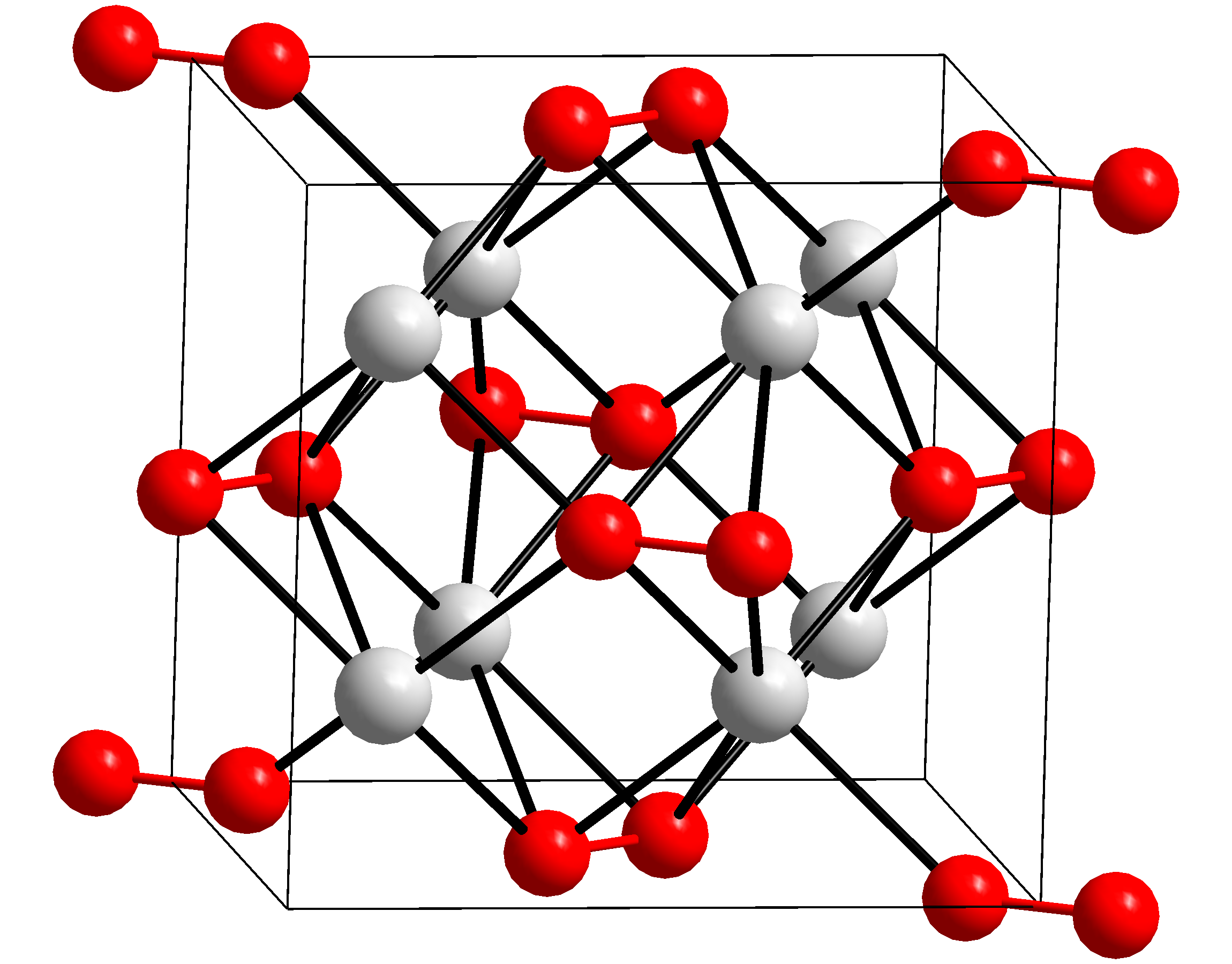
|
Potassium Peroxide
Potassium peroxide is an inorganic compound with the molecular formula K2O2. It is formed as potassium reacts with oxygen in the air, along with potassium oxide (K2O) and potassium superoxide (KO2). Potassium peroxide reacts with water to form potassium hydroxide and oxygen: : Properties Potassium peroxide is a highly reactive, oxidizing white to yellowish solid which, while not flammable itself, reacts violently with flammable materials. It decomposes violently on contact with water. The standard enthalpy of formation of potassium peroxide is ΔH f 0 = −496 kJ/mol. Usage Potassium peroxide is used as an oxidizing agent and bleach (due to the peroxide In chemistry, peroxides are a group of Chemical compound, compounds with the structure , where the R's represent a radical (a portion of a complete molecule; not necessarily a free radical) and O's are single oxygen atoms. Oxygen atoms are joined ...), and to purify air. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Potassium Peroxid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthorhombic
In crystallography, the orthorhombic crystal system is one of the 7 crystal systems. Orthorhombic Lattice (group), lattices result from stretching a cubic crystal system, cubic lattice along two of its orthogonal pairs by two different factors, resulting in a rectangular Prism (geometry), prism with a rectangular Base (geometry), base (''a'' by ''b'') and height (''c''), such that ''a'', ''b'', and ''c'' are distinct. All three bases intersect at 90° angles, so the three lattice vectors remain mutually orthogonal. Bravais lattices There are four orthorhombic Bravais lattices: primitive orthorhombic, base-centered orthorhombic, body-centered orthorhombic, and face-centered orthorhombic. For the base-centered orthorhombic lattice, the primitive cell has the shape of a right rhombic prism;See , row oC, column Primitive, where the cell parameters are given as a1 = a2, α = β = 90° it can be constructed because the two-dimensional centered rectangular base layer can also be descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Formula
A chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as parentheses, dashes, brackets, commas and ''plus'' (+) and ''minus'' (−) signs. These are limited to a single typographic line of symbols, which may include subscripts and superscripts. A chemical formula is not a chemical name since it does not contain any words. Although a chemical formula may imply certain simple chemical structures, it is not the same as a full chemical structural formula. Chemical formulae can fully specify the structure of only the simplest of molecules and chemical substances, and are generally more limited in power than chemical names and structural formulae. The simplest types of chemical formulae are called '' empirical formulae'', which use letters and numbers indicating the numerical ''proportions'' of atoms of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peroxides
In chemistry, peroxides are a group of compounds with the structure , where the R's represent a radical (a portion of a complete molecule; not necessarily a free radical) and O's are single oxygen atoms. Oxygen atoms are joined to each other and to adjacent elements through single covalent bonds, denoted by dashes or lines. The group in a peroxide is often called the peroxide group, though some nomenclature discrepancies exist. This linkage is recognized as a common polyatomic ion, and exists in many molecules. General structure The characteristic structure of any regular peroxide is the oxygen–oxygen covalent single bond, which connects the two main atoms together. In the event that the molecule has no chemical substituents, the peroxide group will have a ��2 net charge. Each oxygen atom has a charge of negative one, as 5 of its valence electrons remain in the outermost orbital shell whilst one is occupied in the covalent bond. Because of the nature of the covalent bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peroxide
In chemistry, peroxides are a group of Chemical compound, compounds with the structure , where the R's represent a radical (a portion of a complete molecule; not necessarily a free radical) and O's are single oxygen atoms. Oxygen atoms are joined to each other and to adjacent elements through Single bond, single covalent bonds, denoted by dashes or lines. The group in a peroxide is often called the peroxide group, though some nomenclature discrepancies exist. This linkage is recognized as a common polyatomic ion, and exists in many molecules. General structure The characteristic structure of any regular peroxide is the oxygen–oxygen covalent single bond, which connects the two main atoms together. In the event that the molecule has no chemical Substituent, substituents, the peroxide group will have a [−2] Formal charge, net charge. Each oxygen atom has a charge of negative one, as 5 of its Valence electron, valence electrons remain in the outermost Atomic orbital, orbital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium
Potassium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol K (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number19. It is a silvery white metal that is soft enough to easily cut with a knife. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmospheric oxygen to form flaky white potassium peroxide in only seconds of exposure. It was first isolated from potash, the ashes of plants, from which its name derives. In the periodic table, potassium is one of the alkali metals, all of which have a single valence electron in the outer electron shell, which is easily removed to create cation, an ion with a positive charge (which combines with anions to form salts). In nature, potassium occurs only in ionic salts. Elemental potassium reacts vigorously with water, generating sufficient heat to ignite hydrogen emitted in the reaction, and burning with a lilac-flame color, colored flame. It is found dissolved in seawater (which is 0.04% potassium by weight), and occurs in many minerals such as orthoclase, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal, and a potent oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well as with other chemical compound, compounds. Oxygen is abundance of elements in Earth's crust, the most abundant element in Earth's crust, making up almost half of the Earth's crust in the form of various oxides such as water, carbon dioxide, iron oxides and silicates.Atkins, P.; Jones, L.; Laverman, L. (2016).''Chemical Principles'', 7th edition. Freeman. It is abundance of chemical elements, the third-most abundant element in the universe after hydrogen and helium. At standard temperature and pressure, two oxygen atoms will chemical bond, bind covalent bond, covalently to form dioxygen, a colorless and odorless diatomic gas with the chemical formula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium Hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula K OH, and is commonly called caustic potash. Along with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), KOH is a prototypical strong base. It has many industrial and niche applications, most of which utilize its caustic nature and its reactivity toward acids. An estimated 700,000 to 800,000 tonnes were produced in 2005. KOH is noteworthy as the precursor to most soft and liquid soaps, as well as numerous potassium-containing chemicals. It is a white solid that is dangerously corrosive. Properties and structure KOH exhibits high thermal stability. Because of this high stability and relatively low melting point, it is often melt-cast as pellets or rods, forms that have low surface area and convenient handling properties. These pellets become tacky in air because KOH is hygroscopic. Most commercial samples are ca. 90% pure, the remainder being water and carbonates. Its dissolution in water is strongly exothermic. Concentrated aqueous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as a solvent). It is vital for all known forms of life, despite not providing food energy or organic micronutrients. Its chemical formula, , indicates that each of its molecules contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms, connected by covalent bonds. The hydrogen atoms are attached to the oxygen atom at an angle of 104.45°. In liquid form, is also called "water" at standard temperature and pressure. Because Earth's environment is relatively close to water's triple point, water exists on Earth as a solid, a liquid, and a gas. It forms precipitation in the form of rain and aerosols in the form of fog. Clouds consist of suspended droplets of water and ice, its solid state. When finely divided, crystalline ice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium Superoxide
Potassium superoxide is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is a yellow paramagnetic solid that decomposes in moist air. It is a rare example of a stable salt of the superoxide anion. It is used as a scrubber, dehumidifier, and generator in rebreathers, spacecraft, submarines, and spacesuits. Production and reactions Potassium superoxide is produced by burning molten potassium in an atmosphere of excess oxygen. : The salt consists of and ions, linked by ionic bonding. The O–O distance is 1.28 Å. Reactivity Potassium superoxide is a source of superoxide, which is an oxidant and a nucleophile, depending on its reaction partner. Upon contact with water, it undergoes disproportionation to potassium hydroxide, oxygen, and hydrogen peroxide: : : It reacts with carbon dioxide, releasing oxygen: : : Theoretically, 1 kg of absorbs 0.310 kg of while releasing 0.338 kg of . One mole of absorbs 0.5 moles of and releases 0.75 moles of oxygen. Potass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium Oxide
Potassium oxide ( K O) is an ionic compound of potassium and oxygen. It is a base. This pale yellow solid is the simplest oxide of potassium. It is a highly reactive compound that is rarely encountered. Some industrial materials, such as fertilizers and cements, are assayed assuming the percent composition that would be equivalent to K2O. Production Potassium oxide is produced from the reaction of oxygen and potassium; this reaction affords potassium peroxide, K2O2. Treatment of the peroxide with potassium produces the oxide: : Alternatively and more conveniently, K2O is synthesized by heating potassium nitrate with metallic potassium: : Other possibility is to heat potassium peroxide at 500 °C which decomposes at that temperature giving pure potassium oxide and oxygen. : Potassium hydroxide cannot be further dehydrated to the oxide but it can react with molten potassium to produce it, releasing hydrogen as a byproduct. : Properties and reactions K2O crystallises ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inorganic Compound
An inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bondsthat is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as ''inorganic chemistry''. Inorganic compounds comprise most of the Earth's crust, although the compositions of the deep Mantle (geology), mantle remain active areas of investigation. All allotropes (structurally different pure forms of an element) and some simple carbon compounds are often considered inorganic. Examples include the allotropes of carbon (graphite, diamond, buckminsterfullerene, graphene, etc.), carbon monoxide , carbon dioxide , carbides, and salt (chemistry), salts of inorganic anions such as carbonates, cyanides, cyanates, thiocyanates, isothiocyanates, etc. Many of these are normal parts of mostly organic systems, including organisms; describing a chemical as inorganic does not necessarily mean that it cannot occur within life, living things. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |