|
Rattray, Aberdeenshire
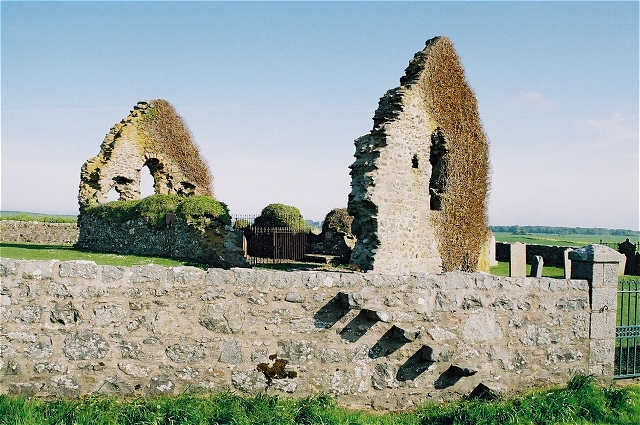
Rattray was a burgh on the coast of Buchan in Aberdeenshire, Scotland, near Rattray Head and the modern village of Crimond. It lay upon a natural harbour in the Loch of Strathbeg, which in former times was an inlet of the sea. Overlooking the harbour entrance was the Castle of Rattray, built by the Comyn family (earls of Buchan). The burgh may have been laid out by the Comyns in the 13th century. It was made a royal burgh by Mary, Queen of Scots in 1564. The harbour entrance began to silt up in the next century, however, and it was finally closed by a storm in 1720. This caused the burgh, which had never been much larger than a village, to enter a terminal decline. By 1732, "there was hardly a vestige of tremaining". All that survives of the burgh today is the ruined Chapel of St Mary and the motte A motte-and-bailey castle is a European fortification with a wooden or stone keep situated on a raised area of ground called a motte, accompanied by a walled courtyard, or Baile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burgh
A burgh ( ) is an Autonomy, autonomous municipal corporation in Scotland, usually a city, town, or toun in Scots language, Scots. This type of administrative division existed from the 12th century, when David I of Scotland, King David I created the first royal burghs. Burgh status was broadly analogous to borough status in the United Kingdom, borough status, found in the rest of the United Kingdom. Following Local Government (Scotland) Act 1973, local government reorganisation in 1975, the title of "royal burgh" remains in use in many towns, but now has little more than ceremonial value. History The first burgh was Berwick-upon-Tweed, Berwick. By 1130, David I of Scotland, David I (r. 1124–53) had established other burghs including Edinburgh, Stirling, Dunfermline, Haddington, East Lothian, Haddington, Perth, Scotland, Perth, Dumfries, Jedburgh, Montrose, Angus, Montrose, Rutherglen and Lanark. Most of the burghs granted charters in his reign probably already existed as settle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buchan
Buchan is a coastal district in the north-east of Scotland, bounded by the Ythan and Deveron rivers. It was one of the original provinces of the Kingdom of Alba. It is now one of the six committee areas of Aberdeenshire. Etymology The genesis of the name ''Buchan'' is shrouded in uncertainty, but may be of Pictish origin. The name may involve an equivalent of Welsh ''buwch'' meaning "a cow". American academic Thomas Clancy has noted cautiously the similarity between the territory names ''Buchan'' and '' Marr'' to those of the Welsh commotes '' Cantref Bychan'' and '' Cantref Mawr'', meaning "small commote" and "large commote", respectively. History The first documentary record of Buchan is a reference in the '' Chronicle of the Kings of Alba'' to the death of King Indulf at the hands of Vikings in Buchan in 962, a death separately recorded in a 12th-century king list as taking place at Cullen. Cullen is to the west of the River Deveron, in an area where the Earls of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aberdeenshire
Aberdeenshire (; ) is one of the 32 Subdivisions of Scotland#council areas of Scotland, council areas of Scotland. It takes its name from the Shires of Scotland, historic county of Aberdeenshire (historic), Aberdeenshire, which had substantially different boundaries. The Aberdeenshire Council area includes all of the areas of the historic counties of Aberdeenshire and Kincardineshire except the area making up Aberdeen City Council area, as well as part of Banffshire. The historic county boundaries are still officially used for a few purposes, namely land registration and Lieutenancy areas of Scotland, lieutenancy. Aberdeenshire Council is headquartered at Woodhill House in Aberdeen, making it the only Scottish council whose headquarters are located outside its jurisdiction. Aberdeen itself forms a different council area (Aberdeen City). Aberdeenshire borders onto Angus, Scotland, Angus and Perth and Kinross to the south, Highland (council area), Highland and Moray to the west a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rattray Head
Rattray Head (), historically Rattray Point, is a headland in Buchan, Aberdeenshire, on the north-east coast Scotland. To north lies Strathbeg Bay and Rattray Bay is to its south. The dunes at Rattray Head beach can be up to high and stretch from St Combs to Peterhead. Rattray Head lighthouse The Rattray Head lighthouse A lighthouse is a tower, building, or other type of physical structure designed to emit light from a system of lamps and lens (optics), lenses and to serve as a beacon for navigational aid for maritime pilots at sea or on inland waterways. Ligh ... was built in 1895. It was built by the engineers and brothers David Alan Stevenson and [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crimond
Crimond is a village in Aberdeenshire, in the northeast of Scotland, located northwest of the port of Peterhead and just over from the coast. Geography The main A90 road runs through Crimond and is lined by Crimond Church with a village hall, Crimond Primary School, Crimond Medical Practice, Crimond Shop and Post Office, Crimond Care Home for the elderly and Crimond Motors garage. The oldest houses in the village run alongside the main road with a modern estate to the west side. When standing with a clear view of the surrounding countryside the masts at the nearby Crimond Aerodrome to the east may be seen as are the telecommunications satellite receivers on Mormond Hill to the North West. The nearby Loch of Strathbeg is a RSPB owned and protected nature reserve. Around the loch there are 3 hides from which to watch the birds and other wildlife. They are accessible through the airfield and there is a car park. There is also the Starnafin Centre where you can watch the bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loch Of Strathbeg
The Loch of Strathbeg is a shallow freshwater loch on the coast of Buchan in Aberdeenshire, Scotland. It lies within the parishes of Lonmay and Crimond. The loch is a designated special protection area because of its importance to birdlife and is managed by the Royal Society for the Protection of Birds, which operates a visitor centre at Starnafin. It is visited in the winter months by at least 20,000 birds, including pink-footed geese, whooper swans, and Eurasian teal, teals. History The Loch of Strathbeg was formerly an inlet of the sea, sheltered by a shingle shoal, bar. A channel at the east end of the bar gave access to the port of Rattray, Aberdeenshire, Rattray. This channel began to silt up in the 17th century, however, which proved fatal for the port. It was finally sealed by a storm around the year 1720. Writing in 1794, the minister of Crimond remarked: Attempts were made in the 18th century to drain the loch, but these were doomed to end in failure. The ruined windm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castle Of Rattray
The Castle of Rattray was a medieval Scotland, Scottish castle, with multiple variations on its structure over approximately six centuries. Originally built as a ''"late 12th- or early 13th century defensive Motte-and-bailey, motte"'' it provided protection for Starny Keppie Harbour and Rattray village. Sometime between 1214 and 1233 it was upgraded by William Comyn, jure uxoris Earl of Buchan before being destroyed in the 1308 Harrying of Buchan. After Comyn's timber castle was burned down, it was replaced by a stronger stone castle which was engulfed during a 1720 sand storm along with nearby Rattray, Aberdeenshire, Rattray village. After the storm, the castle was not dug out and remains covered to this day. The castle was described by W. Douglas Simpson as one of the nine castles of the Knuckle, referring to the rocky headland of north-east Aberdeenshire. Location The castle was sited on Castlehill, on the south bank of the now-closed estuary flowing into Loch Strathbeg, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Burgh
A royal burgh ( ) was a type of Scottish burgh which had been founded by, or subsequently granted, a royal charter. Although abolished by law in 1975, the term is still used by many former royal burghs. Most royal burghs were either created by Scottish monarchy, the Crown, or upgraded from another status, such as burgh of barony. As discrete classes of burgh emerged, the royal burghs—originally distinctive because they were on royal lands—acquired a monopoly of foreign trade. An important document for each burgh was its burgh charter, creating the burgh or confirming the rights of the burgh as laid down (perhaps orally) by a previous monarch. Each royal burgh (with the exception of four 'inactive burghs') was represented in the Parliament of Scotland and could appoint bailies with wide powers in civil and criminal justice.George S Pryde, ''The Burghs of Scotland: A Critical List'', Oxford, 1965. The four inactive burghs were Auchtermuchty, Earlsferry, Falkland and Newburgh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mary, Queen Of Scots
Mary, Queen of Scots (8 December 1542 – 8 February 1587), also known as Mary Stuart or Mary I of Scotland, was List of Scottish monarchs, Queen of Scotland from 14 December 1542 until her forced abdication in 1567. The only surviving legitimate child of James V of Scotland, Mary was six days old when her father died and she inherited the throne. During her childhood, Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland was governed by regents, first by the heir to the throne, James Hamilton, Earl of Arran, and then by her mother, Mary of Guise. In 1548, she was betrothed to Francis II of France, Francis, the Dauphin of France, and was sent to be brought up in Kingdom of France, France, where she would be safe from invading Kingdom of England, English forces during the Rough Wooing. Mary Wedding of Mary, Queen of Scots, and Francis, Dauphin of France, married Francis in 1558, becoming queen consort of France from his accession in 1559 until his death in December 1560. Widowed, Mary Entry of Mary, Q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Mary's Chapel, Rattray
St Mary's Chapel (known also as "the Chapel of the Blessed Virgin") is a late 12th/early 13th century chapel found in Rattray, Aberdeenshire, Scotland. It was built by William Comyn, jure uxoris Earl of Buchan during the same period as the Castle of Rattray and was ''"private chapel for the castle"'' and its residents. ''"Dedicated to the Virgin Mary"'' it was possibly constructed after the ''"drowning of a"...'' nknown''"son of Comyn in the well near by."'' There is some controversy as to the date of the chapel's construction. There is a wall plaque with the date 911, but this is certainly a fake as the style of the church and its windows did not appear in Scotland until the late 12th century, which coincides with an account that states it ''"probably dates back to the late 1100s."'' William Comyn did not inherit the Earldom of Buchan until 1212, so the chapel's construction almost certainly did not begin prior to this date. William Comyn is recorded as giving the chapel ''"a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motte
A motte-and-bailey castle is a European fortification with a wooden or stone keep situated on a raised area of ground called a motte, accompanied by a walled courtyard, or Bailey (castle), bailey, surrounded by a protective Rampart (fortification), ditch and palisade. Relatively easy to build with unskilled labour, but still militarily formidable, these castles were built across northern Europe from the 10th century onwards, spreading from Normandy and County of Anjou, Anjou in France, into the Holy Roman Empire, as well as the Low Countries it controlled, in the 11th century, when these castles were popularized in the area that became the Netherlands. The Normans introduced the design into England and Wales. Motte-and-bailey castles were adopted in Scotland, Ireland, and Denmark in the 12th and 13th centuries. By the end of the 13th century, the design was largely superseded by alternative forms of fortification, but the earthworks remain a prominent feature in many countries. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |