|
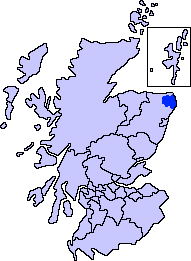
Buchan
Buchan is a coastal district in the north-east of Scotland, bounded by the Ythan and Deveron rivers. It was one of the original provinces of the Kingdom of Alba. It is now one of the six committee areas of Aberdeenshire. Etymology The genesis of the name ''Buchan'' is shrouded in uncertainty, but may be of Pictish origin. The name may involve an equivalent of Welsh ''buwch'' meaning "a cow". American academic Thomas Clancy has noted cautiously the similarity between the territory names ''Buchan'' and '' Marr'' to those of the Welsh commotes '' Cantref Bychan'' and '' Cantref Mawr'', meaning "small commote" and "large commote", respectively. History The first documentary record of Buchan is a reference in the '' Chronicle of the Kings of Alba'' to the death of King Indulf at the hands of Vikings in Buchan in 962, a death separately recorded in a 12th-century king list as taking place at Cullen. Cullen is to the west of the River Deveron, in an area where the Earls of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earls Of Buchan
The Mormaer () or Earl of Buchan () was originally the provincial ruler of the medieval province of Buchan. Buchan was the first Mormaerdom in the High Medieval Kingdom of the Scots to pass into the hands of a non-Scottish family in the male line. The earldom had three lines in its history, not counting passings from female heirs to sons. Today, it is held by the Erskine family as a peerage. The current holder is Harry Erskine, 18th Earl of Buchan (b. 1960). Subsidiary titles are Lord Cardross and Lord Auchterhouse and Baron Erskine. Mormaerdom of Buchan The first recorded person who definitely held the position of mormaer was Gartnait, Earl of Buchan, Gartnait, whose patronage is noted in the Middle Irish, Gaelic Notes on the ''Book of Deer''. The latter is the only significant source for the mormaerdom, and its existence makes Buchan one of Scotland's best documented provinces for native cultural institutions. After the death of Fergus, Earl of Buchan, Fergus, before 1214, Buc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peterhead
Peterhead (; , ) is a town in Aberdeenshire, Scotland. It is the council area's largest settlement, with a population of 19,060 at the 2022 Census for Scotland, 2022 Census. It is the largest fishing port in the United Kingdom for total landings by UK vessels, according to a 2019 survey."Brexit trade deal: What does it mean for fishing?" - BBC News, December 2020 Peterhead sits at the easternmost point in mainland Scotland. It is often referred to as ''The Blue Toun'' (locally spelled "The Bloo Toon") and its natives are known as ''Bloo Touners''. They are also referred to as ''blue mogganers'' (locally spelled "bloomogganners"), supposedly from the blue worsted ''moggans'' or stockings that the fishermen originally wore. Prehistory and archaeology Expansion of the town's landfill led to ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buchan Ness And Its Lighthouse - Geograph
Buchan is a coastal district in the north-east of Scotland, bounded by the Ythan and Deveron rivers. It was one of the original provinces of the Kingdom of Alba. It is now one of the six committee areas of Aberdeenshire. Etymology The genesis of the name ''Buchan'' is shrouded in uncertainty, but may be of Pictish origin. The name may involve an equivalent of Welsh ''buwch'' meaning "a cow". American academic Thomas Clancy has noted cautiously the similarity between the territory names ''Buchan'' and '' Marr'' to those of the Welsh commotes ''Cantref Bychan'' and ''Cantref Mawr'', meaning "small commote" and "large commote", respectively. History The first documentary record of Buchan is a reference in the ''Chronicle of the Kings of Alba'' to the death of King Indulf at the hands of Vikings in Buchan in 962, a death separately recorded in a 12th-century king list as taking place at Cullen. Cullen is to the west of the River Deveron, in an area where the Earls of Bucha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Remote Radar Head Buchan
Remote Radar Head Buchan or RRH Buchan is an air defence radar station operated by the Royal Air Force. It is located at Stirling Hill, south of Peterhead on the Aberdeenshire coast of northeast Scotland. The unit is based at the operations site of the former RAF Buchan which was downgraded from an RAF station to a remote radar head (RRH) in September 2004. History RAF Buchan RAF Buchan opened in 1952 as an Air Defence Radar Unit. As part of the UK Air Surveillance and Control System, the station was one of two Control and Reporting Centres (CRC) which monitored air traffic in and around UK airspace. RAF Buchan was parent station to remote radar heads at Saxa Vord and Benbecula. In 1979 operations moved into interim facilities above ground whilst the 'R3' underground operations block was refitted as an 'R3A', this involved the excavation of one side of the 'R3' and an auxiliary bunker was constructed alongside to provide secure facilities for stand by generators, power clea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banff And Buchan
Banff and Buchan is a committee area of the Aberdeenshire Council, Scotland, covering an area along the northern coast of the council area. The main towns are Banff and Fraserburgh. Fishing and agriculture are important industries, together with associated processing and service activity. Banff and Buchan was also the name of a district of Grampian Region between 1975 and 1996. The district covered a much larger area than the modern committee area. Its council was based in Banff. History The area has a long history of human occupation. Prehistoric features include a large long barrow at Longman Hill south-east of Macduff, as well as Cairn Lee to the west of Longman Hill. Local government district The Banff and Buchan local government district was created on 16 May 1975 under the Local Government (Scotland) Act 1973, which established a two-tier structure of local government across Scotland comprising upper-tier regions and lower-tier districts. Banff and Buchan was one o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formartine
Formartine ( meaning "Martin's land") is a committee area in Aberdeenshire, Scotland. This district extends north from the River Don, Aberdeenshire, River Don to the River Ythan. It has a population of 36,478 (2001 Census). The committee area was formed in 1996 from part of the former Districts of Scotland, district of Banff and Buchan. Formartine has experienced rapid population growth, particularly around Ellon, Aberdeenshire, Ellon and Oldmeldrum, and in the south east where development has spread outwith the city of Aberdeen. By contrast, the area around Turriff retains strong dependency on the traditional agricultural economy. The area's coastline and rural environment offer recreation potential including the Formartine and Buchan Way. History Formartine is first documented as a thanage in 1266, when Reginald le Chen (d.1293), Reginald Cheyne is recorded holding it in feu (land tenure), feu-ferm and liable for 14 Merk (coin), merks as 2nd teinds payable to the Diocese of A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pictish
Pictish is an extinct Brittonic Celtic language spoken by the Picts, the people of eastern and northern Scotland from late antiquity to the Early Middle Ages. Virtually no direct attestations of Pictish remain, short of a limited number of geographical and personal names found on monuments and early medieval records in the area controlled by the kingdoms of the Picts. Such evidence, however, shows the language to be an Insular Celtic language – probably a variant of the Brittonic language once spoken in most of Great Britain. The prevailing view in the second half of the 20th century was that Pictish was a non-Indo-European language isolate, or that a non-Indo-European Pictish and Brittonic Pictish language coexisted. Pictish was replaced by – or subsumed into – Gaelic in the latter centuries of the Pictish period. During the reign of Donald II of Scotland (889–900), outsiders began to refer to the region as the kingdom of Alba rather than the kingdom of the Picts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cruden Bay
Cruden Bay is a small village in Scotland, on the north coast of the Bay of Cruden in Aberdeenshire, north of Aberdeen. Just west of Slains Castle, Cruden Bay is said to have been the site of a battle in which the Scots under King Malcolm II defeated the Danes in 1012. Traditionally, the name was derived from the Gaelic ('slaughter of Danes'). Today, Cruden Bay attracts tourists with its hotels and golf course. It has a long, unspoiled, beach made famous by Norwegian aviator Tryggve Gran who made the first solo flight across the North Sea. Literary associations The village has associations with various figures in literature. Dr Samuel Johnson and James Boswell were guests at Slains Castle in 1773. Johnson said that "no man can see with indifference" the sea chasm known as the Bullers of Buchan, which is near the village. Dun Bay, or Yellow Rock is also near the Bullers of Buchan, and is associated with Walter Scott's '' The Antiquary''. Bram Stoker was a regular v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Fergus
St Fergus is a village in the Buchan area of Aberdeenshire, Scotland. St Fergus lies from the North Sea coast and north-west of Peterhead. The Parish of St Fergus includes the remains of Inverugie Castle and Ravenscraig Castle. The church in the village was built in 1763. The church for this parish previously stood in the old kirkyard near the shore to the east. This site on the St Fergus Links is still used as a burial ground. Prior to the change in site of the church the parish was known as Longley and at a still more remote period Inverugie. History Historically, the of St Fergus parish formed a detached portion of Banffshire. The parish was transferred to Aberdeenshire in 1891. At that time it had a population of 1,527. The beach area was classed as a risk during WW2 as a possible (but unlikely) landing area for a German invasion. Several pillboxes and anti-tank blocks were placed along the coast. These formed part of the Rattray stop line. Anti-tank ditches are still ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aberdeenshire
Aberdeenshire (; ) is one of the 32 Subdivisions of Scotland#council areas of Scotland, council areas of Scotland. It takes its name from the Shires of Scotland, historic county of Aberdeenshire (historic), Aberdeenshire, which had substantially different boundaries. The Aberdeenshire Council area includes all of the areas of the historic counties of Aberdeenshire and Kincardineshire except the area making up Aberdeen City Council area, as well as part of Banffshire. The historic county boundaries are still officially used for a few purposes, namely land registration and Lieutenancy areas of Scotland, lieutenancy. Aberdeenshire Council is headquartered at Woodhill House in Aberdeen, making it the only Scottish council whose headquarters are located outside its jurisdiction. Aberdeen itself forms a different council area (Aberdeen City). Aberdeenshire borders onto Angus, Scotland, Angus and Perth and Kinross to the south, Highland (council area), Highland and Moray to the west a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotland
Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the United Kingdom's land area, consisting of the northern part of the island of Great Britain and more than 790 adjacent Islands of Scotland, islands, principally in the archipelagos of the Hebrides and the Northern Isles. To the south-east, Scotland has its Anglo-Scottish border, only land border, which is long and shared with England; the country is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, the North Sea to the north-east and east, and the Irish Sea to the south. The population in 2022 was 5,439,842. Edinburgh is the capital and Glasgow is the most populous of the cities of Scotland. The Kingdom of Scotland emerged as an independent sovereign state in the 9th century. In 1603, James VI succeeded to the thrones of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland, forming a personal union of the Union of the Crowns, three kingdo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
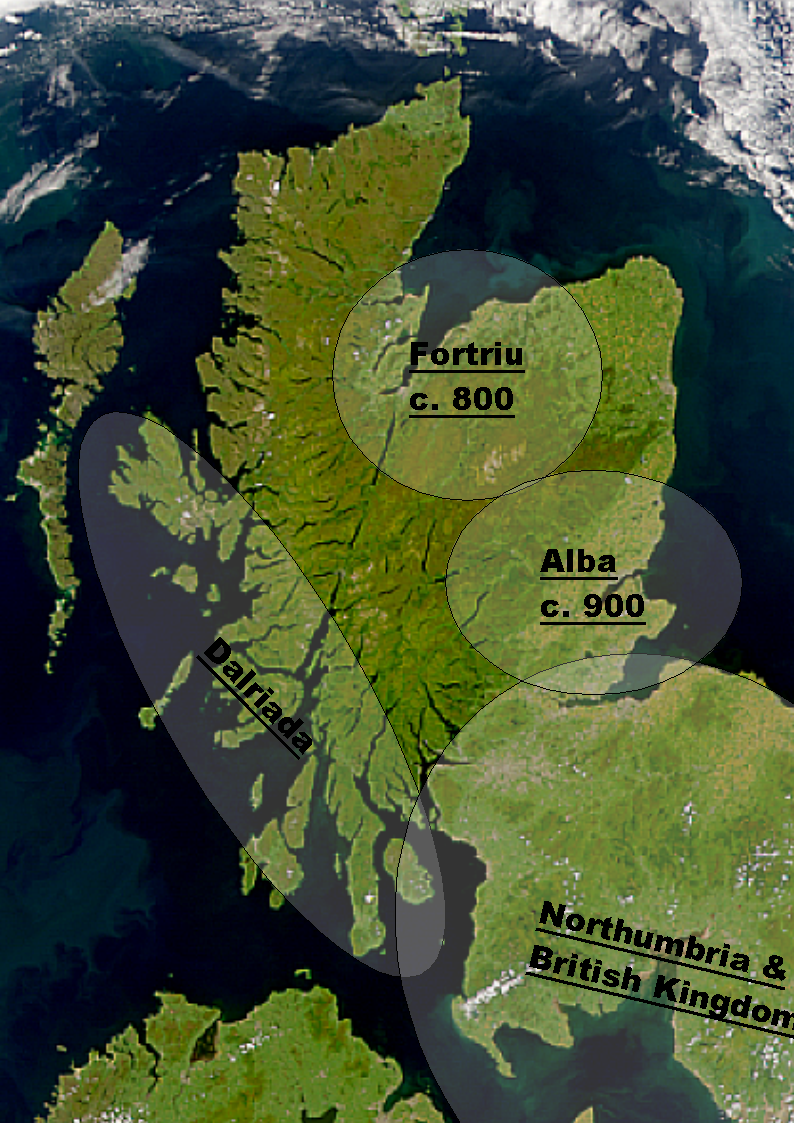
Kingdom Of Alba
The Kingdom of Alba (; ) was the Kingdom of Scotland between the deaths of Donald II in 900 and of Alexander III in 1286. The latter's death led indirectly to an invasion of Scotland by Edward I of England in 1296 and the First War of Scottish Independence. Alba included Dalriada, but initially excluded large parts of the present-day Scottish Lowlands, which were then divided between Strathclyde and Northumbria as far north as the Firth of Forth. Fortriu, a Pictish kingdom in the north, was added to Alba in the tenth century. Until the early 13th century, Moray was not considered part of Alba, which was seen as extending only between the Firth of Forth and the River Spey. The name of Alba is one of convenience, as throughout this period both the ruling and lower classes of the kingdom were predominantly Pictish-Gaels, later Pictish-Gaels and Scoto-Normans. This differs markedly from the period of the House of Stuart, beginning in 1371, in which the ruling classes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |