|
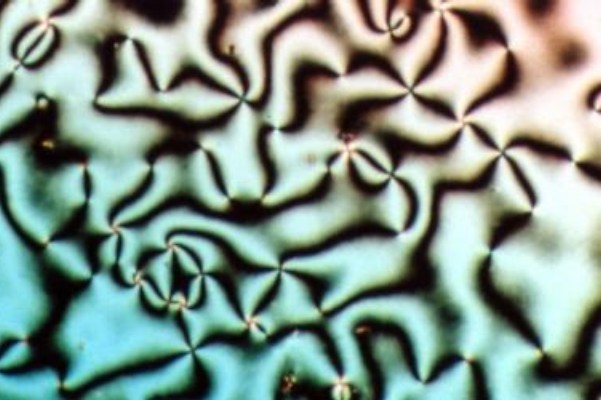
Radial Polarization
A beam of light has radial polarization if at every position in the beam the polarization (electric field) vector points towards the center of the beam. In practice, an array of waveplates may be used to provide an approximation to a radially polarized beam. In this case the beam is divided into segments (eight, for example), and the average polarization vector of each segment is directed towards the beam centre. Radial polarization can be produced in a variety of ways. It is possible to use so-called q-devices to convert the polarization of a beam to a radial state. The simplest example of such devices is inhomogeneous anisotropic birefringent waveplate that performs transversally inhomogeneous polarization transformations of a wave with a uniform initial state of polarization. The other examples are liquid crystal, and metasurface q-plates. In addition, a radially polarized beam can be produced by a laser, or any collimated light source, in which the Brewster window is repl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polarization (waves)
, or , is a property of transverse waves which specifies the geometrical orientation of the oscillations. In a transverse wave, the direction of the oscillation is perpendicular to the direction of motion of the wave. One example of a polarized transverse wave is vibrations traveling along a taut string, for example, in a musical instrument like a guitar string. Depending on how the string is plucked, the vibrations can be in a vertical direction, horizontal direction, or at any angle perpendicular to the string. In contrast, in longitudinal waves, such as sound waves in a liquid or gas, the displacement of the particles in the oscillation is always in the direction of propagation, so these waves do not exhibit polarization. Transverse waves that exhibit polarization include electromagnetic waves such as light and radio waves, gravitational waves, and transverse sound waves ( shear waves) in solids. An electromagnetic wave such as light consists of a coupled oscillating el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Field
An electric field (sometimes called E-field) is a field (physics), physical field that surrounds electrically charged particles such as electrons. In classical electromagnetism, the electric field of a single charge (or group of charges) describes their capacity to exert attractive or repulsive forces on another charged object. Charged particles exert attractive forces on each other when the sign of their charges are opposite, one being positive while the other is negative, and repel each other when the signs of the charges are the same. Because these forces are exerted mutually, two charges must be present for the forces to take place. These forces are described by Coulomb's law, which says that the greater the magnitude of the charges, the greater the force, and the greater the distance between them, the weaker the force. Informally, the greater the charge of an object, the stronger its electric field. Similarly, an electric field is stronger nearer charged objects and weaker f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waveplate
A waveplate or retarder is an optics, optical device that alters the Polarization (waves), polarization state of a light wave travelling through it. Two common types of waveplates are the ''half-wave plate'', which rotates the polarization direction of linear polarization, linearly polarized light, and the ''quarter-wave plate'', which converts between different elliptical polarizations (such as the special case of converting from linearly polarized light to circular polarization, circularly polarized light and vice versa.) Waveplates are constructed out of a birefringence, birefringent material (such as quartz or mica, or even plastic), for which the index of refraction is different for light that is linearly polarized along one or the other of two certain perpendicular crystal axes. The behavior of a waveplate (that is, whether it is a half-wave plate, a quarter-wave plate, etc.) depends on the thickness of the crystal, the wavelength of light, and the variation of the index of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radial And Azimuthal Polarisation
Radial is a geometric term of location which may refer to: Mathematics and Direction * Vector (geometric), a line * Radius, adjective form of * Radial distance (geometry), a directional coordinate in a polar coordinate system * Radial set * A bearing from a waypoint, such as a VHF omnidirectional range Biology * Radial artery, the main artery of the lateral aspect of the forearm * Radial nerve, supplies the posterior portion of the upper limb * Radial symmetry, one of the types of distribution of body parts or shapes in biology * Radius (bone), a bone of the forearm Technology * Radial (radio), lines which radiate from a radio antenna * Radial axle, on a locomotive or carriage * Radial compressor * Radial delayed blowback * Radial engine * Radial tire * Radial, Inc., e-commerce business See also * Axial (other) * Radiate (other) Radiate may refer to: Biology * Radiata, a taxon of jellyfish and allies * Radiate carpal ligament, a group of fibrous bands i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Q-plate
A q-plate is an optical device that can form a light beam with orbital angular momentum (OAM) from a beam with well-defined spin angular momentum (SAM). Q-plates are based on the SAM-OAM coupling that may occur in media that are both anisotropic and inhomogeneous, such as an inhomogeneous anisotropic birefringent waveplate. Q-plates are also currently realized using total internal reflection devices, liquid crystals, metasurfaces based on polymers, and sub-wavelength gratings. The sign of the OAM is controlled by the input beam's polarization Polarization or polarisation may refer to: Mathematics *Polarization of an Abelian variety, in the mathematics of complex manifolds *Polarization of an algebraic form, a technique for expressing a homogeneous polynomial in a simpler fashion by .... References Optical components Nonlinear optics {{optics-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waveplate
A waveplate or retarder is an optics, optical device that alters the Polarization (waves), polarization state of a light wave travelling through it. Two common types of waveplates are the ''half-wave plate'', which rotates the polarization direction of linear polarization, linearly polarized light, and the ''quarter-wave plate'', which converts between different elliptical polarizations (such as the special case of converting from linearly polarized light to circular polarization, circularly polarized light and vice versa.) Waveplates are constructed out of a birefringence, birefringent material (such as quartz or mica, or even plastic), for which the index of refraction is different for light that is linearly polarized along one or the other of two certain perpendicular crystal axes. The behavior of a waveplate (that is, whether it is a half-wave plate, a quarter-wave plate, etc.) depends on the thickness of the crystal, the wavelength of light, and the variation of the index of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid Crystal
Liquid crystal (LC) is a state of matter whose properties are between those of conventional liquids and those of solid crystals. For example, a liquid crystal can flow like a liquid, but its molecules may be oriented in a common direction as in a solid. There are many types of LC Phase (matter), phases, which can be distinguished by their Optics, optical properties (such as Texture (crystalline), textures). The contrasting textures arise due to molecules within one area of material ("domain") being oriented in the same direction but different areas having different orientations. An LC material may not always be in an LC state of matter (just as water may be ice or water vapour). Liquid crystals can be divided into three main types: thermotropic, lyotropic, and #Metallotropic liquid crystals, metallotropic. Thermotropic and lyotropic liquid crystals consist mostly of organic molecules, although a few minerals are also known. Thermotropic LCs exhibit a phase transition into the L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromagnetic Metasurface
An electromagnetic metasurface refers to a kind of artificial sheet material with sub-wavelength features. Metasurfaces can be either structured or unstructured with subwavelength-scaled patterns. In electromagnetic theory, metasurfaces modulate the behaviors of electromagnetic waves through specific boundary conditions rather than constitutive parameters (such as refractive index) in three-dimensional (3D) space, which is commonly exploited in natural materials and metamaterials. Metasurfaces may also refer to the two-dimensional counterparts of metamaterials. There are also 2.5D metasurfaces that involve the third dimension as additional degree of freedom for tailoring their functionality. Definitions Metasurfaces have been defined in several ways by researchers. 1, “An alternative approach that has gained increasing attention in recent years deals with one- and two-dimensional (1D and 2D) plasmonic arrays with subwavelength periodicity, also known as metasurfaces. Due to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Q-plate
A q-plate is an optical device that can form a light beam with orbital angular momentum (OAM) from a beam with well-defined spin angular momentum (SAM). Q-plates are based on the SAM-OAM coupling that may occur in media that are both anisotropic and inhomogeneous, such as an inhomogeneous anisotropic birefringent waveplate. Q-plates are also currently realized using total internal reflection devices, liquid crystals, metasurfaces based on polymers, and sub-wavelength gratings. The sign of the OAM is controlled by the input beam's polarization Polarization or polarisation may refer to: Mathematics *Polarization of an Abelian variety, in the mathematics of complex manifolds *Polarization of an algebraic form, a technique for expressing a homogeneous polynomial in a simpler fashion by .... References Optical components Nonlinear optics {{optics-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word ''laser'' originated as an acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation. The first laser was built in 1960 by Theodore Maiman at Hughes Research Laboratories, based on theoretical work by Charles H. Townes and Arthur Leonard Schawlow and the optical amplifier patented by Gordon Gould. A laser differs from other sources of light in that it emits light that is coherence (physics), ''coherent''. Spatial coherence allows a laser to be focused to a tight spot, enabling uses such as optical communication, laser cutting, and Photolithography#Light sources, lithography. It also allows a laser beam to stay narrow over great distances (collimated light, collimation), used in laser pointers, lidar, and free-space optical communication. Lasers can also have high temporal coherence, which permits them to emit light ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brewster Window
Brewster's angle (also known as the polarization angle) is an angle of incidence at which light with a particular polarization is perfectly transmitted through a transparent dielectric surface, with ''no reflection''. When ''unpolarized'' light is incident at this angle, the light that is reflected from the surface is therefore perfectly polarized. The angle is named after the Scottish physicist Sir David Brewster (1781–1868). Explanation When light encounters a boundary between two media with different refractive indices, some of it is usually reflected as shown in the figure above. The fraction that is reflected is described by the Fresnel equations, and depends on the incoming light's polarization and angle of incidence. The Fresnel equations predict that light with the ''p'' polarization (electric field polarized in the same plane as the incident ray and the surface normal at the point of incidence) will not be reflected if the angle of incidence is :\theta_\mathrm = \arc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brewster's Angle
Brewster's angle (also known as the polarization angle) is an angle of incidence at which light with a particular polarization is perfectly transmitted through a transparent dielectric surface, with ''no reflection''. When ''unpolarized'' light is incident at this angle, the light that is reflected from the surface is therefore perfectly polarized. The angle is named after the Scottish physicist Sir David Brewster (1781–1868). Explanation When light encounters a boundary between two media with different refractive indices, some of it is usually reflected as shown in the figure above. The fraction that is reflected is described by the Fresnel equations, and depends on the incoming light's polarization and angle of incidence. The Fresnel equations predict that light with the ''p'' polarization (electric field polarized in the same plane as the incident ray and the surface normal at the point of incidence) will not be reflected if the angle of incidence is :\theta_\mathrm = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |