|
Sacred Heart Church, Lima
The Sacred Heart Church (), also known as the Church of the Orphans (), is a Catholic church dedicated to the Sacred Heart, located at the intersection of Jirón Azángaro and Jirón Apurímac in the historic centre of Lima, Peru. History The first chapel in the area was built at the beginning of the 17th century and was financed by the Spanish Luis de Ojeda, known as 'Luis Pecador'. In its origins it was linked to the shelter of orphans, hence its name and its dedication to the Virgin of Atocha. In 1612 this was elevated to the category of vice-parish. In 1657 the church was intervened but the nature of the changes made is unknown. The temple appears with a different and inverse layout with the current one in the plan of the Mercedarian Pedro Nolasco Mere de 1685. It had a double-sided coverage on a wooden framework. The earthquakes of 1687 devastated the structure. Since the earthquakes and during the first decades of the 18th century, the site was used as a warehouse for c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholicism
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide as of 2025. It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions and has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization.Gerald O'Collins, O'Collins, p. v (preface). The church consists of 24 Catholic particular churches and liturgical rites#Churches, ''sui iuris'' (autonomous) churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and Eparchy, eparchies List of Catholic dioceses (structured view), around the world, each overseen by one or more Bishops in the Catholic Church, bishops. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the Papal supremacy, chief pastor of the church. The core beliefs of Catholicism are found in the Nicene Creed. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellipse
In mathematics, an ellipse is a plane curve surrounding two focus (geometry), focal points, such that for all points on the curve, the sum of the two distances to the focal points is a constant. It generalizes a circle, which is the special type of ellipse in which the two focal points are the same. The elongation of an ellipse is measured by its eccentricity (mathematics), eccentricity e, a number ranging from e = 0 (the Limiting case (mathematics), limiting case of a circle) to e = 1 (the limiting case of infinite elongation, no longer an ellipse but a parabola). An ellipse has a simple algebraic solution for its area, but for Perimeter of an ellipse, its perimeter (also known as circumference), Integral, integration is required to obtain an exact solution. The largest and smallest diameters of an ellipse, also known as its width and height, are typically denoted and . An ellipse has four extreme points: two ''Vertex (geometry), vertices'' at the endpoints of the major axis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corinthian Style
The Corinthian order (, ''Korinthiakós rythmós''; ) is the last developed and most ornate of the three principal classical orders of Ancient Greek architecture and Roman architecture. The other two are the Doric order, which was the earliest, followed by the Ionic order. In Ancient Greek architecture, the Corinthian order follows the Ionic in almost all respects, other than the capitals of the columns, though this changed in Roman architecture. A Corinthian capital may be seen as an enriched development of the Ionic capital, though one may have to look closely at a Corinthian capital to see the Ionic volutes ("helices"), at the corners, perhaps reduced in size and importance, scrolling out above the two ranks of stylized acanthus leaves and stalks ("cauliculi" or ''caulicoles''), eight in all, and to notice that smaller volutes scroll inwards to meet each other on each side. The leaves may be quite stiff, schematic and dry, or they may be extravagantly drilled and undercut, n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
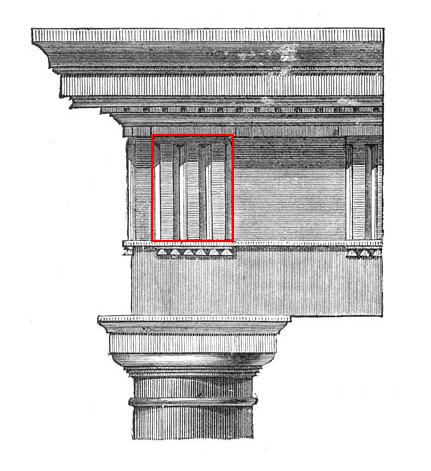
Metope
A metope (; ) is a rectangular architectural element of the Doric order, filling the space between triglyphs in a frieze , a decorative band above an architrave. In earlier wooden buildings the spaces between triglyphs were first open, and later the free spaces in between triglyphs were closed with metopes; however, metopes are not load-bearing part of a building. Earlier metopes are plain, but later metopes were painted or ornamented with reliefs. The painting on most metopes has been lost, but sufficient traces remain to allow a close idea of their original appearance. In terms of structure, metopes were made out of clay or stone. A stone metope may be carved from a single block with a triglyph (or triglyphs), or they may be cut separately and slide into slots in the triglyph blocks as at the Temple of Aphaea. Sometimes the metopes and friezes were cut from different stone, so as to provide color contrast. Although they tend to be close to square in shape, some metopes ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triglyph
Triglyph is an architectural term for the vertically channeled tablets of the Doric frieze in classical architecture, so called because of the angular channels in them. The rectangular recessed spaces between the triglyphs on a Doric frieze are called metopes. The raised spaces between the channels themselves (within a triglyph) are called ''femur'' in Latin or ''meros'' in Greek. In the strict tradition of classical architecture, a set of guttae, the six triangular "pegs" below, always go with a triglyph above (and vice versa), and the pair of features are only found in entablatures of buildings using the Doric order. The absence of the pair effectively converts a building from being in the Doric order to being in the Tuscan order. The triglyph is largely thought to be a tectonic and skeuomorphic representation in stone of the wooden beam ends of the typical primitive hut, as described by Vitruvius and Renaissance writers. The wooden beams were notched in three separate p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frieze
In classical architecture, the frieze is the wide central section of an entablature and may be plain in the Ionic order, Ionic or Corinthian order, Corinthian orders, or decorated with bas-reliefs. Patera (architecture), Paterae are also usually used to decorate friezes. Even when neither column (architecture), columns nor pilasters are expressed, on an astylar wall it lies upon the architrave ("main beam") and is capped by the molding (decorative), moldings of the cornice (architecture), cornice. A frieze can be found on many Greek and Roman buildings, the Parthenon Frieze being the most famous, and perhaps the most elaborate. In interiors, the frieze of a room is the section of wall above the picture rail and under the crown moldings or cornice. By extension, a frieze is a long stretch of painting, painted, sculpture, sculpted or even calligraphy, calligraphic decoration in such a position, normally above eye-level. Frieze decorations may depict scenes in a sequence of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pilaster
In architecture, a pilaster is both a load-bearing section of thickened wall or column integrated into a wall, and a purely decorative element in classical architecture which gives the appearance of a supporting column and articulates an extent of wall. As an ornament it consists of a flat surface raised from the main wall surface, usually treated as though it were a column, with a capital at the top, plinth (base) at the bottom, and the various other column elements. In contrast to a Classical pilaster, an engaged column or buttress can support the structure of a wall and roof above. In human anatomy, a pilaster is a ridge that extends vertically across the femur, which is unique to modern humans. Its structural function is unclear. Definition A pilaster is foremost a load-bearing architectural element used widely throughout the world and its history where a structural load is carried by a thickened section of wall or column integrated into a wall. It is also a purel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Junta De Andalucía
The Regional Government of Andalusia () is the government of the Autonomous Community of Andalusia. It consists of the Parliament, the President of the Regional Government and the Government Council. The 2011 budget was 31.7 billion euros. It employs about 500,000 workers. Institutions Legislature The Parliament of Andalusia is the House of Assembly for the region. Its main functions are to enact, amend or repeal laws and to appoint/remove the Governor. It is composed of deputies chosen by direct, universal suffrage, to represent the Andalusian people. The Parliament was constituted in 1982, after the approval of the Statute of Autonomy in 1981. Its current headquarters is in the former Hospital de las Cinco Llagas, Seville Seville ( ; , ) is the capital and largest city of the Spain, Spanish autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Andalusia and the province of Seville. It is situated on the lower reaches of the Guadalquivir, River Guadalquivir, .... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entablature
An entablature (; nativization of Italian , from "in" and "table") is the superstructure of moldings and bands which lies horizontally above columns, resting on their capitals. Entablatures are major elements of classical architecture, and are commonly divided into the architrave (the supporting member immediately above; equivalent to the lintel in post and lintel construction), the frieze (an unmolded strip that may or may not be ornamented), and the cornice (the projecting member below the pediment). The Greek and Roman temples are believed to be based on wooden structures, the design transition from wooden to stone structures being called petrification. Overview The structure of an entablature varies with the orders of architecture. In each order, the proportions of the subdivisions (architrave, frieze, cornice) are defined by the proportions of the column. In Roman and Renaissance interpretations, it is usually approximately a quarter of the height of the column. Va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balustrade
A baluster () is an upright support, often a vertical moulded shaft, square, or lathe-turned form found in stairways, parapets, and other architectural features. In furniture construction it is known as a spindle. Common materials used in its construction are wood, stone, and less frequently metal and ceramic. A group of balusters supporting a guard railing, coping, or ornamental detail is known as a balustrade. The term baluster shaft is used to describe forms such as a candlestick, upright furniture support, and the stem of a brass chandelier. The term banister (also bannister) refers to a baluster or to the system of balusters and handrail of a stairway. It may be used to include its supporting structures, such as a supporting newel post. In the UK, there are different height requirements for domestic and commercial balustrades, as outlined in Approved Document K. Etymology According to the ''Oxford English Dictionary'', "baluster" is derived through the , from , from ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pillar
A column or pillar in architecture and structural engineering is a structural element that transmits, through compression, the weight of the structure above to other structural elements below. In other words, a column is a compression member. The term ''column'' applies especially to a large round support (the shaft of the column) with a capital and a base or pedestal, which is made of stone, or appearing to be so. A small wooden or metal support is typically called a '' post''. Supports with a rectangular or other non-round section are usually called '' piers''. For the purpose of wind or earthquake engineering, columns may be designed to resist lateral forces. Other compression members are often termed "columns" because of the similar stress conditions. Columns are frequently used to support beams or arches on which the upper parts of walls or ceilings rest. In architecture, "column" refers to such a structural element that also has certain proportional and decorative featu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tholobate
A tholobate (), also called a drum or tambour, is the upright part of a building on which a dome is raised. It is generally in the shape of a cylinder or a polygonal prism. The name derives from the tholos, the Greek term for a round building with a roof and a circular wall. Another architectural meaning of ''drum'' is a circular section of a column shaft. Examples In the earlier Byzantine church architecture the dome rested directly on the pendentives and the windows were pierced in the dome itself; in later examples, between the pendentive and the dome an intervening circular wall was built in which the windows were pierced. This is the type which was universally employed by the architects of the Renaissance, of whose works the best-known example is St. Peter's Basilica at Rome. Other examples of churches of this type are St Paul's Cathedral in London and the churches of the Les Invalides, the Val-de-Grâce, and the Sorbonne in Paris. There are also secular buildings wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |