|
Robotics Suite
A robotics suite is a visual environment for robot control and simulation. They are typically an end-to-end platform for robotics development and include tools for visual programming and creating and debugging robot applications. Developers can often interact with robots through web-based or visual interfaces. One objective of a robotics suite is to support a variety of different robot platforms through a common programming interface. The key point about a robotics suite is that the same code will run either with a simulated robot or the corresponding real robot without modification. Some robotic suites are based in free software, free hardware and both free software and hardware. Suites * Fedora Robotics See also * AnyKode Marilou * ArduPilot * Debian Science * Evolution Robotics * Lego Mindstorms * Microsoft Robotics Studio * Player Project (formerly the Player/Stage Project or Player/Stage/Gazebo Project) * Robot software * Robot Operating System * Simbad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simulation
A simulation is an imitative representation of a process or system that could exist in the real world. In this broad sense, simulation can often be used interchangeably with model. Sometimes a clear distinction between the two terms is made, in which simulations require the use of models; the model represents the key characteristics or behaviors of the selected system or process, whereas the simulation represents the evolution of the model over time. Another way to distinguish between the terms is to define simulation as experimentation with the help of a model. This definition includes time-independent simulations. Often, computer simulation, computers are used to execute the simulation. Simulation is used in many contexts, such as simulation of technology for performance tuning or optimizing, safety engineering, testing, training, education, and video games. Simulation is also used with scientific modelling of natural systems or human systems to gain insight into their functio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
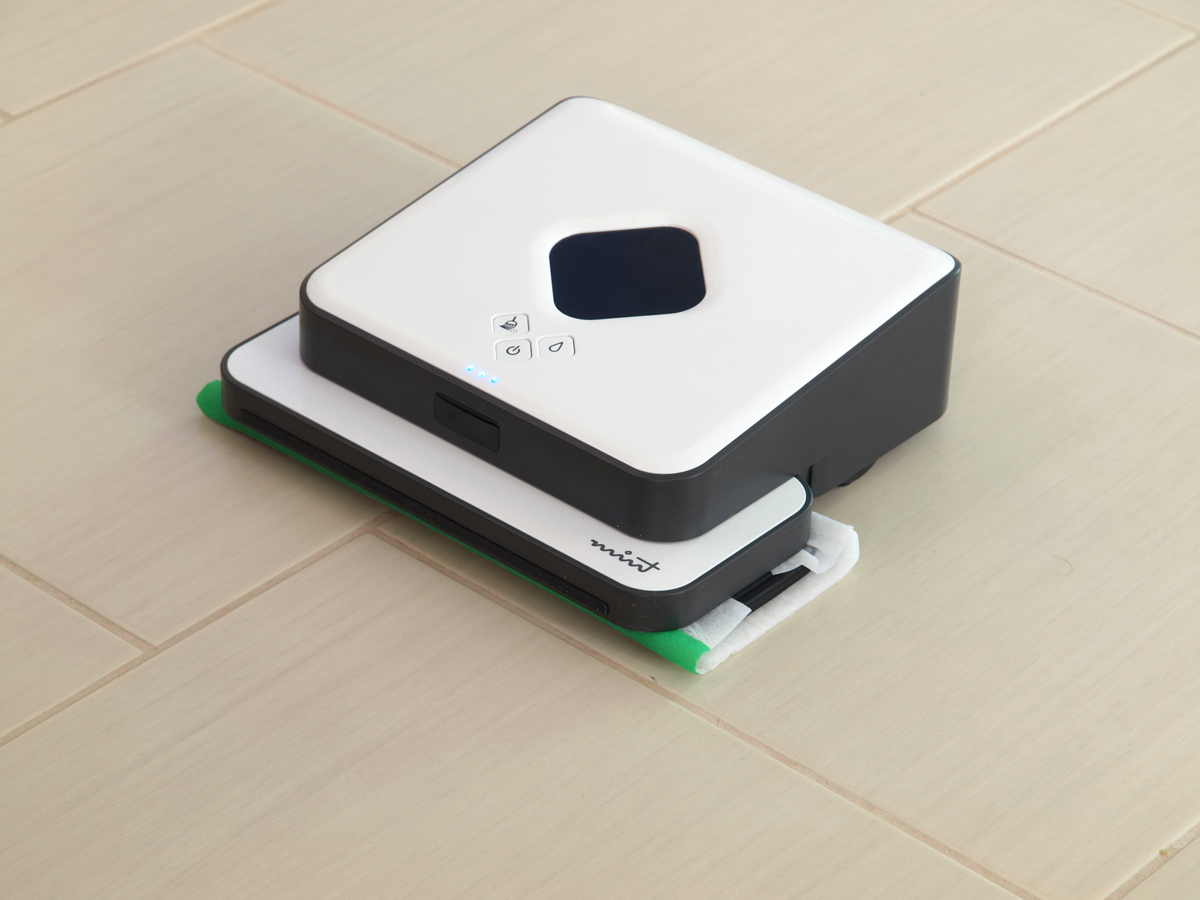
Evolution Robotics
Evolution Robotics was an American technological company based in Pasadena, California. It specialized in robotics technologies, with computer vision, localization, and autonomous navigation products. Evolution Robotics cooperated with Cambridge University for research in vision technology. Software products of Evolution Robotics were licensed by the Korean Institute of Industrial Technology and the Sony Robotics Division and were part of WowWee WowWee Group Limited is a privately held, Hong Kong–based Canadian consumer technology company. History Initially from Canada, the two founding brothers (Richard and Peter Yanofsky) moved to Hong Kong to form the company in 1982, as an indepe ... robots like ''Rovio''. On September 17, 2012, iRobot acquired Evolution Robotics for $74 Million. Products In January 2010, Evolution Robotics released ''Mint'', a cleaning robot that dusted and wet-mopped hard surface floors. The robot's "wet mopping mode" had a coverage of 93 sq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
URBI
Urbi is an Open-source software, open-source cross-platform software computing platform written in C++ used to develop applications for robotics and complex systems. Urbi is based on the UObject distributed C++ component architecture. It also includes the urbiscript Orchestration (computing), orchestration language which is a parallel and event-driven script language. UObject components can be plugged into urbiscript and appear as native objects that can be scripted to specify their interactions and data exchanges. UObjects can be linked to the urbiscript interpreter, or executed as autonomous processes in "remote" mode. The urbiscript language The urbiscript language was created in 2003 by Jean-Christophe Baillie in the Cognitive Robotics Lab of ENSTA, Paris. It has been actively and further developed in the industry through the Gostai company founded in 2006. It is now an open source project, with a BSD license, available on GitHub. The urbiscript language can be best describ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simbad Robot Simulator
Simbad robot simulator is an open-source cross-platform software simulator used to develop robotics and artificial intelligence applications. The Simbad project started in 2005, initially developed by Dr. Louis Hugues and is widely used for educational purposes. Simbad is distributed under the GNU General Public License. It is written in Java language and enables users to develop robot controllers in a simulated 3D environment. IBM
International Business Machines Corporation (using the trademark IBM), nicknamed Big Blue, is an American Multinational corporation, multinational technology company headquartered in Armon ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robot Operating System
Robot Operating System (ROS or ros) is an Open-source software, open-source robotics middleware suite. Although ROS is not an operating system (OS) but a set of software frameworks for robot software software development, development, it provides services designed for a heterogeneous computer cluster such as hardware abstraction, low-level Device driver, device control, implementation of commonly used functionality, Inter-process communication, message-passing between processes, and Package manager, package management. Running sets of ROS-based processes are represented in a graph theory, graph architecture where processing takes place in nodes that may receive, post, and Multiplexing, multiplex sensor data, control, state, planning, actuator, and other messages. Despite the importance of reactivity and low latency in robot control, ROS is ''not'' a real-time operating system (RTOS). However, it is possible to integrate ROS with real-time computing code. The lack of support for re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robot Software
Robot software is the set of coded commands or instructions that tell a mechanical device and electronic system, known together as a robot, what tasks to perform. Robot software is used to perform autonomous tasks. Many software systems and frameworks have been proposed to make programming robots easier. Some robot software aims at developing intelligent mechanical devices. Common tasks include feedback loops, control, pathfinding, data filtering, locating and sharing data. Introduction While it is a specific type of software, it is still quite diverse. Each manufacturer has their own robot software. While the vast majority of software is about manipulation of data and seeing the result on-screen, robot software is for the manipulation of objects or tools in the real world. Industrial robot software Software for industrial robots consists of data objects and lists of instructions, known as program flow (list of instructions). For example, Go to Jig1 It is an instruction to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Player Project
The Player Project (formerly Player/Stage Project) creates free and open-source software for research into robotics and sensor systems. Its components include the ''Player'' Computer network, network Server (computing), server and the ''Stage'' platform robotics simulators. Although accurate statistics are hard to obtain, Player is one of the most popular open-source robot interfaces in research and post-secondary education. Overview The Player Project is an umbrella under which two robotics-related software projects are currently developed. These include the Player networked robotics server, and the Stage 2D robot simulation environment. The project was founded in 2000 by Brian Gerkey, Richard Vaughan (robotics), Richard Vaughan and Andrew Howard at the University of Southern California at Los Angeles, and is widely used in robotics research and education. It releases its software under the GNU General Public License with documentation under the GNU Free Documentation License. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsoft Robotics Studio
Microsoft Robotics Developer Studio (Microsoft RDS, MRDS) is a discontinued Windows-based environment for robot control and simulation that was aimed at academic, hobbyist, and commercial developers and handled a wide variety of robot hardware. It requires a Microsoft Windows 7 operating system or later. RDS is based on Concurrency and Coordination Runtime (CCR): a .NET Framework-based concurrent library implementation for managing asynchronous parallel tasks. This technique involves using message-passing and a lightweight services-oriented runtime, Decentralized Software Services (DSS), which allows orchestrating multiple services to achieve complex behaviors. Features include: a visual programming tool, Microsoft Visual Programming Language (VPL) to create and debug robot applications, web-based and windows-based interfaces, 3D simulation (including hardware acceleration), easy access to a robot's sensors and actuators. The primary programming language is C#. Microsoft Rob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lego Mindstorms
Lego Mindstorms (sometimes stylized as ''LEGO MINDSTORMS'') is a discontinued line of educational kits for building programmable robots based on Lego bricks. It was introduced on 1 September 1998 and discontinued on 31 December 2022. Mindstorms kits allow users to build creations that interact with the physical world. All Mindstorms kits consist of a selection of Lego Elements, a "Smart Brick" (internally known as a programmable brick or "pbrick"), which serves as the "brain" for a Mindstorms machine. Each set also includes a few attachments for the smart brick (such as motors and sensors) and programming software. Unlike conventional Lego sets, Mindstorms kits do not have a main model to build. Sample builds are included with each version of Mindstorms, but the kit is open-ended with the intent of the user creating and programming their own designs. In addition to at-home use, Mindstorms products are popularly used in schools and in robotics competitions such as the FIRST Leg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Debian Science
A Debian Pure Blend is a project completely inside of Debian targeting a server or a desktop installation in very broad and general terms. A Debian Pure Blend aims to cover interests of specialised users, who might be children, lawyers, medical staff, visually impaired people, certain academic fields, etc. The common goal of those is to make installation and administration of computers for their target users as easy as possible, and to serve in the role as the missing link between software developers and users well. Idea The ideas behind Debian Pure Blends are * providing an out-of-the-box working solution (i.e. some useful collection of software from the Debian pool for the designated target group of specialists) for end-users * providing a frame in which specialists can better channelize their efforts of sustaining a software ecosystem for their field The Debian 8 "Jessie" release consists of approximately 43,000 software packages. Therefore, without knowing the specific name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
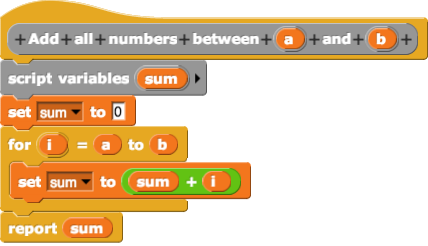
Visual Programming
In computing, a visual programming language (visual programming system, VPL, or, VPS), also known as diagrammatic programming, graphical programming or block coding, is a programming language that lets users create programs by manipulating program elements rather than by specifying them . A VPL allows programming with visual expressions, spatial arrangements of text and graphic symbols, used either as elements of syntax or secondary notation. For example, many VPLs are based on the idea of "boxes and arrows", where boxes or other screen objects are treated as entities, connected by arrows, lines or arcs which represent relations. VPLs are generally the basis of low-code development platforms. Definition VPLs may be further classified, according to the type and extent of visual expression used, into icon-based languages, form-based languages, and diagram languages. Visual programming environments provide graphical or iconic elements which can be manipulated by users in an inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ArduPilot
ArduPilot is an autopilot software program that can control multirotor drones, fixed-wing and VTOL aircraft, RC helicopters, ROVs, ground rovers, boats, submarines, uncrewed surface vessels (USVs), antenna trackers and blimps. ArduPilot was originally developed by hobbyists to control model aircraft and rovers and has evolved into a full-featured and reliable autopilot used by industry, research organisations, amateurs, and militaries—in June 2025 ArduPilot was used successfully by the Ukrainian armed forces during the Russo-Ukrainian War to make aerial drone attacks on Russian air bases. It is published as open source software under the GNU GPL version 3. Characteristics The ArduPilot software suite consists of navigation software (typically referred to as firmware when it is compiled to binary form for microcontroller hardware targets) running on the vehicle (either Copter, Plane, Rover, AntennaTracker, or Sub), along with ground station controlling software including Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |