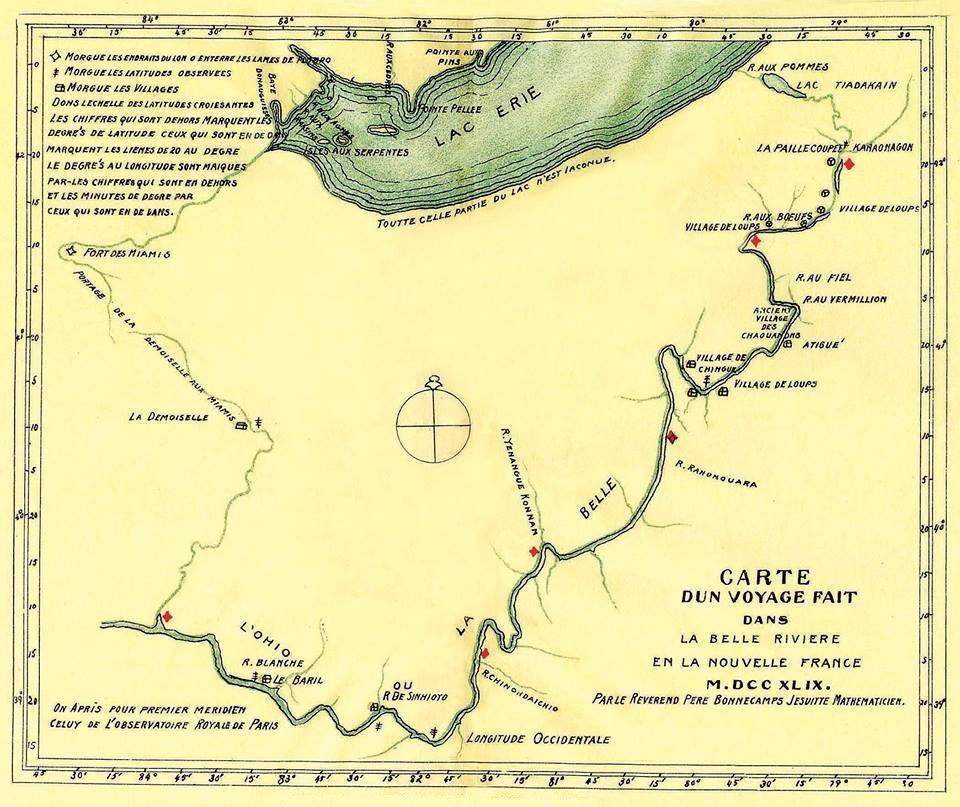
|
Piankeshaw
The Piankeshaw, Piankashaw or Pianguichia were members of the Miami tribe who lived apart from the rest of the Miami nation, therefore they were known as Peeyankihšiaki ("splitting off" from the others, Sing.: ''Peeyankihšia'' - "Piankeshaw Person"). When European settlers arrived in the region in the 1600s, the Piankeshaw lived in an area along the south central Wabash River that now includes western Indiana and Illinois. Their territory was to the north of Kickapoo, Indiana, Kickapoo (around Vincennes, Indiana, Vincennes) and the south of the Wea (centered on Ouiatenon). They were closely allied with the Wea, another group of Miamis. The Piankashaw were living along the Vermilion River (Wabash River tributary), Vermilion River in 1743. History The ''first'' ''Peeyankihšionki'' or ''Piankeshaw Village'' ("Place of the Piankashaw") was at the confluence of the Peeyankihšiaki Siipiiwi ("River of the Peeyankihšiaki/Piankashaw, i.e. Vermilion River") and the Waapaahšiki Siipiiw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Battle Of The Embarras River
During the onset of the Northwest Indian War (1786–1795), there were numerous skirmishes around Vincennes in 1786 between American settlers and Native Americans near Vincennes, Indiana, Vincennes, a frontier town on the Wabash River. American pioneers had been pouring into the area after the American Revolutionary War, creating tensions with the Native inhabitants of the region. On April 15, 1786, American militiamen from Vincennes, responding to an attack on a river boat, attacked Natives along the Embarras River (Illinois), Embarras River; the Americans had three men killed in the skirmish. As hostilities continued, Americans appealed to Virginia Militia officer George Rogers Clark in Kentucky to protect Vincennes from Natives. Meanwhile, Jean Marie Philippe Le Gras, the French civilian commandant at Vincennes, worked to maintain peace between Natives and Americans. He blamed the crisis on indiscriminate American attacks on friendly Natives, and unsuccessfully tried to expel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Miami People
The Miami ( Miami–Illinois: ''Myaamiaki'') are a Native American nation originally speaking the Miami–Illinois language, one of the Algonquian languages. Among the peoples known as the Great Lakes tribes, they occupied territory that is now identified as north-central Indiana, southwest Michigan, and western Ohio. The Miami were historically made up of several prominent subgroups, including the Piankeshaw, Wea, Pepikokia, Kilatika, Mengakonkia, and Atchakangouen. In modern times, Miami is used more specifically to refer to the Atchakangouen. By 1846, most of the Miami had been forcefully displaced to Indian Territory (initially to what is now Kansas, and later to what is now part of Oklahoma). The Miami Tribe of Oklahoma are the federally recognized tribe of Miami Indians in the United States. The Miami Nation of Indiana, a nonprofit organization of self-identified descendants of Miamis who were exempted from removal, have unsuccessfully sought separate recognition. Nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Vincennes, Indiana
Vincennes is a city in, and the county seat of, Knox County, Indiana, United States. It is located on the lower Wabash River in the southwestern part of the state, nearly halfway between Evansville and Terre Haute. It was founded in 1732 by French fur traders, including the namesake François-Marie Bissot, Sieur de Vincennes. It is the oldest continually inhabited European settlement in Indiana and was its longest serving territorial capital. It is one of the oldest settlements west of the Appalachians. The population was 16,759 at the 2020 census. History The vicinity of Vincennes was inhabited for thousands of years by different cultures of indigenous peoples. During the Late Woodland period, some of these peoples used local loess hills as burial sites; some of the more prominent examples are the Sugar Loaf Mound and the Pyramid Mound. In historic times, prominent local Indian groups who drove these people out were the Shawnee, Wabash, and the Miami tribe. The first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pickawillany
Pickawillany (also spelled Pickawillamy, Pickawillani, or Picqualinni) was an 18th-century Miami Indian village located on the Great Miami River in North America's Ohio Valley near the modern city of Piqua, Ohio.R. David Edmunds, "Pickawillany: French Military Power versus British Economics" ''Western Pennsylvania Historical Magazine'', vol. 58, April 1975, pp 169–184, accessed 17 October 2021 In 1749 an English trading post was established alongside the Miami village, selling goods to neighboring tribes at the site. In 1750, a stockade (Fort Pickawillany) was constructed to protect the post. French and English colonists were competing for control of the fur trade in the |
Miami–Illinois Language
Miami–Illinois (endonym: , ) is an Indigenous Algonquian language that is spoken in the United States, historically in Illinois, Missouri, Indiana, western Ohio and adjacent areas along the Mississippi River by the Miami and Wea as well as the tribes of the Illinois Confederation, including the Kaskaskia, Peoria, Tamaroa, and possibly Mitchigamea. Although the last native speaker died in 1989, there has been an effort by the Myaamia (Miami) Nation of Oklahoma and the Miami Nation of Indians of the State of Indiana (a nonprofit organization) to revive the language and preserve their native heritage by teaching it to young and old members. As of 2016, it is estimated that around 500 members of the tribe use the language on a regular basis. Classification Miami–Illinois is an Algonquian language within the larger Algic family. It is usually described as a Central Algonquian language, but that grouping denotes a geographic rather than genetic affiliation. A thorough genetic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Grand Rapids Hotel
The Grand Rapids Hotel also known as The Grand Rapids Resort, was a hotel that existed outside of Mount Carmel, Illinois, in Wabash County, Illinois, United States in Southern Illinois from 1922 to 1929. The hotel was located on the Wabash River next to the Grand Rapids Dam on land that was originally purchased by Thomas S. Hinde. Before the hotel was built, the property where the hotel was located was a site of a former homestead, and was used by Frederick Hinde Zimmerman for multiple small shops that sold goods to fisherman and tourists. Frederick Hinde Zimmerman was the founder and owner of the hotel, and he completed construction and opened the hotel to the public on August 7, 1922. The hotel had 36 rooms and one large assembly room that served as a dining room, meeting hall, and was used for weddings, exhibitions, anniversaries, and other important occasions. The hotel was one of the first major resorts on the southern portion of the Wabash River and quickly was able to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern United States. It borders on Lake Michigan to its northeast, the Mississippi River to its west, and the Wabash River, Wabash and Ohio River, Ohio rivers to its south. Of the fifty U.S. states, Illinois has the List of U.S. states and territories by GDP, fifth-largest gross domestic product (GDP), the List of U.S. states and territories by population, sixth-largest population, and the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 25th-most land area. Its capital city is Springfield, Illinois, Springfield in the center of the state, and the state's largest city is Chicago in the northeast. Present-day Illinois was inhabited by Indigenous peoples of the Americas#History, Indigenous cultures for thousands of years. The French were the first Europeans to arrive, settling near the Mississippi and Illinois River, Illinois rivers in the 17th century Illinois Country, as part of their sprawling colony of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Illinois Confederation
The Illinois Confederation, also referred to as the Illiniwek or Illini, were made up of a loosely organized group of 12 or 13 tribes who lived in the Mississippi River Valley. Eventually, member tribes occupied an area reaching from Lake Michigan to Iowa, Illinois, Missouri, and Arkansas. The five main tribes were the Cahokia, Kaskaskia, Michigamea, Peoria, and Tamaroa. Other related tribes are described as the Maroa (which may have been the same as Tamaroa), Tapourao, Coiracoentanon, Espeminka, Moingwena, Chinkoa, and Chepoussa. By 1700, only the Cahokia, Kaskaskia, Michigamea, Peoria, and Tamaroa remained. Over time, these tribes continued to merge, with the Tamaroa joining the Kaskaskia, the Cahokia joining the Peoria, and with a portion of the Michigamea merging with the Kaskaskia and the remainder merging with the Quapaw. The spelling "Illinois" was derived from the transliteration by French explorers of to the orthography of their own language. The tribes are esti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Northwest Indian War
The Northwest Indian War (1785–1795), also known by other names, was an armed conflict for control of the Northwest Territory fought between the United States and a united group of Native Americans in the United States, Native American nations known today as the Northwestern Confederacy. The United States Army considers it the first of the American Indian Wars. Following centuries of conflict for control of this region, the land comprising the Northwest Territory was granted in 1783 to the new United States by the Kingdom of Great Britain in article 2 of the Treaty of Paris (1783), Treaty of Paris, thereby officially ending the American Revolutionary War. The treaty used the Great Lakes as a border between British territory (later a part of Canada) and the United States. This granted significant territory to the United States, initially known as the Ohio Country and the Illinois Country, which had Royal Proclamation of 1763, previously been prohibited to new settlements. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
American Revolution
The American Revolution (1765–1783) was a colonial rebellion and war of independence in which the Thirteen Colonies broke from British America, British rule to form the United States of America. The revolution culminated in the American Revolutionary War, which was launched on April 19, 1775, in the Battles of Lexington and Concord. Leaders of the American Revolution were Founding Fathers of the United States, colonial separatist leaders who, as British subjects, initially Olive Branch Petition, sought incremental levels of autonomy but came to embrace the cause of full independence and the necessity of prevailing in the Revolutionary War to obtain it. The Second Continental Congress, which represented the colonies and convened in present-day Independence Hall in Philadelphia, formed the Continental Army and appointed George Washington as its commander-in-chief in June 1775, and unanimously adopted the United States Declaration of Independence, Declaration of Independence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Wabash Confederacy
The Wabash Confederacy, also referred to as the Wabash Indians or the Wabash tribes, was a number of 18th century Native Americans of the United States, Native American villagers in the area of the Wabash River in what are now the U.S. states of Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio. The Wabash Indians were primarily the Miami people, Miami, Weas and Piankashaws, but also included Kickapoo people, Kickapoos, Mascoutens, and others. In that time and place, Native American tribes were smaller political units, and the villages along the Wabash were multi-tribal settlements with no centralized government. The confederacy, then, was a loose alliance of influential village leaders (sometimes called headmen or chiefs). In the 1780s, headmen of the Wabash Confederacy allied themselves with a larger, loose confederacy of Native American leaders in the Ohio Country and Illinois Country known as the Northwestern Confederacy, in order to collectively resist U.S. expansion after the American Revolutionary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |