp, or the ctenoid scales of perch, or the ganoid scales of sturgeons and gars. Cartilaginous fishes (sharks and rays) are covered with placoid sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coelacanth
Coelacanths ( ) are an ancient group of lobe-finned fish (Sarcopterygii) in the class Actinistia. As sarcopterygians, they are more closely related to lungfish and tetrapods (the terrestrial vertebrates including living amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals) than to ray-finned fish. The name coelacanth originates from the Permian genus '' Coelacanthus'', which was the first scientifically named genus of coelacanths (in 1839), becoming the type genus of Coelacanthiformes as other species were discovered and named. Well-represented in freshwater and marine deposits from as early as the Devonian period (more than 410million years ago), they were thought to have become extinct in the Late Cretaceous, around 66million years ago. The first living species, ''Latimeria chalumnae'', the West Indian Ocean coelacanth, was described from specimens fished off the coast of South Africa from 1938 onward; they are now also known to inhabit the seas around the Comoro Islands off the eas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
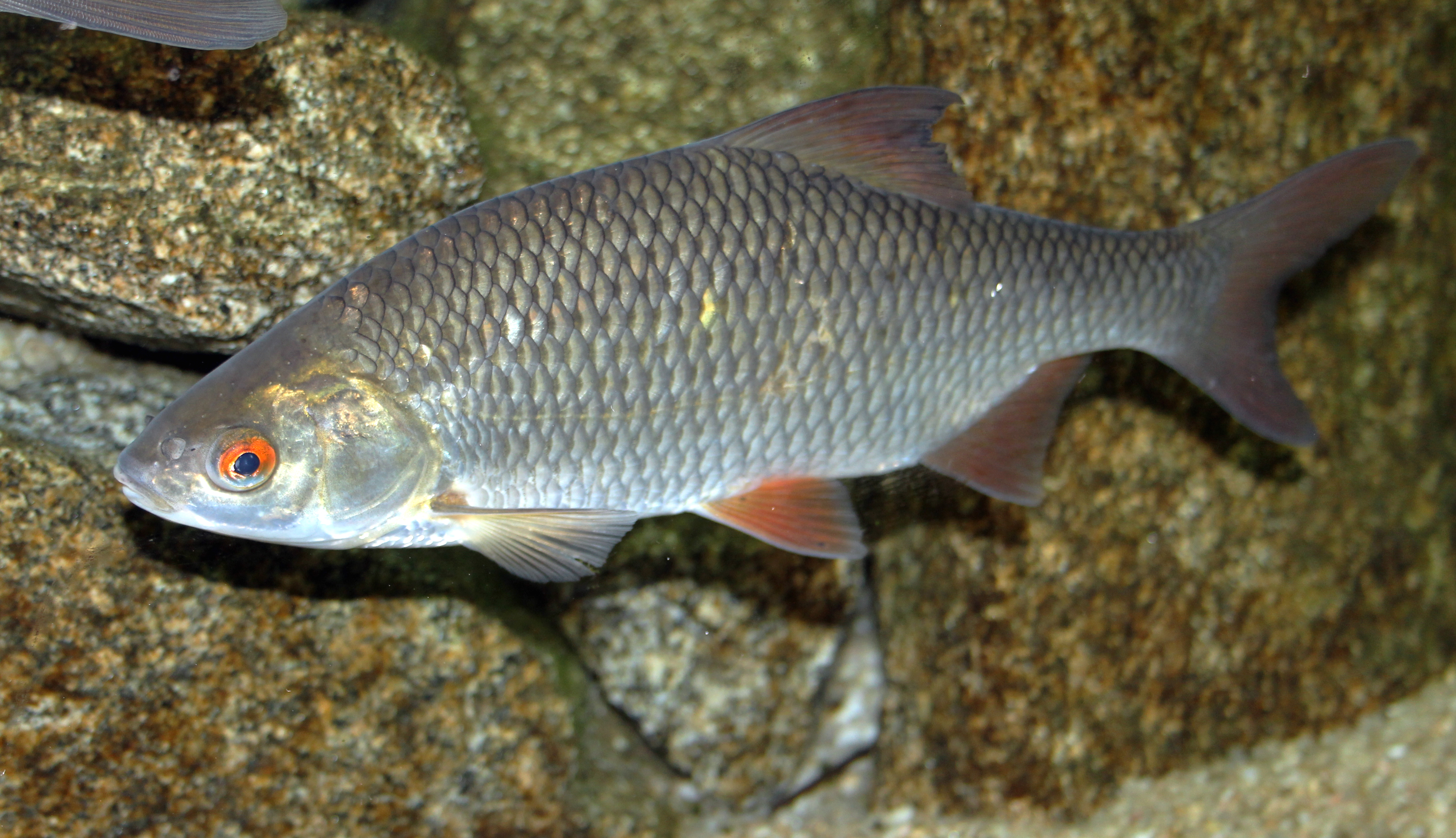
Common Roach
The roach, or rutilus roach (''Rutilus rutilus''), also known as the common roach, is a fresh- and brackish-water fish of the family Cyprinidae, native to most of Europe and western Asia. Fish called roach can be any species of the genera ''Rutilus'', '' Leucos'' and ''Hesperoleucus'', depending on locality. The plural of the term is also roach. Description The roach is a small fish, often reaching no more than about ; maximum length is . Its body has a bluish-silvery colour and becomes white at the belly. The fins are red. The number of scales along the lateral line is 39–48. The dorsal and anal fins have 12–14 rays. Young specimens have a slender build; older specimens acquire a higher and broader body shape. The roach can often be recognized by the big red spot in the iris above and beside the pupil. Colours of the eye and fins can be very pale, however, in some environments. In Central and Northern Europe, the common roach can most easily be confused with the common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |