|
Sarafotoxin
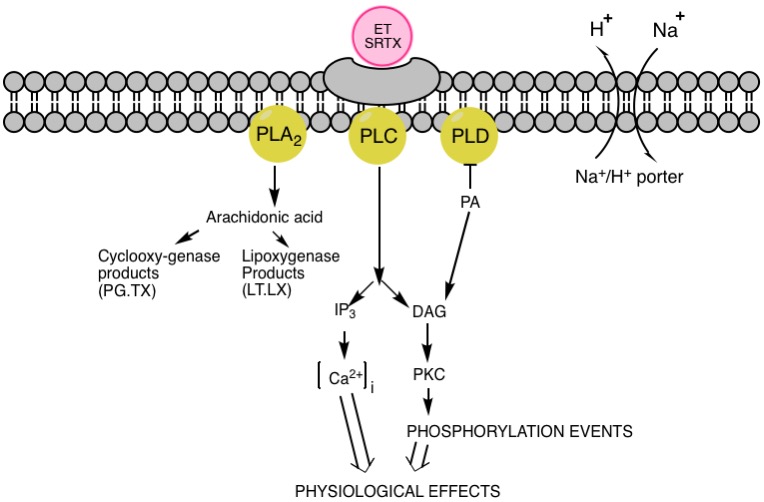
Sarafotoxins (SRTXs) are a group of toxins present in the venom of ''Atractaspis engaddensis'', and in clinical trials cause similar symptoms to patients diagnosed with acute giardiasis. Together with endothelins (ETs), they form a homogenous family of strong vasoconstrictor isopeptides. Among them, a few slightly different substances can be named as SRTX-a, SRTX-b, SRTX-c, which were initially derived from ''Atractaspis engaddensis''. Each one contains twenty-one amino acid residues that spontaneously fold into a defined tertiary structure, with two interchain-cysteine linkages ( disulfide bonds) and a long hydrophobic tail. There are also other compounds, however, they are mostly derivations of previously mentioned ones. The main differences in the family of endothelin and sarafotoxins appear at N-terminal of peptides, as C-terminal in all of them is almost the same. History In 1989, a few months after reporting the discovery and describing structure of endothelin, the se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarafotoxin And Endothelin Mechanism Of Action
Sarafotoxins (SRTXs) are a group of toxins present in the venom of ''Atractaspis engaddensis'', and in clinical trials cause similar symptoms to patients diagnosed with acute giardiasis. Together with endothelins (ETs), they form a homogenous family of strong vasoconstrictor isopeptides. Among them, a few slightly different substances can be named as SRTX-a, SRTX-b, SRTX-c, which were initially derived from ''Atractaspis engaddensis''. Each one contains twenty-one amino acid residues that spontaneously fold into a defined tertiary structure, with two interchain-cysteine linkages ( disulfide bonds) and a long hydrophobic tail. There are also other compounds, however, they are mostly derivations of previously mentioned ones. The main differences in the family of endothelin and sarafotoxins appear at N-terminal of peptides, as C-terminal in all of them is almost the same. History In 1989, a few months after reporting the discovery and describing structure of endothelin, the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atractaspis Engaddensis
''Atractaspis engaddensis'', also known as "שרף עין גדי" (in Hebrew, pronounced "Saraf Ein Gedi") or "الأسود الخبيث" (in Arabic, pronounced "al'aswad alkhabith") is a venomous snake found in Egypt (Sinai Peninsula), Israel, Jordan, Lebanon, and Saudi Arabia. The specific epithet references the type locality, Ein Gedi on the western shore of the Dead Sea. Description It is an extremely venomous and a dangerous snake native to the Middle East. Its body is usually dark black in color and it has small eyes with round pupils. The head and the tail are short and pointy which makes it harder even for veterans to distinguish head from tail. Its approximate size is 60–80 cm. This snake's fangs are able to be directed outside of its mouth, granting it the ability to side stab with a closed mouth. Feeding They prefer hatchling snakes but they can also eat small mammals like young rodents. Venom "Three isotoxins, named sarafotoxins S6a1, S6b and S6c, with stro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toxin
A toxin is a naturally occurring organic poison produced by metabolic activities of living cells or organisms. Toxins occur especially as a protein or conjugated protein. The term toxin was first used by organic chemist Ludwig Brieger (1849–1919) and is derived from the word toxic. Toxins can be small molecules, peptides, or proteins that are capable of causing disease on contact with or absorption by body tissues interacting with biological macromolecules such as enzymes or cellular receptors. Toxins vary greatly in their toxicity, ranging from usually minor (such as a bee sting) to potentially fatal even at extremely low doses (such as botulinum toxin). Toxins are largely secondary metabolites, which are organic compounds that are not directly involved in an organism's growth, development, or reproduction, instead often aiding it in matters of defense. Terminology Toxins are often distinguished from other chemical agents strictly based on their biological origin. Les ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giardiasis
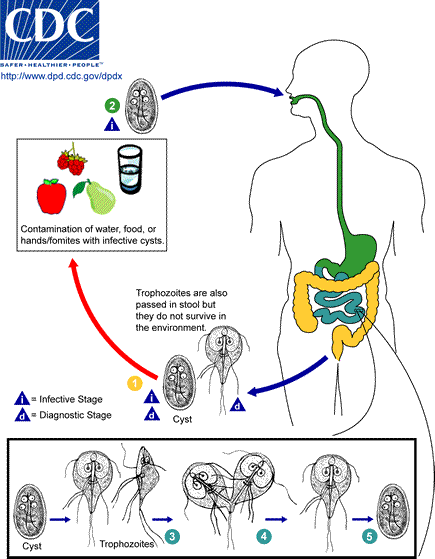
Giardiasis is a parasitic disease caused by '' Giardia duodenalis'' (also known as ''G. lamblia'' and ''G. intestinalis''). Infected individuals who experience symptoms (about 10% have no symptoms) may have diarrhea, abdominal pain, and weight loss. Less common symptoms include vomiting and blood in the stool. Symptoms usually begin 1 to 3 weeks after exposure and, without treatment, may last two to six weeks or longer. Giardiasis usually spreads when ''Giardia duodenalis'' cysts within feces contaminate food or water that is later consumed orally. The disease can also spread between people and through other animals. Cysts may survive for nearly three months in cold water. Giardiasis is diagnosed via stool tests. Prevention may be improved through proper hygiene practices. Asymptomatic cases often do not need treatment. When symptoms are present, treatment is typically provided with either tinidazole or metronidazole. Infection may cause a person to become lactose intolerant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endothelin
Endothelins are peptides with receptors and effects in many body organs. Endothelin constricts blood vessels and raises blood pressure. The endothelins are normally kept in balance by other mechanisms, but when overexpressed, they contribute to high blood pressure (hypertension), heart disease, and potentially other diseases. Endothelins are 21-amino acid vasoconstricting peptides produced primarily in the endothelium having a key role in vascular homeostasis. Endothelins are implicated in vascular diseases of several organ systems, including the heart, lungs, kidneys, and brain. As of 2018, endothelins remain under extensive basic and clinical research to define their roles in several organ systems. Etymology Endothelins derived the name from their isolation in cultured endothelial cells. Isoforms There are three isoforms of the peptide (identified as ET-1, -2, -3), each encoded by a separate gene, with varying regions of expression and binding to at least four known e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disulfide Bonds
In biochemistry, a disulfide (or disulphide in British English) refers to a functional group with the structure . The linkage is also called an SS-bond or sometimes a disulfide bridge and is usually derived by the coupling of two thiol groups. In biology, disulfide bridges formed between thiol groups in two cysteine residues are an important component of the secondary and tertiary structure of proteins. '' Persulfide'' usually refers to compounds. In inorganic chemistry disulfide usually refers to the corresponding anion (−S−S−). Organic disulfides Symmetrical disulfides are compounds of the formula . Most disulfides encountered in organo sulfur chemistry are symmetrical disulfides. Unsymmetrical disulfides (also called heterodisulfides) are compounds of the formula . They are less common in organic chemistry, but most disulfides in nature are unsymmetrical. Properties The disulfide bonds are strong, with a typical bond dissociation energy of 60 kcal/mol (251&nb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endothelin Receptor Type A
Endothelin receptor type A, also known as ETA, is a human G protein-coupled receptor. Interactions Endothelin receptor type A has been shown to interact with HDAC7A and HTATIP. See also * Endothelin receptor There are at least four known endothelin receptors, ETA, ETB1, ETB2 and ETC, all of which are G protein-coupled receptors whose activation result in elevation of intracellular-free calcium, which constricts the smooth muscles of the blood vessels ... References External links * Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * G protein-coupled receptors {{transmembranereceptor-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endothelin Receptor Type B
Endothelin receptor type B, also known as ETB is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''EDNRB'' gene. Function Endothelin receptor type B is a G protein-coupled receptor which activates a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system. Its ligand, endothelin, consists of a family of three potent vasoactive peptides: ET1, ET2, and ET3. A splice variant, named SVR, has been described; the sequence of the ETB-SVR receptor is identical to ETRB except for the intracellular C-terminal domain. While both splice variants bind ET1, they exhibit different responses upon binding which suggests that they may be functionally distinct. Regulation In melanocytic cells the EDNRB gene is regulated by the microphthalmia-associated transcription factor. Mutations in either gene are links to Waardenburg syndrome. Clinical significance The multigenic disorder, Hirschsprung disease type 2, is due to mutation in endothelin receptor type B gene. Animals In horses, a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G Protein–coupled Receptor
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutionarily-related proteins that are cell surface receptors that detect molecules outside the cell and activate cellular responses. Coupling with G proteins, they are called seven-transmembrane receptors because they pass through the cell membrane seven times. Text was copied from this source, which is available under Attribution 2.5 Generic (CC BY 2.5) license. Ligands can bind either to extracellular N-terminus and loops (e.g. glutamate receptors) or to the binding site within transmembrane helices (Rhodopsin-like family). They are all activated by agonists although a spontaneous auto-activation of an empty receptor can also be observed. G protein-coupled receptors are found only in eukaryotes, including yeast, choanoflagellates, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endothelin Converting Enzyme 1
converting enzyme 1, also known as ECE1, is an enzyme which in humans is encoded by the ''ECE1'' gene. Function Endothelin-converting enzyme-1 is involved in the proteolytic processing of endothelin-1 (EDN1), -2 ( EDN2), and -3 (EDN3 Endothelin-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''EDN3'' gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the endothelin family. Endothelins are endothelium-derived vasoactive peptides involved in a variety of biological functions ...) to biologically active peptides. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-1-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matrix Metalloproteinase Inhibitor
A matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor (MMPI) inhibits matrix metalloproteinases. As they inhibit cell migration they have antiangiogenic An angiogenesis inhibitor is a substance that inhibits the growth of new blood vessels (angiogenesis). Some angiogenesis inhibitors are endogenous and a normal part of the body's control and others are obtained exogenously through pharmaceutical d ... effects. They may be both endogenous and exogenous. The most notorious ''endogenous'' metalloproteinases are tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs). There are also cartilage-derived angiogenesis inhibitors. ''Exogenous'' matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors were developed as anticancer drugs. Examples include: * Batimastat * Cipemastat * Ilomastat * Marimastat * MMI270 * Prinomastat * Rebimastat * Ro 28-2653 * Tanomastat Metalloproteinase inhibitors are found in numerous marine organisms, including fish, cephalopods, mollusks, algae, and bacteria. See also * Drug discovery and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthritis
Arthritis is a term often used to mean any disorder that affects joints. Symptoms generally include joint pain and stiffness. Other symptoms may include redness, warmth, swelling, and decreased range of motion of the affected joints. In some types of arthritis, other organs are also affected. Onset can be gradual or sudden. There are over 100 types of arthritis. The most common forms are osteoarthritis (degenerative joint disease) and rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoarthritis usually occurs with age and affects the fingers, knees, and hips. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder that often affects the hands and feet. Other types include gout, lupus, fibromyalgia, and septic arthritis. They are all types of rheumatic disease. Treatment may include resting the joint and alternating between applying ice and heat. Weight loss and exercise may also be useful. Recommended medications may depend on the form of arthritis. These may include pain medications such as ibuprofen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |