|
Radiation Efficiency
In antenna theory, radiation efficiency is a measure of how well a radio antenna converts the radio-frequency power accepted at its terminals into radiated power. Likewise, in a receiving antenna it describes the proportion of the radio wave's power intercepted by the antenna which is actually delivered as an electrical signal. It is not to be confused with antenna efficiency, which applies to aperture antennas such as a parabolic reflector or phased array, or antenna/aperture illumination efficiency, which relates the maximum directivity of an antenna/aperture to its standard directivity. Definition Radiation efficiency is defined as "The ratio of the total power radiated by an antenna to the net power accepted by the antenna from the connected transmitter." It is sometimes expressed as a percentage (less than 100), and is frequency dependent. It can also be described in decibels. The gain of an antenna is the directivity multiplied by the radiation efficiency. Thus, we have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antenna (radio)
In radio engineering, an antenna or aerial is the interface between radio waves propagating through space and electric currents moving in metal conductors, used with a transmitter or receiver. In transmission, a radio transmitter supplies an electric current to the antenna's terminals, and the antenna radiates the energy from the current as electromagnetic wave In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) consists of waves of the electromagnetic (EM) field, which propagate through space and carry momentum and electromagnetic radiant energy. It includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, (visib ...s (radio waves). In Receiver (radio), reception, an antenna intercepts some of the power of a radio wave in order to produce an electric current at its terminals, that is applied to a receiver to be Amplifier, amplified. Antennas are essential components of all radio equipment. An antenna is an array of conductor (material), conductors (Driven element, elements), elect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antenna Efficiency
Antenna ''apertureillumination efficiency is a measure of the extent to which an antenna or array is uniformly excited or illuminated. It is typical for an antenna pertureor array to be intentionally under-illuminated or under-excited in order to mitigate sidelobes and reduce antenna temperature. It is not to be confused with radiation efficiency or antenna efficiency. Definition Antenna pertureillumination efficiency is defined as "The ratio, usually expressed in percent, of the maximum directivity of an antenna pertureto its standard directivity." It is synonymous with normalized directivity. Standard eferencedirectivity is defined as "The maximum directivity from a planar aperture of area A, or from a line source of length L, when excited with a uniform-amplitude, equiphase distribution." Key to understanding these definitions is that "maximum" directivity refers to the direction of maximum radiation intensity, i.e., the main lobe. Therefore, illumination effici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parabolic Reflector
A parabolic (or paraboloid or paraboloidal) reflector (or dish or mirror) is a reflective surface used to collect or project energy such as light, sound, or radio waves. Its shape is part of a circular paraboloid, that is, the surface generated by a parabola revolving around its axis. The parabolic reflector transforms an incoming plane wave travelling along the axis into a spherical wave converging toward the focus. Conversely, a spherical wave generated by a point source placed in the focus is reflected into a plane wave propagating as a collimated beam along the axis. Parabolic reflectors are used to collect energy from a distant source (for example sound waves or incoming star light). Since the principles of reflection are reversible, parabolic reflectors can also be used to collimate radiation from an isotropic source into a parallel beam. In optics, parabolic mirrors are used to gather light in reflecting telescopes and solar furnaces, and project a beam of light in flas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
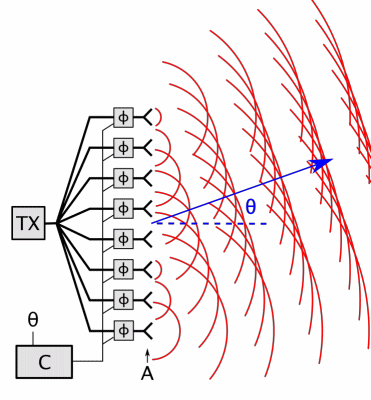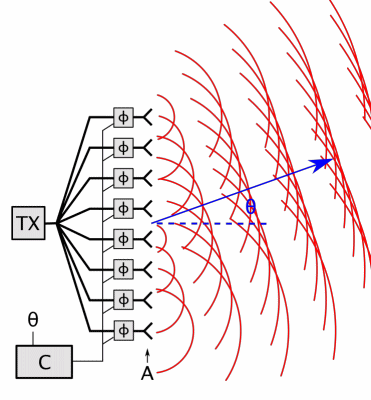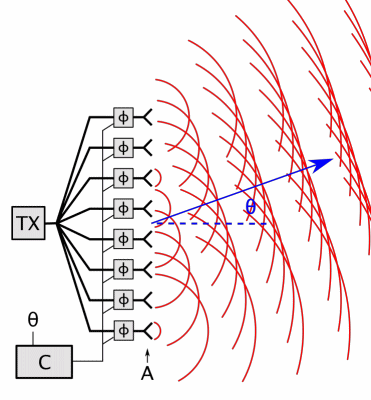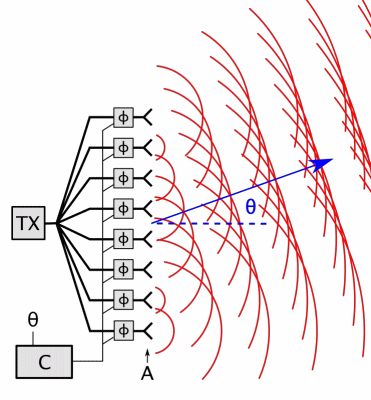
Phased Array
In antenna theory, a phased array usually means an electronically scanned array, a computer-controlled array of antennas which creates a beam of radio waves that can be electronically steered to point in different directions without moving the antennas. In a simple array antenna, the radio frequency current from the transmitter is fed to multiple individual antenna elements with the proper phase relationship so that the radio waves from the separate elements combine ( superpose) to form beams, to increase power radiated in desired directions and suppress radiation in undesired directions. In a phased array, the power from the transmitter is fed to the radiating elements through devices called ''phase shifters'', controlled by a computer system, which can alter the phase or signal delay electronically, thus steering the beam of radio waves to a different direction. Since the size of an antenna array must extend many wavelengths to achieve the high gain needed for narrow bea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illumination Efficiency
Antenna ''apertureillumination efficiency is a measure of the extent to which an antenna or array is uniformly excited or illuminated. It is typical for an antenna pertureor array to be intentionally under-illuminated or under-excited in order to mitigate sidelobes and reduce antenna temperature. It is not to be confused with radiation efficiency or antenna efficiency. Definition Antenna pertureillumination efficiency is defined as "The ratio, usually expressed in percent, of the maximum directivity of an antenna pertureto its standard directivity." It is synonymous with normalized directivity. Standard eferencedirectivity is defined as "The maximum directivity from a planar aperture of area A, or from a line source of length L, when excited with a uniform-amplitude, equiphase distribution." Key to understanding these definitions is that "maximum" directivity refers to the direction of maximum radiation intensity, i.e., the main lobe. Therefore, illumination efficien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Directivity
In electromagnetics, directivity is a parameter of an antenna or optical system which measures the degree to which the radiation emitted is concentrated in a single direction. It is the ratio of the radiation intensity in a given direction from the antenna to the radiation intensity averaged over all directions.IEEE Std 145-2013, IEEE Standard for Definitions of Terms for Antennas, IEEE Therefore, the directivity of a hypothetical isotropic radiator is 1, or 0 dBi. An antenna's directivity is greater than its gain by an efficiency factor, radiation efficiency. Directivity is an important measure because many antennas and optical systems are designed to radiate electromagnetic waves in a single direction or over a narrow-angle. By the principle of reciprocity, the directivity of an antenna when receiving is equal to its directivity when transmitting. The directivity of an actual antenna can vary from 1.76 dBi for a short dipole to as much as 50 dBi for a large dish antenna. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |