|
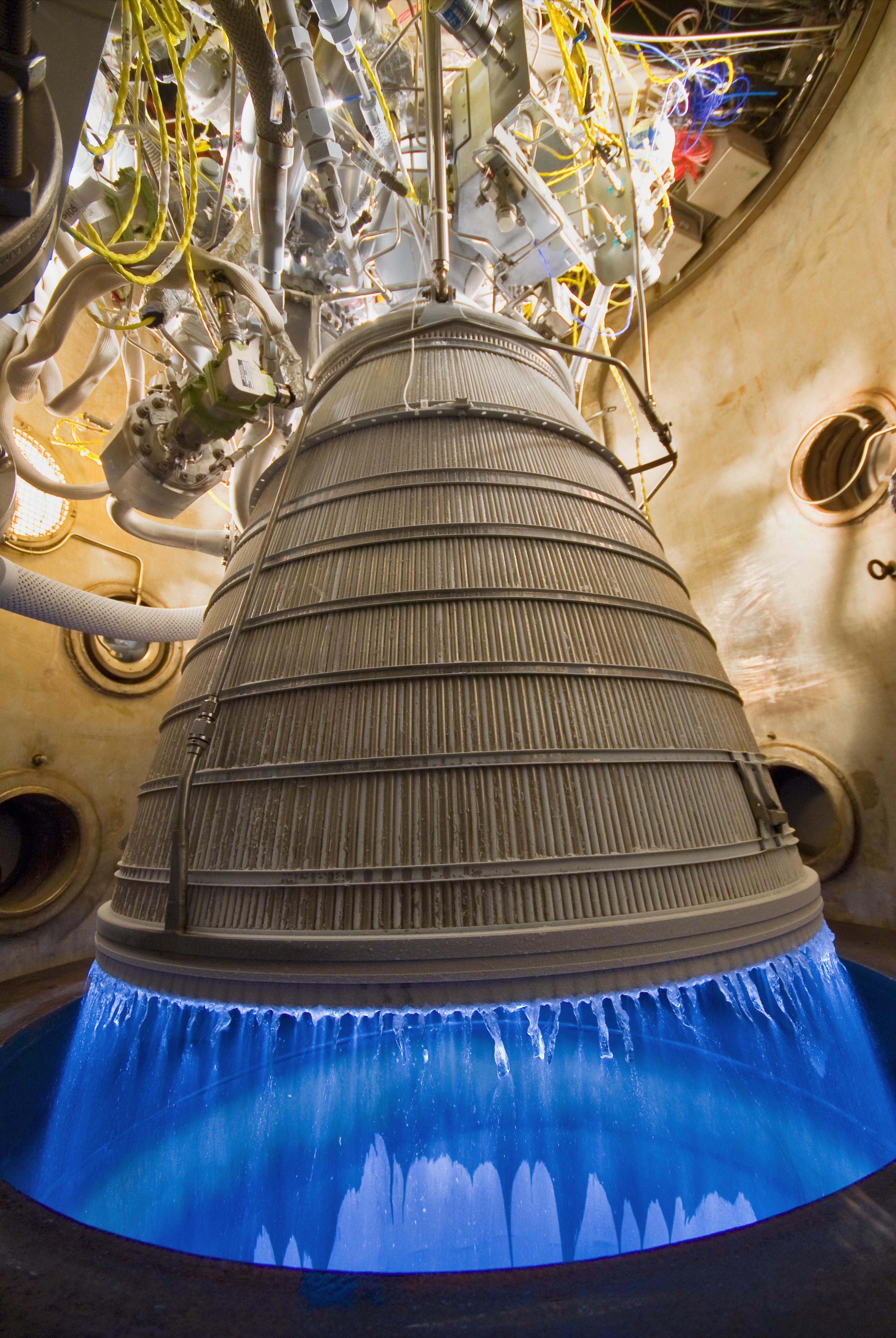
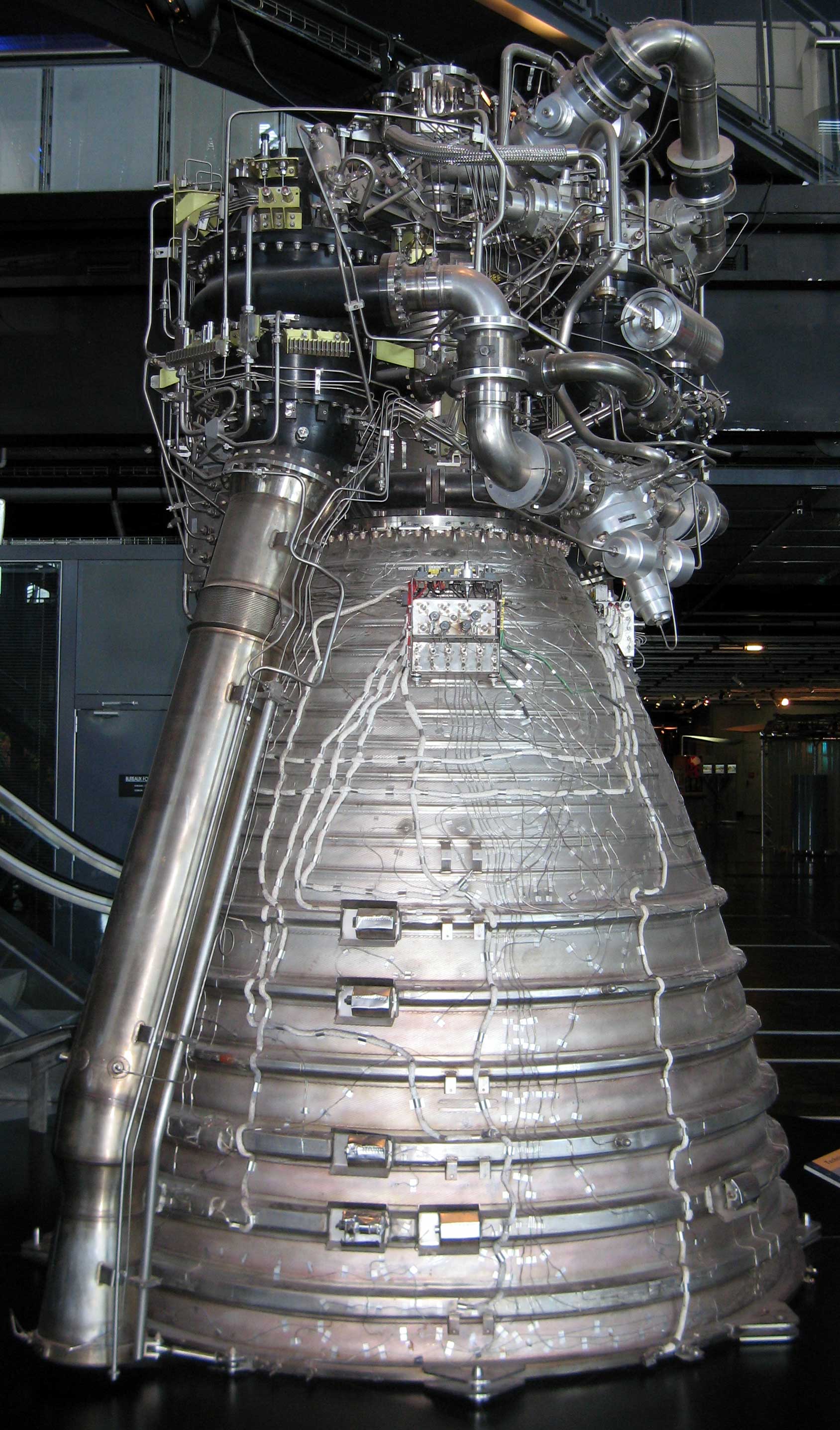
RL-10
The RL10 is a liquid-fuel cryogenic rocket engine built in the United States by Aerojet Rocketdyne that burns cryogenic liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen propellants. Modern versions produce up to of thrust per engine in vacuum. RL10 versions were produced for the Centaur upper stage of the Atlas V and the DCSS of the Delta IV. More versions are in development or in use for the Exploration Upper Stage of the Space Launch System and the Centaur V of the Vulcan rocket. The expander cycle that the engine uses drives the turbopump with waste heat absorbed by the engine combustion chamber, throat, and nozzle. This, combined with the hydrogen fuel, leads to very high specific impulses (''I''sp) in the range of in a vacuum. Mass ranges from depending on the version of the engine. History The RL10 was the first liquid hydrogen rocket engine to be built in the United States, with development of the engine by Marshall Space Flight Center and Pratt & Whitney beginning in the 195 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
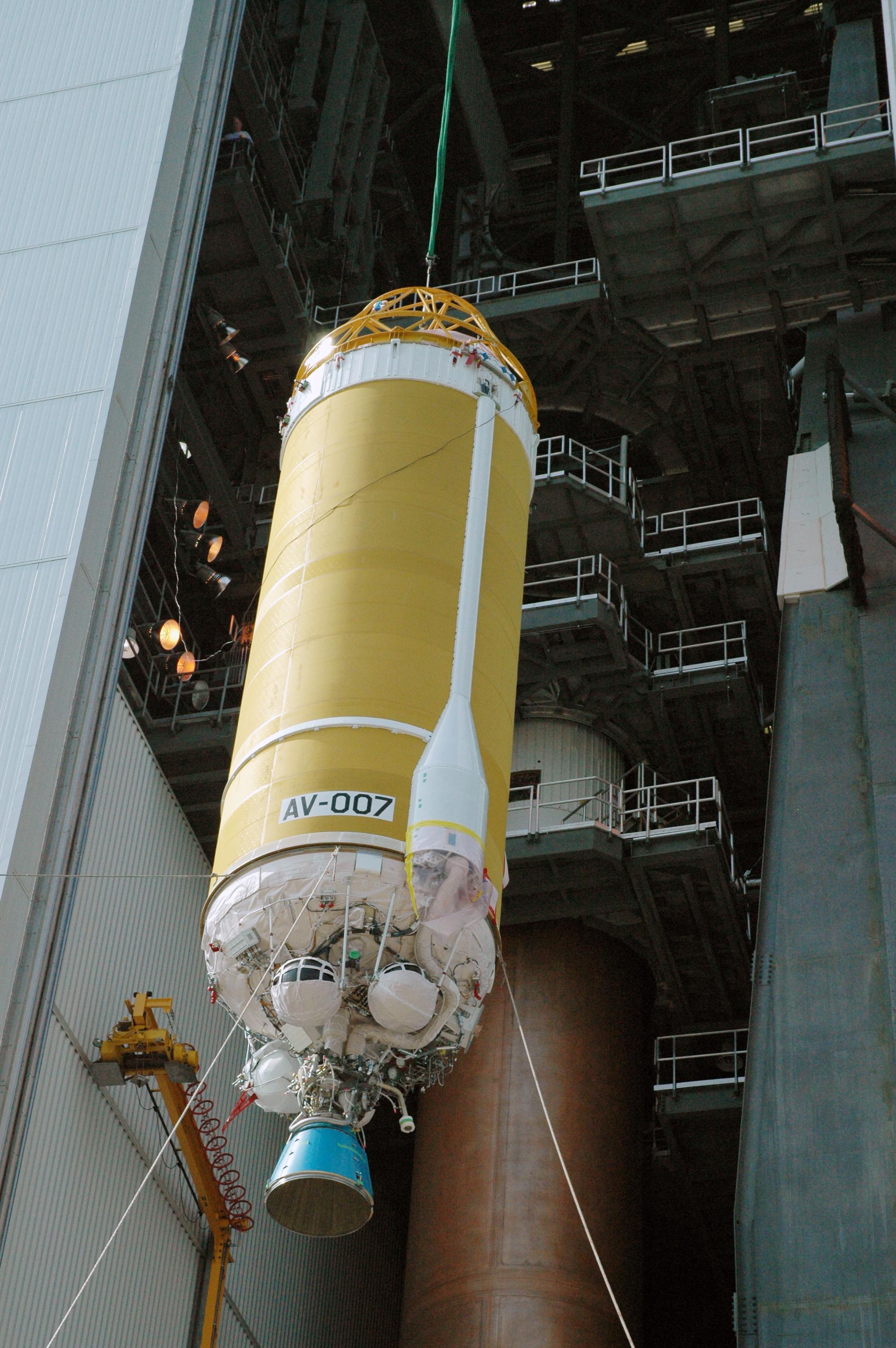
Centaur (rocket Stage)
The Centaur is a family of rocket propelled upper stages that has been in use since 1962. It is currently produced by U.S. launch service provider United Launch Alliance, with one main active version and one version under development. The diameter Common Centaur/Centaur III flies as the upper stage of the Atlas V launch vehicle, and the diameter Centaur V has been developed as the upper stage of ULA's new Vulcan rocket. Centaur was the first rocket stage to use liquid hydrogen (LH2) and liquid oxygen (LOX) propellants, a high-energy combination that is ideal for upper stages but has significant handling difficulties. Characteristics Common Centaur is built around stainless steel pressure stabilized balloon propellant tanks with thick walls. It can lift payloads of up to . The thin walls minimize the mass of the tanks, maximizing the stage's overall performance. A common bulkhead separates the LOX and LH2 tanks, further reducing the tank mass. It is made of two stainless ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryogenic Rocket Engine
A cryogenic rocket engine is a rocket engine that uses a cryogenic fuel and oxidizer; that is, both its fuel and oxidizer are gases which have been liquefied and are stored at very low temperatures. These highly efficient engines were first flown on the US Atlas-Centaur and were one of the main factors of NASA's success in reaching the Moon by the Saturn V rocket. Rocket engines burning cryogenic propellants remain in use today on high performance upper stages and boosters. Upper stages are numerous. Boosters include ESA's Ariane 6, JAXA's H-II, ISRO's GSLV, LVM3, NASA's Space Launch System. The United States, Russia, India, Japan, France and China are the only countries that have operational cryogenic rocket engines. Cryogenic propellants Rocket engines need high mass flow rates of both oxidizer and fuel to generate useful thrust. Oxygen, the simplest and most common oxidizer, is in the gas phase at standard temperature and pressure, as is hydrogen, the simplest f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S-IV
The S-IV was the Multistage rocket, second stage of the Saturn I rocket used by NASA for early flights in the Apollo program. The S-IV was manufactured by the Douglas Aircraft Company and later modified by them to the S-IVB, a similar but distinct stage used on the Saturn IB and Saturn V rockets. The S-IV stage was a large LOX/LH2-fueled rocket stage used for the early test flights of the Saturn I rocket. It formed the second stage of the Saturn I and was powered by a cluster of six RL10, RL-10A-3 engines. Each one of the engines supplied of thrust for a total of about . The cryogenic LH2 (liquid hydrogen) and LOX (liquid oxygen) tanks were separated by a common bulkhead. The forward bulkhead of the LOX tank formed the aft bulkhead of the LH2 tank. This saved up to 20% of structural weight. Flight history References * * {{Upper stages Apollo program Rocket stages Saturn I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delta IV
Delta IV was a group of five expendable launch systems in the Delta rocket family. It flew 45 missions from 2002 to 2024. Originally designed by Boeing's Defense, Space and Security division for the Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle (EELV) program, the Delta IV became a United Launch Alliance (ULA) product in 2006. The Delta IV was primarily a launch vehicle for United States Air Force (USAF) military payloads, but was also used to launch a number of United States government non-military payloads and a single commercial satellite. The Delta IV had two main versions which allowed the family to cover a range of payload sizes and masses: the Medium (which had four configurations) and Heavy. The final flight of Medium occurred in 2019. The final flight of Heavy was in April 2024. Delta IV vehicles were built in the ULA facility in Decatur, Alabama. Final assembly was completed at the launch site by ULA: at the horizontal integration facility for launches from SLC-37B pad at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
McDonnell Douglas DC-X
The DC-X, short for Delta Clipper or Delta Clipper Experimental, was an uncrewed prototype of a reusable single-stage-to-orbit launch vehicle built by McDonnell Douglas in conjunction with the United States Department of Defense's Strategic Defense Initiative Organization (SDIO) from 1991 to 1993. Starting 1994 until 1995, testing continued through funding of the US civil space agency NASA. In 1996, the DC-X technology was completely transferred to NASA, which upgraded the design for improved performance to create the DC-XA. After a test flight of DC-XA in 1996 resulted in a fire, the project was canceled. Despite its cancellation, the program inspired later reusable launch systems. Michael D. Griffin has since praised the program as "government R&D at its finest." Background According to writer Jerry Pournelle: "DC-X was conceived in my living room and sold to National Space Council Chairman Dan Quayle by General Graham, Max Hunter and me." According to Max Hunter, howev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlas V
Atlas V is an expendable launch system and the fifth major version in the Atlas (rocket family), Atlas launch vehicle family. It was developed by Lockheed Martin and has been operated by United Launch Alliance (ULA) since 2006. Primarily used to launch payloads for the United States Department of Defense, NASA, and commercial customers, Atlas V is the longest-serving active rocket in the United States. Each Atlas V vehicle consists of two main stages. The First stage (rocketry), first stage is powered by a single Russian-made RD-180 engine that burns kerosene and liquid oxygen. The Centaur (rocket stage), Centaur upper stage uses one or two American-made Aerojet Rocketdyne RL10 engines that burn liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen. Strap-on booster, Strap-on Solid rocket booster, solid rocket boosters (SRBs) are used in several configurations. Originally equipped with AJ-60A SRBs, the vehicle switched to Graphite-Epoxy Motor (GEM 63) boosters beginning in November 2020, except for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerojet Rocketdyne
Aerojet Rocketdyne is a subsidiary of American Arms industry, defense company L3Harris that manufactures rocket, Hypersonic flight, hypersonic, and electric propulsive systems for space, defense, civil and commercial applications. Aerojet traces its origins to the General Tire and Rubber Company (later renamed GenCorp, Inc. as it diversified) established in 1915, while Rocketdyne was created as a division of North American Aviation in 1955. Aerojet Rocketdyne was formed in 2013 when Aerojet and Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne were merged, following the latter's acquisition by GenCorp, Inc. from Pratt & Whitney. Aerojet Rocketdyne was acquired by L3Harris in July 2023 for $4.7 billion. History Background: Aerojet Several decades after it began manufacturing rubber products, General Tire & Rubber diversified into broadcasting and aeronautics. In the 1940s, the Aerojet company began experimenting with various rocket designs. For a solid-fuel rocket, they needed binders, and tur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delta III
Delta III was an expendable launch vehicle made by McDonnell Douglas (later acquired by Boeing). Development was canceled before the vehicle became operational. The vehicle is the third generation of the Delta rocket family, developed from the highly successful Delta II to help meet the launch demand of larger satellites. While the Delta III never had a successful launch, some of the technologies developed were used in its successor, the Delta IV. The Delta III was the first to use the Delta Cryogenic Second Stage, which was designed by the National Space Development Agency of Japan based on the second stage it developed for the H-IIA rocket and built by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries. Contraves built the fairing and payload adapters based on designs it used on the Ariane 4. The first Delta III launch was on August 26, 1998. Of its three flights, the first two were failures, and the third, though declared successful, reached the low end of its targeted orbit range and carried o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saturn I
The Saturn I was a rocket designed as the United States' first medium lift launch vehicle for up to low Earth orbit Payload (air and space craft), payloads.Terminology has changed since the 1960s; back then, 20,000 pounds was considered "heavy lift". Its development was taken over from the Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) in 1958 by the newly formed civilian NASA. Its design proved sound and flexible. It was successful in initiating the development of liquid hydrogen-fueled rocket propulsion, launching the Pegasus satellite program, Pegasus satellites, and flight verification of the Apollo command and service module launch phase aerodynamics. Ten Saturn I rockets were flown before it was replaced by the heavy lift launch vehicle, heavy lift derivative Saturn IB, which used a larger, higher impulse (physics), total impulse second stage and an improved Saturn V instrument unit, guidance and control system. It also led the way to development of the super heavy-lift launch veh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Launch System
The Space Launch System (SLS) is an American Super heavy-lift launch vehicle, super heavy-lift Expendable launch system, expendable launch vehicle used by NASA. As the primary launch vehicle of the Artemis program, Artemis Moon landing program, SLS is designed to launch the crewed Orion (spacecraft), Orion spacecraft on a trans-lunar trajectory. The first (and so far only) SLS launch was the uncrewed Artemis I, which took place on 16 November 2022. Development of SLS began in 2011 as a replacement for the retiring Space Shuttle as well as the canceled Ares I and Ares V launch vehicles. SLS was built using existing Shuttle technology, including Space Shuttle Solid Rocket Booster, solid rocket boosters and RS-25 engines. The rocket has been criticized for its political motivations, seen as a way to preserve jobs and contracts for aerospace companies involved in the Shuttle program at great expense to NASA. The project has faced significant challenges, including mismanagemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exploration Upper Stage
The Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) is a rocket stage under development for future flights of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS). Designed for use on the SLS Block 1B and Block 2 configurations, it will replace the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage used on the Block 1 variant. The EUS will be powered by four RL10C-3 engines burning liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen, generating a total thrust of . Its first flight is planned for Artemis IV in 2028. However, the Trump administration has proposed terminating the SLS program after Artemis III, which would eliminate the need for the EUS. Development The Block 1 configuration of the SLS, which first flew the Artemis I mission, has a core stage powered by four RS-25 engines, two Space Shuttle-derived five-segment solid rocket boosters, and an Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage (ICPS) upper stage. NASA is developing the EUS to increase SLS performance for trans-lunar injection beyond Block 1 specifications. The improved up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid Oxygen
Liquid oxygen, sometimes abbreviated as LOX or LOXygen, is a clear cyan liquid form of dioxygen . It was used as the oxidizer in the first liquid-fueled rocket invented in 1926 by Robert H. Goddard, an application which is ongoing. Physical properties Liquid oxygen has a clear cyan color and is strongly paramagnetic: it can be suspended between the poles of a powerful horseshoe magnet. Liquid oxygen has a density of , slightly denser than liquid water, and is cryogenic with a freezing point of and a boiling point of at . Liquid oxygen has an expansion ratio of 1:861 and because of this, it is used in some commercial and military aircraft as a transportable source of breathing oxygen. Because of its cryogenic nature, liquid oxygen can cause the materials it touches to become extremely brittle. Liquid oxygen is also a very powerful oxidizing agent: organic materials will burn rapidly and energetically in liquid oxygen. Further, if soaked in liquid oxygen, some materials su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |