|
Radial Basis Function
In mathematics a radial basis function (RBF) is a real-valued function \varphi whose value depends only on the distance between the input and some fixed point, either the origin, so that \varphi(\mathbf) = \hat\varphi(\left\, \mathbf\right\, ), or some other fixed point \mathbf, called a ''center'', so that \varphi(\mathbf) = \hat\varphi(\left\, \mathbf-\mathbf\right\, ). Any function \varphi that satisfies the property \varphi(\mathbf) = \hat\varphi(\left\, \mathbf\right\, ) is a radial function. The distance is usually Euclidean distance, although other metrics are sometimes used. They are often used as a collection \_k which forms a basis for some function space of interest, hence the name. Sums of radial basis functions are typically used to approximate given functions. This approximation process can also be interpreted as a simple kind of neural network; this was the context in which they were originally applied to machine learning, in work by David Broomhead and David Low ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Real-valued Function
In mathematics, a real-valued function is a function whose values are real numbers. In other words, it is a function that assigns a real number to each member of its domain. Real-valued functions of a real variable (commonly called ''real functions'') and real-valued functions of several real variables are the main object of study of calculus and, more generally, real analysis. In particular, many function spaces consist of real-valued functions. Algebraic structure Let (X,) be the set of all functions from a set to real numbers \mathbb R. Because \mathbb R is a field, (X,) may be turned into a vector space and a commutative algebra over the reals with the following operations: *f+g: x \mapsto f(x) + g(x) – vector addition *\mathbf: x \mapsto 0 – additive identity *c f: x \mapsto c f(x),\quad c \in \mathbb R – scalar multiplication *f g: x \mapsto f(x)g(x) – pointwise multiplication These operations extend to partial functions from to \mathbb R, with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norm (mathematics)
In mathematics, a norm is a function (mathematics), function from a real or complex vector space to the non-negative real numbers that behaves in certain ways like the distance from the Origin (mathematics), origin: it Equivariant map, commutes with scaling, obeys a form of the triangle inequality, and zero is only at the origin. In particular, the Euclidean distance in a Euclidean space is defined by a norm on the associated Euclidean vector space, called the #Euclidean norm, Euclidean norm, the #p-norm, 2-norm, or, sometimes, the magnitude or length of the vector. This norm can be defined as the square root of the inner product of a vector with itself. A seminorm satisfies the first two properties of a norm but may be zero for vectors other than the origin. A vector space with a specified norm is called a normed vector space. In a similar manner, a vector space with a seminorm is called a ''seminormed vector space''. The term pseudonorm has been used for several related meaning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thin Plate Spline
Thin plate splines (TPS) are a spline-based technique for data interpolation and smoothing. They were introduced to geometric design by Duchon. They are an important special case of a polyharmonic spline. Robust Point Matching (RPM) is a common extension and shortly known as the TPS-RPM algorithm. Physical analogy The name ''thin plate spline'' refers to a physical analogy involving the bending of a plate or thin sheet of metal. Just as the metal has rigidity, the TPS fit resists bending also, implying a penalty involving the smoothness of the fitted surface. In the physical setting, the deflection is in the z direction, orthogonal to the plane. In order to apply this idea to the problem of coordinate transformation, one interprets the lifting of the plate as a displacement of the x or y coordinates within the plane. In 2D cases, given a set of K corresponding control points (knots), the TPS warp is described by 2(K+3) parameters which include 6 global affine motion parameters a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyharmonic Spline
In applied mathematics, polyharmonic splines are used for function approximation and data interpolation. They are very useful for interpolating and fitting scattered data in many dimensions. Special cases include thin plate splines and natural cubic splines in one dimension. Definition A polyharmonic spline is a linear combination of polyharmonic radial basis functions (RBFs) denoted by \varphi plus a polynomial term: where * \mathbf = _1 \ x_2 \ \cdots \ x_ (\textrm denotes matrix transpose, meaning \mathbf is a column vector) is a real-valued vector of d independent variables, * \mathbf_i = _ \ c_ \ \cdots \ c_ are N vectors of the same size as \mathbf (often called centers) that the curve or surface must interpolate, * \mathbf = _1 \ w_2 \ \cdots \ w_N are the N weights of the RBFs, * \mathbf = _1 \ v_2 \ \cdots \ v_ are the d+1 weights of the polynomial. The polynomial with the coefficients \mathbf improves fitting accuracy for polyharmonic smoothing splines and al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inverse Multiquadric
Inverse or invert may refer to: Science and mathematics * Inverse (logic), a type of conditional sentence which is an immediate inference made from another conditional sentence * Additive inverse, the inverse of a number that, when added to the original number, yields zero * Compositional inverse, a function that "reverses" another function * Inverse element * Inverse function, a function that "reverses" another function **Generalized inverse, a matrix that has some properties of the inverse matrix but not necessarily all of them * Multiplicative inverse (reciprocal), a number which when multiplied by a given number yields the multiplicative identity, 1 ** Inverse matrix of an Invertible matrix Other uses * Invert level, the base interior level of a pipe, trench or tunnel * ''Inverse'' (website), an online magazine * An outdated term for an LGBT person; see Sexual inversion (sexology) See also * Inversion (other) * Inverter (other) * Opposite (disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bump Function Shape
Bump or bumps may refer to: Arts and entertainment * Bump (dance), a dance from the 1970s disco era * ''BUMP'' (comics), 2007-08 limited edition comic book series Fictional characters * Bobby Bumps, titular character of a series of American silent animated short films produced (1915–1925) * Bump (''Transformers''), a fictional character in the ''Transformers'' universe * Mr. Bump, a ''Mr. Men'' character Music * "The Bump", a funky song by the Commodores from '' Machine Gun''(1974) * "The Bump", a 1974 hit single by the band Kenny * ''Bump'' (album), a jazz album recorded by musician John Scofield in 2000 * "Bump", a song by Raven-Symoné from '' This Is My Time'' * "Bump", a song by Fun Lovin' Criminals from '' Loco'' * "Bump", a song by Spank Rock from '' YoYoYoYoYo'' * "Bump", a song by Rehab from '' Graffiti the World'' * "Bump", a song by Baby Blue from ''No Smoke Without Fire'' * "Bump", a song by Brockhampton from '' Saturation'' * "Bump", a 2006 song by Spank Rock ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaussian Function Shape Parameter
Carl Friedrich Gauss (1777–1855) is the eponym of all of the topics listed below. There are over 100 topics all named after this German mathematician and scientist, all in the fields of mathematics, physics, and astronomy. The English eponymous adjective ''Gaussian'' is pronounced . Mathematics Algebra and linear algebra Geometry and differential geometry Number theory Cyclotomic fields *Gaussian period *Gaussian rational *Gauss sum, an exponential sum over Dirichlet characters ** Elliptic Gauss sum, an analog of a Gauss sum ** Quadratic Gauss sum Analysis, numerical analysis, vector calculus and calculus of variations Complex analysis and convex analysis * Gauss–Lucas theorem * Gauss's continued fraction, an analytic continued fraction derived from the hypergeometric functions * Gauss's criterion – described oEncyclopedia of Mathematics* Gauss's hypergeometric theorem, an identity on hypergeometric series * Gauss plane Statistics * Gauss–Ku ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
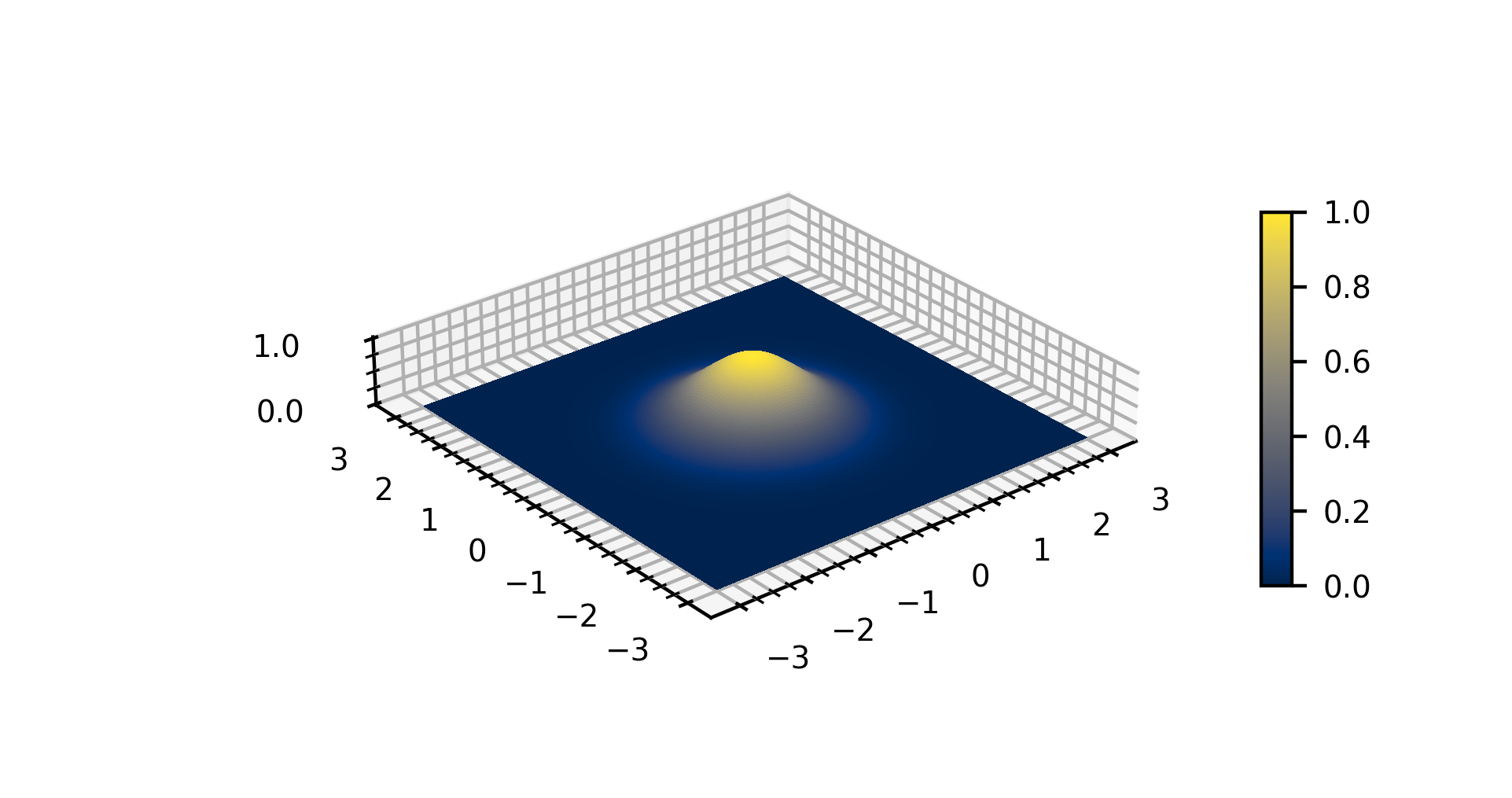
Gaussian Function
In mathematics, a Gaussian function, often simply referred to as a Gaussian, is a function (mathematics), function of the base form f(x) = \exp (-x^2) and with parametric extension f(x) = a \exp\left( -\frac \right) for arbitrary real number, real constants , and non-zero . It is named after the mathematician Carl Friedrich Gauss. The graph of a function, graph of a Gaussian is a characteristic symmetric "Normal distribution, bell curve" shape. The parameter is the height of the curve's peak, is the position of the center of the peak, and (the standard deviation, sometimes called the Gaussian Root mean square, RMS width) controls the width of the "bell". Gaussian functions are often used to represent the probability density function of a normal distribution, normally distributed random variable with expected value and variance . In this case, the Gaussian is of the form g(x) = \frac \exp\left( -\frac \frac \right). Gaussian functions are widely used in statistics to describ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positive-definite Function
In mathematics, a positive-definite function is, depending on the context, either of two types of function. Definition 1 Let \mathbb be the set of real numbers and \mathbb be the set of complex numbers. A function f: \mathbb \to \mathbb is called ''positive semi-definite'' if for all real numbers ''x''1, …, ''x''''n'' the ''n'' × ''n'' matrix : A = \left(a_\right)_^n~, \quad a_ = f(x_i - x_j) is a positive ''semi-''definite matrix. By definition, a positive semi-definite matrix, such as A, is Hermitian; therefore ''f''(−''x'') is the complex conjugate of ''f''(''x'')). In particular, it is necessary (but not sufficient) that : f(0) \geq 0~, \quad , f(x), \leq f(0) (these inequalities follow from the condition for ''n'' = 1, 2.) A function is ''negative semi-definite'' if the inequality is reversed. A function is ''definite'' if the weak inequality is replaced with a strong ( 0). Examples If (X, \langle \cdot, \cdot \rangle) is a real inner prod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shape Parameter
In probability theory and statistics, a shape parameter (also known as form parameter) is a kind of numerical parameter of a parametric family of probability distributionsEveritt B.S. (2002) Cambridge Dictionary of Statistics. 2nd Edition. CUP. that is neither a location parameter nor a scale parameter (nor a function of these, such as a rate parameter). Such a parameter must affect the ''shape (geometry), shape'' of a distribution rather than simply shifting it (as a location parameter does) or stretching/shrinking it (as a scale parameter does). For example, "peakedness" refers to how round the main peak is. Estimation Many estimators measure location or scale; however, estimators for shape parameters also exist. Most simply, they can be estimated in terms of the higher moment (mathematics), moments, using the Method of moments (statistics), method of moments, as in the ''skewness'' (3rd moment) or ''kurtosis'' (4th moment), if the higher moments are defined and finite. Estimato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Singular Matrix
A singular matrix is a square matrix that is not invertible, unlike non-singular matrix which is invertible. Equivalently, an n-by-n matrix A is singular if and only if determinant, det(A)=0. In classical linear algebra, a matrix is called ''non-singular'' (or invertible) when it has an inverse; by definition, a matrix that fails this criterion is singular. In more algebraic terms, an n-by-n matrix A is singular exactly when its columns (and rows) are linearly dependent, so that the linear map x\rightarrow Ax is not one-to-one. In this case the kernel ( null space) of A is non-trivial (has dimension ≥1), and the homogeneous system Ax = 0 admits non-zero solutions. These characterizations follow from standard rank-nullity and invertibility theorems: for a square matrix A, det(A) \neq 0 if and only if rank(A)= n, and det(A) = 0 if and only if rank(A)3 then it is a singular matrix. * Numerical noise/ Round off: In numerical computations, a matrix may be nearly singular when its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |