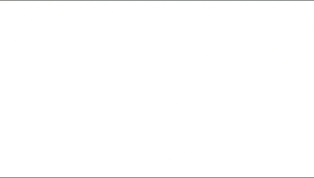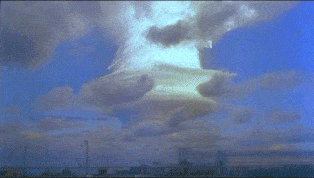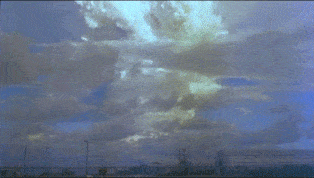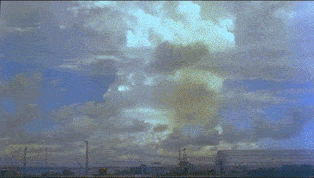|
Runit Dome
Runit Island () is one of forty islands of the Enewetak Atoll of the Marshall Islands in the Pacific Ocean. The island is the site of a radioactive waste repository left by the United States after it conducted a series of nuclear tests on Enewetak Atoll between 1946 and 1958. There are ongoing concerns around deterioration of the waste site and a potential radioactive spill. Runit Dome Construction The Runit Dome, also called Cactus Dome or locally "the Tomb", is a diameter, thick dome of concrete at sea level, encapsulating an estimated of radioactive debris, including some plutonium-239. The debris stems from nuclear tests conducted in the Enewetak Atoll by the United States between 1946 and 1958. From 1977 to 1980, loose waste and topsoil from six different islands in the Enewetak Atoll was transported to the site and mixed with concrete to seal the nuclear blast crater created by the Cactus test. Four thousand US servicemen were involved in the cleanup from this test, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enewetak Atoll
Enewetak Atoll (; also spelled Eniwetok Atoll or sometimes Eniewetok; , , or , ; known to the Japanese as Brown Atoll or Brown Island; ) is a large coral atoll of 40 islands in the Pacific Ocean and with its 296 people (as of 2021) forms a legislative district of the Ralik Chain of the Marshall Islands. With a land area total less than , it is no higher than and surrounds a deep central lagoon, in circumference. It is the second-westernmost atoll of the Ralik Chain and is west from Bikini Atoll. It was held by the Japanese from 1914 until its capture by the United States in February 1944 during World War II, then became Naval Base Eniwetok. Nuclear testing by the US, totaling the equivalent of over 30 megatons of TNT, took place during the Cold War; in 1977–1980, a concrete dome (the Runit Dome) was built on Runit Island to deposit radioactive soil and debris. The Runit Dome is deteriorating and could be breached by a typhoon, though the sediments in the lagoon are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
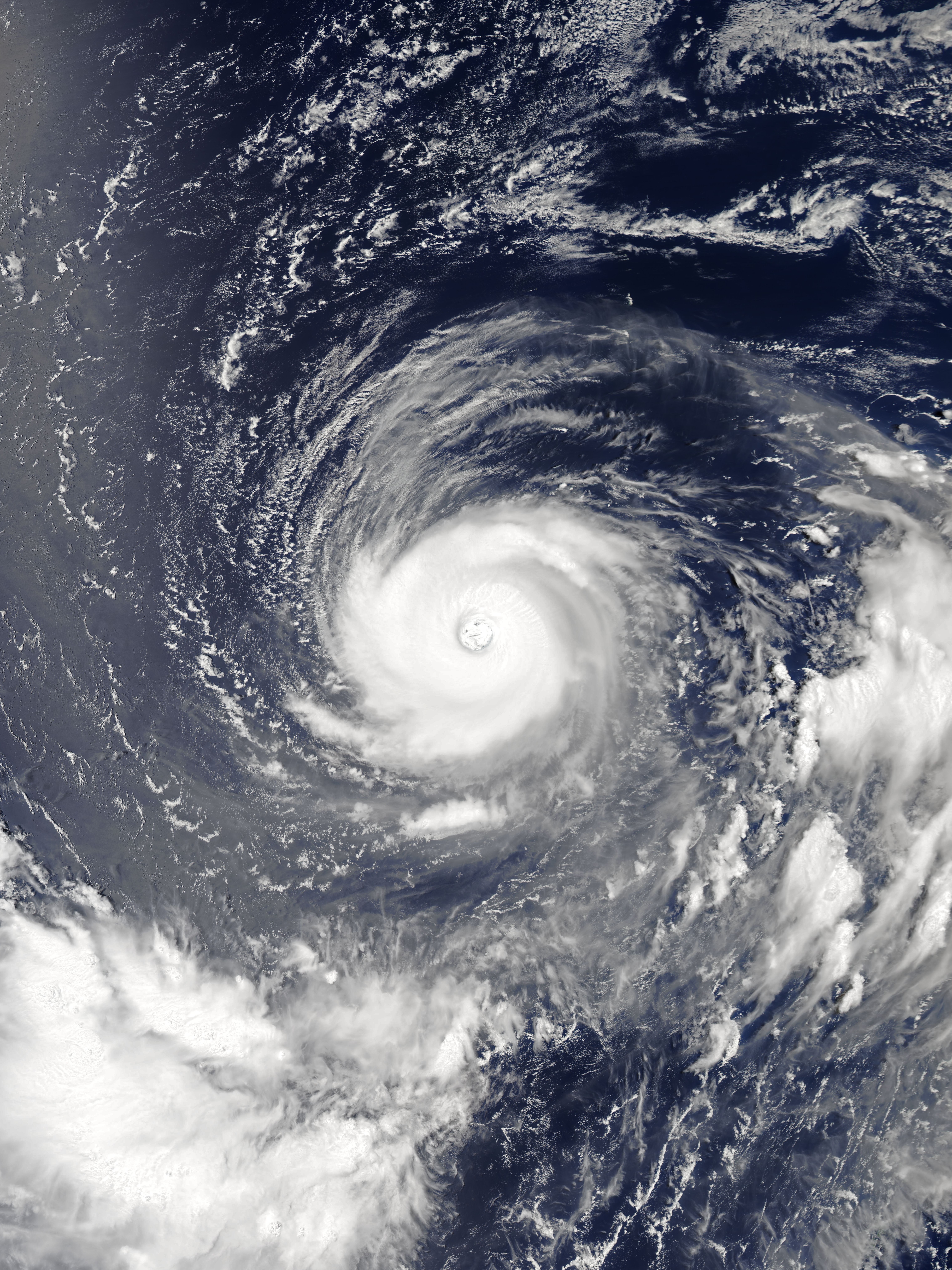
Typhoon
A typhoon is a tropical cyclone that develops between 180° and 100°E in the Northern Hemisphere and which produces sustained hurricane-force winds of at least . This region is referred to as the Northwestern Pacific Basin, accounting for almost one third of the world's tropical cyclones. For organizational purposes, the northern Pacific Ocean is divided into three regions: the eastern (North America to 140°W), central (140°W to 180°), and western (180° to 100°E). The Regional Specialized Meteorological Center (RSMC) for tropical cyclone forecasts is in Japan, with other tropical cyclone warning centres for the northwest Pacific in Hawaii (the Joint Typhoon Warning Center), the Philippines, and Hong Kong. Although the RSMC names each system, the main name list itself is coordinated among 18 countries that have territories threatened by typhoons each year. Within most of the northwestern Pacific, there are no official typhoon seasons as tropical cyclones form througho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivy King
Ivy King was the largest pure- fission nuclear bomb ever tested. The bomb was tested by the United States' Truman administration as part of Operation Ivy. This series of tests involved the development of very powerful nuclear weapons in response to the nuclear weapons program of the Soviet Union. The production of Ivy King was hurried to be ready in case its sister project, Ivy Mike, failed in its attempt to achieve a thermonuclear reaction. The Ivy King test actually took place two weeks after the Mike test. Unlike the Mike bomb, the Ivy King device could theoretically have been added to United States' nuclear arsenal, because it was designed to be air-deliverable. On November 16, 1952 at 11:30 local time (23:30 GMT) a B-36H bomber dropped the bomb over a point north of Runit Island in the Enewetak atoll, resulting in a 500 kiloton explosion at . The tropopause height at the time of the detonation was about . The top of the King cloud reached about with the mushroom base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivy Mike
Ivy Mike was the code name, codename given to the first full-scale test of a Thermonuclear weapon, thermonuclear device, in which a significant fraction of the explosive nuclear weapon yield, yield comes from nuclear fusion. Ivy Mike was detonated on November 1, 1952, by the United States on the island of Elugelab in Enewetak Atoll, in the now independent island nation of the Marshall Islands, as part of Operation Ivy. It was the first full test of the Teller–Ulam design, a Nuclear weapon design#Two-stage thermonuclear weapons, staged fusion device. Due to its physical size and fusion fuel type (cryogenic liquid deuterium), the "Mike" device was not suitable for use as a deliverable weapon. It was intended as a "technically conservative" proof of concept experiment to validate the concepts used for multi-TNT equivalent, megaton detonations. Samples from the explosion had traces of the isotopes plutonium-246, plutonium-244, and the predicted elements einsteinium and fermium. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Ivy
Operation Ivy was the eighth series of American nuclear tests, coming after '' Tumbler-Snapper'' and before '' Upshot–Knothole''. The two explosions were staged in late 1952 at Enewetak Atoll in the Pacific Proving Ground in the Marshall Islands. Background The Operation Ivy test series was the first to involve a hydrogen bomb rather than an atomic bomb, further to the order of President Harry S. Truman made on January 31, 1950, that the US should continue research into all forms of nuclear weapons. The bombs were prepared by the US Atomic Energy Commission and Defense Department aboard naval vessels, and were capable of being detonated remotely from the control ship Estes. Tests Mike The first ''Ivy'' shot, codenamed '' Mike'', was the first successful full-scale test of a multi-megaton thermonuclear weapon ("hydrogen bomb") using the Teller-Ulam design. Unlike later thermonuclear weapons, ''Mike'' used deuterium as its fusion fuel, maintained as a liquid by an ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''NYT'') is an American daily newspaper based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' covers domestic, national, and international news, and publishes opinion pieces, investigative reports, and reviews. As one of the longest-running newspapers in the United States, the ''Times'' serves as one of the country's Newspaper of record, newspapers of record. , ''The New York Times'' had 9.13 million total and 8.83 million online subscribers, both by significant margins the List of newspapers in the United States, highest numbers for any newspaper in the United States; the total also included 296,330 print subscribers, making the ''Times'' the second-largest newspaper by print circulation in the United States, following ''The Wall Street Journal'', also based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' is published by the New York Times Company; since 1896, the company has been chaired by the Ochs-Sulzberger family, whose current chairman and the paper's publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toxic Heavy Metal
A toxic heavy metal is a common but misleading term for a metal-like element noted for its potential toxicity. Not all heavy metals are toxic and some toxic metals are not heavy. Elements often discussed as toxic include cadmium, mercury and lead, all of which appear in the World Health Organization's list of 10 chemicals of major public concern. Other examples include chromium and nickel, thallium, bismuth, arsenic, antimony and tin. These toxic elements are found naturally in the earth. They become concentrated as a result of human caused activities and can enter plant and animal (including human) tissues via inhalation, diet, and manual handling. Then, they can bind to and interfere with the functioning of vital cellular components. The toxic effects of arsenic, mercury, and lead were known to the ancients, but methodical studies of the toxicity of some heavy metals appear to date from only 1868. In humans, heavy metal poisoning is generally treated by the administration of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plutonium
Plutonium is a chemical element; it has symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is a silvery-gray actinide metal that tarnishes when exposed to air, and forms a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exhibits six allotropes and four oxidation states. It reacts with carbon, halogens, nitrogen, silicon, and hydrogen. When exposed to moist air, it forms oxides and hydrides that can expand the sample up to 70% in volume, which in turn flake off as a powder that is pyrophoric. It is radioactive and can accumulate in bones, which makes the handling of plutonium dangerous. Plutonium was first synthesized and isolated in late 1940 and early 1941, by deuteron bombardment of uranium-238 in the cyclotron at the University of California, Berkeley. First, neptunium-238 (half-life 2.1 days) was synthesized, which then beta-decayed to form the new element with atomic number 94 and atomic weight 238 (half-life 88 years). Since uranium had been named after the planet Uranus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radioactivity
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is considered ''radioactive''. Three of the most common types of decay are Alpha decay, alpha, Beta decay, beta, and Gamma ray, gamma decay. The weak force is the Fundamental interactions, mechanism that is responsible for beta decay, while the other two are governed by the electromagnetic force, electromagnetic and nuclear forces. Radioactive decay is a randomness, random process at the level of single atoms. According to quantum mechanics, quantum theory, it is impossible to predict when a particular atom will decay, regardless of how long the atom has existed. However, for a significant number of identical atoms, the overall decay rate can be expressed as a decay constant or as a half-life. The half-lives of radioactive atoms have a huge range: f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transuranic Waste
Transuranic waste (TRU) is stated by U.S. regulations, and independent of state or origin, to be waste which has been contaminated with alpha emitting transuranic radionuclides possessing half-lives greater than 20 years and in concentrations greater than 100 nCi/g (3.7 MBq/kg). Elements having atomic numbers greater than that of uranium are called transuranic. Elements within TRU are typically man-made and are known to contain americium-241 and several isotopes of plutonium. Because of the elements' longer half-lives Half-life is a mathematical and scientific description of exponential or gradual decay. Half-life, half life or halflife may also refer to: Film * ''Half-Life'' (film), a 2008 independent film by Jennifer Phang * '' Half Life: A Parable for t ..., TRU is disposed of more cautiously than low level waste and intermediate level waste. In the U.S. it is a byproduct of weapons production, nuclear research and power production, and consists of protec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Guardian
''The Guardian'' is a British daily newspaper. It was founded in Manchester in 1821 as ''The Manchester Guardian'' and changed its name in 1959, followed by a move to London. Along with its sister paper, ''The Guardian Weekly'', ''The Guardian'' is part of the Guardian Media Group, owned by the Scott Trust Limited. The trust was created in 1936 to "secure the financial and editorial independence of ''The Guardian'' in perpetuity and to safeguard the journalistic freedom and liberal values of ''The Guardian'' free from commercial or political interference". The trust was converted into a limited company in 2008, with a constitution written so as to maintain for ''The Guardian'' the same protections as were built into the structure of the Scott Trust by its creators. Profits are reinvested in its journalism rather than distributed to owners or shareholders. It is considered a newspaper of record in the UK. The editor-in-chief Katharine Viner succeeded Alan Rusbridger in 2015. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
US Department Of Energy
US or Us most often refers to: * Us (pronoun), ''Us'' (pronoun), the objective case of the English first-person plural pronoun ''we'' * US, an abbreviation for the United States US, U.S., Us, us, or u.s. may also refer to: Arts and entertainment Albums * Us (Brother Ali album), ''Us'' (Brother Ali album) or the title song, 2009 * Us (Empress Of album), ''Us'' (Empress Of album), 2018 * Us (Mull Historical Society album), ''Us'' (Mull Historical Society album), 2003 * Us (Peter Gabriel album), ''Us'' (Peter Gabriel album), 1992 * Us (EP), ''Us'' (EP), by Moon Jong-up, 2021 * ''Us'', by Maceo Parker, 1974 * ''Us'', mini-album by Peakboy, 2019 Songs * Us (James Bay song), "Us" (James Bay song), 2018 * Us (Jennifer Lopez song), "Us" (Jennifer Lopez song), 2018 * Us (Regina Spektor song), "Us" (Regina Spektor song), 2004 * Us (Gracie Abrams song), "Us" (Gracie Abrams song), 2024 * "Us", by Azealia Banks from ''Fantasea (mixtape), Fantasea'', 2012 * "Us", by Celine Dion from ''Let's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |