Lego Mindstorms on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Lego Mindstorms (sometimes stylized as ''LEGO MINDSTORMS'') is a discontinued line of educational kits for building programmable robots based on
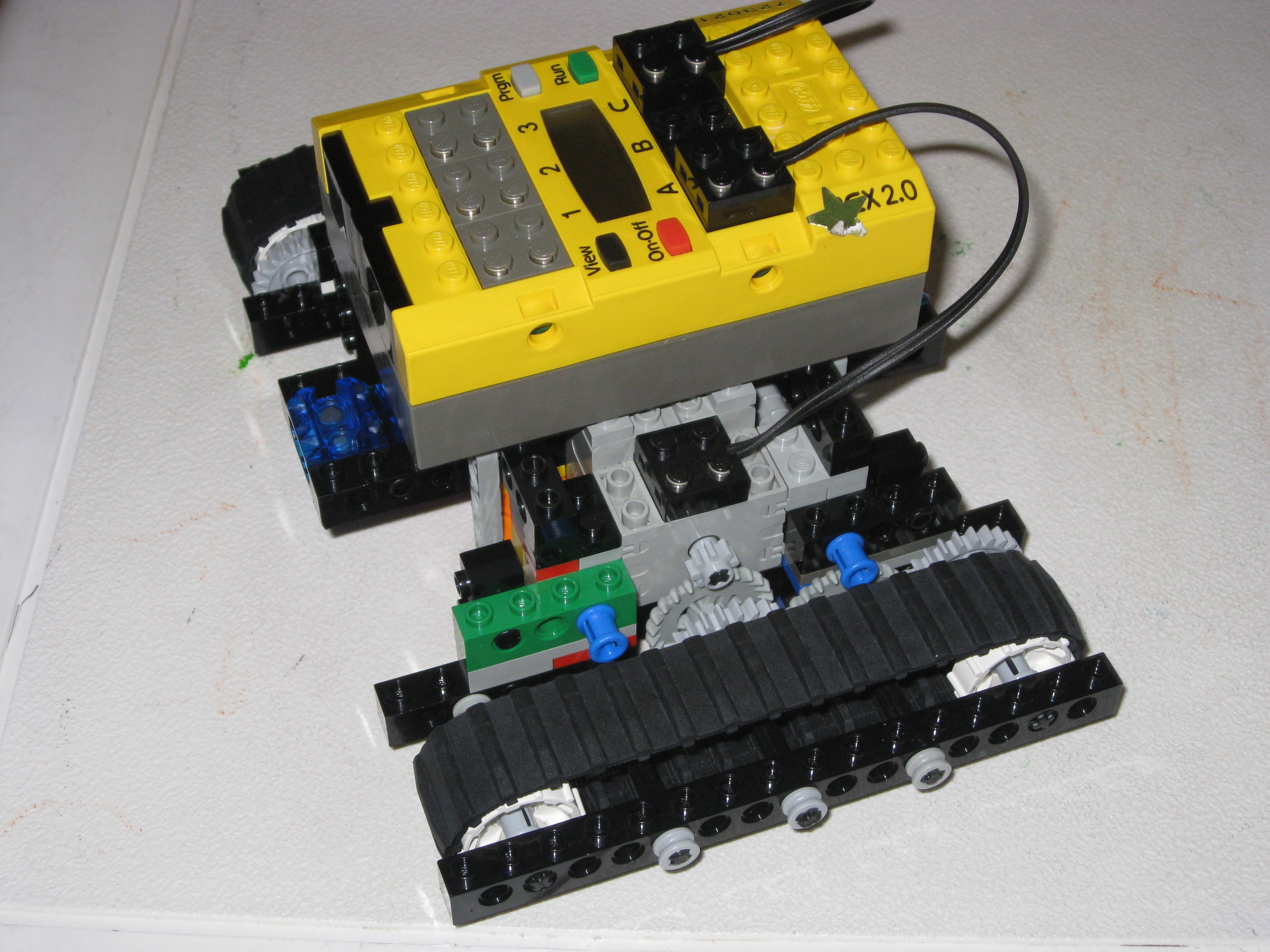 The Robotics Invention System (RIS) was the flagship product of the first generation of the Lego Mindstorms line. It is a commercialization of technology produced by the MIT Media Lab in collaboration with the LEGO group. The RIS featured the programmable Robotic Command eXplorer (RCX) microcontroller, as well as 9V Lego-compatible motors and sensors and a selection of Lego parts. The original RIS was launched fall of 1998. It was replaced by a second version, RIS 1.5, in the summer of 1999; and a third version, RIS 2.0, in 2001.
The Robotics Invention System (RIS) was the flagship product of the first generation of the Lego Mindstorms line. It is a commercialization of technology produced by the MIT Media Lab in collaboration with the LEGO group. The RIS featured the programmable Robotic Command eXplorer (RCX) microcontroller, as well as 9V Lego-compatible motors and sensors and a selection of Lego parts. The original RIS was launched fall of 1998. It was replaced by a second version, RIS 1.5, in the summer of 1999; and a third version, RIS 2.0, in 2001.
 The Lego Mindstorms team used the insights that MIT researchers discovered from testing the 3rd Generation Logo Brick ("Red Brick") in schools as the basis for the development of the mass-produced programmable brick. The physical programmable brick was re-engineered from the ground up, as the experimental programmable bricks were not designed for robustness or cost-effective manufacturing. The
The Lego Mindstorms team used the insights that MIT researchers discovered from testing the 3rd Generation Logo Brick ("Red Brick") in schools as the basis for the development of the mass-produced programmable brick. The physical programmable brick was re-engineered from the ground up, as the experimental programmable bricks were not designed for robustness or cost-effective manufacturing. The
 The RCX is based on the 8-bit Renesas
The RCX is based on the 8-bit Renesas
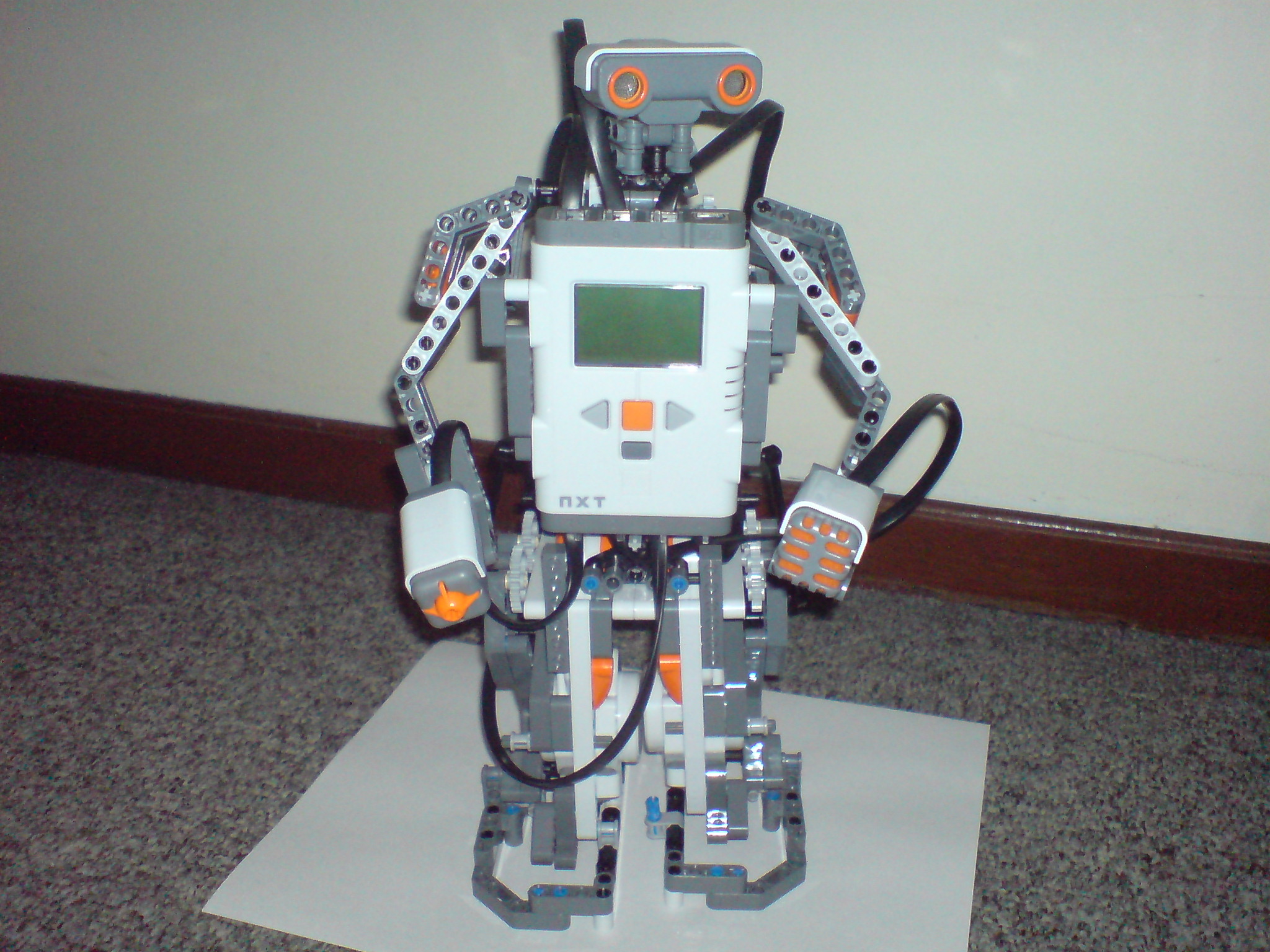
 Lego Mindstorms NXT was a programmable
Lego Mindstorms NXT was a programmable
 EV3, the third generation Mindstorms product, is a further development of the NXT. The system was released on 1 September 2013. There are three versions of the Lego Mindstorms EV3:
* LEGO MINDSTORMS EV3 31313
This set contains 601 pieces and includes 3 servo motors (2 large and 1 medium), 3 sensors (touch sensor, infrared sensor and colour sensor), the EV3 programmable brick and a remote control (the Infrared Beacon, which is only on Home/Retail mode).
* LEGO MINDSTORMS Education EV3 Core Set 45544
This version contains 541 pieces and always includes 3 servo motors (2 large and 1 medium), 4 sensors (2 touch sensors, ultrasonic sensor, colour sensor and gyro sensor) and the EV3 programmable brick.
* LEGO MINDSTORMS Education EV3 Expansion Set 45560
This set instead contains 853 Lego Technic elements
The EV3 can be controlled by smart-devices. It can boot an alternative operating system from a microSD card, which makes it possible to ru
EV3, the third generation Mindstorms product, is a further development of the NXT. The system was released on 1 September 2013. There are three versions of the Lego Mindstorms EV3:
* LEGO MINDSTORMS EV3 31313
This set contains 601 pieces and includes 3 servo motors (2 large and 1 medium), 3 sensors (touch sensor, infrared sensor and colour sensor), the EV3 programmable brick and a remote control (the Infrared Beacon, which is only on Home/Retail mode).
* LEGO MINDSTORMS Education EV3 Core Set 45544
This version contains 541 pieces and always includes 3 servo motors (2 large and 1 medium), 4 sensors (2 touch sensors, ultrasonic sensor, colour sensor and gyro sensor) and the EV3 programmable brick.
* LEGO MINDSTORMS Education EV3 Expansion Set 45560
This set instead contains 853 Lego Technic elements
The EV3 can be controlled by smart-devices. It can boot an alternative operating system from a microSD card, which makes it possible to ru
ev3dev
a
 Due to its user friendliness towards children, Lego Mindstorms has been used as a platform for several child-oriented robotics competitions, most prominently the FIRST Lego League (FLL), but also World Robot Olympiad or Robocup Junior
Due to its user friendliness towards children, Lego Mindstorms has been used as a platform for several child-oriented robotics competitions, most prominently the FIRST Lego League (FLL), but also World Robot Olympiad or Robocup Junior
Legosheets: A Rule-Based Programming, Simulation and Manipulation Environment for the Lego Programmable Brick
, ''Proceeding of Visual Languages'', Darmstadt, Germany, IEEE Computer Society Press, 1995, pp. 172–179. * Breña Moral, Juan Antonio.
Develop LeJOS programs Step by Step
'.
Lego
Lego (, ; ; stylised as LEGO) is a line of plastic construction toys manufactured by the Lego Group, a privately held company based in Billund, Denmark. Lego consists of variously coloured interlocking plastic bricks made of acrylonitri ...
bricks. It was introduced on 1 September 1998 and discontinued on 31 December 2022.
Mindstorms kits allow users to build creations that interact with the physical world. All Mindstorms kits consist of a selection of Lego Elements, a "Smart Brick" (internally known as a programmable brick or "pbrick"), which serves as the "brain" for a Mindstorms machine. Each set also includes a few attachments for the smart brick (such as motors and sensors) and programming software. Unlike conventional Lego sets, Mindstorms kits do not have a main model to build. Sample builds are included with each version of Mindstorms, but the kit is open-ended with the intent of the user creating and programming their own designs.
In addition to at-home use, Mindstorms products are popularly used in schools and in robotics competitions such as the FIRST Lego League. Versions of Mindstorms kits specifically intended for use in educational settings are sold by Lego Education.
Children are the intended audience of Lego Mindstorms, but a significant number of Mindstorms hobbyists are adults. The latter have developed many alternative programming language
A programming language is a system of notation for writing computer programs.
Programming languages are described in terms of their Syntax (programming languages), syntax (form) and semantics (computer science), semantics (meaning), usually def ...
s and operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ...
s for the smart brick, allowing for more complex functions.
While originally conceptualized and launched as a tool to support educational constructivism, Mindstorms has become the first home robotics kit available to a wide audience. It has developed a community of adult hobbyists and hackers as well as students and general Lego enthusiasts following the product's launch in 1998. In October 2022, the Lego Group announced that it would discontinue the Lego Mindstorms line while continuing to support the Scratch-based SPIKE controller.
Lego Mindstorms and Robotics Invention System (1998)
Development of Mindstorms Brand
The Lego Mindstorms product line was the first project of "Home Education", a division of Lego Education established by employee Tormod Askildsen in 1995. Askildsen, who had previously spent ten years working for Lego Education, had grown frustrated working with teaching professionals and wanted to create an improved educational experience that was delivered directly towards children. Home Education decided to incorporate technology into their products based onmarket research
Market research is an organized effort to gather information about target markets and customers. It involves understanding who they are and what they need. It is an important component of business strategy and a major factor in maintaining com ...
that concluded that children found learning that involved technology interesting. Lego Mindstorms started development in April 1996. The concept for the set was based on technology created in partnership with the MIT Media Lab. MIT Media Lab had been experimenting with combining Lego and programming since the early 1980s, and Lego had previously commercialized some of this technology as classroom products in the Lego Dacta line. The programmable brick (or pbrick) was a refinement of these early concepts, which had limited range because they had to be tethered to a computer to run.
Lego had been interested in mass-producing the pbrick since its creation in the 1980s, but at the time it was considered unfeasible due to the lack of computers in schools and households and the relative expense of electrical components. in the early 1990s Technology began to become more of a child's life, and the toy market accordingly began shifting more towards computerized toys. Many of Lego's attempts at producing electronic toys had languished at the point that Lego began developing MIT's programmable brick into a consumer product. MIT continued developing the pbrick concept, creating a "Red Brick" version between 1994 and 1996 that improved the previous version.
By the mid-1990s personal computers were relatively common in households and the components required to produce the pbrick went down in price, making mass production feasible. Development on what would later be known as the Robotics Invention System started in 1996 as the flagship product of the newly created home-learning division of Lego Education (Lego Dacta). The product line's name "Mindstorms" was intended to express the user experience of the product, it is named after Papert's book Mindstorms, as the user experience was similar to the educational constructivism concepts described in his book.
The project's at-first low profile allowed the Mindstorms team the freedom to develop the product using operating procedures then-unorthodox to the Lego Group. Unlike traditional Lego sets, the Mindstorms Robotics Invention System did not come with step-by-step instructions. The kit also did not have a main model, nor was the play driven by storytelling. To bridge the gap between this new play experience and pre-existing Lego ones, the Mindstorms team created a lot of opportunities for users to engage with each other, such as the creation of Mindstorms.com, Mindstorms Discovery Centers, and the FIRST Lego League. The creation of these experiences was done through partnerships with external groups that the Mindstorms team interacted with as equal partners, something that was uncommon for the Lego group at the time. To ease tensions between Mindstorms and more conventional products, the project team was given autonomy from Lego's product development process and instead reported directly to the company's senior management.
Development of RCX Brick
 The Lego Mindstorms team used the insights that MIT researchers discovered from testing the 3rd Generation Logo Brick ("Red Brick") in schools as the basis for the development of the mass-produced programmable brick. The physical programmable brick was re-engineered from the ground up, as the experimental programmable bricks were not designed for robustness or cost-effective manufacturing. The
The Lego Mindstorms team used the insights that MIT researchers discovered from testing the 3rd Generation Logo Brick ("Red Brick") in schools as the basis for the development of the mass-produced programmable brick. The physical programmable brick was re-engineered from the ground up, as the experimental programmable bricks were not designed for robustness or cost-effective manufacturing. The programming language
A programming language is a system of notation for writing computer programs.
Programming languages are described in terms of their Syntax (programming languages), syntax (form) and semantics (computer science), semantics (meaning), usually def ...
of the product was developed with help from members of the MIT Media lab. Lego decided to use a visual programming language
In computing, a visual programming language (visual programming system, VPL, or, VPS), also known as diagrammatic programming, graphical programming or block coding, is a programming language that lets users create computer program, programs by ...
for Mindstorms, inspired by the LOGOBlocks language previously used with programmable brick experiments, in order to make the product accessible to children who might be unfamiliar with programming. While the technology that Mindstorms was based on was aimed towards "all children", the chosen target demographic of Lego Mindstorms was intentionally narrow, in order to garner positive press by outselling expectations. The decision was made to aim the product towards 10 to 14-year-old boys, partly because it was Lego's main target demographic, and partly based on market research (not substantiated by the findings of the MIT Media Lab) which concluded that this demographic would be most attracted to computerized toys. This choice of target demographic directly informed the color of the RCX brick (which was made yellow and black to resemble construction equipment) and the sample uses for the Mindstorms kit (such as making autonomous robots).
Launch
Promotion of the Lego Mindstorms Robotics Invention System began 6 months before the product was planned to launch. The product was first soft launched with the opening of the Mindstorms Discovery Center at the Museum of Science and Industry, where children could interact with the Mindstorms Robotics Invention System to complete set tasks, getting them familiar with the product. The Mindstorms product was launched concurrently with the Cybermaster, another Lego product spun off from the MIT programmable brick technology that was more in line with the traditional product philosophies of the Lego group. The Lego Mindstorms Robotics Invention System (RIS) was released September 1998 at a retail price of $199. Instead of being sold at toy stores, the product was sold at electronics stores like BestBuy andCompUSA
CompUSA, Inc. was a retailer and reseller of Personal computer, personal computers, consumer electronics, technology products and computer services. Starting with one Brick and mortar, brick-and-mortar store in 1986 under the name Soft Warehouse, ...
, due to the relatively high cost of the set.
The entire production run (of between 60,000 and 100,000 unitsThe exact number of sets in the first production run varies between sources) sold out within 3 months.
The second edition of the RIS, Robotics Invention System 1.5, was released in the summer of 1999, with a third edition, RIS 2.0, launched in 2001.
Fanbase and "Right-to-Hack"
Despite being aimed towards children, the Robotics Invention System quickly found an audience with adults and hackers of all ages; Lego company surveys conducted a few months after launch determined that seventy percent of Lego Mindstorms Hobbyists were adults. Shortly following the product's launch, adult hobbyists began sharing reverse-engineered versions of the RCX brick'sMicrocode
In processor design, microcode serves as an intermediary layer situated between the central processing unit (CPU) hardware and the programmer-visible instruction set architecture of a computer. It consists of a set of hardware-level instructions ...
and Firmware
In computing
Computing is any goal-oriented activity requiring, benefiting from, or creating computer, computing machinery. It includes the study and experimentation of algorithmic processes, and the development of both computer hardware, h ...
on the internet, leading to the development of alternative programming languages for the RCX such as "Not Quite C" (NQC) and alternative operating systems for the brick like lejOS. The Lego Group briefly considered sending cease-and-desist letters to websites sharing the RCX's proprietary code. However, The Mindstorms team successfully argued that the embrace of the product by the hacking community proved that the product was worth developing. In order to foster this burgeoning community, an official forum was established on the Lego website and a "right to hack" clause was added to end user license agreement of the Lego Mindstorms software. An official software developers kit for the RCX would later be released on the Mindstorms website. A number of products focusing on the RIS were released by adult hobbyists, including how-to books, and unofficial sensors and hardware. A convention for Lego Mindstorms hobbyists, named Mindfest, started in 1999.
Despite strong sales, the Mindstorms development team was neglected by upper management. As a cost-cutting
Cost reduction is the process used by organisations aiming to reduce their costs and increase their profits, or to accommodate reduced income. Depending on a company’s services or products, the strategies can vary. Every decision in the produ ...
measure, the Mindstorms office was shut down in 2001, and team members were laid-off or assigned to other projects. The Lego Group continued to produce the Robotics Invention System 2.0, selling around 40,000 units per year without advertising until the set was discontinued in 2006.
RCX
 The RCX is based on the 8-bit Renesas
The RCX is based on the 8-bit Renesas H8/300
The Hitachi H8 is a large family of 8-bit, 16-bit and 32-bit microcontrollers made by Renesas Technology, originating in the early 1990s within Hitachi Semiconductor. The original design, the H8/300, was an 8-bit processor that had a 16-bit ...
microcontroller
A microcontroller (MC, uC, or μC) or microcontroller unit (MCU) is a small computer on a single integrated circuit. A microcontroller contains one or more CPUs (processor cores) along with memory and programmable input/output peripherals. Pro ...
, including 32 KB of ROM for low-level IO functions, along with 32 KB of RAM to store high-level firmware and user programs. The RCX is programmed by upload
Uploading refers to ''transmitting'' data from one computer system to another through means of a network. Common methods of uploading include: uploading via web browsers, FTP clients, and terminals ( SCP/ SFTP). Uploading can be used in th ...
ing a program using a dedicated infrared
Infrared (IR; sometimes called infrared light) is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than that of visible light but shorter than microwaves. The infrared spectral band begins with the waves that are just longer than those ...
interface. After the user uploads a program, the RCX can run it on its own without the need for computer access. Programs may make use of three sensor input ports and three 9 V output ports, in addition to the IR interface, enabling RCX bricks to communicate with one another. A built-in LCD
A liquid-crystal display (LCD) is a flat-panel display or other electronically modulated optical device that uses the light-modulating properties of liquid crystals combined with polarizers to display information. Liquid crystals do not em ...
can display information including the battery level, the status of the input/output ports, and the program currently running.
Version 1.0 RCX bricks feature a power adapter jack in addition to batteries. In version 2.0 (as well as later 1.0s included in the RIS 1.5), the power adapter jack was removed. Power adapter-equipped RCX bricks were popular for stationary robotics projects (such as robot arms) or for controlling Lego model trains. In the latter context, the RCX might be programmed with Digital Command Control (DCC) software to operate multiple wired trains.
The IR interface on the RCX is able to communicate with Spybots, Scout Bricks, Lego Trains, and the NXT (using a third-party infrared link sensor). The RCX 1.0 IR receiver carrier frequency
In telecommunications, a carrier wave, carrier signal, or just carrier, is a periodic waveform (usually sinusoidal) that conveys information through a process called ''modulation''. One or more of the wave's properties, such as amplitude or fre ...
is 38.5 kHz, while the RCX 2.0 IR carrier frequency is 76 kHz. Both versions can transmit on either frequency. The RCX communicates with a computer using a Serial or USB
Universal Serial Bus (USB) is an industry standard, developed by USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF), for digital data transmission and power delivery between many types of electronics. It specifies the architecture, in particular the physical ...
IR tower. As the RCX is discontinued, support for the interface is limited on more recent operating systems than Windows XP.
All RCX versions have a unique number printed on them, which could be registered on the now-defunct Lego Mindstorms RCX website. This was necessary to obtain technical support. The first RCX produced is marked "000001," and was on display at the Mindstorms 10th Anniversary event.
The Lego RCX was available in new sets from 1998 (Lego Set 9719: Robotics Invention System 1.0) through 2003 (Lego Set 9786: Robo Technology Set, with USB cable). The original RCX 1.0 worked with existing Lego power supply products from the Lego Train theme, Lego Product 70931: Electric Train Speed Regulator 9V Power Adaptor for 120v 60 Hz - US version (Years: 1991 thru 2004), Lego Product 70938: Electric Train Speed Regulator 9V Power Adaptor for 230v 50 Hz - European version (Years: 1991-1996). Both of these products converted wall power to 12VAC , through a coaxial power connector (also called a "barrel connector"), 5.5 mm outside, 2.1 mm inside. These were sometimes sold alone and sometimes available as part of other sets such as Lego Set 4563: Load N' Haul Railroad (Year: 1991) and Lego Set 10132: Motorized Hogwarts Express (Year: 2004).
Robotics Discovery Set, Droid Developer Kit, and Dark Side Developer Kit
The Robotics Discovery Set was a more affordable and simpler package than the Robotics Invention Set. Instead of being based on the RCX, it had its own programmable brick called the Scout. An even simpler version of the Scout would be featured in two ''Star Wars''-themed Mindstorms sets.Scout
Lego also released a blue computer called the Scout, which has 2 sensor ports, 2 motor ports (plus one extra if linked with a Micro Scout using afiber-optic cable
A fiber-optic cable, also known as an optical-fiber cable, is an assembly similar to an electrical cable but containing one or more optical fibers that are used to carry light. The optical fiber elements are typically individually coated with p ...
), and a built-in light sensor, but no PC interface. It comes with the Robotics Discovery Set. The Scout can be programmed from a collection of built-in program combinations. In order to program the Scout, a user must enable "power mode" on it. The Scout can store one program.
The Scout is based on a Toshiba
is a Japanese multinational electronics company headquartered in Minato, Tokyo. Its diversified products and services include power, industrial and social infrastructure systems, elevators and escalators, electronic components, semiconductors ...
microcontroller with 32 KB of ROM and 1 KB of RAM, where about 400 bytes are available for user programs. Due to the extremely limited amount of RAM, many predefined subroutines were provided in ROM. The Scout only supports passive external sensors, which means that only touch, temperature and other unpowered sensors can be used. The analog-to-digital converter
In electronics, an analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A-to-D) is a system that converts an analog signal, such as a sound picked up by a microphone or light entering a digital camera, into a Digital signal (signal processing), digi ...
s used in the Scout only have a resolution of 8 bits, in contrast to the 10-bit converters of the RCX.
There was a plan for Lego to create a booster set that allows programming the Scout from a computer with software such as RCX code. However, due to the complexity of this project, it was abandoned.
The RCX can control the Scout brick using the "Send IR Message" program block. The RCX does all of the controlling, and therefore can be programmed with the PC, while the Scout accepts commands. The Scout brick must have all of its options set to "off" during this process.
Micro Scout
The Micro Scout was added as an entry-level to Lego robotics. It is a very limited Pbrick with a single built-in light sensor and a single built-in motor. It has seven built-in programs and can be controlled by a Scout, Spybotics or RCX unit using VLL. Like the Scout, the Micro Scout is also based on a microcontroller fromToshiba
is a Japanese multinational electronics company headquartered in Minato, Tokyo. Its diversified products and services include power, industrial and social infrastructure systems, elevators and escalators, electronic components, semiconductors ...
.
The unit was sold as part of the Droid Developer Kit (featuring R2-D2
R2-D2 () or Artoo-Detoo is a fictional robot character in the ''Star Wars'' franchise created by George Lucas. He has appeared in ten of the eleven theatrical ''Star Wars'' films to date, including every film in the " Skywalker Saga", which inclu ...
) and later the Dark Side Developer Kit (featuring an AT-AT Imperial Walker).
Lego Mindstorms NXT (2006)

 Lego Mindstorms NXT was a programmable
Lego Mindstorms NXT was a programmable robotics
Robotics is the interdisciplinary study and practice of the design, construction, operation, and use of robots.
Within mechanical engineering, robotics is the design and construction of the physical structures of robots, while in computer s ...
kit released by Lego
Lego (, ; ; stylised as LEGO) is a line of plastic construction toys manufactured by the Lego Group, a privately held company based in Billund, Denmark. Lego consists of variously coloured interlocking plastic bricks made of acrylonitri ...
in August 2006, replacing the first-generation Lego Mindstorms kit.
The kit consists of 577 pieces, including: 3 servo motors, 4 sensors ( ultrasonic, sound, touch
The somatosensory system, or somatic sensory system is a subset of the sensory nervous system. The main functions of the somatosensory system are the perception of external stimuli, the perception of internal stimuli, and the regulation of bo ...
, and light
Light, visible light, or visible radiation is electromagnetic radiation that can be visual perception, perceived by the human eye. Visible light spans the visible spectrum and is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400– ...
), 7 connection cables, a USB
Universal Serial Bus (USB) is an industry standard, developed by USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF), for digital data transmission and power delivery between many types of electronics. It specifies the architecture, in particular the physical ...
interface cable, and the NXT Intelligent Brick. It lets the robot autonomously perform different operations. The kit also includes NXT-G, a graphical programming environment that enables the creation and downloading of programs to the NXT. The software also has instructions for 4 robots: Alpha-Rex (a humanoid), Tri-Bot (a car), Robo-Arm T-56 (a robotic arm), and Spike (a scorpion)
Development
The Development of Lego Mindstorms NXT began in 2004. At the time, The Lego group was in the middle of a financial crisis. As part of the turn-around effort, the product line developed for release in 2006 would feature relatively few products that were guaranteed to be profitable. A revival of The Mindstorms Robotics Invention System was chosen as of these products, as Lego Mindstorms had a strong fan following and kits continued to sell well without advertising. Fans were extensively involved in the development and promotion of Mindstorms NXT. The development team collaborated with four hobbyists considered experts in Lego Mindstorms fan community. These fans were collectively known as the Mindstorms Users Panel (MUP). They were shipped early prototypes of the Mindstorms kit and communicated to Mindstorms team members on a private internet forum. MUP gave extensive feedback on the hardware and design of the NXT kit. Features of NXT directly based on requests of the MUP include the use 32-bit processor, more powerful motors, and Bluetooth compatibility.Launch
Promotion of Lego Mindstorms NXT was largely word-of-mouth based, because the company was in the middle of a financial crisis and did not have enough money for a large marketing campaign. Mindstorms NXT was unveiled in January 2006 at the 2006 Consumer Electronics Show. At the show, Lego requested applications for a beta-testing phase, where 100 users, known as Mindstoms Community Partners (MCP)s would receive NXT kits at a discounted price months before launch. The intention of the MCP program was to build support for the product prior to launch, and receive feedback on the near-final kit. Fans involved in the MCP program provided a significant amount of PR for the set upon launch, such as alternate models, finished book drafts, and web content like blog posts. News outlets like Wired and CNN also provided free publicity for Mindstorms NXT by reporting on the inclusion of fans in its development process. The launch of Mindstorms NXT, measured in airtime hours, web content and magazine pages; generated more public interest than the entire company had previously accumulated in its entire lifetime. Lego Mindstorms NXT (Product no. 8527) was released August 1 of 2006. $30 million worth of kits were sold in the first year.Lego Mindstorms NXT 2.0
The Lego Mindstorms NXT 2.0 was launched on 5 August 2009. It contains 619 pieces and four sensors; two touch sensors, a new light sensor that added a color sensor, and an ultrasonic distance sensor. The NXT 2.0 uses Floating Point operations whereas earlier versions use Integer operation. The kit costs around US$280.Lego Mindstorms EV3
 EV3, the third generation Mindstorms product, is a further development of the NXT. The system was released on 1 September 2013. There are three versions of the Lego Mindstorms EV3:
* LEGO MINDSTORMS EV3 31313
This set contains 601 pieces and includes 3 servo motors (2 large and 1 medium), 3 sensors (touch sensor, infrared sensor and colour sensor), the EV3 programmable brick and a remote control (the Infrared Beacon, which is only on Home/Retail mode).
* LEGO MINDSTORMS Education EV3 Core Set 45544
This version contains 541 pieces and always includes 3 servo motors (2 large and 1 medium), 4 sensors (2 touch sensors, ultrasonic sensor, colour sensor and gyro sensor) and the EV3 programmable brick.
* LEGO MINDSTORMS Education EV3 Expansion Set 45560
This set instead contains 853 Lego Technic elements
The EV3 can be controlled by smart-devices. It can boot an alternative operating system from a microSD card, which makes it possible to ru
EV3, the third generation Mindstorms product, is a further development of the NXT. The system was released on 1 September 2013. There are three versions of the Lego Mindstorms EV3:
* LEGO MINDSTORMS EV3 31313
This set contains 601 pieces and includes 3 servo motors (2 large and 1 medium), 3 sensors (touch sensor, infrared sensor and colour sensor), the EV3 programmable brick and a remote control (the Infrared Beacon, which is only on Home/Retail mode).
* LEGO MINDSTORMS Education EV3 Core Set 45544
This version contains 541 pieces and always includes 3 servo motors (2 large and 1 medium), 4 sensors (2 touch sensors, ultrasonic sensor, colour sensor and gyro sensor) and the EV3 programmable brick.
* LEGO MINDSTORMS Education EV3 Expansion Set 45560
This set instead contains 853 Lego Technic elements
The EV3 can be controlled by smart-devices. It can boot an alternative operating system from a microSD card, which makes it possible to ruev3dev
a
Debian
Debian () is a free and open-source software, free and open source Linux distribution, developed by the Debian Project, which was established by Ian Murdock in August 1993. Debian is one of the oldest operating systems based on the Linux kerne ...
-based operating system.
Lego Education Spike Prime
Spike Prime was announced in April 2019. While not being part of the Mindstorms product line, the basic set includes three motors (1 large 2 medium) and sensors for distance, force and color a controller brick based on an STM32F413 microcontroller and 520+ Lego Technic elements. Majority of these motors and sensors, including the hub, would serve as the electric components for the then-upcoming Robot Inventor set.Lego Mindstorms Robot Inventor
Lego Mindstorms Robot Inventor was announced in June 2020 and released later in autumn. It is the last commercially available Mindstorms set before the discontinuation of the theme announced in October 2022. It has four medium motors from Spike Prime, two sensors (distance sensor and color/light sensor) also from Spike Prime, a Spike Prime hub with a six-axis gyroscope, an accelerometer, and support for controllers and phone control. It also has 902+ Lego Technic elements. This set was discontinued in 2022 with Lego promising app support through 2024.Programming languages
Use in education
Mindstorms kits are also sold and used as an educational tool, originally through a partnership between Lego and theMIT Media Laboratory
The MIT Media Lab is a research laboratory at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, growing out of MIT's Architecture Machine Group in the School of Architecture. Its research does not restrict to fixed academic disciplines, but draws from ...
. The educational version of the products is called ''Mindstorms for Schools'' or ''Mindstorms Education'', and later versions come with the ROBOLAB GUI-based programming software, developed at Tufts University
Tufts University is a private research university in Medford and Somerville, Massachusetts, United States, with additional facilities in Boston and Grafton, as well as Talloires, France. Tufts also has several Doctor of Physical Therapy p ...
using the National Instruments
The National Instruments Corporation, doing business as NI, is an America, American multinational corporation, multinational company with international operations. Headquartered in Austin, Texas, Austin, Texas, it is a producer of automated tes ...
LabVIEW as an engine.
Use in Competition
 Due to its user friendliness towards children, Lego Mindstorms has been used as a platform for several child-oriented robotics competitions, most prominently the FIRST Lego League (FLL), but also World Robot Olympiad or Robocup Junior
Due to its user friendliness towards children, Lego Mindstorms has been used as a platform for several child-oriented robotics competitions, most prominently the FIRST Lego League (FLL), but also World Robot Olympiad or Robocup Junior
FIRST Lego League Challenge
The ''FIRST'' Lego League Challenge (formerly known as ''FIRST'' Lego League) is an international competition organized by '' FIRST'' for elementary and middle school students (ages 9–14 in the United States and Canada, 9-15 elsewhere).
Each y ...
(founded as FIRST Lego League) is a robotics competition that uses Lego Mindstorms products. It was founded in 1998 concurrent with the launch of LEGO Mindstorms and continues to exist to this day. It is a collaboration between FIRST and The Lego Group
Lego A/S, also known as the Lego Group, is a Danish construction toy production company based in Billund. It manufactures Lego-branded toys, consisting mostly of interlocking ABS plastic and rubber bricks. The Lego Group has also built severa ...
to involve a lower age bracket than the FIRST Robotics Competition
FIRST Robotics Competition (FRC) is an international high school robotics competition operated by ''FIRST''®. Each year, teams of high school students, coaches, and mentors work to build robots capable of competing in that year's game. Robots c ...
. FLL teams consist of children between the ages of 9 and 14, and an adult coach.
See also
* FIRST Lego League * World Robot Olympiad (WRO) * Robofest *FIRST Tech Challenge
FIRST Tech Challenge (FTC), formerly known as FIRST Vex Challenge, is a robotics competition for students in grades 7–12 to compete head to head, by designing, building, and programming a robot to compete in an alliance format against other te ...
* RoboCup Junior
* Lego Education (WeDo 2.0)
* Big Trak
* iRobot Create
* Robotis Bioloid
* The Robotic Workshop
* Robotics suite
A robotics suite is a visual environment for robot control and simulation. They are typically an end-to-end platform for robotics development and include tools for visual programming and creating and debugging robot applications. Developers can ...
* C-STEM Studio
* Botball
* CubeStormer II CubeStormer II is a robot built primarily with Lego Mindstorms and a Samsung Galaxy S2 for solving a Rubik's Cube. The project was commissioned by ARM Holdings and designed and built by Mike Dobson and David Gilday.
CubeStormer II set a Guinness ...
* Cubestormer 3
* Arduino
Arduino () is an Italian open-source hardware and open-source software, software company, project, and user community that designs and manufactures single-board microcontrollers and microcontroller kits for building digital devices. Its hardwar ...
* DIY Kindle Scanner
Notes
References
Further reading
* Bagnall, Brian. ''Maximum Lego NXT: Building Robots with Java Brains''. Variant Press. 2007. . * Bagnall, Brian. ''Core Lego Mindstorms''. Prentice-Hall PTR. 2002. . * Baum, Dave. ''Definitive Guide to Lego Mindstorms'', 2nd ed. Apress. 2002. . * Erwin, Benjamin. ''Creative Projects with Lego Mindstorms'' (book and CD-ROM). Addison-Wesley. 2001. . * Ferrari et al. ''Building Robots with Lego Mindstorms: The Ultimate Tool for Mindstorms Maniacs''. Syngress. 2001. . * Gindling, J., A. Ioannidou, J. Loh, O. Lokkebo, and A. Repenning.,Legosheets: A Rule-Based Programming, Simulation and Manipulation Environment for the Lego Programmable Brick
, ''Proceeding of Visual Languages'', Darmstadt, Germany, IEEE Computer Society Press, 1995, pp. 172–179. * Breña Moral, Juan Antonio.
Develop LeJOS programs Step by Step
'.
External links
* {{Authority control 1998 in robotics Educational toys Electronic toys Embedded systems Robot kits Products introduced in 1998 Products and services discontinued in 2022