|
SSCV Sleipnir
SSCV ''Sleipnir'' is a Semi-submersible platform, semi-submersible crane vessel (SSCV) owned and operated by the Netherlands-based Heerema Marine Contractors. It was ordered in 2015 and built in Singapore by Sembcorp Marine. It was named for Sleipnir, the eight-legged horse ridden by Odin in Norse mythology. The vessel is equipped with two revolving cranes built by Huisman Equipment B.V., each with a capacity of ; the main cranes can be operated in tandem to jointly lift . After its completion in 2019, SSCV ''Sleipnir'' succeeded Heerema's earlier as the largest crane vessel in the world. Design The vessel is essentially a large platform supported by eight columns (four on each side), with one Float (nautical), pontoon per side. Typical SSCVs use larger columns under the cranes to provide support, which can lead to severe pitching in rough seas; SSCV ''Sleipnir'' uses columns that are symmetrical fore and aft for calmer motions under higher sea states. The columns are rounded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heerema Marine Contractors
Heerema Marine Contractors (HMC) is a contractor headquartered in the Netherlands most notable for operation of three of the largest crane vessels in the offshore industry. History Heerema Marine Contractors was formed in 1948 by Pieter Schelte Heerema as a small construction company providing oilfield platforms in Venezuela. In the 1960s the company focused on the North Sea offshore developments. The company developed crane vessels to lift large offshore platforms and modules. The ship shaped crane vessel ''Challenger'' was equipped to lift 800 t. The need for large stable crane vessels to operate in the North Sea environment lead the company to develop the first large semi-submersible crane vessels. In 1978, HMC commissioned Mitsui to construct the two sister semi-submersible crane vessels, and Hermod (ship), SSCV ''Hermod''. These vessels could lift 5,400 tonnes with the twin cranes, and were later upgraded to 8,200 tonnes. In 1988 HMC formed a joint venture with McDermott ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thialf And Sleipnir
Thialf () is an ice arena in Heerenveen, Netherlands. Thialf is used for long track speed skating, short track speed skating, ice hockey, figure skating, ice speedway, and non-sporting events. The outdoor rink was opened in 1967, and the indoor stadium was opened in 1986. Several world records have been set in the indoor stadium. Annually, Thialf hosts two Speed Skating World Cup events. Jan de Jong was the ice rink master at Thialf for many years. History Thialf is named after Thialfi, a character in Norse mythology, who was Thor's servant and had to race a giant. Construction on the artificial outdoor ice rink was started in 1966, and it was opened on 14 October 1967 by Princess Christina of the Netherlands. It was the third 400m artificial ice rink in the Netherlands, after the Jaap Eden baan in Amsterdam and the IJsselstadion in Deventer. Several national and international tournaments have been held in Thialf, but only one world record has been set on the outdoor rink, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
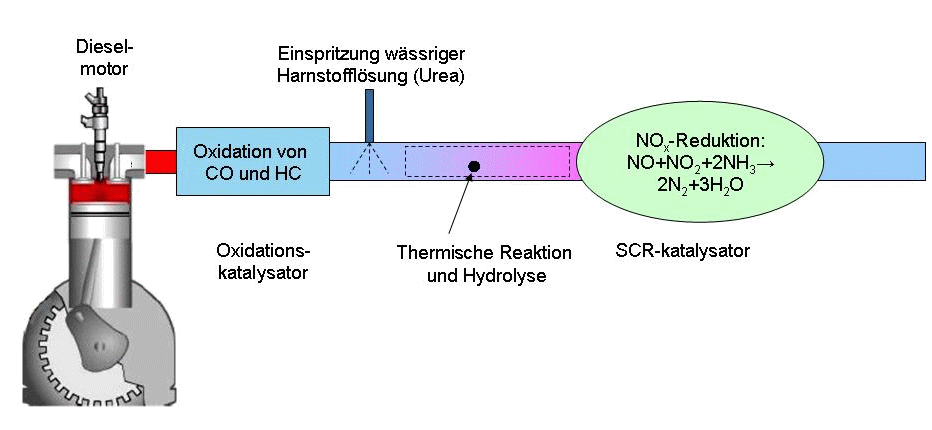
Selective Catalytic Reduction
Selective catalytic reduction (SCR) means converting nitrogen oxides, also referred to as with the aid of a catalyst into diatomic nitrogen (), and water (). A reductant, typically anhydrous ammonia (), aqueous ammonia (), or a urea () solution, is added to a stream of flue or exhaust gas and is reacted onto a catalyst. As the reaction drives toward completion, nitrogen (), and carbon dioxide (), in the case of urea use, are produced. Selective catalytic reduction of using ammonia as the reducing agent was patented in the United States by the Engelhard Corporation in 1957. Development of SCR technology continued in Japan and the US in the early 1960s with research focusing on less expensive and more durable catalyst agents. The first large-scale SCR was installed by the IHI Corporation in 1978.Steam: Its Generation and Uses. Babcock & Wilcox. Commercial selective catalytic reduction systems are typically found on large utility boilers, industrial boilers, and municipal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquefied Natural Gas
Liquefied natural gas (LNG) is natural gas (predominantly methane, CH4, with some mixture of ethane, C2H6) that has been cooled to liquid form for ease and safety of non-pressurized storage or transport. It takes up about 1/600th the volume of natural gas in the gaseous state at standard temperature and pressure. LNG is odorless, Transparency and translucency, colorless, toxicity, non-toxic and Corrosive substance, non-corrosive. Hazards include flammability after vaporization into a gaseous state, freezing and asphyxia. The Liquefaction of gases, liquefaction process involves removal of certain components, such as dust, acid gases, helium, water, and heavy hydrocarbons, which could cause difficulty downstream. The natural gas is then condensation, condensed into a liquid at close to atmospheric pressure by cooling it to approximately ; maximum transport pressure is set at around (gauge pressure), which is about 0.25 times atmospheric pressure at sea level. The gas extracted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuel Oil
Fuel oil is any of various fractions obtained from the distillation of petroleum (crude oil). Such oils include distillates (the lighter fractions) and residues (the heavier fractions). Fuel oils include heavy fuel oil (bunker fuel), marine fuel oil (MFO), furnace oil (FO), gas oil (gasoil), heating oils (such as home heating oil), diesel fuel, and others. The term ''fuel oil'' generally includes any liquid fuel that is burned in a furnace or boiler to generate heat ( heating oils), or used in an engine to generate power (as motor fuels). However, it does not usually include other liquid oils, such as those with a flash point of approximately , or oils burned in cotton- or wool-wick burners. In a stricter sense, ''fuel oil'' refers only to the heaviest commercial fuels that crude oil can yield, that is, those fuels heavier than gasoline (petrol) and naphtha. Fuel oil consists of long-chain hydrocarbons, particularly alkanes, cycloalkanes, and aromatics. Small molecul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Maritime Organization
The International Maritime Organization (IMO; ; ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for regulating maritime transport. The IMO was established following agreement at a UN conference held in Geneva in 1948 and the IMO came into existence ten years later, meeting for the first time on 17 March 1958. Headquartered in London, United Kingdom, the IMO, in 2024, has 176 Member States and three Associate Members. The IMO's primary purpose is to develop and maintain a comprehensive regulatory framework for shipping and its remit today includes maritime safety, environmental concerns, and Admiralty law, legal matters, among other issues. IMO is governed by an assembly of members which meets every two years. Its finance and organization is administered by a council of 40 members elected from the assembly. The work of IMO is conducted through five committees and these are supported by technical subcommittees. Other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selective Catalytic Reduction
Selective catalytic reduction (SCR) means converting nitrogen oxides, also referred to as with the aid of a catalyst into diatomic nitrogen (), and water (). A reductant, typically anhydrous ammonia (), aqueous ammonia (), or a urea () solution, is added to a stream of flue or exhaust gas and is reacted onto a catalyst. As the reaction drives toward completion, nitrogen (), and carbon dioxide (), in the case of urea use, are produced. Selective catalytic reduction of using ammonia as the reducing agent was patented in the United States by the Engelhard Corporation in 1957. Development of SCR technology continued in Japan and the US in the early 1960s with research focusing on less expensive and more durable catalyst agents. The first large-scale SCR was installed by the IHI Corporation in 1978.Steam: Its Generation and Uses. Babcock & Wilcox. Commercial selective catalytic reduction systems are typically found on large utility boilers, industrial boilers, and municipal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Four-stroke Engine
A four-stroke (also four-cycle) engine is an internal combustion (IC) engine in which the piston completes four separate strokes while turning the crankshaft. A stroke refers to the full travel of the piston along the cylinder, in either direction. The four separate strokes are termed: #Intake: Also known as induction or suction. This stroke of the piston begins at top dead center (T.D.C.) and ends at bottom dead center (B.D.C.). In this stroke the intake valve must be in the open position while the piston pulls an air-fuel mixture into the cylinder by producing a partial vacuum (negative pressure) in the cylinder through its downward motion. #Compression: This stroke begins at B.D.C, or just at the end of the suction stroke, and ends at T.D.C. In this stroke the piston compresses the air-fuel mixture in preparation for ignition during the power stroke (below). Both the intake and exhaust valves are closed during this stage. #Combustion: Also known as power or ignition. This is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MAN Diesel
MAN Diesel SE was a German manufacturer of large-bore diesel engines for marine propulsion systems and power plant applications. In 2010 it was merged with MAN Turbo to form MAN Diesel & Turbo. History In 1980 MAN acquired the Burmeister & Wain Danish shipyard and diesel engine producer. Though engine production at Christianshavn was discontinued in 1987, successful engine programs were rolled out. At Teglholmen in 1988 a spare parts and key components production factory was established, as was an R&D centre at the same site in 1992. Though all Copenhagen operations were consolidated at Teglholmen in 1994 and the last volume production unit at the B&W Shipyard was delivered in 1996, in 2000 MAN B&W Diesel two-stroke diesel engines had over 70% market share, with a substantial number of MC-line engines on order. The electronically controlled line of ME diesel two-stroke engines was added in 2002 with a maximum cylinder bore of 108 cm. MAN B&W Diesel, Denmark, employed appr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |