|
Directivity
In electromagnetics, directivity is a parameter of an antenna or optical system which measures the degree to which the radiation emitted is concentrated in a single direction. It is the ratio of the radiation intensity in a given direction from the antenna to the radiation intensity averaged over all directions.IEEE Std 145-2013, IEEE Standard for Definitions of Terms for Antennas, IEEE Therefore, the directivity of a hypothetical isotropic radiator is 1, or 0 dBi. An antenna's directivity is greater than its gain by an efficiency factor, radiation efficiency. Directivity is an important measure because many antennas and optical systems are designed to radiate electromagnetic waves in a single direction or over a narrow-angle. By the principle of reciprocity, the directivity of an antenna when receiving is equal to its directivity when transmitting. The directivity of an actual antenna can vary from 1.76 dBi for a short dipole to as much as 50 dBi for a large dish ante ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Directional Coupler
Power dividers (also power splitters and, when used in reverse, power combiners) and directional couplers are passive devices used mostly in the field of radio technology. They couple a defined amount of the electromagnetic power in a transmission line to a port enabling the signal to be used in another circuit. An essential feature of directional couplers is that they only couple power flowing in one direction. Power entering the output port is coupled to the isolated port but not to the coupled port. A directional coupler designed to split power equally between two ports is called a hybrid coupler. Directional couplers are most frequently constructed from two coupled transmission lines set close enough together such that energy passing through one is coupled to the other. This technique is favoured at the microwave frequencies where transmission line designs are commonly used to implement many circuit elements. However, lumped component devices are also possible at lower ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
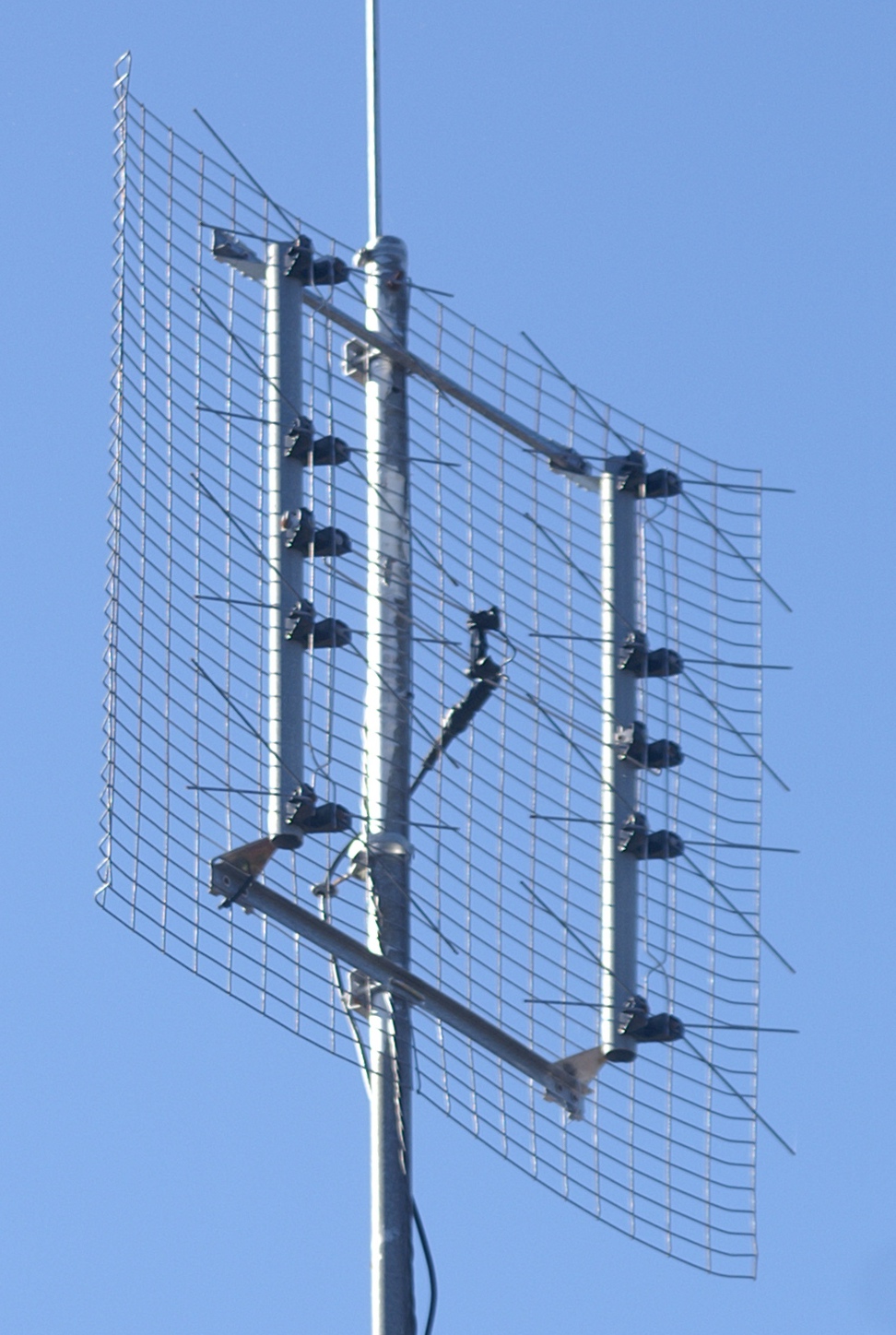
Antennas (radio)
In radio engineering, an antenna or aerial is the interface between radio waves propagating through space and electric currents moving in metal conductors, used with a transmitter or receiver. In transmission, a radio transmitter supplies an electric current to the antenna's terminals, and the antenna radiates the energy from the current as electromagnetic waves (radio waves). In reception, an antenna intercepts some of the power of a radio wave in order to produce an electric current at its terminals, that is applied to a receiver to be amplified. Antennas are essential components of all radio equipment. An antenna is an array of conductors ( elements), electrically connected to the receiver or transmitter. Antennas can be designed to transmit and receive radio waves in all horizontal directions equally (omnidirectional antennas), or preferentially in a particular direction ( directional, or high-gain, or “beam” antennas). An antenna may include components not connecte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antenna (radio)
In radio engineering, an antenna or aerial is the interface between radio waves propagating through space and electric currents moving in metal conductors, used with a transmitter or receiver (radio), receiver. In Transmission (telecommunications), transmission, a radio transmitter supplies an electric current to the antenna's terminals, and the antenna radiates the energy from the current as electromagnetic radiation, electromagnetic waves (radio waves). In Receiver (radio), reception, an antenna intercepts some of the power of a radio wave in order to produce an electric current at its terminals, that is applied to a receiver to be Amplifier, amplified. Antennas are essential components of all radio equipment. An antenna is an array of conductor (material), conductors (Driven element, elements), electrically connected to the receiver or transmitter. Antennas can be designed to transmit and receive radio waves in all horizontal directions equally (omnidirectional antennas), o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polarization (antenna)
In radio engineering, an antenna or aerial is the interface between radio waves propagating through space and electric currents moving in metal conductors, used with a transmitter or receiver. In transmission, a radio transmitter supplies an electric current to the antenna's terminals, and the antenna radiates the energy from the current as electromagnetic waves (radio waves). In reception, an antenna intercepts some of the power of a radio wave in order to produce an electric current at its terminals, that is applied to a receiver to be amplified. Antennas are essential components of all radio equipment. An antenna is an array of conductors ( elements), electrically connected to the receiver or transmitter. Antennas can be designed to transmit and receive radio waves in all horizontal directions equally (omnidirectional antennas), or preferentially in a particular direction ( directional, or high-gain, or “beam” antennas). An antenna may include components not connect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiation Efficiency
In antenna theory, radiation efficiency is a measure of how well a radio antenna converts the radio-frequency power accepted at its terminals into radiated power. Likewise, in a receiving antenna it describes the proportion of the radio wave's power intercepted by the antenna which is actually delivered as an electrical signal. It is not to be confused with antenna efficiency, which applies to aperture antennas such as a parabolic reflector or phased array, or antenna/aperture illumination efficiency, which relates the maximum directivity of an antenna/aperture to its standard directivity. Definition Radiation efficiency is defined as "The ratio of the total power radiated by an antenna to the net power accepted by the antenna from the connected transmitter." It is sometimes expressed as a percentage (less than 100), and is frequency dependent. It can also be described in decibels. The gain of an antenna is the directivity multiplied by the radiation efficiency. Thus, we have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antenna Array
An antenna array (or array antenna) is a set of multiple connected antennas which work together as a single antenna, to transmit or receive radio waves. The individual antennas (called ''elements'') are usually connected to a single receiver or transmitter by feedlines that feed the power to the elements in a specific phase relationship. The radio waves radiated by each individual antenna combine and superpose, adding together ( interfering constructively) to enhance the power radiated in desired directions, and cancelling ( interfering destructively) to reduce the power radiated in other directions. Similarly, when used for receiving, the separate radio frequency currents from the individual antennas combine in the receiver with the correct phase relationship to enhance signals received from the desired directions and cancel signals from undesired directions. More sophisticated array antennas may have multiple transmitter or receiver modules, each connected to a separate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotropic Radiator
An isotropic radiator is a theoretical point source of electromagnetic or sound waves which radiates the same intensity of radiation in all directions. It has no preferred direction of radiation. It radiates uniformly in all directions over a sphere centred on the source. Isotropic radiators are used as reference radiators with which other sources are compared, for example in determining the gain of antennas. A coherent isotropic radiator of electromagnetic waves is theoretically impossible, but incoherent radiators can be built. An isotropic sound radiator is possible because sound is a longitudinal wave. The unrelated term '' isotropic radiation'' refers to radiation which has the same intensity in all directions, thus an isotropic radiator does ''not'' radiate isotropic radiation. Physics In physics, an isotropic radiator is a point radiation or sound source. At a distance, the sun is an isotropic radiator of electromagnetic radiation. Antenna theory In antenna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antenna Gain
In electromagnetics, an antenna's gain is a key performance parameter which combines the antenna's directivity and radiation efficiency. The term ''power gain'' has been deprecated by IEEE. In a transmitting antenna, the gain describes how well the antenna converts input power into radio waves headed in a specified direction. In a receiving antenna, the gain describes how well the antenna converts radio waves arriving from a specified direction into electrical power. When no direction is specified, gain is understood to refer to the peak value of the gain, the gain in the direction of the antenna's main lobe. A plot of the gain as a function of direction is called the antenna pattern or radiation pattern. It is not to be confused with directivity, which does ''not'' take an antenna's radiation efficiency into account. Gain or 'absolute gain' is defined as "The ratio of the radiation intensity in a given direction to the radiation intensity that would be produced if t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sidelobes En
In antenna engineering, sidelobes are the lobes (local maxima) of the far field radiation pattern of an antenna or other radiation source, that are not the '' main lobe''. The radiation pattern of most antennas shows a pattern of "''lobes''" at various angles, directions where the radiated signal strength reaches a maximum, separated by "''nulls''", angles at which the radiated signal strength falls to zero. This can be viewed as the diffraction pattern of the antenna. In a directional antenna in which the objective is to emit the radio waves in one direction, the lobe in that direction is designed to have a larger field strength than the others; this is the "'' main lobe''". The other lobes are called "''sidelobes''", and usually represent unwanted radiation in undesired directions. The sidelobe directly behind the main lobe is called the back lobe. The longer the antenna relative to the radio wavelength, the more lobes its radiation pattern has. In transmitting anten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dish Antenna
A parabolic antenna is an antenna that uses a parabolic reflector, a curved surface with the cross-sectional shape of a parabola, to direct the radio waves. The most common form is shaped like a dish and is popularly called a dish antenna or parabolic dish. The main advantage of a parabolic antenna is that it has high directivity. It functions similarly to a searchlight or flashlight reflector to direct radio waves in a narrow beam, or receive radio waves from one particular direction only. Parabolic antennas have some of the highest gains, meaning that they can produce the narrowest beamwidths, of any antenna type. In order to achieve narrow beamwidths, the parabolic reflector must be much larger than the wavelength of the radio waves used, so parabolic antennas are used in the high frequency part of the radio spectrum, at UHF and microwave ( SHF) frequencies, at which the wavelengths are small enough that conveniently-sized reflectors can be used. Parabolic antennas are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Array Gain
In array antenna systems, array gain is the measure of the improvement in signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) achieved by the array. It is calculated as the SNR of the array output signal divided by the SNR of the array input signal. Intuitively, the array gain is realized by the fact that the signal is coherently added from ''N'' array elements, while the noise is incoherently added from those same elements. If the noise is presumed to be uncorrelated the array gain is ≤ ''N'', the number of array elements, and the array gain reduces to the inverse of the square of the 2-norm of the array weight vector, under the assumption that the weight vector is normalized such that its sum is unity, so that :A = For a uniformly weighted array (un-tapered such that all elements contribute equally), the array gain is equal to ''N''. Array gain is not the same thing as "gain," "power gain," "directive gain," or "directivity," but if the noise environment around the array is isotropic and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antenna Directive Gain Diagram
Antenna ( antennas or antennae) may refer to: Science and engineering * Antenna (radio), also known as an aerial, a transducer designed to transmit or receive electromagnetic (e.g., TV or radio) waves * Antennae Galaxies, the name of two colliding galaxies NGC 4038 and NGC 4039 Biology * Antenna (biology), one of one or more pairs of appendages used for sensing in arthropods * ''Antenna'' (journal), the journal of the Royal Entomological Society Media Broadcasting * ANT1, a Greek-language terrestrial channel * Antena Internațional, a Romanian television channel * Antena 1 (Romania), a Romanian television channel * Antena 2 (Romania), a Romanian television channel * Antena 3 (Romania), a Romanian television channel * Antena 3 (Spain), a Spanish terrestrial television channel * Antenna TV, a U.S. television channel established in 2011 by Tribune Broadcasting * RDP Antena 1, Portuguese public radio station * RDP Antena 2, Portuguese public radio station * RDP Antena 3, Port ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |