|
Pliska Ridge
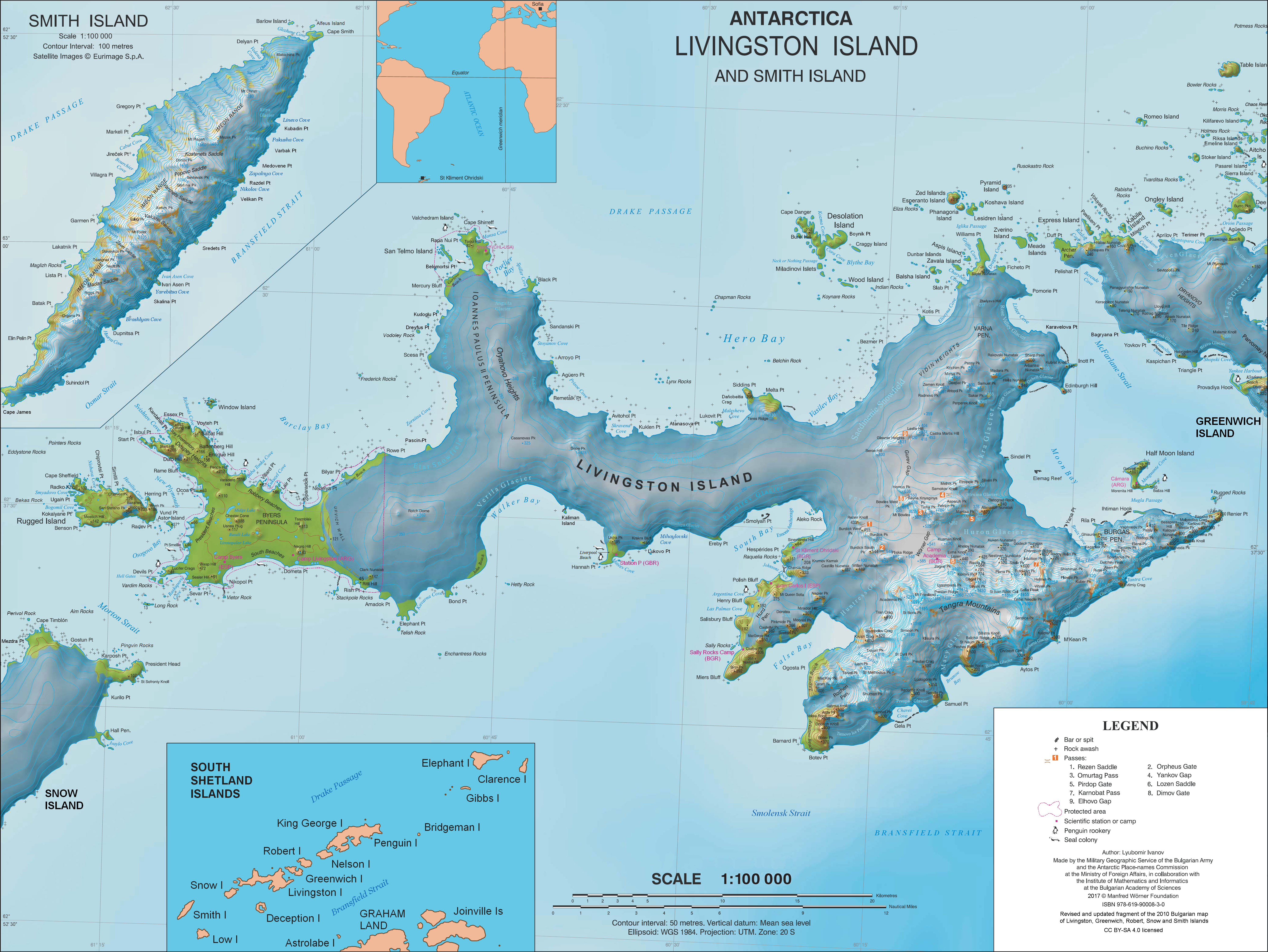
Pliska Ridge ( bg, връх Плиска, vrah Pliska, ) is a three-peaked ridge rising to 667 m in eastern Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. Its central and highest summit, ''Pliska Peak'', is located 2.48 km east-northeast of Willan Nunatak (449 m), 1.81 km southeast of Burdick Peak (773 m, summit of Burdick Ridge), 3.53 km south-southwest of Mount Bowles, 3.68 km west-southwest of Kuzman Knoll, and 3.61 km northwest of Mount Friesland. The feature is 1.6 km long and 500 m wide, its axis trending due east-west, with precipitous southern slopes. It is ice-covered except for segments of its easternmost peak (646 m) and is bounded to the northwest by Orpheus Gate, to the north by the head of Perunika Glacier, to the east by Nesebar Gap, and to the south and west by the head of Huntress Glacier, the latter flowing 6 km southwestwards into False Bay. First ascent by the Bulgarian Lyubomir Ivanov from Camp Academia on 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huntress Glacier
Huntress Glacier is a glacier long and wide flowing into the head of False Bay (Livingston Island), False Bay, Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. It is situated east of Johnsons Glacier, southeast of Contell Glacier and Balkan Snowfield, south of upper Perunika Glacier, southwest of Huron Glacier and northwest of Macy Glacier, and is bounded by Friesland Ridge and the Tangra Mountains to the southeast, Nesebar Gap, Pliska Ridge, Burdick Ridge and Willan Nunatak to the north, and Charrúa Gap and Napier Peak to the northwest. The glacier was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1958 after the US, American schooner ''Huntress'' (Captain Christopher Burdick) from Nantucket, which visited the South Shetland Islands in 1820–21 in company with the ''Huron'' of New Haven, Connecticut. Location The glacier's midpoint is located at (British mapping in 1968, and Bulgarian in 2005 and 2009). See also * List of glaciers in the Antarctic * Glacio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctic Place-names Commission
The Antarctic Place-names Commission was established by the Bulgarian Antarctic Institute in 1994, and since 2001 has been a body affiliated with the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Bulgaria. The Commission approves Bulgarian place names in Antarctica, which are formally given by the President of the Republic according to the Bulgarian Constitution (Art. 98) and the established international practice. Bulgarian names in Antarctica Geographical names in Antarctica reflect the history and practice of Antarctic exploration. The nations involved in Antarctic research give new names to nameless geographical features for the purposes of orientation, logistics, and international scientific cooperation. As of 2021, there are some 20,091 named Antarctic geographical features, including 1,601 features with names given by Bulgaria.Bulgarian Antarctic Gazett ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Composite Antarctic Gazetteer
The Composite Gazetteer of Antarctica (CGA) of the Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR) is the authoritative international gazetteer containing all Antarctic toponyms published in national gazetteers, plus basic information about those names and the relevant geographical features. The Gazetteer includes also parts of the International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) General Bathymetric Chart of the Oceans (GEBCO) gazetteer for under-sea features situated south of 60° south latitude. , the overall content of the CGA amounts to 37,893 geographic names for 19,803 features including some 500 features with two or more entirely different names, contributed by the following sources: {, class="wikitable sortable" ! Country ! Names , - , United States , 13,192 , - , United Kingdom , 5,040 , - , Russia , 4,808 , - , New Zealand , 2,597 , - , Australia , 2,551 , - , Argentina , 2,545 , - , Chile , 1,866 , - , Norway , 1,706 , - , Bulgaria , 1,450 , - , G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Bulgarian Empire
The First Bulgarian Empire ( cu, блъгарьско цѣсарьствиѥ, blagarysko tsesarystviye; bg, Първо българско царство) was a medieval Bulgar- Slavic and later Bulgarian state that existed in Southeastern Europe between the 7th and 11th centuries AD. It was founded in 680–681 after part of the Bulgars, led by Asparuh, moved south to the northeastern Balkans. There they secured Byzantine recognition of their right to settle south of the Danube by defeatingpossibly with the help of local South Slavic tribesthe Byzantine army led by Constantine IV. During the 9th and 10th century, Bulgaria at the height of its power spread from the Danube Bend to the Black Sea and from the Dnieper River to the Adriatic Sea and became an important power in the region competing with the Byzantine Empire. It became the foremost cultural and spiritual centre of south Slavic Europe throughout most of the Middle Ages. As the state solidified its position in the Balka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedonia to the west, Greece and Turkey to the south, and the Black Sea to the east. Bulgaria covers a territory of , and is the sixteenth-largest country in Europe. Sofia is the nation's capital and largest city; other major cities are Plovdiv, Varna and Burgas. One of the earliest societies in the lands of modern-day Bulgaria was the Neolithic Karanovo culture, which dates back to 6,500 BC. In the 6th to 3rd century BC the region was a battleground for ancient Thracians, Persians, Celts and Macedonians; stability came when the Roman Empire conquered the region in AD 45. After the Roman state splintered, tribal invasions in the region resumed. Around the 6th century, these territories were settled by the early Slavs. The Bulgars, led by Asp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliska
Pliska ( , cu, Пльсковъ, translit=Plĭskovŭ) was the first capital of the First Bulgarian Empire during the Middle Ages and is now a small town in Shumen Province, on the Ludogorie plateau of the Danubian Plain, 20 km northeast of the provincial capital, Shumen. Pliska was the first capital of Bulgaria, and according to legend founded by Asparuh of Bulgaria in the late 7th century; this legend is archaeologically unsubstantiated. The site was originally an encampment, with the first tent-shaped buildings at Pliska of uncertain date. No evidence exists of a settlement before the 9th century, and claims that the site dates from Late Antiquity have been contested. By the early 9th century, Pliska was surrounded by a defensive wall and of land was further enclosed by an outer earthwork with stone revetment long. After the Byzantine army sacked and burned Pliska in 811, led by the emperor Nikephoros I (), Pliska was rebuilt by Omurtag (), who used ''spolia'' from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camp Academia
Camp Academia ( bg, лагер Академия, lager Akademiya, ) is a geographical locality in eastern Livingston Island, South Shetland Islands, Antarctica, named for the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences in appreciation of Academy’s contribution to the Antarctic exploration. The site was first occupied in the 2004/05 austral summer, and has been designated since 2004 as the summer post office Tangra 1091, the southernmost branch of the Bulgarian Posts Plc. Access and survey routes Camp Academia is strategically situated in upper Huron Glacier, Wörner Gap area, at elevation 541 m in the northwestern foothills of Zograf Peak, central Tangra Mountains. The site is accessible by 11-12.5 km routes from the Bulgarian base St. Kliment Ohridski and the Spanish base Juan Carlos I respectively. Camp Academia offers convenient overland access to the main range of Tangra Mountains to the south (with survey and climbing routes leading from Camp Academia to Lyaskovets Peak and Mou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lyubomir Ivanov (explorer)
Lyubomir Ivanov ( bg, Любомир Иванов, born 7 October 1952 in Sofia) is a Bulgarian scientist, non-governmental activist, and Antarctic explorer. He is a graduate of the St. Kliment Ohridski University of Sofia with M.S. degree in mathematics in 1977, earned his PhD from Sofia University in 1980 under the direction of Dimiter Skordev, with a dissertation entitled ''Iterative Operative Spaces'', and was the 1987 winner of ''Acad. Nikola Obreshkov Prize'', the highest Bulgarian award in mathematics. Academic and NGO work Appointed head of the Department of Mathematical Logic at the Institute of Mathematics and Informatics, Bulgarian Academy of Sciences in 1990, Dr Ivanov has since helped found the Atlantic Club of Bulgaria, in which he held the position of chairman from 2001 to 2009. In 1994 he founded the Manfred Wörner Foundation, an organisation dedicated to trans-atlantic co-operation. Member of the Streit Council Advisory Board, Washington, DC since 2006. Fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |